Deck 4: Bipolar Junction Transistors
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/33
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Bipolar Junction Transistors
1
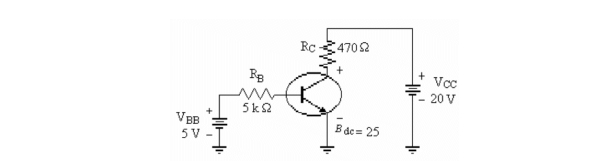
Refer to the figure above. If the value of VBB were increased to 10 V, the transistor would be operating in
A)the active region.
B)cutoff.
C)saturation.
D)Cannot be determined.
C
2
The base- to- emitter junction of a certain transistor is checked with a DMM on diode check in the forward bias direction. If the DMM indicates 0.700, the transistor is
A)germanium and measuring normal.
B)open between the base and emitter.
C)silicon and measuring normal.
D)definitely defective.
A)germanium and measuring normal.
B)open between the base and emitter.
C)silicon and measuring normal.
D)definitely defective.
C
3
A BJT has an IB of 75 µA and a fidc of 100. The value of IC is
A)7.5 mA.
B)10 mA.
C)75 mA.
D)175 µA.
A)7.5 mA.
B)10 mA.
C)75 mA.
D)175 µA.
A
4
An open base resistor RB)in a transistor switch will result in the
A)transistor being instantly destroyed.
B)transistor always being ON.
C)transistor always being OFF.
D)transistor operating in the active region.
A)transistor being instantly destroyed.
B)transistor always being ON.
C)transistor always being OFF.
D)transistor operating in the active region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
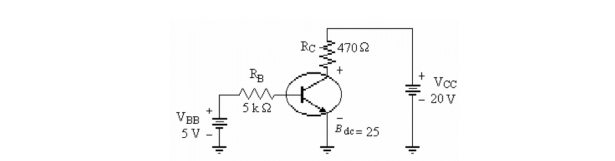
Refer to the figure above. This circuit is operating
A)in saturation.
B)in the active region.
C)incorrectly because the bias voltages are wrong.
D)in cutoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

Refer to the figure above. The value of IB is
A)8.6 mA.
B)860 µA.
C)0.7 µA.
D)1 mA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
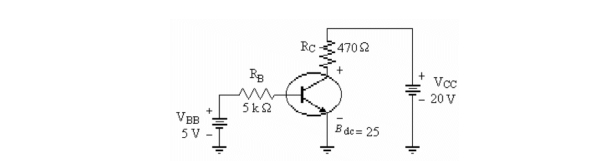
Refer to the figure above. If this transistor is operating in saturation, the value of ICsat)is
A)42.6 mA.
B)4.26 mA.
C)9.4 mA.
D)28.6 mA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The signal voltage gain of an amplifier, AV, is defined as
A)AV = IB x RB.
B)AV = Rc .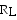
C)AV = Vout .
D)AV = r'e .
Vin RC
A)AV = IB x RB.
B)AV = Rc .
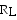
C)AV = Vout .
D)AV = r'e .
Vin RC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a transistor switch is on, the collector current is limited by
A)the base voltage.
B)the collector resistance.
C)the base current.
D)the base resistance.
A)the base voltage.
B)the collector resistance.
C)the base current.
D)the base resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Besides operating as an amplifier, the BJT is often applied as a
A)varactor.
B)voltage controlled capacitance.
C)variable inductor.
D)switch.
A)varactor.
B)voltage controlled capacitance.
C)variable inductor.
D)switch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Normal operation of an NPN BJT requires the base to be _ with respect to the emitter, and with respect to the collector.
A)negative, negative
B)positive, negative
C)positive, positive
D)negative, positive
A)negative, negative
B)positive, negative
C)positive, positive
D)negative, positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The symbol hFE is the same as
A)fiDC.
B)aDC.
C)fiac.
D)hj- fj.
A)fiDC.
B)aDC.
C)fiac.
D)hj- fj.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
VCE approximately equals when a transistor switch is in saturation.
A)0.7 V
B)VB
C)VC
D)0.2 V
A)0.7 V
B)VB
C)VC
D)0.2 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Most of the electrons in the base of an NPN transistor flow
A)into the collector.
B)out of the base lead.
C)into the base supply.
D)into the emitter.
A)into the collector.
B)out of the base lead.
C)into the base supply.
D)into the emitter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
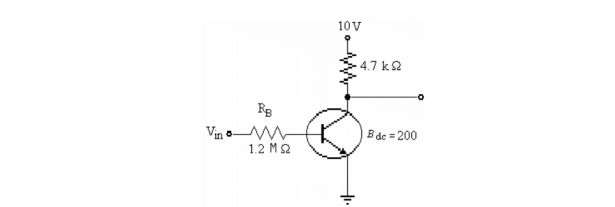
Refer to the figure above. If the value of the collector resistor is increased to 6.8 k▲, the new value of ICsat)is
A)2.13 mA.
B)1.47 mA.
C)0.68 mA.
D)0 mA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The signal output voltage Vout)is a function of the
A)changing collector current IC)through the collector resistor RC.
B)current from base to collector.
C)voltage drop from base to collector.
D)power being dissipated by the base supply voltage.
A)changing collector current IC)through the collector resistor RC.
B)current from base to collector.
C)voltage drop from base to collector.
D)power being dissipated by the base supply voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the collector resistance in a transistor amplifier is open, the dc voltage at the collector will be closest to
A)VCC.
B)VCC/2.
C)VBB.
D)0 V.
A)VCC.
B)VCC/2.
C)VBB.
D)0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A transistor collector characteristic curve is a graph showing
A)emitter current IE)versus collector- emitter voltage VCE)for specified values of base current IB).
B)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VC)for specified values of base current IB).
C)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VCC)for specified values of base current IB).
D)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VCE)for specified values of base current IB).
A)emitter current IE)versus collector- emitter voltage VCE)for specified values of base current IB).
B)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VC)for specified values of base current IB).
C)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VCC)for specified values of base current IB).
D)collector current IC)versus collector- emitter voltage VCE)for specified values of base current IB).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The base of an NPN transistor is thin and
A)lightly doped.
B)doped by a pentavalent material.
C)metallic.
D)heavily doped.
A)lightly doped.
B)doped by a pentavalent material.
C)metallic.
D)heavily doped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A transistor amplifier has an input voltage of 67 mV and an output voltage of 2..48 V. The voltage gain is
A)27.
B)67.
C)17.
D)37.
A)27.
B)67.
C)17.
D)37.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 22 mV signal is applied to the base of a properly biased transistor that has an r'e = 7 ▲ and an RC = 1.2 k▲. The output voltage at the collector is
A)17.1 V.
B)3.77 V.
C)22 mV.
D)7 V.
A)17.1 V.
B)3.77 V.
C)22 mV.
D)7 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a bipolar junction transistor, collector current is controlled by
A)base current.
B)collector voltage.
C)collector resistance.
D)All of the above.
A)base current.
B)collector voltage.
C)collector resistance.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In an NPN transistor, the majority carriers in the base are
A)free electrons.
B)holes.
C)Neither A nor B.
D)Both A and B.
A)free electrons.
B)holes.
C)Neither A nor B.
D)Both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A transistor has a fiDC of 250 and a base current, IB, of 20 µA. The collector current, IC, equals
A)5 mA.
B)50 mA.
C)5 A.
D)500 µA.
A)5 mA.
B)50 mA.
C)5 A.
D)500 µA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a transistor is operated in the active region, changes in the collector supply voltage VCC
A)produce changes in collector current.
B)have little or no effect on collector current.
C)produce changes in base voltage.
D)produce changes in emitter voltage.
A)produce changes in collector current.
B)have little or no effect on collector current.
C)produce changes in base voltage.
D)produce changes in emitter voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A bipolar junction transistor has regions of operation.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A certain transistor has an IC = 12 mA and an IB = 125 µA. fidc is
A)15.
B)96.
C)12.
D)150.
A)15.
B)96.
C)12.
D)150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When transistors are used in digital circuits they usually operate in the
A)active region.
B)saturation and cutoff regions.
C)linear region.
D)breakdown region.
A)active region.
B)saturation and cutoff regions.
C)linear region.
D)breakdown region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The region in a transistor that has to dissipate the most heat is the
A)anode.
B)emitter.
C)base.
D)collector.
A)anode.
B)emitter.
C)base.
D)collector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 35 mV signal is applied to the base of a properly biased transistor with an r'e = 8 ▲ and RC = 1 k ▲. The output signal voltage at the collector is
A)4.375 mV.
B)28.57 V.
C)4.375 V.
D)3.5 V.
A)4.375 mV.
B)28.57 V.
C)4.375 V.
D)3.5 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
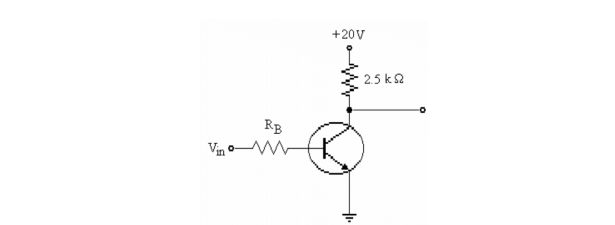
Refer to the figure above. This circuit is saturated. To get the circuit to operate close to its linear range
A)RB should be decreased.
B)RB should be increased.
C)RC should be decreased.
D)Vin should be increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a transistor, the relation of the three transistor currents is
A)IC = IB - 2IE.
B)IE = IC + IB.
C)IC = IE + VC/RC.
D)IC = IE + IB.
A)IC = IB - 2IE.
B)IE = IC + IB.
C)IC = IE + VC/RC.
D)IC = IE + IB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
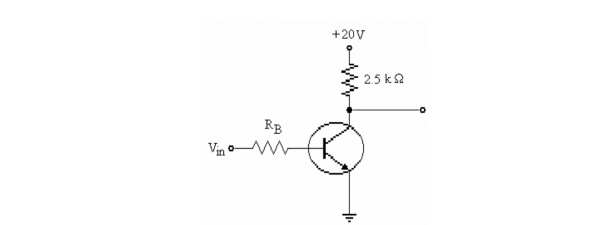
Refer to the figure above. The voltage VCE was measured and found to be 20 V. The transistor is operating in
A)saturation.
B)the active region.
C)cutoff.
D)Not enough data to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



