Deck 10: Keynesian Macroeconomics and Economic Instability a Critique of the Self Regulating Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Keynesian Macroeconomics and Economic Instability a Critique of the Self Regulating Economy
1
The part of consumption that is dependent on disposable income is called autonomous consumption.
False
2
The economy can be in equilibrium and in a recessionary gap simultaneously.
True
3
Efficiency wage models imply that workers are more productive when they are paid a higher wage, as compared to when they are paid a lower wage.
True
4
An increase in autonomous consumption, an increase in disposable income, or a decrease in the marginal propensity to consume can all increase consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In reality, idle resources must exist in the economy in order for the multiplier process to lead to an increase in Real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The work of John Maynard Keynes led to a major revolution in economic thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When total expenditure (TE) exceeds total production (TP), inventory levels rise unexpectedly, which sends a signal to firms that they have overproduced, so they cut back on production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the simple Keynesian model, the aggregate supply curve has a horizontal segment at levels of output below the level of natural Real GDP and a vertical segment at the level of natural Real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Many economists argue that the labor market may take a long time for wages to adjust to new equilibrium level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Classical economists used efficiency wage models to support their belief in a self-regulating economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) can be found using the equation: (1 - MPC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Keynes asserted that the interest rate is important in determining investment, but not as important as other variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A simple Keynesian model is representative of a closed economy, with no foreign sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Classical economists and Keynes shared the belief that increased saving would necessarily stimulate an equal amount of increased investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A consumption function is a statement that shows the relationship between interest rates and consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to Keynes, the economy is inherently unstable and may get stuck in a recessionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) refers to the proportion of disposable income that is spent on consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a simple Keynesian model, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In Keynes' view, labor unions would resist wage cuts, but individual employees would go along with wage cuts initiated by his/her employer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A change in autonomous spending leads to an even greater change in total spending through the multiplier process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 10-1
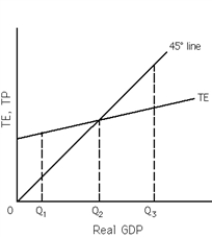
Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q1,
A)TE > TP, and there are decreases in inventory.
B)TP > TE, and there are increases in inventory.
C)TE = TP, and there are no changes in inventory.
D)TE > TP, and there are increases in inventory.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q1,
A)TE > TP, and there are decreases in inventory.
B)TP > TE, and there are increases in inventory.
C)TE = TP, and there are no changes in inventory.
D)TE > TP, and there are increases in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When there is economy-wide equilibrium, there is a tendency for
A)total output to rise.
B)total output to fall.
C)total output to remain unchanged.
D)prices to fall.
E)prices to rise.
A)total output to rise.
B)total output to fall.
C)total output to remain unchanged.
D)prices to fall.
E)prices to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At all points on the 45-degree line,
A)TP = Real GDP.
B)TP > Real GDP.
C)TP < Real GDP.
D)all of the above are possible.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At all points on the 45-degree line,
A)TP = Real GDP.
B)TP > Real GDP.
C)TP < Real GDP.
D)all of the above are possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Equilibrium Real GDP occurs at
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q1 and Q3.
E)none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. Equilibrium Real GDP occurs at
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q1 and Q3.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q2, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q2, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to Keynes, the dollar amount households plan to save
A)always equals the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
B)sometimes equals the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
C)is always greater than the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
D)is always less than the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
A)always equals the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
B)sometimes equals the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
C)is always greater than the dollar amount firms plan to invest.
D)is always less than the dollar amount firms plan to invest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A decline in housing prices can help to push the economy into a recessionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The two major curves or lines in the TE-TP diagram are:
A)the total expenditure curve and the 45-degree line.
B)the supply and demand curves.
C)the total expenditures and national income curves.
D)the total production and national income curves.
A)the total expenditure curve and the 45-degree line.
B)the supply and demand curves.
C)the total expenditures and national income curves.
D)the total production and national income curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the economy is in short-run equilibrium,
A)there are increases in inventory.
B)there are decreases in inventory.
C)total expenditures equal total production.
D)people want to buy more than will be produced.
A)there are increases in inventory.
B)there are decreases in inventory.
C)total expenditures equal total production.
D)people want to buy more than will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If households, businesses, and government buy more than businesses have produced,
A)the economy is in equilibrium.
B)total expenditures are greater than total production.
C)there will be an increase in inventory.
D)there will be a decrease in total output.
A)the economy is in equilibrium.
B)total expenditures are greater than total production.
C)there will be an increase in inventory.
D)there will be a decrease in total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q3,
A)TE > TP, and there are decreases in inventory.
B)TE = TP, and there are no changes in inventory.
C)TP > TE, and there are increases in inventory.
D)TE > TP, and there are increases in inventory.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q3,
A)TE > TP, and there are decreases in inventory.
B)TE = TP, and there are no changes in inventory.
C)TP > TE, and there are increases in inventory.
D)TE > TP, and there are increases in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When total expenditures are greater than total production, __________ is produced than households want to buy, which leads to __________ in inventory, which signals firms that they have __________, which causes firms to increase production.
A)less; decreases; underproduced
B)more; increases; underproduced
C)less; increases; underproduced
D)more; decreases; overproduced
A)less; decreases; underproduced
B)more; increases; underproduced
C)less; increases; underproduced
D)more; decreases; overproduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Keynes held that saving is more responsive to changes in income than to changes in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q3, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q3, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If total production is greater than total expenditures,
A)there will be an increase in saving.
B)there will be an increase in inventories.
C)firms will then increase production.
D)firms will then increase prices.
A)there will be an increase in saving.
B)there will be an increase in inventories.
C)firms will then increase production.
D)firms will then increase prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exhibit 10-1

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q1, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Refer to Exhibit 10-1. At Q1, there is a tendency for Real GDP to
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged.
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If total production is greater than total expenditures, then business firms
A)have underproduced.
B)will step up production.
C)will lower production.
D)will experience decreases in inventory.
E)a and b
A)have underproduced.
B)will step up production.
C)will lower production.
D)will experience decreases in inventory.
E)a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If total production is less than total expenditures, then business firms
A)have overproduced.
B)will cut back on production.
C)will raise production.
D)will experience increases in inventory.
E)a and d
A)have overproduced.
B)will cut back on production.
C)will raise production.
D)will experience increases in inventory.
E)a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If households purchase $60,000 worth of consumer goods and firms produce $50,000 worth of consumer goods, then
A)inventory changes are -$10,000.
B)inventory changes are +$10,000.
C)new capital goods expenditures (by firms) are $10,000.
D)consumer goods expenditures are $10,000.
A)inventory changes are -$10,000.
B)inventory changes are +$10,000.
C)new capital goods expenditures (by firms) are $10,000.
D)consumer goods expenditures are $10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When total production is greater than total expenditures, __________ is produced than households want to buy, which leads to __________ in inventory, which signals firms that they have __________, which causes firms to cut back production.
A)less; decreases; underproduced
B)less; increases; overproduced
C)more; decreases; underproduced
D)more; increases; overproduced
A)less; decreases; underproduced
B)less; increases; overproduced
C)more; decreases; underproduced
D)more; increases; overproduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consumption and disposable income are
A)indirectly related.
B)directly related.
C)not related.
D)sometimes directly and sometimes indirectly related, depending upon whether consumption is planned or unplanned.
A)indirectly related.
B)directly related.
C)not related.
D)sometimes directly and sometimes indirectly related, depending upon whether consumption is planned or unplanned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The classical economists believed __________ determined savings, while Keynes said it was __________.
A)interest rates; income
B)income; investment
C)investment; interest rates
D)interest rates; investment
A)interest rates; income
B)income; investment
C)investment; interest rates
D)interest rates; investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The efficiency wage model is an explanation of wage __________ and thus a support for the ____________________ view.
A)flexibility; Keynesian
B)flexibility; classical
C)inflexibility; Keynesian
D)inflexibility; classical
A)flexibility; Keynesian
B)flexibility; classical
C)inflexibility; Keynesian
D)inflexibility; classical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Who would be most likely to agree that "People do not always save more as interest rates rise"?
A)a classical economist
B)John Maynard Keynes
C)an efficiency wage theorist
D)a and b
E)a, b, and c
A)a classical economist
B)John Maynard Keynes
C)an efficiency wage theorist
D)a and b
E)a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 10-2
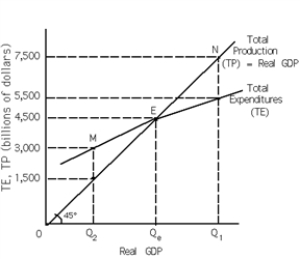
Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Equilibrium Real GDP occurs at
A)$3,000 billion.
B)$1,500 billion.
C)$7,500 billion.
D)$4,000 billion.
E)$4,500 billion.

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Equilibrium Real GDP occurs at
A)$3,000 billion.
B)$1,500 billion.
C)$7,500 billion.
D)$4,000 billion.
E)$4,500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Keynes's major work, The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, was published during the
A)late 1800s.
B)mid-1700s.
C)1930s.
D)Panic of 1907.
A)late 1800s.
B)mid-1700s.
C)1930s.
D)Panic of 1907.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the efficiency wage model, firms tend to pay workers
A)the market-clearing wage that efficiently equates labor supplied and demanded.
B)in excess of the market-clearing wage to provide an incentive for productivity and efficiency.
C)less than the market-clearing wage to assure themselves a pool of workers ready to replace workers who quit.
D)less than the market-clearing wage to minimize labor cost per unit of production.
A)the market-clearing wage that efficiently equates labor supplied and demanded.
B)in excess of the market-clearing wage to provide an incentive for productivity and efficiency.
C)less than the market-clearing wage to assure themselves a pool of workers ready to replace workers who quit.
D)less than the market-clearing wage to minimize labor cost per unit of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
John Maynard Keynes drew many economists ______________ the classical view. The classical view held that a market economy __________ regulate itself to avoid long periods of excessive unemployment.
A)toward; can
B)toward; cannot
C)away from; can
D)away from; cannot
A)toward; can
B)toward; cannot
C)away from; can
D)away from; cannot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When total production is greater than total expenditures,
A)the economy is in disequilibrium.
B)there are increases in inventory.
C)total output will decrease.
D)all of the above
A)the economy is in disequilibrium.
B)there are increases in inventory.
C)total output will decrease.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Two economists, Smith and Jones, are discussing the currently high unemployment rate. Smith says that something ought to be done quickly because the economy may not be able to restore itself to full employment. Jones says that it is better to take a "hands-off" approach. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
A)Smith and Jones are most likely both Keynesian economists with a few minor differences of opinion.
B)Smith and Jones are most likely both classical economists with a few minor differences of opinion.
C)Jones is likely to be a Keynesian economist and Smith is likely to be a classical economist.
D)Smith is likely to be a Keynesian economist and Jones is likely to be a classical economist.
E)none of the above.
A)Smith and Jones are most likely both Keynesian economists with a few minor differences of opinion.
B)Smith and Jones are most likely both classical economists with a few minor differences of opinion.
C)Jones is likely to be a Keynesian economist and Smith is likely to be a classical economist.
D)Smith is likely to be a Keynesian economist and Jones is likely to be a classical economist.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Total production
A)always equals total expenditures.
B)equals total expenditures in equilibrium.
C)is always greater than total expenditures.
D)is always less than total expenditures.
A)always equals total expenditures.
B)equals total expenditures in equilibrium.
C)is always greater than total expenditures.
D)is always less than total expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Exhibit 10-2

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. At M,
A)TP = TE.
B)TP > TE.
C)TE > TP.
D)the relationship between TP and TE cannot be determined.

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. At M,
A)TP = TE.
B)TP > TE.
C)TE > TP.
D)the relationship between TP and TE cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a recessionary gap, the implications of downward wage inflexibility are that there will be
A)further leftward shifts of AD that worsen unemployment.
B)no further leftward shifts of AD, allowing the shifts in SRAS to close the recessionary gap.
C)no further leftward shifts of SRAS, allowing the shifts in AD to close the recessionary gap.
D)no rightward shifts of SRAS, allowing for the possibility of persistent high unemployment.
A)further leftward shifts of AD that worsen unemployment.
B)no further leftward shifts of AD, allowing the shifts in SRAS to close the recessionary gap.
C)no further leftward shifts of SRAS, allowing the shifts in AD to close the recessionary gap.
D)no rightward shifts of SRAS, allowing for the possibility of persistent high unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Exhibit 10-2

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. If autonomous consumption increases, the TE curve will shift ____________ and the new level of equilibrium Real GDP will be ___________ than $4,500.
A)downward; greater
B)downward; less
C)upward; less
D)upward; greater

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. If autonomous consumption increases, the TE curve will shift ____________ and the new level of equilibrium Real GDP will be ___________ than $4,500.
A)downward; greater
B)downward; less
C)upward; less
D)upward; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 10-2

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. If autonomous investment decreases, the TE curve will shift ____________ and the new level of equilibrium Real GDP will be ___________ than $4,500.
A)downward; greater
B)downward; less
C)upward; less
D)upward; greater

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. If autonomous investment decreases, the TE curve will shift ____________ and the new level of equilibrium Real GDP will be ___________ than $4,500.
A)downward; greater
B)downward; less
C)upward; less
D)upward; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 10-2

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Which of the following is correct about point M?
A)TE is $4,500 billion and TP is only $1,500 billion.
B)TP is $4,500 billion and TE is only $1,500 billion.
C)TE is $7,500 and TP is only $5,500 billion.
D)TP is only $7,500 billion and TE is only $5,500 billion.
E)TE is $3,000 billion and TP is only $1,500 billion.

Refer to Exhibit 10-2. Which of the following is correct about point M?
A)TE is $4,500 billion and TP is only $1,500 billion.
B)TP is $4,500 billion and TE is only $1,500 billion.
C)TE is $7,500 and TP is only $5,500 billion.
D)TP is only $7,500 billion and TE is only $5,500 billion.
E)TE is $3,000 billion and TP is only $1,500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The horizontal investment curve used to derive the TE curve implies that investment is
A)directly related to Real GDP.
B)indirectly related to Real GDP.
C)independent of Real GDP.
D)sometimes directly and sometimes indirectly related to Real GDP, depending upon whether it is planned capital or planned inventory investment.
A)directly related to Real GDP.
B)indirectly related to Real GDP.
C)independent of Real GDP.
D)sometimes directly and sometimes indirectly related to Real GDP, depending upon whether it is planned capital or planned inventory investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The efficiency wage model contains the assumption that labor productivity __________ the wage rate, so that a firm maximizing its profits __________ pay workers an above-market wage rate.
A)is independent of; may
B)is independent of; will never
C)depends on; may
D)depends on; will never
A)is independent of; may
B)is independent of; will never
C)depends on; may
D)depends on; will never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Keynesian macroeconomists believe that the time it takes for falling wages and prices to eliminate a recessionary gap is __________ enough to say that the economy is __________.
A)long; not self-regulating
B)long; self-regulating
C)short; not self-regulating
D)short; self-regulating
A)long; not self-regulating
B)long; self-regulating
C)short; not self-regulating
D)short; self-regulating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Autonomous consumption is
A)the change in consumption that results as a person's (or nation's) income increases or decreases.
B)that portion of total consumption that is dependent upon the level of income.
C)the steady increase in the consumption of goods and services that automatically occurs as a person grows from a child to an adult.
D)that portion of total consumption that is independent of the level of income.
A)the change in consumption that results as a person's (or nation's) income increases or decreases.
B)that portion of total consumption that is dependent upon the level of income.
C)the steady increase in the consumption of goods and services that automatically occurs as a person grows from a child to an adult.
D)that portion of total consumption that is independent of the level of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The larger the marginal propensity to save,
A)the smaller the multiplier.
B)the larger the multiplier.
C)the smaller the change in Real GDP, given a change in autonomous consumption.
D)a and c
E)none of the above
A)the smaller the multiplier.
B)the larger the multiplier.
C)the smaller the change in Real GDP, given a change in autonomous consumption.
D)a and c
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If autonomous consumption rises by $40 and, as a result, Real GDP rises by $240, then the multiplier is
A)4.
B)5.
C)6.
D)10.
E)none of the above
A)4.
B)5.
C)6.
D)10.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The consumption function is a function showing the relationship between consumption and
A)disposable income.
B)exports.
C)interest rates.
D)investment.
A)disposable income.
B)exports.
C)interest rates.
D)investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Keynes believed that
A)Say's law would hold in a laissez-faire economy.
B)the economy would always be near or on its production possibilities frontier.
C)wages and prices are often inflexible in the downward direction.
D)the equilibrium level of output will always be at the full-employment level of output.
A)Say's law would hold in a laissez-faire economy.
B)the economy would always be near or on its production possibilities frontier.
C)wages and prices are often inflexible in the downward direction.
D)the equilibrium level of output will always be at the full-employment level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
On a TE-TP diagram consider a level of Real GDP at which the vertical distance to the TE line exceeds the vertical distance to the 45-degree line. This level of Real GDP is __________ its equilibrium level, with __________.
A)above; TE > TP
B)above; TE < TP
C)below; TE > TP
D)below; TE < TP
A)above; TE > TP
B)above; TE < TP
C)below; TE > TP
D)below; TE < TP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is false?
A)Keynes believed that monopolistic elements in the economy will prevent immediate price declines.
B)Keynes believed that during periods of high unemployment, labor unions will prevent wages from falling fast enough to restore full employment.
C)Keynes believed that interest rate flexibility will ensure that saving is equal to investment.
D)Keynes did not believe in Say's law.
A)Keynes believed that monopolistic elements in the economy will prevent immediate price declines.
B)Keynes believed that during periods of high unemployment, labor unions will prevent wages from falling fast enough to restore full employment.
C)Keynes believed that interest rate flexibility will ensure that saving is equal to investment.
D)Keynes did not believe in Say's law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Here is a consumption function: C = C0 + MPC(Yd). The C0 term is usually defined as
A)autonomous consumption.
B)point-zero consumption.
C)mandatory consumption.
D)propensitory consumption.
E)none of the above
A)autonomous consumption.
B)point-zero consumption.
C)mandatory consumption.
D)propensitory consumption.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The marginal propensity to consume plus the marginal propensity to save is always
A)equal to zero.
B)greater than zero but less than one.
C)equal to one.
D)greater than one.
A)equal to zero.
B)greater than zero but less than one.
C)equal to one.
D)greater than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On a TE-TP diagram consider a level of Real GDP at which the vertical distance to the TE line is less than the vertical distance to the 45-degree line. This level of Real GDP is __________ its equilibrium level, with __________.
A)above; TE > TP
B)above; TE < TP
C)below; TE > TP
D)below; TE < TP
A)above; TE > TP
B)above; TE < TP
C)below; TE > TP
D)below; TE < TP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Keynes believed that saving is
A)more responsive to changes in income than to changes in interest rates.
B)less responsive to changes in income than to changes in interest rates.
C)equally responsive to changes in income and to changes in interest rates.
D)dependent only on changes in interest rates.
A)more responsive to changes in income than to changes in interest rates.
B)less responsive to changes in income than to changes in interest rates.
C)equally responsive to changes in income and to changes in interest rates.
D)dependent only on changes in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The ratio of the change in consumption to the change in disposable income is called the
A)marginal utility of consumption.
B)average utility of consumption.
C)marginal propensity to consume.
D)average propensity to consume.
A)marginal utility of consumption.
B)average utility of consumption.
C)marginal propensity to consume.
D)average propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If income rises from $10,000 to $10,600 and consumption rises from $9,100 to $9,622, the marginal propensity to save (MPS) is
A)0.13.
B)0.87.
C)0.25.
D)0.10.
A)0.13.
B)0.87.
C)0.25.
D)0.10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Keynes believed that investment is
A)dependent on a number of factors, including business expectations.
B)mainly determined by changes in interest rates.
C)unrelated to business expectations.
D)related to business expectations only during recessionary periods.
A)dependent on a number of factors, including business expectations.
B)mainly determined by changes in interest rates.
C)unrelated to business expectations.
D)related to business expectations only during recessionary periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Keynes believed that
A)the internal structure of the economy is extremely competitive and that wage-price flexibility exists.
B)monopolistic elements in the economy prevent immediate and sharp price declines in response to falling demand.
C)even though there are monopolistic elements in the economy, wage-price flexibility exists.
D)in spite of the competitiveness of the economy, wage-price flexibility does not exist.
A)the internal structure of the economy is extremely competitive and that wage-price flexibility exists.
B)monopolistic elements in the economy prevent immediate and sharp price declines in response to falling demand.
C)even though there are monopolistic elements in the economy, wage-price flexibility exists.
D)in spite of the competitiveness of the economy, wage-price flexibility does not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If income rises from $12,000 to $12,400 and consumption rises from $11,800 to $12,176, the marginal propensity to consume is __________ percent.
A)8
B)85
C)16
D)94
A)8
B)85
C)16
D)94

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which statement is consistent with what Keynes believed about consumption and disposable income?
A)Consumption depends upon disposable income and falls as disposable income rises.
B)Consumption rises by the same amount as disposable income rises.
C)Consumption rises by less than disposable income rises.
D)Disposable income depends upon consumption.
A)Consumption depends upon disposable income and falls as disposable income rises.
B)Consumption rises by the same amount as disposable income rises.
C)Consumption rises by less than disposable income rises.
D)Disposable income depends upon consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to the Keynesian consumption function, an increase in disposable income will result in
A)a decrease in consumption.
B)an increase in consumption.
C)a decrease in investment.
D)an increase in investment.
A)a decrease in consumption.
B)an increase in consumption.
C)a decrease in investment.
D)an increase in investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Here is a consumption function: C = C0 + MPC(Yd). If C0 = $200, then we know that
A)if Yd is zero, C will be $200.
B)when Yd rises, C rises by $200.
C)when Yd falls, C falls by MPC times C0.
D)C will always equal C0.
A)if Yd is zero, C will be $200.
B)when Yd rises, C rises by $200.
C)when Yd falls, C falls by MPC times C0.
D)C will always equal C0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Here is a consumption function: C = C0 + MPC(Yd). If MPC is 0.80, then we know that
A)as Yd rises by $1, Co rises by $0.80.
B)as Yd rises by $1, C rises by $0.80.
C)Yd rises by $0.80.
D)as C0 rises by $0.80, Yd rises by $1.
A)as Yd rises by $1, Co rises by $0.80.
B)as Yd rises by $1, C rises by $0.80.
C)Yd rises by $0.80.
D)as C0 rises by $0.80, Yd rises by $1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If autonomous consumption rises by $70 and, as a result, Real GDP rises by $350, then the marginal propensity to consume is
A)0.20.
B)0.80.
C)0.25.
D)0.75.
E)none of the above
A)0.20.
B)0.80.
C)0.25.
D)0.75.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



