Deck 17: Standard Costing and Variance Analysis 1
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Standard Costing and Variance Analysis 1
1
An unfavourable materials usage variance may be caused by
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.
A
2
Variances indicate
A) the cause of the variance.
B) who is responsible for the variance.
C) that actual performance is not going according to plan.
D) when the variance should be investigated.
A) the cause of the variance.
B) who is responsible for the variance.
C) that actual performance is not going according to plan.
D) when the variance should be investigated.
C
3
For better control of direct material prices, when should direct material price variance be recognized?
A) when material is purchased
B) when material is issued from the storeroom
C) when material is put into production
D) when production is completed
A) when material is purchased
B) when material is issued from the storeroom
C) when material is put into production
D) when production is completed
A
4
To determine the unit standard cost for a particular input, a company must decide how much
A) input should be used per unit of output and how much should be paid for the quantity of the input to be used.
B) input should be used per unit of output and how much output should be produced.
C) output should be produced and how much should be paid for each unit produced.
D) should be paid for the quantity of the input to be used and how much input should be purchased.
A) input should be used per unit of output and how much should be paid for the quantity of the input to be used.
B) input should be used per unit of output and how much output should be produced.
C) output should be produced and how much should be paid for each unit produced.
D) should be paid for the quantity of the input to be used and how much input should be purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An unfavourable materials price variance with a favourable materials usage variance would most likely be the result of
A) machines breaking down.
B) problems with labour efficiency.
C) purchase of high quality materials.
D) problems with labour rates.
A) machines breaking down.
B) problems with labour efficiency.
C) purchase of high quality materials.
D) problems with labour rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The purchase of inferior direct materials at a lower price might affect which of the following variances?
A) materials price variance
B) materials usage variance
C) labour efficiency variance
D) all of the above
A) materials price variance
B) materials usage variance
C) labour efficiency variance
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 5 per cent wage increase for all factory employees would affect which of the following variances?
A) materials price variance
B) labour rate variance
C) labour efficiency variance
D) variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
A) materials price variance
B) labour rate variance
C) labour efficiency variance
D) variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The two variances for variable overhead are
A) spending and efficiency variances.
B) spending and budget variances.
C) budget and volume variances.
D) budget and efficiency variances.
A) spending and efficiency variances.
B) spending and budget variances.
C) budget and volume variances.
D) budget and efficiency variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An unfavourable materials price variance may be caused by
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Efficiency variances focus on the difference between
A) actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed for estimated activity.
B) actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
C) quantity allowed for estimated production and standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
D) none of the above.
A) actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed for estimated activity.
B) actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
C) quantity allowed for estimated production and standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A favourable materials usage variance may be caused by
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The labour rate variance is calculated as
A) (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) *Actual direct labour hours used.
B) (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) * Standard direct labour hours that should have been used.
C) (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) * Actual hourly wage rate.
D) (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) *Standard hourly wage rate.
A) (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) *Actual direct labour hours used.
B) (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) * Standard direct labour hours that should have been used.
C) (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) * Actual hourly wage rate.
D) (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) *Standard hourly wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Standard cost systems can enhance operational control through the use of
A) price variances, which indicate the need for enhanced spending control.
B) efficiency variances, which indicate the need for corrective action.
C) standard costs, which indicate the desired cost of a unit of input.
D) actual costs, which indicate the price received for units sold.
A) price variances, which indicate the need for enhanced spending control.
B) efficiency variances, which indicate the need for corrective action.
C) standard costs, which indicate the desired cost of a unit of input.
D) actual costs, which indicate the price received for units sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Who is responsible for unfavourable labour efficiency variances caused by poor quality materials?
A) warehouse manager
B) production manager
C) purchasing manager
D) engineering manager
A) warehouse manager
B) production manager
C) purchasing manager
D) engineering manager

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Labour efficiency variances may be caused by
A) the use of highly skilled workers.
B) frequent machinery breakdowns.
C) the use of marginally skilled workers.
D) all of the above.
A) the use of highly skilled workers.
B) frequent machinery breakdowns.
C) the use of marginally skilled workers.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Labour rate variances can be the result of
A) the use of an average wage rate.
B) unexpected overtime.
C) seniority mix changes.
D) all of the above.
A) the use of an average wage rate.
B) unexpected overtime.
C) seniority mix changes.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Price variances focus on the difference between
A) actual price and standard price for actual quantity allowed for units actually produced.
B) actual price and standard price for standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
C) actual price and standard price for actual quantity allowed for estimated activity.
D) none of the above.
A) actual price and standard price for actual quantity allowed for units actually produced.
B) actual price and standard price for standard quantity allowed for units actually produced.
C) actual price and standard price for actual quantity allowed for estimated activity.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A favourable materials price variance may be caused by
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.
A) excessive rework.
B) a special price offered by suppliers.
C) use of experienced workers.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Using more highly skilled direct labourers might affect which of the following variances?
A) materials usage variance
B) labour efficiency variance
C) variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
D) all of the above
A) materials usage variance
B) labour efficiency variance
C) variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is information that would be included in the standard cost card (sheet)?
A) quantity and price of direct materials for each unit of output
B) retail price of the product charged to the customers
C) delivery cost per unit of product
D) all of the above
A) quantity and price of direct materials for each unit of output
B) retail price of the product charged to the customers
C) delivery cost per unit of product
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 17-2
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: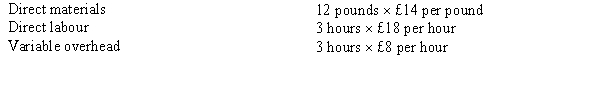 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's labour rate variance would be
A) £4,300 favourable.
B) £4,300 unfavourable.
C) £2,500 favourable.
D) £2,500 unfavourable.
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's labour rate variance would be
A) £4,300 favourable.
B) £4,300 unfavourable.
C) £2,500 favourable.
D) £2,500 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During May, 6,000 pounds of raw materials were purchased at a cost of £2.60 per pound. If there was a favourable materials price variance of £900 for December, the standard cost per pound must be
A) £2.75.
B) £2.60.
C) £2.45.
D) none of the above.
A) £2.75.
B) £2.60.
C) £2.45.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 17-2
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's materials usage variance would be
A) £8,400 unfavourable.
B) £8,400 favourable.
C) £5,600 unfavourable.
D) £5,600 favourable.
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's materials usage variance would be
A) £8,400 unfavourable.
B) £8,400 favourable.
C) £5,600 unfavourable.
D) £5,600 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 17-1
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's labour rate variance would be
A) £920 unfavourable.
B) £920 favourable.
C) £800 unfavourable.
D) £800 favourable.
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's labour rate variance would be
A) £920 unfavourable.
B) £920 favourable.
C) £800 unfavourable.
D) £800 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 17-1
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's materials price variance would be
A) £50,000 favourable.
B) £50,000 unfavourable.
C) £10,000 unfavourable.
D) £10,000 favourable.
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's materials price variance would be
A) £50,000 favourable.
B) £50,000 unfavourable.
C) £10,000 unfavourable.
D) £10,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 17-1
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £7,200 unfavourable.
B) £7,200 favourable.
C) £6,280 unfavourable.
D) £6,280 favourable.
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £7,200 unfavourable.
B) £7,200 favourable.
C) £6,280 unfavourable.
D) £6,280 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The volume variance provides information to management about
A) utilization of plant facilities.
B) cost control.
C) performance for evaluation purposes.
D) all of the above.
A) utilization of plant facilities.
B) cost control.
C) performance for evaluation purposes.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The standard fixed overhead rate is calculated as
A) Actual fixed overhead/Actual activity.
B) Budgeted fixed overhead/Budgeted activity.
C) Budgeted fixed overhead/Actual activity.
D) Budgeted overhead/Budgeted activity.
A) Actual fixed overhead/Actual activity.
B) Budgeted fixed overhead/Budgeted activity.
C) Budgeted fixed overhead/Actual activity.
D) Budgeted overhead/Budgeted activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 17-2
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's materials price variance would be
A) £4,000 unfavourable.
B) £4,000 favourable.
C) £1,600 unfavourable.
D) £1,600 favourable.
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's materials price variance would be
A) £4,000 unfavourable.
B) £4,000 favourable.
C) £1,600 unfavourable.
D) £1,600 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During December, 6,000 pounds of raw materials were purchased at a cost of £16 per pound. If there was an unfavourable materials price variance of £6,000 for December, the standard cost per pound must be
A) £17.
B) £16.
C) £15.
D) none of the above.
A) £17.
B) £16.
C) £15.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 17-1
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's variable standard cost per unit would be
A) £392.
B) £336.
C) £296.
D) £152.
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's variable standard cost per unit would be
A) £392.
B) £336.
C) £296.
D) £152.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 17-2
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's variable standard cost per unit would be
A) £78.
B) £192.
C) £246.
D) £222.
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's variable standard cost per unit would be
A) £78.
B) £192.
C) £246.
D) £222.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During September, 40,000 units of product were produced. The standard quantity of material allowed per unit was four pounds at a standard cost of £6.00 per pound. If there was a favourable materials usage variance of £30,000 for April, the actual quantity of materials used must be
A) 41,250 pounds.
B) 38,750 pounds.
C) 165,000 pounds.
D) 155,000 pounds.
A) 41,250 pounds.
B) 38,750 pounds.
C) 165,000 pounds.
D) 155,000 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The two variances for fixed overhead are
A) spending and efficiency variances.
B) efficiency and volume variances.
C) spending and volume variances.
D) budget and efficiency variances.
A) spending and efficiency variances.
B) efficiency and volume variances.
C) spending and volume variances.
D) budget and efficiency variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
During October, 16,000 direct labour hours were worked at a standard cost of £6 per hour. If the labour rate variance for October was £4,000 unfavourable, the actual cost per labour hour must be
A) £6.25.
B) £6.00.
C) £5.75.
D) none of the above.
A) £6.25.
B) £6.00.
C) £5.75.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If variable overhead is applied based on direct labour hours and there is an unfavourable labour efficiency variance,
A) the materials usage variance will be unfavourable.
B) the labour rate variance will be favourable.
C) the variable overhead efficiency variance will be unfavourable.
D) the variable overhead spending variance will be unfavourable.
A) the materials usage variance will be unfavourable.
B) the labour rate variance will be favourable.
C) the variable overhead efficiency variance will be unfavourable.
D) the variable overhead spending variance will be unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 17-2
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £4,300 unfavourable.
B) £4,300 favourable.
C) £1,800 unfavourable.
D) £1,800 favourable.
Rax Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-2. Rax's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £4,300 unfavourable.
B) £4,300 favourable.
C) £1,800 unfavourable.
D) £1,800 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 17-1
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's materials usage variance would be
A) £40,000 unfavourable.
B) £40,000 favourable.
C) £4,800 unfavourable.
D) £4,800 favourable.
Max Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Direct materials
15 pounds *£16 per pound
Direct labour
4 hours*£24 per hour
Variable overhead
4 hours * £14 per hour
The following activities occurred during the month of October:
Materials purchased
10,000 pounds costing £170,000
Materials used
7,200 pounds
Units produced
500 units
Direct labour
2,300 hours at £23.60 per hour
Actual variable overhead
£30,000
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
-Refer to Figure 17-1. Max's materials usage variance would be
A) £40,000 unfavourable.
B) £40,000 favourable.
C) £4,800 unfavourable.
D) £4,800 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
During April, 80,000 units of product were produced. The standard quantity of material allowed per unit was two pounds at a standard cost of £5 per pound. If there was a favourable materials usage variance of £40,000 for April, the actual quantity of materials used must have been
A) 168,000 pounds.
B) 152,000 pounds.
C) 84,000 pounds.
D) 76,000 pounds.
A) 168,000 pounds.
B) 152,000 pounds.
C) 84,000 pounds.
D) 76,000 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a company was concerned with controlling expenditures on overhead items, which variance would be useful?
A) fixed overhead volume variance
B) variable overhead efficiency variance
C) variable overhead spending variance
D) both b and c
A) fixed overhead volume variance
B) variable overhead efficiency variance
C) variable overhead spending variance
D) both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Fixed overhead was budgeted at £500,000 and 25,000 direct labour hours were budgeted. If the fixed overhead volume variance was £12,000 favourable and the fixed overhead spending variance was £16,000 unfavourable, fixed overhead applied must be
A) £516,000.
B) £512,000.
C) £504,000.
D) £528,000.
A) £516,000.
B) £512,000.
C) £504,000.
D) £528,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 17-6 
Refer to Figure 17-6. The fixed overhead volume variance would be
A) £2,500 unfavourable.
B) £2,500 favourable.
C) £1,000 unfavourable.
D) £1,000 favourable.

Refer to Figure 17-6. The fixed overhead volume variance would be
A) £2,500 unfavourable.
B) £2,500 favourable.
C) £1,000 unfavourable.
D) £1,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 17-6 
Refer to Figure 17-6. The fixed overhead spending variance would be
A) £2,500 unfavourable.
B) £2,500 favourable.
C) £1,000 unfavourable.
D) £1,000 favourable.

Refer to Figure 17-6. The fixed overhead spending variance would be
A) £2,500 unfavourable.
B) £2,500 favourable.
C) £1,000 unfavourable.
D) £1,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 17-4
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. If Shannon's actual labour cost was £136,500, Shannon's labour rate variance was
A) £32,500 unfavourable.
B) £32,500 favourable.
C) £6,500 unfavourable.
D) £6,500 favourable.
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. If Shannon's actual labour cost was £136,500, Shannon's labour rate variance was
A) £32,500 unfavourable.
B) £32,500 favourable.
C) £6,500 unfavourable.
D) £6,500 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If actual fixed overhead was £120,000 and there was a £2,600 favourable spending variance and a £2,000 unfavourable volume variance, budgeted fixed overhead must have been
A) £124,600.
B) £122,000.
C) £120,000.
D) £122,600.
A) £124,600.
B) £122,000.
C) £120,000.
D) £122,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: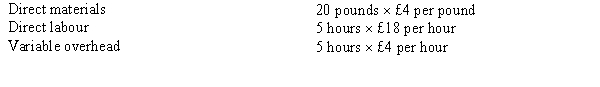 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 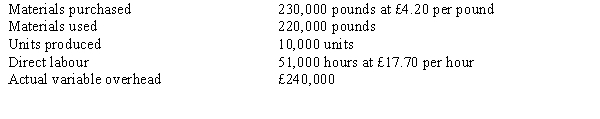 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's materials usage variance would be
A) £120,000 favourable.
B) £120,000 unfavourable.
C) £80,000 unfavourable.
D) £80,000 favourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 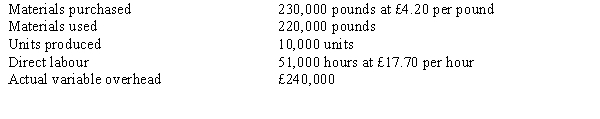 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's materials usage variance would be
A) £120,000 favourable.
B) £120,000 unfavourable.
C) £80,000 unfavourable.
D) £80,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 17-6 
Refer to Figure 17-6. The variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £2,000 favourable.
B) £1,200 favourable.
C) £400 favourable.
D) £200 favourable.

Refer to Figure 17-6. The variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £2,000 favourable.
B) £1,200 favourable.
C) £400 favourable.
D) £200 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 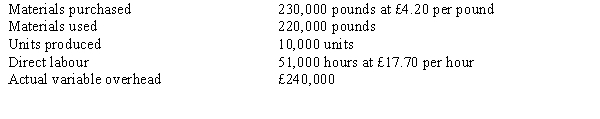 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £18,000 favourable.
B) £18,000 unfavourable.
C) £17,700 unfavourable.
D) £17,700 favourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 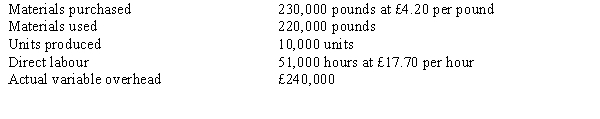 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £18,000 favourable.
B) £18,000 unfavourable.
C) £17,700 unfavourable.
D) £17,700 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 17-4
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. Shannon's labour efficiency variance was
A) £4,625 unfavourable.
B) £4,000 unfavourable.
C) £27,750 unfavourable.
D) £24,000 unfavourable.
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. Shannon's labour efficiency variance was
A) £4,625 unfavourable.
B) £4,000 unfavourable.
C) £27,750 unfavourable.
D) £24,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 17-4
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. Shannon's standard hours allowed for production was
A) 12,500.
B) 15,000.
C) 16,250.
D) 13,000.
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours * £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12,000 units. Shannon actually made 10,000 units using 13,000 hours.
-Refer to Figure 17-4. Shannon's standard hours allowed for production was
A) 12,500.
B) 15,000.
C) 16,250.
D) 13,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 17-3
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:
During October, 14,000 direct labour hours were worked at a standard cost of £40 per hour. If the labour rate variance for October was £70,000 favourable, the actual cost per labour hour must be
A) £35.
B) £40.
C) £45.
D) none of the above.
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:

During October, 14,000 direct labour hours were worked at a standard cost of £40 per hour. If the labour rate variance for October was £70,000 favourable, the actual cost per labour hour must be
A) £35.
B) £40.
C) £45.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 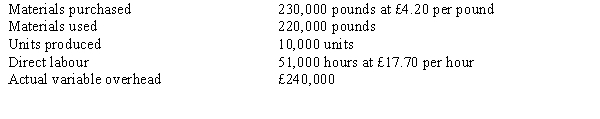 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £36,000 favourable.
B) £36,000 unfavourable.
C) £40,000 favourable.
D) £40,000 unfavourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 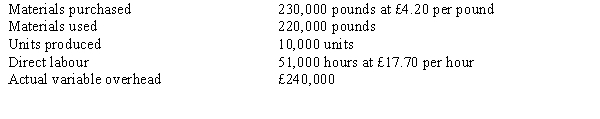 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £36,000 favourable.
B) £36,000 unfavourable.
C) £40,000 favourable.
D) £40,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 17-3
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Refer to Figure 17-3. Tuvok's materials usage variance is
A) £1,000 unfavourable.
B) £1,100 unfavourable.
C) £2,000 unfavourable.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:

Refer to Figure 17-3. Tuvok's materials usage variance is
A) £1,000 unfavourable.
B) £1,100 unfavourable.
C) £2,000 unfavourable.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 17-3
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:
Refer to Figure 17-3. Tuvok's material price variance is
A) £1,000 unfavourable.
B) £2,000 unfavourable.
C) £1,100 unfavourable.
D) cannot be computed from the information given.
Tuvok Ltd. has developed the following standards for one of its products:

Refer to Figure 17-3. Tuvok's material price variance is
A) £1,000 unfavourable.
B) £2,000 unfavourable.
C) £1,100 unfavourable.
D) cannot be computed from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 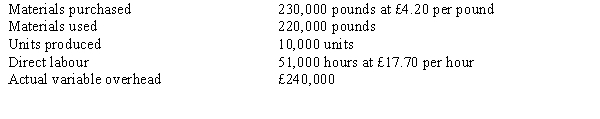 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £4,000 favourable.
B) £4,000 unfavourable.
C) £8,000 favourable.
D) £12,000 unfavourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 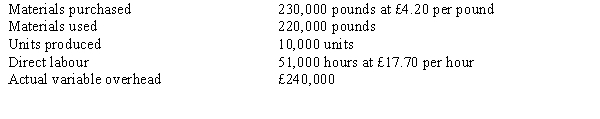 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £4,000 favourable.
B) £4,000 unfavourable.
C) £8,000 favourable.
D) £12,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure 17-6 
Refer to Figure 17-6. The variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £1,000 favourable.
B) £600 favourable.
C) £400 favourable.
D) £200 favourable.

Refer to Figure 17-6. The variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £1,000 favourable.
B) £600 favourable.
C) £400 favourable.
D) £200 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 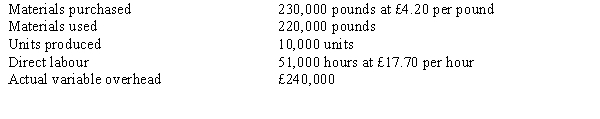 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's materials price variance would be
A) £46,000 favourable.
B) £46,000 unfavourable.
C) £44,000 favourable.
D) £44,000 unfavourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 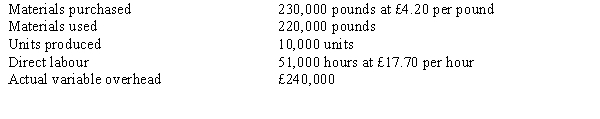 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's materials price variance would be
A) £46,000 favourable.
B) £46,000 unfavourable.
C) £44,000 favourable.
D) £44,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Fortensky Construction planned to produce 275,000 units using 34,375 machine hours. Actual output was 290,000 units using 37,425 machine hours. Fortensky's volume variance
A) was favourable.
B) was unfavourable.
C) was zero.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
A) was favourable.
B) was unfavourable.
C) was zero.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 17-5
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 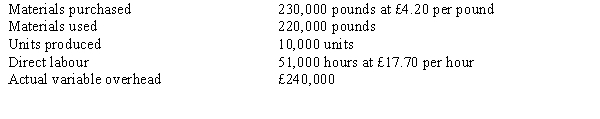 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's labour rate variance would be
A) £15,000 unfavourable.
B) £15,000 favourable.
C) £15,300 unfavourable.
D) £15,300 favourable.
Ebola Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of October:
The following activities occurred during the month of October: 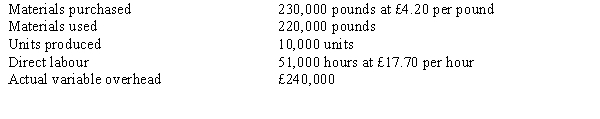 The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-5. Ebola's labour rate variance would be
A) £15,000 unfavourable.
B) £15,000 favourable.
C) £15,300 unfavourable.
D) £15,300 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 17-6 
Refer to Figure 17-6. The standard rate for total overhead is
A) £14.
B) £13.
C) £10.
D) £4.

Refer to Figure 17-6. The standard rate for total overhead is
A) £14.
B) £13.
C) £10.
D) £4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's standard fixed overhead rate is
A) £14.82.
B) £14.48.
C) £14.34.
D) £14.00.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's standard fixed overhead rate is
A) £14.82.
B) £14.48.
C) £14.34.
D) £14.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's materials price variance would be
A) £22,000 unfavourable.
B) £18,000 unfavourable.
C) £6,000 unfavourable.
D) £4,000 unfavourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's materials price variance would be
A) £22,000 unfavourable.
B) £18,000 unfavourable.
C) £6,000 unfavourable.
D) £4,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's fixed overhead spending variance would be
A) £10,000 unfavourable.
B) £11,000 unfavourable.
C) £21,000 favourable.
D) £31,000 favourable.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's fixed overhead spending variance would be
A) £10,000 unfavourable.
B) £11,000 unfavourable.
C) £21,000 favourable.
D) £31,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The following standard costs were developed for one of Commodore Company's products:  The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period: 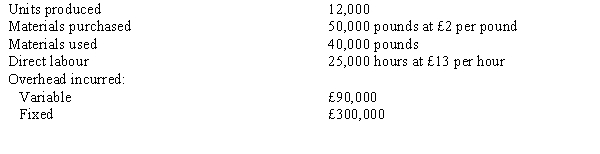 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £280,000, and expected capacity for the period is 28,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £280,000, and expected capacity for the period is 28,000 direct labour hours.
Required:
a.
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate.
b.
Complete the standard cost card for the product.
 The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:  Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £280,000, and expected capacity for the period is 28,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £280,000, and expected capacity for the period is 28,000 direct labour hours.Required:
a.
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate.
b.
Complete the standard cost card for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £12,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £8,400 favourable.
D) £3,600 unfavourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's labour efficiency variance would be
A) £12,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £8,400 favourable.
D) £3,600 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's fixed overhead volume variance would be
A) £10,000 unfavourable.
B) £11,000 unfavourable.
C) £21,000 favourable.
D) £31,000 favourable.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's fixed overhead volume variance would be
A) £10,000 unfavourable.
B) £11,000 unfavourable.
C) £21,000 favourable.
D) £31,000 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Taylor Company's budgeted sales were 10,000 units at £200 per unit. Actual sales were 9,200 units at £210 per unit. Taylor's sales price variance is
A) £68,000 (U).
B) £100,000 (U).
C) £8,000 (U).
D) £92,000 (F).
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Taylor Company's budgeted sales were 10,000 units at £200 per unit. Actual sales were 9,200 units at £210 per unit. Taylor's sales price variance is
A) £68,000 (U).
B) £100,000 (U).
C) £8,000 (U).
D) £92,000 (F).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £7,000 favourable.
B) £8,000 unfavourable.
C) £15,000 favourable.
D) £23,000 unfavourable.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £7,000 favourable.
B) £8,000 unfavourable.
C) £15,000 favourable.
D) £23,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The volume variance is caused by:
A) the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the budgeted activity used in computing the fixed overhead rate.
B) the difference between total budgeted fixed overhead and total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
C) the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
D) the difference between the standard fixed overhead rate and the actual fixed overhead rate.
A) the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the budgeted activity used in computing the fixed overhead rate.
B) the difference between total budgeted fixed overhead and total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
C) the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
D) the difference between the standard fixed overhead rate and the actual fixed overhead rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Franklin Company expected sales were 2,000 units at £100 per unit. During 2011, it had actual sales of 1,800 units at £110 per unit. Budgeted variable costs were £60 per unit. What is Franklin's sales price variance?
A) £8,000 (U)
B) £20,000 (U)
C) £18,000 (F)
D) £2,000 (U)
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Franklin Company expected sales were 2,000 units at £100 per unit. During 2011, it had actual sales of 1,800 units at £110 per unit. Budgeted variable costs were £60 per unit. What is Franklin's sales price variance?
A) £8,000 (U)
B) £20,000 (U)
C) £18,000 (F)
D) £2,000 (U)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £7,000 favourable.
B) £8,000 unfavourable.
C) £15,000 favourable.
D) £23,000 unfavourable.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

Refer to Figure 17-8. Noelle's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £7,000 favourable.
B) £8,000 unfavourable.
C) £15,000 favourable.
D) £23,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's materials usage variance would be
A) £22,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £10,000 unfavourable.
D) £4,000 unfavourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's materials usage variance would be
A) £22,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £10,000 unfavourable.
D) £4,000 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's labour rate variance would be
A) £12,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £8,400 favourable.
D) £3,600 unfavourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's labour rate variance would be
A) £12,000 unfavourable.
B) £12,000 favourable.
C) £8,400 favourable.
D) £3,600 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
A sales volume variance will be favourable when:
A) actual units sold is greater than budgeted sales volume.
B) actual units sold is less than budgeted sales volume.
C) actual selling price is greater than budgeted selling price.
D) actual contribution margin is greater than budgeted contribution margin.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

A sales volume variance will be favourable when:
A) actual units sold is greater than budgeted sales volume.
B) actual units sold is less than budgeted sales volume.
C) actual selling price is greater than budgeted selling price.
D) actual contribution margin is greater than budgeted contribution margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For planning and control purposes, fixed overhead is NOT included in the standard cost per unit because:
A) it is incurred based on the number of units produced.
B) the number of units produced do not vary from period to period.
C) it can best be controlled on a lump-sum basis.
D) of all of the above
A) it is incurred based on the number of units produced.
B) the number of units produced do not vary from period to period.
C) it can best be controlled on a lump-sum basis.
D) of all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 17-8
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company: Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
The sales price variance is created by a difference between
A) actual and standard contribution margin.
B) actual and expected sales price.
C) expected and standard net income.
D) actual and expected sales volume.
The following information was extracted from the accounting records of Noelle Company:
 Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £420,000, and the budgeted fixed overhead rate is based on an expected capacity of 30,000 direct labour hours.The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:

The sales price variance is created by a difference between
A) actual and standard contribution margin.
B) actual and expected sales price.
C) expected and standard net income.
D) actual and expected sales volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £1,200 unfavourable.
B) £3,600 unfavourable.
C) £4,800 unfavourable.
D) £4,800 favourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
A) £1,200 unfavourable.
B) £3,600 unfavourable.
C) £4,800 unfavourable.
D) £4,800 favourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 17-7
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products: The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £4,800 favourable.
B) £4,800 unfavourable.
C) £3,600 unfavourable.
D) £1,200 unfavourable.
Orient Company has developed the following standards for one of its products:
 The following activities occurred during the month of November:
The following activities occurred during the month of November:  The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.
The company records materials price variances at the time of purchase.Refer to Figure 17-7. Orient's variable overhead spending variance would be
A) £4,800 favourable.
B) £4,800 unfavourable.
C) £3,600 unfavourable.
D) £1,200 unfavourable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Mills Company uses standard costing for direct materials and direct labour. Management would like to use standard costing for variable and fixed overhead.
The following monthly cost functions were developed for overhead items: The cost functions are considered reliable within a relevant range of 70,000 to 100,000 direct labour hours. The company expects to operate at 80,000 direct labour hours per month.
The cost functions are considered reliable within a relevant range of 70,000 to 100,000 direct labour hours. The company expects to operate at 80,000 direct labour hours per month.
Information for the month of September is as follows: Required:
Required: 
The following monthly cost functions were developed for overhead items:
 The cost functions are considered reliable within a relevant range of 70,000 to 100,000 direct labour hours. The company expects to operate at 80,000 direct labour hours per month.
The cost functions are considered reliable within a relevant range of 70,000 to 100,000 direct labour hours. The company expects to operate at 80,000 direct labour hours per month.Information for the month of September is as follows:
 Required:
Required: 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The following standard costs were developed for one of Commodore Company's products:
STANDARD COST CARD
PER UNIT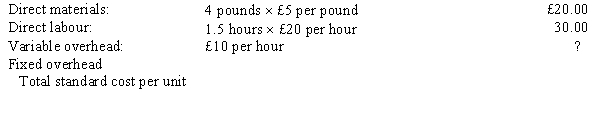 The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
Units produced
15,000
Materials purchased
90,000 pounds at £3.60 per pound
Materials used
80,000 pounds
Direct labour
9,000 hours at £16.50 per hour
Overhead incurred:
Variable
£220,000
Fixed
£640,000
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £600,000, and expected capacity for the period is 20,000 direct labour hours.
Required:
a.
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate.
b.
Complete the standard cost card for the product.
STANDARD COST CARD
PER UNIT
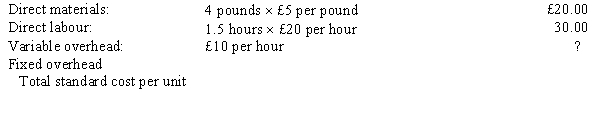 The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:
The following information is available regarding the company's operations for the period:Units produced
15,000
Materials purchased
90,000 pounds at £3.60 per pound
Materials used
80,000 pounds
Direct labour
9,000 hours at £16.50 per hour
Overhead incurred:
Variable
£220,000
Fixed
£640,000
Budgeted fixed overhead for the period is £600,000, and expected capacity for the period is 20,000 direct labour hours.
Required:
a.
Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate.
b.
Complete the standard cost card for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



