Deck 11: Carbohydrates: Structure and Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Carbohydrates: Structure and Function
1
Which of the following is NOT a function of carbohydrates?
A) Carbohydrates are used for long term energy storage.
B) Carbohydrates are fuels for cells.
C) Carbohydrates are part of DNA and RNA.
D) Carbohydrates are used in cellular recognition.
E) Carbohydrates make some foods taste sweet.
A) Carbohydrates are used for long term energy storage.
B) Carbohydrates are fuels for cells.
C) Carbohydrates are part of DNA and RNA.
D) Carbohydrates are used in cellular recognition.
E) Carbohydrates make some foods taste sweet.
Carbohydrates are used for long term energy storage.
2
In what part of the body does the metabolism of carbohydrates begin?
A) in the mouth
B) in the stomach
C) in the pancreas
D) in the small intestine
E) in the large intestine
A) in the mouth
B) in the stomach
C) in the pancreas
D) in the small intestine
E) in the large intestine
in the mouth
3
The Fischer projection for fructose is shown below. Which functional group(s) does fructose contain? 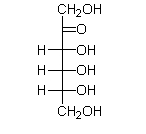
A) an aldehyde only
B) hydroxyl groups only
C) hydroxyl groups and an alkene
D) hydroxyl groups and a ketone
E) hydroxyl groups and an aldehyde

A) an aldehyde only
B) hydroxyl groups only
C) hydroxyl groups and an alkene
D) hydroxyl groups and a ketone
E) hydroxyl groups and an aldehyde
hydroxyl groups and a ketone
4
Which carbon(s) in the Fischer projection below is/are a center of chirality? 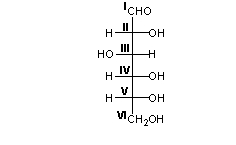
A) all carbons
B) carbon I only
C) carbon I and VI only
D) carbons II, II, IV , and V
E) carbons II through IV

A) all carbons
B) carbon I only
C) carbon I and VI only
D) carbons II, II, IV , and V
E) carbons II through IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following classes of biomolecules causes dental caries?
A) carbohydrates
B) proteins
C) fats
D) nucleic acids
E) All foods cause dental caries.
A) carbohydrates
B) proteins
C) fats
D) nucleic acids
E) All foods cause dental caries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following structures is a monosaccharide? 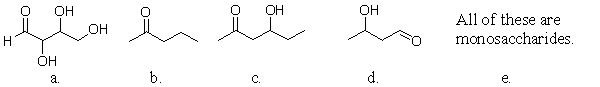
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following types of carbohydrates can be hydrolyzed to give smaller molecules? I. monosaccharides
II) disaccharides
III) oligosaccharides
IV) polysaccharides
A) I only
B) II and IV only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) II, III, and IV
II) disaccharides
III) oligosaccharides
IV) polysaccharides
A) I only
B) II and IV only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which carbon(s) in the Fischer projection below is/are tetrahedral?
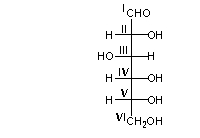
A) all carbons
B) carbon I only
C) carbon I and VI only
D) carbons II, III, IV , and V
E) carbons II through VI

A) all carbons
B) carbon I only
C) carbon I and VI only
D) carbons II, III, IV , and V
E) carbons II through VI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Fischer projection for fructose is shown below. Is it a d-sugar or an l-sugar?

A) It is a D-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon A is to the right.
B) It is a D-sugar because the carbonyl at carbon B is to the right.
C) It is a D-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon C is to the right
D) It is an L-sugar because the carbonyl at carbon B is to the right.
E) It is an L-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon C is to the right.

A) It is a D-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon A is to the right.
B) It is a D-sugar because the carbonyl at carbon B is to the right.
C) It is a D-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon C is to the right
D) It is an L-sugar because the carbonyl at carbon B is to the right.
E) It is an L-sugar because the hydroxyl at carbon C is to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Do you expect monosaccharides to be soluble in water?
A) Yes, because monosaccharides are acidic
B) No, because monosaccharides have too many carbons to be soluble
C) Yes, because monosaccharides can hydrogen bond with water
D) No, because monosaccharides cannot form intermolecular attractive forces with water
E) Yes, because monosaccharides are basic
A) Yes, because monosaccharides are acidic
B) No, because monosaccharides have too many carbons to be soluble
C) Yes, because monosaccharides can hydrogen bond with water
D) No, because monosaccharides cannot form intermolecular attractive forces with water
E) Yes, because monosaccharides are basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is produced by cellular respiration?
A) oxygen
B) sugars
C) carbon dioxide, water, and energy
D) oxygen and energy
E) oxygen, sugars, and energy
A) oxygen
B) sugars
C) carbon dioxide, water, and energy
D) oxygen and energy
E) oxygen, sugars, and energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The most common disease in the world is
A) heart disease.
B) cancer.
C) tooth decay.
D) amoebic dysentery.
E) malaria.
A) heart disease.
B) cancer.
C) tooth decay.
D) amoebic dysentery.
E) malaria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements best describes photosynthesis?
A) the breakdown of starch into CO2, H2O, and energy
B) the breakdown of starch into CO2 and H2O using energy
C) the synthesis of starch from CO2, H2O, and energy
D) the synthesis of starch and energy from CO2 and H2O
E) Photosynthesis applies to all of the above processes.
A) the breakdown of starch into CO2, H2O, and energy
B) the breakdown of starch into CO2 and H2O using energy
C) the synthesis of starch from CO2, H2O, and energy
D) the synthesis of starch and energy from CO2 and H2O
E) Photosynthesis applies to all of the above processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements related to the formation of dental caries is FALSE?
A) Anaerobic bacteria produce lactic acid.
B) Anaerobic bacteria convert glucose into carbon dioxide and water.
C) Lactic acid reduces the pH of the environment of the tooth enamel to pH 4-5.
D) Tooth enamel dissolves in a pH 4-5 environment.
E) Brushing removes sugars from the teeth.
A) Anaerobic bacteria produce lactic acid.
B) Anaerobic bacteria convert glucose into carbon dioxide and water.
C) Lactic acid reduces the pH of the environment of the tooth enamel to pH 4-5.
D) Tooth enamel dissolves in a pH 4-5 environment.
E) Brushing removes sugars from the teeth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following foods contain carbohydrates?
A) pineapple
B) tomatoes
C) potatoes
D) wheat
E) All of these foods contain carbohydrates.
A) pineapple
B) tomatoes
C) potatoes
D) wheat
E) All of these foods contain carbohydrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following best describes how brushing your teeth prevents cavities?
A) Toothpaste stops the metabolism of glucose.
B) Toothpaste neutralizes lactic acid.
C) Brushing removes sugars.
D) Brushing removes anaerobic bacteria.
E) Toothpaste increases pH in the mouth.
A) Toothpaste stops the metabolism of glucose.
B) Toothpaste neutralizes lactic acid.
C) Brushing removes sugars.
D) Brushing removes anaerobic bacteria.
E) Toothpaste increases pH in the mouth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following features is NOT shared by all monosaccharides?
A) Monosaccharides cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates.
B) Monosaccharides all contain six carbons.
C) Monosaccharides have an aldehyde or a ketone.
D) Monosaccharides contain two or more alcohols.
E) Actually, all of these statements are true.
A) Monosaccharides cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates.
B) Monosaccharides all contain six carbons.
C) Monosaccharides have an aldehyde or a ketone.
D) Monosaccharides contain two or more alcohols.
E) Actually, all of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Fischer projection for fructose is shown below. How many carbons does fructose contain? 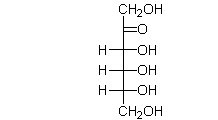
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Fischer projection for fructose is shown below. Which carbon determines whether the sugar is d- or l-? 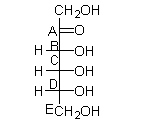
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
A) cellulose
B) starch
C) glucose
D) sucrose
E) maltose
A) cellulose
B) starch
C) glucose
D) sucrose
E) maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements best describes mutarotation?
A) The open chain, α-anomer and β-anomer of a sugar are in equilibrium in solution.
B) The sugar spins around (rotates) in solution.
C) The sugar mutates in solution.
D) The sugar decomposes in solution.
E) The sugar both spins around and mutates in solution.
A) The open chain, α-anomer and β-anomer of a sugar are in equilibrium in solution.
B) The sugar spins around (rotates) in solution.
C) The sugar mutates in solution.
D) The sugar decomposes in solution.
E) The sugar both spins around and mutates in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How can it be determined whether a sugar is α- or β- by looking at the Haworth projection?
A) α-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is above the ring. β-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is below the ring.
B) α-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is above the ring. β-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is below the ring.
C) α-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is below the ring. β-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is above the ring.
D) α-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is below the ring. β-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is above the ring.
E) Both b and d are true.
A) α-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is above the ring. β-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is below the ring.
B) α-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is above the ring. β-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is below the ring.
C) α-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is below the ring. β-anomer: The -OH on the anomeric carbon is above the ring.
D) α-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is below the ring. β-anomer: The -CH2OH of carbon 6 is above the ring.
E) Both b and d are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Only one of the following molecules is a naturally occurring sugar. Which of the following statements is a reason that only one of the sugars is naturally occurring? 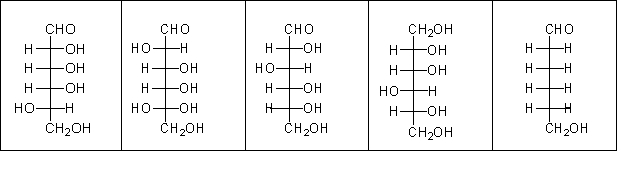
A) Naturally occurring sugars do not have multiple hydroxyl groups on a single carbon.
B) D-sugars are much more common than l-sugars.
C) Naturally occurring sugars are polyhydroxylated.
D) Naturally occurring sugars contain a carbonyl.
E) All of the above are true statements.

A) Naturally occurring sugars do not have multiple hydroxyl groups on a single carbon.
B) D-sugars are much more common than l-sugars.
C) Naturally occurring sugars are polyhydroxylated.
D) Naturally occurring sugars contain a carbonyl.
E) All of the above are true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How are disaccharides separated into two monosaccharides?
A) It is not possible to separate disaccharides into monosaccharides.
B) by esterification
C) by hydration
D) by hydrolysis
E) by amidation
A) It is not possible to separate disaccharides into monosaccharides.
B) by esterification
C) by hydration
D) by hydrolysis
E) by amidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following structures is an α-anomer?
A)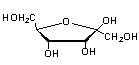
B)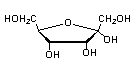
C)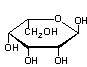
D)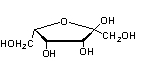
E)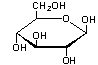
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The open chain form of a carbohydrate contains a carbonyl group. This carbonyl group reacts to become an alcohol when the ring closes, forming the anomeric carbon. The type of carbonyl determines which type of ring is formed. Select the choice in which the type of carbonyl is paired with the correct type of ring that is formed.
A) ketone and pyranose
B) aldehyde and pyranose
C) carboxylic acid and furanose
D) carboxylic acid and pyranose
E) aldehyde and furanose
A) ketone and pyranose
B) aldehyde and pyranose
C) carboxylic acid and furanose
D) carboxylic acid and pyranose
E) aldehyde and furanose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The structures of mannose and galactose are given below. What is the relationship between these two monosaccharides? 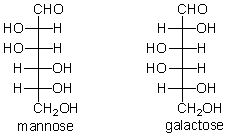
A) They are identical.
B) They are constitutional isomers.
C) They are diastereomers.
D) They are enantiomers.
E) They are conformers.

A) They are identical.
B) They are constitutional isomers.
C) They are diastereomers.
D) They are enantiomers.
E) They are conformers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which carbon determines whether the sugar below is d- or l-? 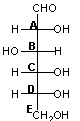
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the relationship between d- and l-glucose?
A) They are identical.
B) They are constitutional isomers.
C) They are diastereomers.
D) They are enantiomers.
E) They are conformers.
A) They are identical.
B) They are constitutional isomers.
C) They are diastereomers.
D) They are enantiomers.
E) They are conformers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The circled carbon in the cyclic structure of glucose corresponds to which boxed carbon in the linear structure? 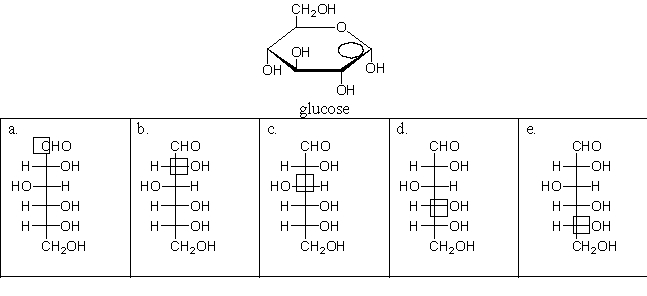
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The circled oxygen in the cyclic structure of glucose corresponds to which boxed oxygen in the linear structure? 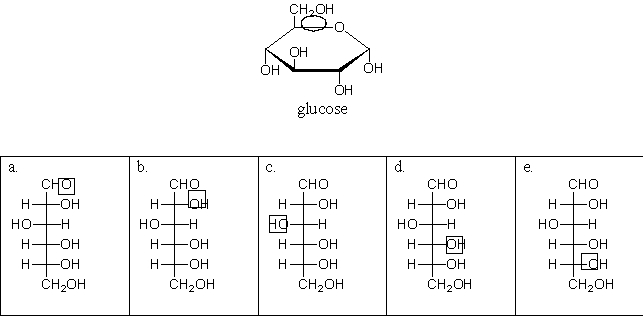
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Nature produces predominantly _______-carbohydrates and _______-amino acids.
A) d, d
B) d, l
C) l, d
D) l, l
E) Nature does not favor one stereoisomer over another.
A) d, d
B) d, l
C) l, d
D) l, l
E) Nature does not favor one stereoisomer over another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements best explains how mutarotation occurs in solution?
A) Any C-C can break, opening the ring.
B) The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon "floats" between the α and the β position.
C) The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon comes off and then reattaches.
D) The bond between the ring oxygen and the anomeric carbon breaks, opening the ring, and then reforms, closing the ring again.
E) All of the above can occur in solution.
A) Any C-C can break, opening the ring.
B) The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon "floats" between the α and the β position.
C) The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon comes off and then reattaches.
D) The bond between the ring oxygen and the anomeric carbon breaks, opening the ring, and then reforms, closing the ring again.
E) All of the above can occur in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements does NOT describe the anomeric carbon?
A) It is the carbon of the carbonyl in the open-chain form of the sugar.
B) This carbon is attached to two oxygens.
C) The hydroxyl group on this carbon can be above or below the ring.
D) Glucose does not contain an anomeric carbon.
E) The anomeric carbon is a center of chirality.
A) It is the carbon of the carbonyl in the open-chain form of the sugar.
B) This carbon is attached to two oxygens.
C) The hydroxyl group on this carbon can be above or below the ring.
D) Glucose does not contain an anomeric carbon.
E) The anomeric carbon is a center of chirality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In which of the following Haworth projections is the arrow pointing to the anomeric carbon? 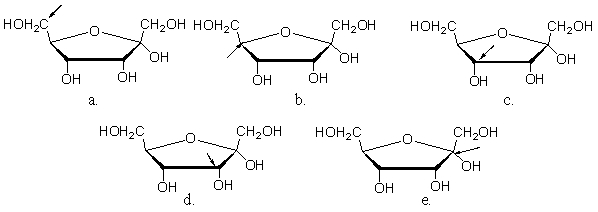
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ring form with the ring structure shown at left below is called a ________, and the ring form with the ring structure to the right below is called a _________. 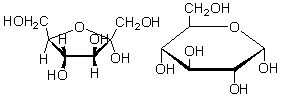
A) pyranose; pyranose
B) pyranose; furanose
C) furanose; furanose
D) furanose; pyranose
E) The choices given do not apply to ring forms of sugars.

A) pyranose; pyranose
B) pyranose; furanose
C) furanose; furanose
D) furanose; pyranose
E) The choices given do not apply to ring forms of sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following species does equilibrium favor in solution? 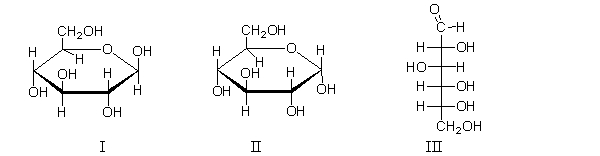
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III
E) There are equal concentrations of these three species in solution.

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III
E) There are equal concentrations of these three species in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Below is the open-chain form of fructose, followed by several cyclic monosaccharides. Choose the cyclic monosaccharides that are the ring form of fructose. 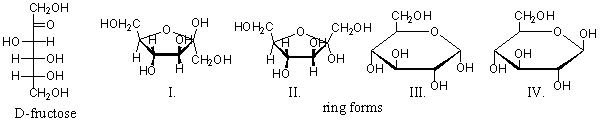
A) Only structure II is d-fructose.
B) Only structure III is d-fructose.
C) Both structures I and II are d-fructose.
D) Both structure III and IV are d-fructose.
E) All of these structures are d-fructose.

A) Only structure II is d-fructose.
B) Only structure III is d-fructose.
C) Both structures I and II are d-fructose.
D) Both structure III and IV are d-fructose.
E) All of these structures are d-fructose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which one of these molecules is a naturally occurring sugar? 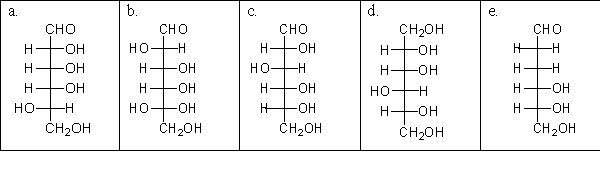
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The figure below illustrates a(n) 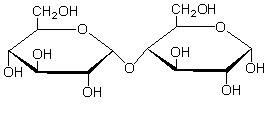
A) monosaccharide.
B) simple sugar.
C) disaccharide.
D) polysaccharide.
E) oligosaccharide.

A) monosaccharide.
B) simple sugar.
C) disaccharide.
D) polysaccharide.
E) oligosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
This disaccharide is the common type of sugar that comes from sugar cane or beets.
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
This disaccharide is composed of two glucose molecules.
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following glycosidic linkages does the sugar shown below contain? 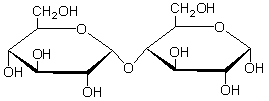
A) " -(2→4)"
B) " -(1→4)"
C) " -(1→4)"
D) " -(2→4)"
E) " -(2→6)"

A) " -(2→4)"
B) " -(1→4)"
C) " -(1→4)"
D) " -(2→4)"
E) " -(2→6)"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Cellobiose, shown below, cannot be hydrolyzed into monosaccharides by humans. Which statement best describes why this is the case? 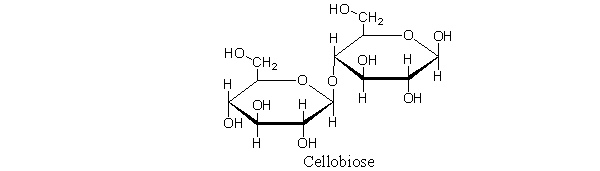
A) Cellobiose contains a -(1→4) glycosidic linkage, which is not a substrate for glycosidases in the human stomach.
B) Human enzymes do not accept glucose molecules as substrates.
C) Cellobiose is composed of monosaccharides that are not part of the human diet.
D) The glycosidic bond in this disaccharide is unusually strong.
E) No disaccharide is hydrolyzed by humans.

A) Cellobiose contains a -(1→4) glycosidic linkage, which is not a substrate for glycosidases in the human stomach.
B) Human enzymes do not accept glucose molecules as substrates.
C) Cellobiose is composed of monosaccharides that are not part of the human diet.
D) The glycosidic bond in this disaccharide is unusually strong.
E) No disaccharide is hydrolyzed by humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following molecules is NOT a polysaccharide?
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) cellulose
D) glycogen
E) glucose
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) cellulose
D) glycogen
E) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Starches in our diet contain _________ of glucose units bonded together.
A) tens
B) hundreds
C) thousands
D) millions
E) billions
A) tens
B) hundreds
C) thousands
D) millions
E) billions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the product(s) of the hydrolysis of the following sugar? 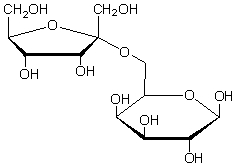 Sucrose
Sucrose 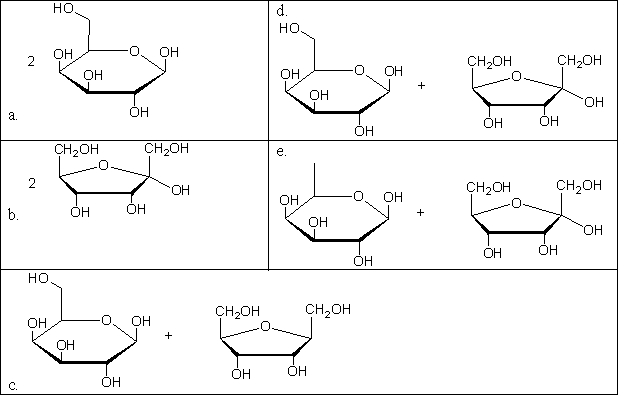
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e
 Sucrose
Sucrose 
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How are glycosidic linkages broken during catabolism of sugars?
A) by oxidation
B) by reduction
C) by hydrolysis
D) by hydrogenation
E) by dehydration
A) by oxidation
B) by reduction
C) by hydrolysis
D) by hydrogenation
E) by dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Plants store energy in the form of
A) amylose.
B) amylopectin.
C) glycogen.
D) cellulose.
E) amylose and amylopectin.
A) amylose.
B) amylopectin.
C) glycogen.
D) cellulose.
E) amylose and amylopectin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
This disaccharide is found in milk.
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A large molecule composed of many repeating units of smaller molecules is called a
A) polymer.
B) monomer.
C) manymer.
D) macromere.
E) carbohydrate.
A) polymer.
B) monomer.
C) manymer.
D) macromere.
E) carbohydrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The most common polysaccharides found in plants and animals are polymers of
A) galactose.
B) glucose.
C) fructose.
D) glucose and fructose.
E) glucose, fructose, and galactose.
A) galactose.
B) glucose.
C) fructose.
D) glucose and fructose.
E) glucose, fructose, and galactose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following arrows is pointing to a glycosidic bond? 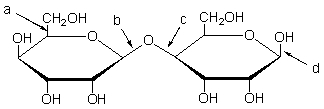
A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) b and c
E) b, c, and d

A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) b and c
E) b, c, and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
This disaccharide has glycosidic bonds to the anomeric carbons of both monosaccharides.
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose
A) lactose
B) sucrose
C) cellobiose
D) maltose
E) both cellobiose and maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Animals store energy in the form of
A) amylose.
B) amylopectin.
C) glycogen.
D) cellulose.
E) amylose and amylopectin.
A) amylose.
B) amylopectin.
C) glycogen.
D) cellulose.
E) amylose and amylopectin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A disaccharide has an -(1→4) glycosidic linkage. Which statement about this sugar is true?
A) Both monosaccharides in the disaccharide are linked at their anomeric carbon.
B) Both monosaccharides in the disaccharide are the anomer.
C) No part of the disaccharide can undergo mutarotation.
D) The closed ring form of the sugar linked at its carbon-4 is in equilibrium with its open-chain form.
E) All of these statements are true.
A) Both monosaccharides in the disaccharide are linked at their anomeric carbon.
B) Both monosaccharides in the disaccharide are the anomer.
C) No part of the disaccharide can undergo mutarotation.
D) The closed ring form of the sugar linked at its carbon-4 is in equilibrium with its open-chain form.
E) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What type of saccharide is the following molecule? 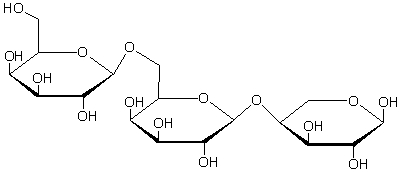
A) a monosaccharide
B) a disaccharide
C) an oligosaccharide
D) a polysaccharide
E) This molecule is not a sugar.

A) a monosaccharide
B) a disaccharide
C) an oligosaccharide
D) a polysaccharide
E) This molecule is not a sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How many monosaccharides are produced when the following sugar is hydrolyzed? 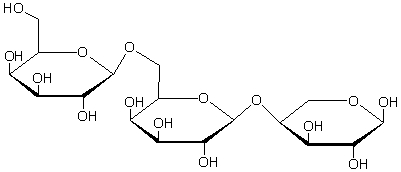
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following arrows is pointing to a glycosidic bond? 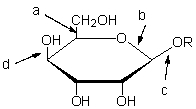
A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) b and c
E) b, c, and d

A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) b and c
E) b, c, and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following glycosidic linkages does the sugar shown below contain? 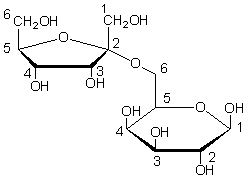
A) " -(2→4)"
B) " -(1→4)"
C) " -(1→4)"
D) " -(2→4)"
E) " -(2→6)"

A) " -(2→4)"
B) " -(1→4)"
C) " -(1→4)"
D) " -(2→4)"
E) " -(2→6)"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
These polysaccharides are made of glucose.
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) all of the above
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Most animals cannot digest cellulose. However, those with a second stomach, containing specific bacteria that produce β-glycosidases, can digest cellulose. What is the role of the β-glycosidase in digesting cellulose?
A) β-glycosidase catalyzes the oxidation of cellulose.
B) β-glycosidase catalyzes the isomerization of β-glycosidic bonds into -glycosidic bonds.
C) β-glycosidase catalyzes the reduction of cellulose.
D) β-glycosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of cellulose.
E) β-glycosidase catalyzes the dehydration of cellulose.
A) β-glycosidase catalyzes the oxidation of cellulose.
B) β-glycosidase catalyzes the isomerization of β-glycosidic bonds into -glycosidic bonds.
C) β-glycosidase catalyzes the reduction of cellulose.
D) β-glycosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of cellulose.
E) β-glycosidase catalyzes the dehydration of cellulose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which statement best describes how a cell distinguishes between a host cell and foreign cell?
A) Antibodies detect foreign cells.
B) This is what T-cells do.
C) Oligosaccharide cell markers on the surface of the cell do this.
D) A cell sends out special proteins to do this.
E) The proteins within the cell membrane do this.
A) Antibodies detect foreign cells.
B) This is what T-cells do.
C) Oligosaccharide cell markers on the surface of the cell do this.
D) A cell sends out special proteins to do this.
E) The proteins within the cell membrane do this.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Cellulose and starch are similar in that they are both polymers of glucose. Cellulose, however, forms sheet-like structures, which give rigidity to a plant, whereas starch forms spirals. What accounts for this difference in macroscopic structure?
A) Cellulose is composed of d-glucose, whereas starch is composed of l-glucose.
B) Cellulose and starch are connected together on different carbons.
C) Cellulose is composed of l-glucose, whereas starch is composed of d-glucose.
D) Cellulose has a -(1→4) linkage, whereas starch has an -(1→4) linkage.
E) Starch has a -(1→4) linkage, whereas cellulose has an -(1→4) linkage.
A) Cellulose is composed of d-glucose, whereas starch is composed of l-glucose.
B) Cellulose and starch are connected together on different carbons.
C) Cellulose is composed of l-glucose, whereas starch is composed of d-glucose.
D) Cellulose has a -(1→4) linkage, whereas starch has an -(1→4) linkage.
E) Starch has a -(1→4) linkage, whereas cellulose has an -(1→4) linkage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Animals cannot digest________, but ruminants such as horses and cows have bacteria in their digestive track that can digest it.
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) amylose and amylopectin
A) amylose
B) amylopectin
C) glycogen
D) cellulose
E) amylose and amylopectin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following blood types can be donated to someone with type A blood?
A) type A only
B) type A or type O
C) type A or type AB
D) any of the blood types except A
E) Type A can receive blood from any of the blood types.
A) type A only
B) type A or type O
C) type A or type AB
D) any of the blood types except A
E) Type A can receive blood from any of the blood types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A patient with chronic pancreatitis has her pancreas removed. Which of the following effects would be most likely?
A) nothing
B) the regeneration of the pancreas
C) Type I diabetes
D) Type II diabetes
E) hypoglycemia
A) nothing
B) the regeneration of the pancreas
C) Type I diabetes
D) Type II diabetes
E) hypoglycemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Why can't insulin be taken orally?
A) It does not taste very good.
B) Enzymes in the saliva break it down.
C) Hydrolysis of insulin occurs in the stomach.
D) It is not possible to store insulin.
E) All of the above
A) It does not taste very good.
B) Enzymes in the saliva break it down.
C) Hydrolysis of insulin occurs in the stomach.
D) It is not possible to store insulin.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The result of a patient's Fasting Plasma Glucose Test is 60 mg glucose per deciliter. This patient is
A) normal.
B) hypoglycemic.
C) hyperglycemic.
D) diabetic.
E) both hyperglycemic and diabetic.
A) normal.
B) hypoglycemic.
C) hyperglycemic.
D) diabetic.
E) both hyperglycemic and diabetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Insulin acts to __________, whereas glucagon __________.
A) increase blood sugar; decreases blood sugar
B) stimulate gluconeogenesis; stimulates glycogenesis
C) suppress gluconeogenesis; suppresses glycogenesis
D) decrease blood sugar; increases blood sugar
E) stimulate glycogenesis; suppresses glycogenesis
A) increase blood sugar; decreases blood sugar
B) stimulate gluconeogenesis; stimulates glycogenesis
C) suppress gluconeogenesis; suppresses glycogenesis
D) decrease blood sugar; increases blood sugar
E) stimulate glycogenesis; suppresses glycogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which statement best describes at the molecular level why AB is the universal acceptor?
A) It is the least common blood type.
B) It contains both the type A and type B monosaccharides in addition to the core trisaccharide.
C) It only contains the core trisaccharide and does not have any additional sugars on it.
D) Red blood cells of this type do not have any oligosaccharide markers.
E) Type AB has a completely different oligosaccharide marker than A, B, and O.
A) It is the least common blood type.
B) It contains both the type A and type B monosaccharides in addition to the core trisaccharide.
C) It only contains the core trisaccharide and does not have any additional sugars on it.
D) Red blood cells of this type do not have any oligosaccharide markers.
E) Type AB has a completely different oligosaccharide marker than A, B, and O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following choices matches the descriptions of Type I and Type II diabetes and their treatments? 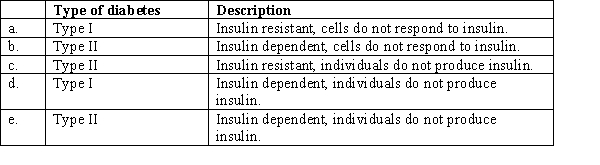
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements describes the role of insulin in the body? I. Insulin signals to cells to allow glucose to enter.
II) Insulin stimulates the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
III) Insulin stimulates the hydrolysis of glucose from glycogen.
A) All of these describe the role of insulin in the body.
B) I only
C) II only
D) III only
E) I and II
II) Insulin stimulates the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
III) Insulin stimulates the hydrolysis of glucose from glycogen.
A) All of these describe the role of insulin in the body.
B) I only
C) II only
D) III only
E) I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Type _____ blood is the universal donor, whereas type _____ is the universal recipient.
A) O; AB
B) AB; O
C) A; B
D) B; A
E) O; A or B
A) O; AB
B) AB; O
C) A; B
D) B; A
E) O; A or B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A patient undergoing a kidney transplant is given a kidney from a person with type B blood when the patient is, in fact, type O. What effect of this mistake would be most likely?
A) Nothing, blood type does not matter in organ transplants.
B) Nothing, Type O is the universal recipient.
C) organ failure
D) coma
E) a mild allergic reaction
A) Nothing, blood type does not matter in organ transplants.
B) Nothing, Type O is the universal recipient.
C) organ failure
D) coma
E) a mild allergic reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following blood types is most common?
A) A
B) B
C) AB
D) O
E) They are equally common.
A) A
B) B
C) AB
D) O
E) They are equally common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is the best definition for diabetes?
A) Diabetes is hypoglycemia due to an excess of insulin.
B) Diabetes is hypoglycemia due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin.
C) Diabetes is hyperglycemia due to an excess of insulin.
D) Diabetes is hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin.
E) Diabetes is any disorder of blood sugar.
A) Diabetes is hypoglycemia due to an excess of insulin.
B) Diabetes is hypoglycemia due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin.
C) Diabetes is hyperglycemia due to an excess of insulin.
D) Diabetes is hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin.
E) Diabetes is any disorder of blood sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following sugars is called "blood sugar"?
A) glucose
B) glycogen
C) fructose
D) sucrose
E) All of the above
A) glucose
B) glycogen
C) fructose
D) sucrose
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



