Deck 8: Circuit Theorems and Conversions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Circuit Theorems and Conversions
1

The superposition method for calculating voltages and currents requires:
A) opening the load resistance.
B) taking one source at a time, with other voltage sources replaced by an open circuit.
C) taking one source at a time, and replacing other sources with their internal resistances.
D) replacing the load resistance with a short circuit.
taking one source at a time, and replacing other sources with their internal resistances.
2
An ideal current source has internal resistance.
A) infinite
B) low
C) high
D) zero
A) infinite
B) low
C) high
D) zero
infinite
3
The superposition theorem is used to simplify circuit analysis where two or more sources are present.
True
4
An ideal current source has infinite internal resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 8-2
Figure 8-2If two currents are in opposing directions through a branch of a circuit, in what direction will the net current flow?
A) in the direction of the smaller current
B) The net current always flows down through a resistor.
C) in the direction of the larger current
D) Opposing currents will always cancel each other out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An ideal current source produces an) value of current through a load, regardless of the value of the load.
A) proportional
B) decreasing
C) increasing
D) constant
A) proportional
B) decreasing
C) increasing
D) constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An ideal voltage source has infinite internal resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A practical current source has infinite internal resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The first step in Nortonizing a circuit is to short out the load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

What is the equivalent current source when VS = 100 V, RS = 40 Ω?
A) IS = 2.0 A, RS = 40 Ω
B) IS = 2.5 A, RS = 40 Ω
C) IS = 2.5 A, RS = zero Ω
D) IS = 2.5 A, RS = infinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Calculate the voltage output of a source, when the source voltage equals 50 V, the source internal resistance is 10 Ω and the load resistance is 50 Ω.
A) 8.33 V
B) 40 V
C) 41.67 V
D) 10 V
A) 8.33 V
B) 40 V
C) 41.67 V
D) 10 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Given the circuit in Figure 8-1, find the total current through the load.
A) 12 mA
B) 20 mA
C) 1.2 mA
D) 1.0 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Open circuit voltage refers to:
A) the voltage taken across a high value load resistor.
B) the output voltage with no load.
C) the voltage taken across a low value load resistor.
D) zero internal resistance.
A) the voltage taken across a high value load resistor.
B) the output voltage with no load.
C) the voltage taken across a low value load resistor.
D) zero internal resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
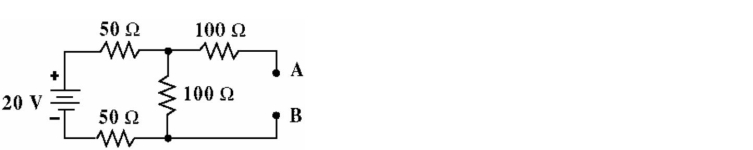
Given the circuit in Figure, Calculate VTH and RTH.
A) VTH = 10 V, RTH = 50 Ω
B) VTH = 10 V, RTH = 150 Ω
C) VTH = 6.7 V, RTH = 150 Ω
D) VTH = 5.0 V, RTH = 50 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Figure 8-2
Figure 8-2Maximum power is delivered to the load under what conditions?
A) when the load resistance equals zero
B) when the load resistance equals the source resistance
C) when the load resistance is greater than the source resistance
D) when the load resistance is open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A practical voltage source has infinite internal resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Maximum power transfer occurs when the load resistance equals the source resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Figure 8-2
Figure 8-2Given the circuit in Figure 8-2, Calculate the total current through R2, using the superposition method.
A) 133 mA
B) 67 mA
C) 16 mA
D) 83 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Thevenin's theorem is used to simplify complex networks to a simple voltage source with its source resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The internal resistance of an ideal voltage source is:
A) infinite
B) low
C) zero
D) high
A) infinite
B) low
C) zero
D) high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When converting a wye configuration with all equal resistors to a delta configuration, the delta resistor will always be _ times its related wye resistor.
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Thevenin's theorem states that the Thevenin voltage is equal to:
A) open circuit current at the networks terminals
B) short circuit voltage at the networks terminals
C) open circuit voltage at the networks terminals
D) short circuit current at the networks terminals
A) open circuit current at the networks terminals
B) short circuit voltage at the networks terminals
C) open circuit voltage at the networks terminals
D) short circuit current at the networks terminals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Power effects in a dc network cannot be determined using superposition because:
A) power computations require a voltage and a current source in each circuit.
B) power is proportional to the square of the current or voltage.
C) open sources and shorted sources neither consume nor produce power.
D) all voltage and current sources are ideal devices that consume no power.
A) power computations require a voltage and a current source in each circuit.
B) power is proportional to the square of the current or voltage.
C) open sources and shorted sources neither consume nor produce power.
D) all voltage and current sources are ideal devices that consume no power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When using the superposition theorem on a two source network, if the current produced by one source is in one direction, while that produced by the other source is in the opposite direction through the same resistor:
A) all voltage sources were not properly converted to current sources.
B) the absolute values of the two currents add algebraically, and the direction is the same as the direction of the larger current.
C) the resulting current is the difference of the two and has the direction of the larger current.
D) a mistake in the sign of the result occurred.
A) all voltage sources were not properly converted to current sources.
B) the absolute values of the two currents add algebraically, and the direction is the same as the direction of the larger current.
C) the resulting current is the difference of the two and has the direction of the larger current.
D) a mistake in the sign of the result occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

-The first steps to Nortonizing a circuit are:
A) open RL, determine RN, make VS = IN
B) short RL, determine IL, make IL = IN
N
C) short RL, determine RN, make VS = IN
D) open RL, determine IL, make IL = IN
N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under maximum power transfer conditions, which one is true?
A) The algebraic sum of all resistances in the source equals the algebraic sum of all the resistances in the load.
B) The equivalent load resistance is very large compared to the equivalent of the source.
C) The Thevenin resistance of the source equals the equivalent resistance of the load.
D) The equivalent load resistance is very small compared to the equivalent of the source.
A) The algebraic sum of all resistances in the source equals the algebraic sum of all the resistances in the load.
B) The equivalent load resistance is very large compared to the equivalent of the source.
C) The Thevenin resistance of the source equals the equivalent resistance of the load.
D) The equivalent load resistance is very small compared to the equivalent of the source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a thermistor is used in a basic Wheatstone bridge measuring circuit, the bridge becomes as the thermistor's resistance changes with .
A) balanced, changes in current
B) balanced, changes in light
C) balanced, changes in pressure
D) unbalanced, changes in temperature
A) balanced, changes in current
B) balanced, changes in light
C) balanced, changes in pressure
D) unbalanced, changes in temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
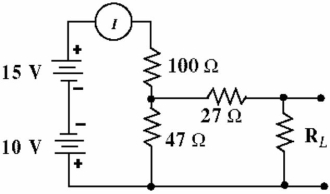
Given the circuit in Figure , Calculate the current IN,) and RN, with RL disconnected.
A) IN = 296 mA, RN = 59 Ω
B) IN = 296 mA, RN = 174 Ω
C) IN = 27.1 mA, RN = 59 Ω
D) IN = 27.1 mA, RN = 14.6 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
 Figure 8-4
Figure 8-4Given the circuit in Figure 8-4, Thevenize the bridge circuit between points "A" and "B". Find the current flow through the load RL).
A) 0.69 mA
B) 1.92 mA
C) 3.2 mA
D) 0.45 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

The concept that states the equivalency of two voltage sources means that for any given load resistance connected to the two sources, the same load voltage and load current are produced by both sources is called:
A) junction equivalency
B) loop equivalency
C) terminal equivalency
D) load equivalency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the symbol usually used inside a circle to designate a current source?
A) an arrow
B) a circle
C) a current wave
D) a sine wave
A) an arrow
B) a circle
C) a current wave
D) a sine wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

Convert the Delta network in Figure into a Wye network.
A) R1 = 25.7 kΩ, R2 = 143.8 kΩ, R3 = 78.3 kΩ
B) R1 = 42.1 kΩ, R2 = 174.9 kΩ, R3 = 78.3 kΩ
C) R1 = 37.9 kΩ, R2 = 143.8 kΩ, R3 = 64.8 kΩ
D) R1 = 25.7 kΩ, R2 = 174.9 kΩ, R3 = 64.8 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Delta to wye configurations are used in:
A) non-sinusoidal networks
B) polyphase circuits
C) bridge circuits
D) resonance circuits
A) non-sinusoidal networks
B) polyphase circuits
C) bridge circuits
D) resonance circuits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Norton's theorem states that you can replace a dc network with an equivalent circuit consisting of:
A) a current source and a parallel resistor
B) a current source and a series resistor
C) a voltage source and a series resistor
D) a voltage source and a parallel resistor
A) a current source and a parallel resistor
B) a current source and a series resistor
C) a voltage source and a series resistor
D) a voltage source and a parallel resistor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of these statements is true of two or more current sources in parallel?
A) They violate Kirchhoff's current law.
B) A series resistor must be placed in each branch.
C) They may be replaced by one current source.
D) The magnitude of the combined current is always less than the smallest individual current.
A) They violate Kirchhoff's current law.
B) A series resistor must be placed in each branch.
C) They may be replaced by one current source.
D) The magnitude of the combined current is always less than the smallest individual current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



