Deck 9: Branch, Loop, and Node Analyses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Branch, Loop, and Node Analyses
1
The loop current is not necessarily the actual current in a branch.
True
2
A loop is a closed current path in a circuit.
True
3
A node is a junction of two or more current paths.
False
4
What circuit law is used in the mesh current method?
A) Kirchhoff's current law
B) Kirchhoff's voltage law
C) the power law
D) Ohm's law
A) Kirchhoff's current law
B) Kirchhoff's voltage law
C) the power law
D) Ohm's law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To convert from a wye to an equivalent delta, superimpose the two and take the sum of the products of the wye, then divide by the opposite wye resistor from the delta resistor you are trying to find.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An advantage of mesh currents over branch currents is:
A) The mesh current method can be applied to circuits with any number of loops.
B) The mesh current method requires fewer equations than the branch method.
C) There are no negative answers for current.
D) There are no advantages.
A) The mesh current method can be applied to circuits with any number of loops.
B) The mesh current method requires fewer equations than the branch method.
C) There are no negative answers for current.
D) There are no advantages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A node is where the voltage is connected to the circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Mesh currents flow in a counter-clockwise direction through each loop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The branch method is based on loop currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Loop/Mesh analysis uses simultaneous equations to calculate the current through each component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The branch current method involves using:
A) loops and nodes
B) voltages and nodes
C) junctions and nodes
D) loops and junctions
A) loops and nodes
B) voltages and nodes
C) junctions and nodes
D) loops and junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following are useful for analyzing circuits with two or more voltage or current sources?
A) mesh current method
B) node-voltage method
C) branch current method
D) all of the above
A) mesh current method
B) node-voltage method
C) branch current method
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The rule, when solving for several unknown quantities is:
A) You must have the same number of equations as there are unknown values.
B) You must use substitution.
C) You must use determinants.
D) Use Ohm's law.
A) You must have the same number of equations as there are unknown values.
B) You must use substitution.
C) You must use determinants.
D) Use Ohm's law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the equation; 5I1 - 8I2 = 10, which is the coefficient for I1?
A) 10
B) -8
C) 5
D) 8
A) 10
B) -8
C) 5
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The loop current direction must be drawn:
A) counter-clockwise
B) clockwise
C) It doesn't matter, as long as you are consistent.
A) counter-clockwise
B) clockwise
C) It doesn't matter, as long as you are consistent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Delta to wye configurations are used in bridge circuits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is a loop current?
A) Loop currents are assigned currents
B) Loop currents are actual currents.
A) Loop currents are assigned currents
B) Loop currents are actual currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Simultaneous equations can be solved by substitution or by using determinants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the significance of a negative sign in the answer for current, when solving network problems?
A) It means you must chose the correct direction for the actual, net, current flow.
B) It means that the negative current flows in the opposite direction from the assigned current.
C) It means you must subtract the negative value from the other value.
D) It means there is a negative current flow.
A) It means you must chose the correct direction for the actual, net, current flow.
B) It means that the negative current flows in the opposite direction from the assigned current.
C) It means you must subtract the negative value from the other value.
D) It means there is a negative current flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What circuit law is used in the node voltage method?
A) Kirchhoff's current law
B) Kirchhoff's voltage law
C) Ohm's law
D) the power law
A) Kirchhoff's current law
B) Kirchhoff's voltage law
C) Ohm's law
D) the power law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Give the two equations, 2I1 = 8 - 5I2 and 0 = 4I2 - 5I1 + 6, in standard form.
A) 2I1 + 3I2 = 6
4I1 - 2I2 = 8
B) 2I1 + 5I2 = 8
5I1 - 4I2 = 6
C) 3I1 + 5I2 = 6
2I1 + 4I2 = 8
A) 2I1 + 3I2 = 6
4I1 - 2I2 = 8
B) 2I1 + 5I2 = 8
5I1 - 4I2 = 6
C) 3I1 + 5I2 = 6
2I1 + 4I2 = 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

See Figure 9-3. Using R = 100 Ω, compute the current through the 50 Ω resistor.
A) 2.14 mA
B) 21.47 µA
C) 21.47 A
D) 21.47 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

See Figure 9-3. If R = 100 Ω, compute the current through the 50 Ω resistor. Use the delta-wye conversion method.
A) 21.5 mA, Left to Right
B) 31.8 mA, Right to Left
C) 21.5 mA, Right to Left
D) 31.8 mA, Left to Right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

See Figure 9-5. The equation obtained from performing loop analysis on loop #1 is:
A) 3I1 + 7I2 - I1) + 5 V = 0
B) 3I2 + 7I2 - I1) - 5 V = 0
C) 3I2 + 7I1 - I2) + 5 V = 0
D) -3I2 + 7I2 - I1) + 5 V = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the characteristic determinant from the following equations? 5I1 - 8I2 = 10
L0I1 + 5I2 = 20
A) 10
B) 55
C) 105
D) -90
L0I1 + 5I2 = 20
A) 10
B) 55
C) 105
D) -90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

Which of the following terms describes the voltage across the 7 Ω resistor when using mesh analysis?
A) 7 Ω) I2
B) 7 Ω) I1 + I2
C) 7 Ω) I1
D) 7 Ω) I1 - I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A branch is a path that connects:
A) two components
B) two multiple loop circuits
C) two loops
D) two nodes
A) two components
B) two multiple loop circuits
C) two loops
D) two nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

In Figure what value of R will result in a balanced bridge?
A) 60 Ω
B) 300 Ω
C) 30 Ω
D) 3 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Solve for I1 and I2 in the following equation: 100I1 + 30I2 = 30
75I1 - 45I2 = 20
A) I1 = 28.9 mA, I2 = 3.7 mA
B) I1 = 0.289 A, I2 = 0.037 A
C) I1 = 0.037 A, I2 = 0.368 A
D) I1 = 0.289 A, I2 = -0.037 A
75I1 - 45I2 = 20
A) I1 = 28.9 mA, I2 = 3.7 mA
B) I1 = 0.289 A, I2 = 0.037 A
C) I1 = 0.037 A, I2 = 0.368 A
D) I1 = 0.289 A, I2 = -0.037 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
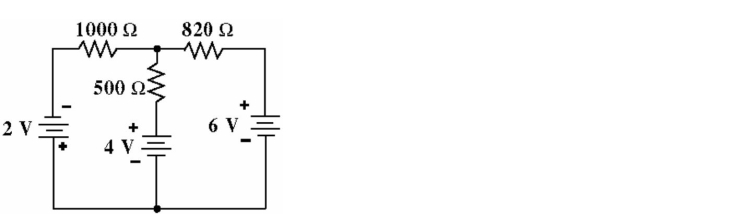
Given the circuit in Figure , find the approximate current flow through the 500 Ω resistor.
A) 1.69 mA
B) 3.47 mA
C) 8.63 mA
D) 5.16 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

See Figure 9-4. If nodal analysis were to be used to solve for unknown voltages in this circuit, how many nodes would be needed including the reference node)?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The node voltage method for the Bridged-T circuit:
A) creates a source node and a reference node.
B) results in two unknowns.
C) results in two equations.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) creates a source node and a reference node.
B) results in two unknowns.
C) results in two equations.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How many general steps are used in applying the branch current method?
A) 5
B) 4
C) 1
D) 3
A) 5
B) 4
C) 1
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A branch current is an current through a branch, whereas: loop currents are .
A) actual, circuit dependent
B) assumed, mathematical quantities
C) actual, mathematical
D) both A and B
A) actual, circuit dependent
B) assumed, mathematical quantities
C) actual, mathematical
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
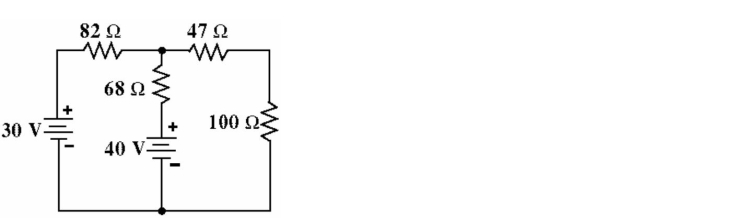
Given the circuit in Figure , find the approximate voltage drop across the 68 Ω resistor.
A) 1.36 V
B) 14.28 V
C) 11.69 V
D) 12.92 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

If the branch current method is used, which equation describes loop 1?
A) 0 = -5 V - 3 Ω)I1 + 7 Ω)I2
B) 0 = +5 V - 3 Ω)I1 + 7 Ω)I2
C) 0 = +5 V + 3 Ω)I1 - 7 Ω)I2
D) 0 = -5 V - 3 Ω)I1 - 7 Ω)I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Which statement is true if the loop current I2 is found to be a negative number?
A) The 10 V battery and 10 Ω resistor should have been converted to a current source.
B) The determinant used to compute the current should have been third order, not second order.
C) The nodal analysis approach should have been used, not the mesh analysis approach.
D) The original direction assumed for I2 is wrong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Simultaneous equations can be solved by which two methods?
A) substitution and loop
B) determinant and mesh
C) substitution and coefficient
D) substitution and determinant
A) substitution and loop
B) determinant and mesh
C) substitution and coefficient
D) substitution and determinant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

See Figure 9-5. Which equation describes node X?
A) I3 = I2 + I1
B) I1 + I2 + I3 = 0
C) -I1 - I2 - I3 = 0
D) I3 = I2 - I1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



