Deck 8: Articulations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/111
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Articulations
1
A ligamentous connection such as an interosseus ligament is termed a
A) symphysis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) gomphosis.
D) synostosis.
E) synchondrosis.
A) symphysis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) gomphosis.
D) synostosis.
E) synchondrosis.
B
2
C:\User  Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Use Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following movements is a good example of depression?
A) extreme bending of the head backwards
B) moving the hand toward the shoulder
C) spreading the fingers
D) opening the mouth
E) turning the hand palm upward
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following movements is a good example of depression?
A) extreme bending of the head backwards
B) moving the hand toward the shoulder
C) spreading the fingers
D) opening the mouth
E) turning the hand palm upward
D
3
In the knee joint, the medial and lateral menisci
A) take the place of bursae.
B) are cartilages that bind the knee to the tibia.
C) act as cushions and conform to the shape of the articulating surfaces.
D) are found between the patella and femur.
E) both A and D
A) take the place of bursae.
B) are cartilages that bind the knee to the tibia.
C) act as cushions and conform to the shape of the articulating surfaces.
D) are found between the patella and femur.
E) both A and D
C
4
Nodding your head "yes" is an example of
A) lateral and medial rotation.
B) circumduction.
C) protraction and retraction.
D) flexion and extension.
E) pronation and supination.
A) lateral and medial rotation.
B) circumduction.
C) protraction and retraction.
D) flexion and extension.
E) pronation and supination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Bursae are found in all of the following areas, except
A) tendon sheaths.
B) around many synovial joints.
C) around blood vessels.
D) within connective tissue exposed to friction or pressure.
E) beneath the skin covering a bone.
A) tendon sheaths.
B) around many synovial joints.
C) around blood vessels.
D) within connective tissue exposed to friction or pressure.
E) beneath the skin covering a bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole of the foot outward is known as
A) plantar flexion.
B) dorsiflexion.
C) inversion.
D) eversion.
E) none of the above
A) plantar flexion.
B) dorsiflexion.
C) inversion.
D) eversion.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
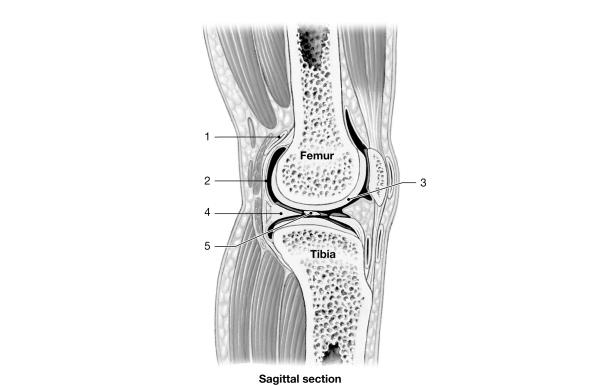 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "2."
A) synovial membrane
B) periosteum
C) serous membrane
D) joint capsule
E) intracapsular ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
C:\User  Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Use Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following ligaments is not associated with the hip joint?
A) ischiofemoral ligament
B) anterior cruciate ligament
C) iliofemoral ligament
D) ligamentum teres
E) pubofemoral ligament
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following ligaments is not associated with the hip joint?
A) ischiofemoral ligament
B) anterior cruciate ligament
C) iliofemoral ligament
D) ligamentum teres
E) pubofemoral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Contraction of the muscle that is attached to the radial tuberosity results in
A) rotation of the shoulder.
B) flexion of the forearm.
C) adduction of the forearm.
D) abduction of the forearm.
E) extension of the forearm.
A) rotation of the shoulder.
B) flexion of the forearm.
C) adduction of the forearm.
D) abduction of the forearm.
E) extension of the forearm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
To pinch with a thumb and finger involves a movement called
A) eversion.
B) rotation.
C) circumduction.
D) retraction.
E) opposition.
A) eversion.
B) rotation.
C) circumduction.
D) retraction.
E) opposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An epiphyseal line is an example of a
A) symphysis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) synchondrosis.
D) gomphosis.
E) synostosis.
A) symphysis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) synchondrosis.
D) gomphosis.
E) synostosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
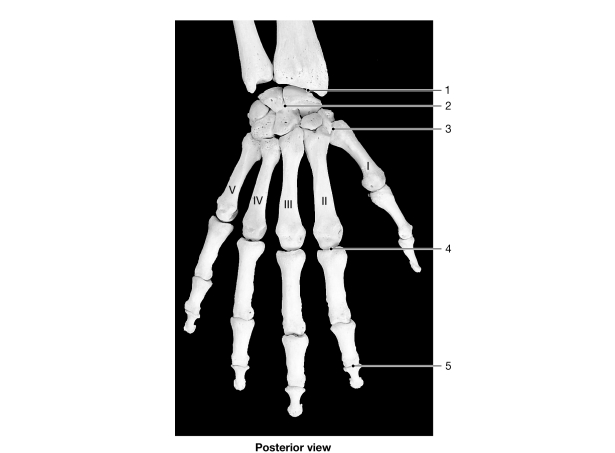 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "3."
A) hinge
B) saddle
C) pivot
D) ellipsoid
E) gliding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Dislocations are quite painful due to stimulation of pain receptors. One place these receptors are absent is
A) inside the joint cavity.
B) within the joint capsule.
C) within the tendons around the joint.
D) within the ligaments around the joint.
E) both C and D
A) inside the joint cavity.
B) within the joint capsule.
C) within the tendons around the joint.
D) within the ligaments around the joint.
E) both C and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following movements is a good example of supination?
A) moving the hand toward the shoulder
B) spreading the fingers
C) opening the mouth
D) extreme bending of the head backwards
E) turning the hand palm upward
A) moving the hand toward the shoulder
B) spreading the fingers
C) opening the mouth
D) extreme bending of the head backwards
E) turning the hand palm upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The joints that are subjected to the greatest load are found in the
A) ankles.
B) hips.
C) knees.
D) spine.
E) hands.
A) ankles.
B) hips.
C) knees.
D) spine.
E) hands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following movements would you associate with chewing food?
A) abduction
B) elevation
C) pronation
D) circumduction
E) flexion
A) abduction
B) elevation
C) pronation
D) circumduction
E) flexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
C:\User  Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Use Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "1."
A) ellipsoid
B) pivot
C) hinge
D) saddle
E) gliding
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "1."
A) ellipsoid
B) pivot
C) hinge
D) saddle
E) gliding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not a function of synovial fluid?
A) provides nutrients
B) protects articular cartilages
C) shock absorption
D) increases osmotic pressure within joint
E) lubrication
A) provides nutrients
B) protects articular cartilages
C) shock absorption
D) increases osmotic pressure within joint
E) lubrication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
A movement away from the midline of the body is termed
A) abduction.
B) inversion.
C) flexion.
D) extension.
E) adduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The joint that permits the greatest range of mobility of any joint in the body is the joint.
A) elbow
B) hip
C) knee
D) wrist
E) shoulder
A) elbow
B) hip
C) knee
D) wrist
E) shoulder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
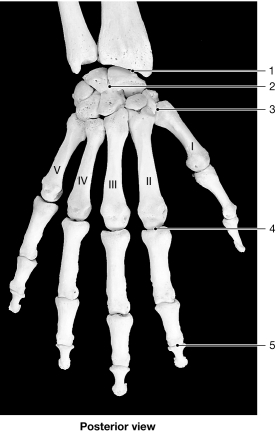 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "4."
A) pivot
B) hinge
C) gliding
D) saddle
E) ellipsoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following occurs when the articular cartilage is damaged?
A) The exposed surface changes to a rough feltwork.
B) The matrix begins to break down.
C) Friction in the joint increases.
D) Normal synovial joint function is unable to continue.
E) all of the above
A) The exposed surface changes to a rough feltwork.
B) The matrix begins to break down.
C) Friction in the joint increases.
D) Normal synovial joint function is unable to continue.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The joints between vertebrae are examples of joints.
A) gliding
B) ellipsoid
C) saddle
D) hinge
E) pivot
A) gliding
B) ellipsoid
C) saddle
D) hinge
E) pivot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The synarthrosis that binds the teeth to the bony sockets is a
A) synotosis.
B) suture.
C) synchondrosis.
D) gomphosis.
E) none of the above
A) synotosis.
B) suture.
C) synchondrosis.
D) gomphosis.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The surface of articular cartilage is
A) slick.
B) flat.
C) smooth.
D) rough.
E) both A and C
A) slick.
B) flat.
C) smooth.
D) rough.
E) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which ligament connects the clavicle and the acromion?
A) coracoclavicular
B) coracoacromial
C) acromioclavicular
D) coracohumeral
E) glenohumeral
A) coracoclavicular
B) coracoacromial
C) acromioclavicular
D) coracohumeral
E) glenohumeral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A suture is an example of an)
A) syndesmosis.
B) diarthrosis.
C) synarthrosis.
D) symphysis.
E) amphiarthrosis.
A) syndesmosis.
B) diarthrosis.
C) synarthrosis.
D) symphysis.
E) amphiarthrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following movements is a good example of abduction?
A) spreading the fingers
B) extreme bending of the head backwards
C) moving the hand toward the shoulder
D) opening the mouth
E) turning the hand palm upward
A) spreading the fingers
B) extreme bending of the head backwards
C) moving the hand toward the shoulder
D) opening the mouth
E) turning the hand palm upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The elbow joint is an example of an) joint.
A) hinge
B) gliding
C) ellipsoid
D) saddle
E) pivot
A) hinge
B) gliding
C) ellipsoid
D) saddle
E) pivot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The "rotator cuff" of the shoulder functions to
A) reinforce the joint capsule.
B) limit the range of movements.
C) allow biaxial movement.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) reinforce the joint capsule.
B) limit the range of movements.
C) allow biaxial movement.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A slightly movable joint is an)
A) gomphosis.
B) synostosis.
C) diarthrosis.
D) amphiarthrosis.
E) synarthrosis.
A) gomphosis.
B) synostosis.
C) diarthrosis.
D) amphiarthrosis.
E) synarthrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following movements is a good example of flexion?
A) extreme bending of the head backwards
B) spreading the fingers
C) turning the hand palm upward
D) opening the mouth
E) moving the hand toward the shoulder
A) extreme bending of the head backwards
B) spreading the fingers
C) turning the hand palm upward
D) opening the mouth
E) moving the hand toward the shoulder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of these is not a property of articular cartilage?
A) enclosed by a capsule
B) smooth, low- friction surface
C) lubricated by synovial fluid
D) similar to hyaline cartilage
E) covered by perichondrium
A) enclosed by a capsule
B) smooth, low- friction surface
C) lubricated by synovial fluid
D) similar to hyaline cartilage
E) covered by perichondrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A freely movable joint is an)
A) synarthrosis.
B) diarthrosis.
C) syndesmosis.
D) symphysis.
E) amphiarthrosis.
A) synarthrosis.
B) diarthrosis.
C) syndesmosis.
D) symphysis.
E) amphiarthrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
A herniated intervertebral disc is caused by
A) ossification of the vertebral disc.
B) loss of annulus fibrosis elasticity.
C) protrusion of the nucleus pulposus.
D) transformation of fibrocartilage to hyaline cartilage.
E) slippage of the fibrocartilage disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a triaxial articulation
A) no movement is possible.
B) movement can occur in all three axes.
C) movement can occur in only two axes.
D) movement can occur in only one axis.
E) only circumduction is possible.
A) no movement is possible.
B) movement can occur in all three axes.
C) movement can occur in only two axes.
D) movement can occur in only one axis.
E) only circumduction is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Monaxial joints are known as joints.
A) saddle
B) ball- and- socket
C) ellipsoid
D) hinge
E) gliding
A) saddle
B) ball- and- socket
C) ellipsoid
D) hinge
E) gliding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Factors that increase the stability of the hip joint include
A) supporting ligaments.
B) tough capsule.
C) almost complete bony socket.
D) strong muscular padding.
E) all of the above
A) supporting ligaments.
B) tough capsule.
C) almost complete bony socket.
D) strong muscular padding.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Syndesmosis is to ligament as symphysis is to
A) rigid cartilaginous bridge.
B) periodontal ligament.
C) completely fused.
D) fibrous cartilage.
E) dense regular connective tissue.
A) rigid cartilaginous bridge.
B) periodontal ligament.
C) completely fused.
D) fibrous cartilage.
E) dense regular connective tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
The medial surface of the knee joint is reinforced by the _ ligament.
A) cruciate
B) fibular collateral
C) popliteal
D) tibial collateral
E) patellar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
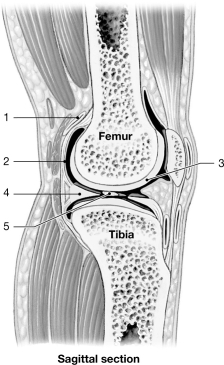 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure at label "1."
A) synovial membrane
B) articular cartilage
C) bursa
D) meniscus
E) joint cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All of the following are structural classifications of synovial joints, except
A) pivot.
B) hinge.
C) saddle.
D) gliding.
E) rolling.
A) pivot.
B) hinge.
C) saddle.
D) gliding.
E) rolling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Lifting a stone with the tip of foot is
A) eversion.
B) circumduction.
C) inversion.
D) plantar flexion.
E) dorsiflexion.
A) eversion.
B) circumduction.
C) inversion.
D) plantar flexion.
E) dorsiflexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following movements is a good example of hyperextension?
A) moving the hand toward the shoulder
B) extreme bending of the head backwards
C) opening the mouth
D) spreading the fingers
E) turning the hand palm upward
A) moving the hand toward the shoulder
B) extreme bending of the head backwards
C) opening the mouth
D) spreading the fingers
E) turning the hand palm upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
C:\User 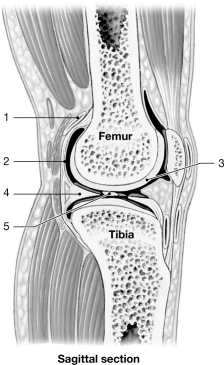 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Use Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "5."
A) intracapsular ligament
B) synovial membrane
C) serous membrane
D) joint capsule
E) periosteum
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "5."
A) intracapsular ligament
B) synovial membrane
C) serous membrane
D) joint capsule
E) periosteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of these is not considered to be an accessory synovial structure?
A) menisci
B) bursae
C) synovial membrane
D) tendons
E) fat pads
A) menisci
B) bursae
C) synovial membrane
D) tendons
E) fat pads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An extension past the anatomical position is known as
A) rotation.
B) extension.
C) hyperextension.
D) flexion.
E) double jointed.
A) rotation.
B) extension.
C) hyperextension.
D) flexion.
E) double jointed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The joint between the trapezium and metacarpal bone of the thumb is an example of an) joint.
A) gliding
B) hinge
C) pivot
D) saddle
E) ellipsoid
A) gliding
B) hinge
C) pivot
D) saddle
E) ellipsoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
An immovable joint is an)
A) symphysis.
B) syndesmosis.
C) amphiarthrosis.
D) synarthrosis.
E) diarthrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The radiocarpal joint is an) _ joint.
A) ellipsoid
B) saddle
C) immovable
D) gliding
E) hinge
A) ellipsoid
B) saddle
C) immovable
D) gliding
E) hinge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which foot movement enables the ballerina to stand on her toes?
A) eversion
B) inversion
C) rotation
D) dorsiflexion
E) plantar flexion
A) eversion
B) inversion
C) rotation
D) dorsiflexion
E) plantar flexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
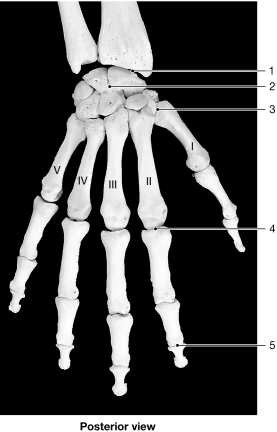 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "5."
A) hinge
B) saddle
C) ellipsoid
D) pivot
E) gliding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Joints can be classified structurally as
A) cartilaginous.
B) bony.
C) fibrous.
D) synovial.
E) all of the above
A) cartilaginous.
B) bony.
C) fibrous.
D) synovial.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
The movements known as dorsiflexion and plantar flexion involve moving the
A) leg.
B) hip.
C) hand.
D) foot.
E) arm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A common injury to the ankle occurs by excessive turning of the sole inward, termed
A) inversion.
B) protraction.
C) eversion.
D) dorsiflexion.
E) plantar flexion.
A) inversion.
B) protraction.
C) eversion.
D) dorsiflexion.
E) plantar flexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The elbow joint is extremely stable because
A) the capsule lacks ligaments.
B) the joint lacks bursae.
C) the articular capsule is thin.
D) the ulna and humerus interlock.
E) several muscles support the joint capsule.
A) the capsule lacks ligaments.
B) the joint lacks bursae.
C) the articular capsule is thin.
D) the ulna and humerus interlock.
E) several muscles support the joint capsule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following is not a characteristic of articular cartilage?
A) Surfaces are normally slick and smooth.
B) The matrix contains more water than other cartilages.
C) It is composed of hyaline cartilage.
D) There is no perichondrium.
E) It secretes synovial fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following ligaments assist in stabilization of the shoulder joint?
A) coracoacromial
B) subscapularis
C) coracoclavicular
D) all of the above
E) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ligament that provides support to the front of the knee joint is the _ ligament.
A) patellar
B) posterior cruciate
C) tibial collateral
D) anterior cruciate
E) popliteal
A) patellar
B) posterior cruciate
C) tibial collateral
D) anterior cruciate
E) popliteal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A synovial joint is an example of an)
A) synarthrosis.
B) symphysis.
C) syndesmosis.
D) amphiarthrosis.
E) diarthrosis.
A) synarthrosis.
B) symphysis.
C) syndesmosis.
D) amphiarthrosis.
E) diarthrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
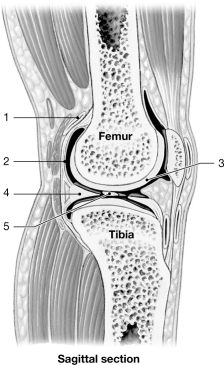 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Which structure acts as a cushion and consists of fibrocartilage?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
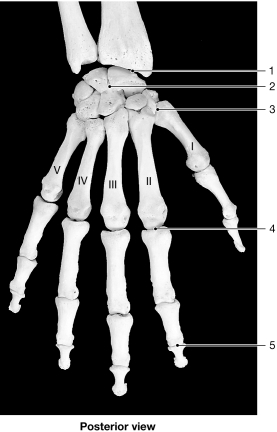 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the type of joint at label "2."
A) hinge
B) gliding
C) ellipsoid
D) saddle
E) pivot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
The ligaments that limit the anterior- posterior movement of the femur and maintain the alignment of the femoral and tibial condyles are the ligaments.
A) fibular collateral
B) cruciate
C) patellar
D) tibial collateral
E) popliteal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
All of the following statements are true, except one. Identify the exception.
A) The more movement a joint allows, the stronger the joint.
B) The tension produced by muscle tendons surrounding a joint help stabilize the joint.
C) The rotator cuff functions to limit the range of movements of the shoulder joint.
D) The tighter two bones are held together within a joint, the stronger the joint.
E) The shapes of the articulating surfaces within the joint help prevent movement in a particular direction and strengthen and stabilize the joint.
A) The more movement a joint allows, the stronger the joint.
B) The tension produced by muscle tendons surrounding a joint help stabilize the joint.
C) The rotator cuff functions to limit the range of movements of the shoulder joint.
D) The tighter two bones are held together within a joint, the stronger the joint.
E) The shapes of the articulating surfaces within the joint help prevent movement in a particular direction and strengthen and stabilize the joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
C:\User  Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Use Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Dense connective tissue is to a suture as a periodontal ligament is to an)
A) syndesmosis.
B) amphiarthrosis.
C) gomphosis.
D) synchondrosis.
E) synostosis.
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Dense connective tissue is to a suture as a periodontal ligament is to an)
A) syndesmosis.
B) amphiarthrosis.
C) gomphosis.
D) synchondrosis.
E) synostosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
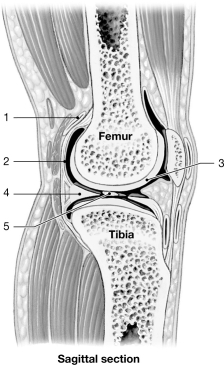 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
The ankle joint is an example of an) joint.
A) hinge
B) ellipsoid
C) gliding
D) saddle
E) ball- and- socket

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following athletes are at greatest risk of developing a rotator cuff injury?
A) tennis players
B) white- water kayakers
C) runners
D) baseball pitchers
E) both B and D
A) tennis players
B) white- water kayakers
C) runners
D) baseball pitchers
E) both B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
Which of the following types of joints is monoaxial, but capable of only rotation?
A) pivot
B) ball- and- socket
C) gliding
D) saddle
E) hinge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
What type of tissue occurs at the structure labeled "3"?
A) hyaline cartilage
B) fibrocartilage
C) dense connective tissue
D) synovial membrane
E) bone tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
All of the following movements occur at the intervertebral joints, except
A) extension.
B) rotation.
C) dorsiflexion.
D) flexion.
E) lateral flexion.
A) extension.
B) rotation.
C) dorsiflexion.
D) flexion.
E) lateral flexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of these is one of the four major types of synarthrotic joints?
A) gomphosis
B) synostosis
C) suture
D) synchondrosis
E) all of the above
A) gomphosis
B) synostosis
C) suture
D) synchondrosis
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
The joints that connect the four fingers with the metacarpal bones are
A) hinge joints.
B) pivot joints.
C) ellipsoid joints.
D) condyloid joints.
E) saddle joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following joints is an example of a ball- and- socket joint?
A) wrist
B) elbow
C) knee
D) shoulder
E) ankle
A) wrist
B) elbow
C) knee
D) shoulder
E) ankle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The normal movement of the hip joint during walking involves
A) abduction.
B) adduction.
C) flexion.
D) extension.
E) both C and D
A) abduction.
B) adduction.
C) flexion.
D) extension.
E) both C and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The intercarpal articulations are joints.
A) ball- and- socket
B) saddle
C) gliding
D) hinge
E) ellipsoid
A) ball- and- socket
B) saddle
C) gliding
D) hinge
E) ellipsoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Muscles that extend the elbow attach to the
A) medial epicondyle.
B) radial tuberosity.
C) coronoid process.
D) lateral epicondyle.
E) olecranon process.
A) medial epicondyle.
B) radial tuberosity.
C) coronoid process.
D) lateral epicondyle.
E) olecranon process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The largest and strongest articulation at the elbow is the
A) ulnaradial joint.
B) humeroradial joint.
C) ulnar joint.
D) radial joint.
E) humero- ulnar joint.
A) ulnaradial joint.
B) humeroradial joint.
C) ulnar joint.
D) radial joint.
E) humero- ulnar joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which type of joint is found between the carpal bones?
A) saddle
B) pivot
C) hinge
D) ball- and- socket
E) gliding
A) saddle
B) pivot
C) hinge
D) ball- and- socket
E) gliding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint
Figure 8- 2 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee JointUse Figure 8- 2 to answer the following questions:
The structures that assist the bursae in reducing friction between the patella and other tissues are the
A) medial menisci.
B) lateral menisci.
C) fat pads.
D) popliteal ligaments.
E) cruciate ligaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
 Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and Hand
Figure 8- 1 Bones of the Wrist and HandUse Figure 8- 1 to answer the following questions:
Complete dislocation of the knee is a rare because
A) the femur articulates with the tibia at the knee.
B) the knee contains seven major ligaments.
C) the knee is extremely resilient.
D) the knee is protected by the patella.
E) the knee contains fat pads to absorb shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



