Deck 5: Series Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Series Circuits
1
A series connection provides two or more paths for current to flow.
False
2
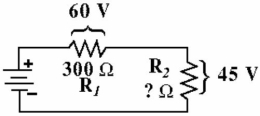
Given the circuit in Figure , the voltage drop across R1 is 60 V. The drop across R2 is 45 V. What is the resistance value of R2?
A) 345 Ω
B) 225 Ω
C) 400 Ω
D) 450 Ω
225 Ω
3

Given the circuit in Figure 5-11, the voltage drop across R1 is 75 V. What is the voltage drop across R2?
A) 75 V
B) 100 V
C) 25 V
D) 20 V
25 V
4
 Figure 5-9
Figure 5-9The total current flowing in the circuit in Figure 5-9 is:
A) 1.06 A
B) 2.82 A
C) 0.53 A
D) 0.35 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a series circuit, current is not the same when measured at different points in the circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A voltage divider is a series arrangement of resistors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 Figure 5-7
Figure 5-7Given the circuit in Figure 5-7, the voltage drop across R1 is 18 V. What is the voltage drop across R2?
A) 36 V
B) 20 V
C) 45 V
D) 54 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

What is the current flowing in the circuit in Figure 5-6?
A) 0.5 mA
B) 0.05 mA
C) 25 mA
D) 2.5 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A series circuit has the same voltage across every component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

Given the circuit in Figure 5-4, what is the current through resistor R2?
A) 1 A
B) 0.2 A
C) 1.2 A
D) 100 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The product of all the voltage drops in a series circuit will equal source voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the circuits Figure 5-1, 5-2 or 5-3) is a circuit with resistors in series?
A) Figure 5-2
B) Figure 5-3
C) Figure 5-1
A) Figure 5-2
B) Figure 5-3
C) Figure 5-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

The total resistance in the series circuit in Figure is:
A) 498 Ω
B) 590 Ω
C) 534 Ω
D) 578 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
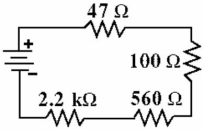
The total resistance in the circuit in Figure is:
A) 23,416.2 Ω
B) 2907 Ω
C) 709.2 kΩ
D) 927 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ground is a common reference point in a circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The current entering a point in a circuit is equal to the current leaving the point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the average of all the resistance values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
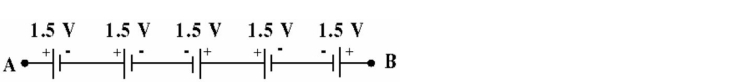 Figure 5-10
Figure 5-10Figure 5-10 shows 5 D-size batteries connected in a series circuit. What is the total voltage measured between points A and B?
A) 4.5 V
B) 3.0 V
C) 7.5 V
D) 1.5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

The total resistance in the circuit in Figure is:
A) 90 Ω + 10 Ω
B) 90 Ω
C) 90 Ω / 10 Ω
D) 10 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As you add resistors to a series circuit, total current will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The voltage drop across a series resistor is proportional to what other value?
A) Total resistance
B) Its own resistance
C) Wattage rating
D) The amount of time the circuit is on
A) Total resistance
B) Its own resistance
C) Wattage rating
D) The amount of time the circuit is on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
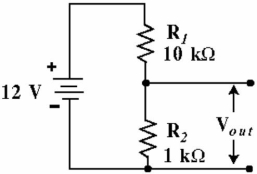 Figure 5-14
Figure 5-14Given the voltage divider circuit, in Figure 5-14, what is the circuit current?
A) 6.0 mA
B) 10.9 mA
C) 2.75 mA
D) 1.09 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
 Figure 5-12
Figure 5-12Given the circuit in Figure 5-12, the voltage drop across R2 is:
A) 22.2 V
B) 2.22 V
C) 3.33 V
D) 4.44 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
 Figure 5-12
Figure 5-12Given the circuit in Figure 5-12, the circuit current is:
A) 0.022 A
B) 220 mA
C) 2.22 mA
D) 22.2 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the effect on total current if the voltage supplying a circuit is halved, and the circuit resistance stays the same?
A) It doubles
B) It remains the same.
C) It goes to zero
D) It decreases by half.
A) It doubles
B) It remains the same.
C) It goes to zero
D) It decreases by half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
 Figure 5-14
Figure 5-14Given the voltage divider, in Figure 5-14, the output voltage Vout) is:
A) 0.91 V
B) 2.75 V
C) 6.0 V
D) 1.09 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

Given the circuit in Figure , what is the resistance value of R2?
A) 25 Ω
B) 75 Ω
C) 20 Ω
D) 100 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a series circuit, the voltage measured across an open will be:
A) source voltage
B) the normal voltage drop
C) zero
D) infinite voltage
A) source voltage
B) the normal voltage drop
C) zero
D) infinite voltage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

Given the special series circuit, called a voltage divider, in Figure 5-13, the output voltage Vout) is:
A) 10 V
B) 3.75 V
C) 5.0 V
D) 2.5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A voltage divider is always a:
A) bridge circuit
B) series-parallel circuit
C) parallel circuit
D) series circuit
A) bridge circuit
B) series-parallel circuit
C) parallel circuit
D) series circuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which measuring device requires no circuit power to obtain a reading?
A) Ammeter
B) Wattmeter
C) Voltmeter
D) Ohmmeter
A) Ammeter
B) Wattmeter
C) Voltmeter
D) Ohmmeter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the total voltage applied in a series circuit of three resistors is 120 V and the voltage drop across R1 is 20 V and R2 drops 30 V, what is the voltage drop for R3?
A) 120 V
B) 70 V
C) 40 V
D) 50 V
A) 120 V
B) 70 V
C) 40 V
D) 50 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to:
A) the average of all the resistance values
B) the largest resistance value
C) the sum of all the resistance values
D) the smallest resistance value
A) the average of all the resistance values
B) the largest resistance value
C) the sum of all the resistance values
D) the smallest resistance value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 Figure 5-12
Figure 5-12Given the circuit in Figure 5-12, the voltage drop across R3 is:
A) 0.333 V
B) 2.22 V
C) 3.33 V
D) 4.44 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given a series circuit containing resistors of different values, which statement is not true?
A) The total resistance is the sum of the value of the resistors.
B) The current through each resistor is the same.
C) The voltage drop across each resistor is the same.
D) The sum of the voltage drops across each resistive element will be equal to the voltage source.
A) The total resistance is the sum of the value of the resistors.
B) The current through each resistor is the same.
C) The voltage drop across each resistor is the same.
D) The sum of the voltage drops across each resistive element will be equal to the voltage source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Kirchhoff's voltage law states that:
A) the algebraic sum of the potential rises and drops around a closed loop is zero
B) the algebraic sum of the individual currents around a closed loop is zero
C) the algebraic sum of the resistances is equal to the sum of the voltages
D) the voltages developed across each element in a series circuit are identical
A) the algebraic sum of the potential rises and drops around a closed loop is zero
B) the algebraic sum of the individual currents around a closed loop is zero
C) the algebraic sum of the resistances is equal to the sum of the voltages
D) the voltages developed across each element in a series circuit are identical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Given the voltage divider circuit,. Suppose resistors R1 and R2 are changed to 10 Ω. What is the new output voltage Vout)?
A) 2.25 V
B) 1.0 V
C) 5.0 V
D) 3.75 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A series circuit has:
A) more than two current paths
B) only one current path
C) different currents at different points
D) two current paths
A) more than two current paths
B) only one current path
C) different currents at different points
D) two current paths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
 Figure 5-12
Figure 5-12Given the circuit in Figure 5-12, the voltage drop across R1 is:
A) 33.3 V
B) 2.22 V
C) 3.33 V
D) 1.22 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the supply voltage when a 5 kΩ and a 4 kΩ resistor are in series and 6 V is measured across the smaller resistor?
A) 13.5 V
B) 16 V
C) 6 V
D) 12 V
A) 13.5 V
B) 16 V
C) 6 V
D) 12 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the total current of a series circuit with a 9 V battery, a 4.7 kΩ, a 6.1 kΩ resistor, and a 450 Ω resistor?
A) 20 mA
B) 23.4 mA
C) 1.9 mA
D) 800 µA
A) 20 mA
B) 23.4 mA
C) 1.9 mA
D) 800 µA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The voltage drop across a series resistor is proportional to what other value?
A) The wattage rating
B) The direction of current flow
C) Its own resistance
D) The amount of time the circuit is on
A) The wattage rating
B) The direction of current flow
C) Its own resistance
D) The amount of time the circuit is on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the voltage of a lamp is to be measured by a voltmeter, then:
A) connect the voltmeter in the same current path as the lamp
B) remove the lamp and put the voltmeter in the same current path as the lamp was in
C) open the circuit and connect the leads across the lamp
D) connect the leads across the lamp without opening the circuit
A) connect the voltmeter in the same current path as the lamp
B) remove the lamp and put the voltmeter in the same current path as the lamp was in
C) open the circuit and connect the leads across the lamp
D) connect the leads across the lamp without opening the circuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is a true statement concerning potentiometers?
A) Potentiometers can only be classified as linear
B) Potentiometers do not have a schematic symbol.
C) Potentiometers can be used as voltage dividers
D) Potentiometers have only two terminals.
A) Potentiometers can only be classified as linear
B) Potentiometers do not have a schematic symbol.
C) Potentiometers can be used as voltage dividers
D) Potentiometers have only two terminals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



