Deck 8: Testing Associations Between Categorical Variables
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Testing Associations Between Categorical Variables
1
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.
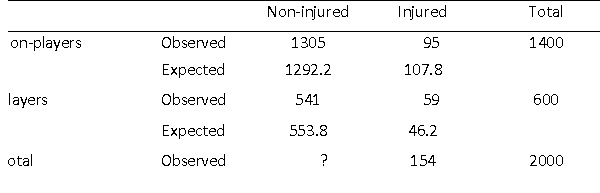

How many injured sports players took part in the study?
A)1305
B)59
C)95
D)600



How many injured sports players took part in the study?
A)1305
B)59
C)95
D)600
59
2
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.



What should we conclude from this study?
A)Sports players are significantly less likely to attend accident and emergency
B)Sports players are significantly more likely to attend accident and emergency
C)There is no association between playing sport and attending accident and emergency
D)None of the above



What should we conclude from this study?
A)Sports players are significantly less likely to attend accident and emergency
B)Sports players are significantly more likely to attend accident and emergency
C)There is no association between playing sport and attending accident and emergency
D)None of the above
Sports players are significantly more likely to attend accident and emergency
3
In the study described in Question 2, the following preferences were observed: flavour A - 12 flavour B - 217 flavour C - 100 flavour D - 171
Which test could you use to test whether this distribution differs significantly from chance?
A)One variable χ2 test
B)Cramer's V
C)Fisher's Exact Test
D)None of the above
Which test could you use to test whether this distribution differs significantly from chance?
A)One variable χ2 test
B)Cramer's V
C)Fisher's Exact Test
D)None of the above
One variable χ2 test
4
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.



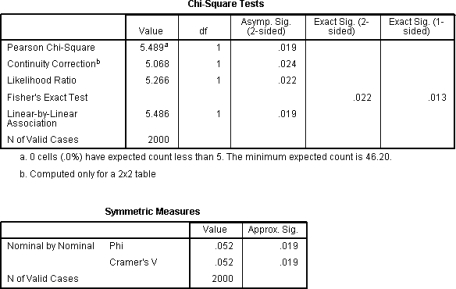
What will the degrees of freedom be for a χ2 test of a 56 contingency table?
A)11
B)1
C)30
D)20



What will the degrees of freedom be for a χ2 test of a 56 contingency table?
A)11
B)1
C)30
D)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.



What number should replace the '?' in contingency table?
A)2000
B)1400
C)754
D)1846



What number should replace the '?' in contingency table?
A)2000
B)1400
C)754
D)1846

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.



How should the significance level for the χ2 test be reported?
A)p=.019
B)p>.05
C)p=.000
D)p<.001



How should the significance level for the χ2 test be reported?
A)p=.019
B)p>.05
C)p=.000
D)p<.001

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The χ2 test may be used for
A)2 × 2 tables
B)2 × 3 tables
C)one variable tests
D)any of the above
A)2 × 2 tables
B)2 × 3 tables
C)one variable tests
D)any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
500 participants are recruited to a study assessing patient preference for 4 different flavours of cough medicine.If all the medicines are equally palatable, how many participants would you expect to prefer each medicine?
A)100
B)500
C)125
D)0
A)100
B)500
C)125
D)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When working with categorical variables it is fine to collapse categories together if:
A)The resulting category is theoretically meaningful
B)You have only a few people in some categories
C)You have violated the assumptions of the χ2 test if you do not
D)Categories may never be collapsed
A)The resulting category is theoretically meaningful
B)You have only a few people in some categories
C)You have violated the assumptions of the χ2 test if you do not
D)Categories may never be collapsed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Questions are based on a fictional dataset addressing the association of being a regular sports player and having attended accident and emergency with an unintentional injury.



What percentage of sports players have been injured?
A)6.8%
B)9.8%
C)11.0%
D)78.3%



What percentage of sports players have been injured?
A)6.8%
B)9.8%
C)11.0%
D)78.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



