Deck 5: Modern Portfolio Concepts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Modern Portfolio Concepts
1
U. S. based companies such as Coca Cola and Caterpillar have no exchange rate risk.
False
2
Correlation is a measure of the relationship between two series of numbers.
True
3
Negatively correlated assets reduce risk more than positively correlated assets.
True
4
Hannah owns the following portfolio of stocks. What is the return on her portfolio?
A) 7.27%
B) 10.93%
C) 11.49%
D) 32.8%
A) 7.27%
B) 10.93%
C) 11.49%
D) 32.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In severe market downturns different asset classes become less correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The stock of a technology company has an expected return of 15% and a standard deviation of 20%. The stock of a pharmaceutical company has an expected return of 13% and a standard deviation of 18%. A portfolio consisting of 50% invested in each stock will have an expected return of 14 % and a standard deviation
A) less than the average of 20% and 18%.
B) the average of 20% and 18%.
C) greater than the average of 20% and 18%.
D) The answer cannot be determined with the information given.
A) less than the average of 20% and 18%.
B) the average of 20% and 18%.
C) greater than the average of 20% and 18%.
D) The answer cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Xander owns the following portfolio of stocks. What is the return on his portfolio?
A) 3.93%
B) 6.61%
C) 10.76%
D) 9.97%
A) 3.93%
B) 6.61%
C) 10.76%
D) 9.97%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Investing in emerging markets is an effective means of diversifying a U.S. portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The statement "A portfolio is less than the sum of its parts." means
A) it is less expensive to buy a group of assets than to buy those assets individually.
B) portfolio returns will always be lower than the returns on individual stocks.
C) a diversified group of assets will be less volatile than the individual assets within the group.
D) for reasons that are not well understood, the value of a portfolio is less than the sum of the values of its components.
A) it is less expensive to buy a group of assets than to buy those assets individually.
B) portfolio returns will always be lower than the returns on individual stocks.
C) a diversified group of assets will be less volatile than the individual assets within the group.
D) for reasons that are not well understood, the value of a portfolio is less than the sum of the values of its components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Coefficients of correlation range from a maximum of +10 to a minimum of -10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most assets show a slight degree of negative correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
By plotting the efficient frontier, investors can find the unique portfolio that is ideal for all investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the actual rate of return on an investment portfolio is constant from year to year, the standard deviation of that portfolio is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Portfolio objectives should be established independently of tax considerations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Portfolio objectives should be established before beginning to invest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All possible combinations of assets in a given portfolio will lie along the efficient frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An efficient portfolio maximizes the rate of return without consideration of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Investing globally offers better diversification than investing only domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Studies have shown that about half of all stocks listed on the major exchanges are negatively correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A portfolio consisting of four stocks is expected to produce returns of 9%, -11%, 13% and 17%, respectively, over the next four years. What is the standard deviation of these expected returns?
A) 10.05%
B) 11.60%
C) 12.44%
D) 33.42%
A) 10.05%
B) 11.60%
C) 12.44%
D) 33.42%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The returns on the stock of DEF and GHI companies over a 4 year period are shown below: From this limited data you should conclude that returns on
A) DEF and GHI are negatively correlated.
B) DEF and GHI are somewhat positively correlated.
C) DEF and GHI are perfectly positively correlated.
D) DEF and GHI are uncorrelated.
A) DEF and GHI are negatively correlated.
B) DEF and GHI are somewhat positively correlated.
C) DEF and GHI are perfectly positively correlated.
D) DEF and GHI are uncorrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Combining perfectly, positively correlated assets will
A) increase the overall risk level of a portfolio.
B) decrease the overall risk level of a portfolio.
C) not change the overall risk level of a portfolio.
D) increase or decrease the portfolio's risk depending on the risk of each single asset portfolio.
A) increase the overall risk level of a portfolio.
B) decrease the overall risk level of a portfolio.
C) not change the overall risk level of a portfolio.
D) increase or decrease the portfolio's risk depending on the risk of each single asset portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Standard deviation is a measure that indicates how the price of an individual security responds to market forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The index used to represent market returns is always assigned a beta of 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the real world, most of the assets available to investors
A) tend to be somewhat positively correlated.
B) tend to be somewhat negatively correlated.
C) tend to be uncorrelated.
D) tend to be either perfectly positively or perfectly negatively correlated.
A) tend to be somewhat positively correlated.
B) tend to be somewhat negatively correlated.
C) tend to be uncorrelated.
D) tend to be either perfectly positively or perfectly negatively correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
American Depositary Receipts (ADR) are
A) dollar denominated shares of foreign companies traded on the U.S. markets.
B) shares of American companies traded on foreign markets.
C) foreign currency deposits in American banks.
D) American currency deposits in foreign banks.
A) dollar denominated shares of foreign companies traded on the U.S. markets.
B) shares of American companies traded on foreign markets.
C) foreign currency deposits in American banks.
D) American currency deposits in foreign banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A negative beta means that on average a stock moves in the opposite direction of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The betas of most stocks are constant over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If there is no relationship between the rates of return of two assets over time, these assets are
A) positively correlated.
B) negatively correlated.
C) perfectly negatively correlated.
D) uncorrelated.
A) positively correlated.
B) negatively correlated.
C) perfectly negatively correlated.
D) uncorrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following investments will provide some measure of international diversification to a portfolio?
A) mutual funds with an international focus
B) stocks of U.S. based companies with extensive foreign sales and/or operations
C) American Depositary Receipts
D) All of the above
A) mutual funds with an international focus
B) stocks of U.S. based companies with extensive foreign sales and/or operations
C) American Depositary Receipts
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following will provide the greatest international diversification?
A) directly purchasing a foreign stock
B) purchasing stock of a U.S. multinational firm
C) purchasing an ADR
D) purchasing shares of an international mutual fund
A) directly purchasing a foreign stock
B) purchasing stock of a U.S. multinational firm
C) purchasing an ADR
D) purchasing shares of an international mutual fund

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Diversifiable risk is also called systematic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Market return is estimated from the average return on a large sample of stocks such as those in the Standard & Poor's 500 Stock Composite Index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The risk measured by beta can be reduced by diversification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Explain the relationship between correlation, diversification, and risk reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A beta of 0.5 means that a stock is half as risky the overall market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Two assets have a coefficient of correlation of -.4. Asset A has a standard deviation of 20% and asset B has a standard deviation of 40%. Relative to holding a portfolio consisting of 100% of Asset B, what happens to risk if you combine these assets into a 50-50 weighted portfolio?
A) Combining these assets will increase risk.
B) Combining these assets will have no effect on risk.
C) Combining these assets may either raise or lower risk.
D) Combining these assets will reduce risk.
A) Combining these assets will increase risk.
B) Combining these assets will have no effect on risk.
C) Combining these assets may either raise or lower risk.
D) Combining these assets will reduce risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The risk of a portfolio consisting of two uncorrelated assets will be
A) equal to zero.
B) greater than the risk of the least risky asset but less than the risk level of the more risky asset.
C) greater than zero but less than the risk of the more risky asset.
D) equal to the average of the risk level of the two assets.
A) equal to zero.
B) greater than the risk of the least risky asset but less than the risk level of the more risky asset.
C) greater than zero but less than the risk of the more risky asset.
D) equal to the average of the risk level of the two assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Returns on the stock of First Boston and Midas Metals for the years 2017-2020 are shown below.
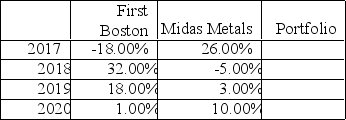 a. Compute the average annual return for each stock and a portfolio consisting of 50% First Boston and 50% Midas.
a. Compute the average annual return for each stock and a portfolio consisting of 50% First Boston and 50% Midas.
b. Compute the standard deviation for each stock and the portfolio.
c. Are the stocks positively or negatively correlated and what is the effect on risk?
 a. Compute the average annual return for each stock and a portfolio consisting of 50% First Boston and 50% Midas.
a. Compute the average annual return for each stock and a portfolio consisting of 50% First Boston and 50% Midas.b. Compute the standard deviation for each stock and the portfolio.
c. Are the stocks positively or negatively correlated and what is the effect on risk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Betas for actively traded stocks. are readily available from online sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Stock of Gould and Silber Inc. has a beta of -1. If the market declines by 10%, Gould and Silber would be expected to
A) decline by 10%.
B) rise by 10%.
C) not respond to market fluctuations.
D) decline by 1%.
A) decline by 10%.
B) rise by 10%.
C) not respond to market fluctuations.
D) decline by 1%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following represent undiversifiable risks?
I) The Federal Reserve raises interest rates.
II) A product is recalled because of safety problems.
III) The economy slips into a recession.
IV) The CEO 's divorce settlement forces him to sell off half of his stock holdings.
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III only
I) The Federal Reserve raises interest rates.
II) A product is recalled because of safety problems.
III) The economy slips into a recession.
IV) The CEO 's divorce settlement forces him to sell off half of his stock holdings.
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Beta can be defined as the slope of the line that explains the relationship between
A) the return on a security and the return on the market.
B) the returns on a security and various points in time.
C) the return on stocks and the returns on bonds.
D) the risk free rate of return versus the market rate of return.
A) the return on a security and the return on the market.
B) the returns on a security and various points in time.
C) the return on stocks and the returns on bonds.
D) the risk free rate of return versus the market rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following represent systematic risks?
I) the president of a company suddenly resigns
II) the economy goes into a recessionary period
III) a company's product is recalled for defects
IV) the Federal Reserve unexpectedly changes interest rates
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III only
I) the president of a company suddenly resigns
II) the economy goes into a recessionary period
III) a company's product is recalled for defects
IV) the Federal Reserve unexpectedly changes interest rates
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In designing a portfolio, relevant risk is
A) total risk.
B) unsystematic risk.
C) event risk.
D) nondiversifiable risk.
A) total risk.
B) unsystematic risk.
C) event risk.
D) nondiversifiable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which one of the following conditions can be effectively eliminated through portfolio diversification?
A) a general price increase nationwide
B) an interest rate reduction by the Federal Reserve
C) increased government regulation of auto emissions
D) change in the political party that controls Congress
A) a general price increase nationwide
B) an interest rate reduction by the Federal Reserve
C) increased government regulation of auto emissions
D) change in the political party that controls Congress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A stock with a higher beta is riskier than a stock with a lower beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The total risk of a portfolio is measured by its
A) beta.
B) coefficient of correlation.
C) standard deviation.
D) standard deviation plus beta.
A) beta.
B) coefficient of correlation.
C) standard deviation.
D) standard deviation plus beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which one of the following conditions can be effectively eliminated through portfolio diversification?
A) a general price increase nationwide
B) an interest rate reduction by the Federal Reserve
C) increased government regulation of auto emissions
D) change in the political party that controls Congress
A) a general price increase nationwide
B) an interest rate reduction by the Federal Reserve
C) increased government regulation of auto emissions
D) change in the political party that controls Congress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The beta of the market is
A) -1.0.
B) 0.0.
C) 1.0.
D) undefined.
A) -1.0.
B) 0.0.
C) 1.0.
D) undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following best describes the relationship between a stock's beta and the standard deviation of the stock's returns?
A) The higher the standard deviation, the higher the beta.
B) The higher the standard deviation, the lower the beta.
C) The relationship depends on the correlation between the stock's returns and the market's returns.
D) Standard deviation and beta are different ways of measuring the same thing.
A) The higher the standard deviation, the higher the beta.
B) The higher the standard deviation, the lower the beta.
C) The relationship depends on the correlation between the stock's returns and the market's returns.
D) Standard deviation and beta are different ways of measuring the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
By design, half of all stocks betas are positive betas and half are negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the returns on a stock are positively correlated with market returns, the stock will have a positive beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which one of the following types of risk cannot be effectively eliminated through portfolio diversification?
A) inflation risk
B) labor problems
C) materials shortages
D) product recalls
A) inflation risk
B) labor problems
C) materials shortages
D) product recalls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A measure of systematic risk is
A) standard deviation.
B) correlation coefficient.
C) beta.
D) variance.
A) standard deviation.
B) correlation coefficient.
C) beta.
D) variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Adding stocks with higher standard deviations to a portfolio will necessarily increase the portfolio's risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The best stock to own when the stock market is at a peak and is expected to decline in value is one with a beta of
A) +1.5.
B) +1.0.
C) -1.0.
D) -0.5.
A) +1.5.
B) +1.0.
C) -1.0.
D) -0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When the stock market has bottomed out and is beginning to recover, the best portfolio to own is the one with a beta of
A) 0.0.
B) +0.5.
C) +1.5.
D) +2.0.
A) 0.0.
B) +0.5.
C) +1.5.
D) +2.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exposure to systematic or market risk can be reduced by
A) investing in a variety of economic sectors.
B) adding low or negative beta stocks to the portfolio.
C) diversifying internationally.
D) cannot be reduced or avoided.
A) investing in a variety of economic sectors.
B) adding low or negative beta stocks to the portfolio.
C) diversifying internationally.
D) cannot be reduced or avoided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Estimates of a stock's beta may vary depending on
I) when the estimate was made.
II) the risk-free rate of interest used.
III) how many months of returns were used to estimate the beta.
IV) the index used to represent market returns.
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I, III and IV only
D) I, II and III only
I) when the estimate was made.
II) the risk-free rate of interest used.
III) how many months of returns were used to estimate the beta.
IV) the index used to represent market returns.
A) I, II and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) I, III and IV only
D) I, II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
You have gathered the following information concerning a particular investment and conditions in the market. According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model, the required return for this investment is
A) 8.15.50%.
B) 11.48%.
C) 11.75%.
D) 13.00%.
A) 8.15.50%.
B) 11.48%.
C) 11.75%.
D) 13.00%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the Capital Asset Pricing Model, a stock's expected rate of return will depend on its total risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Beta is the slope of the best fit line for the points with coordinates representing the______ and the_____ for each one of several years.
A) rate of return; level of risk for an individual security
B) rate of inflation; rate of return for an individual security
C) risk level of a stock; market rate of return
D) market rate of return; security's rate of return
A) rate of return; level of risk for an individual security
B) rate of inflation; rate of return for an individual security
C) risk level of a stock; market rate of return
D) market rate of return; security's rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a mathematical model that depicts the
A) positive relationship between risk and return.
B) standard deviation between a risk premium and an investment's expected return.
C) exact price that an investor should be willing to pay for any given investment.
D) difference between a risk-free return and the expected rate of inflation.
A) positive relationship between risk and return.
B) standard deviation between a risk premium and an investment's expected return.
C) exact price that an investor should be willing to pay for any given investment.
D) difference between a risk-free return and the expected rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to MSN money, the stock of Orange Corporation has a beta of 1.5, but according to Yahoo Finance it is 1.75. The expected rate of return on the market is 12% and the risk free rate is 2%. What is the difference between the required rates of return calculated using each of these betas?
A) 1.50%
B) 1.75%
C) 2.0%
D) 2.5%
A) 1.50%
B) 1.75%
C) 2.0%
D) 2.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The risk premium to be used in the Capital Asset Pricing Model is calculated as (rf-rm).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
According to the CAPM, the required rate of a return on a stock can be estimated using only beta and the risk-free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Analysts commonly use the______ to measure market return.
A) the Dow Jones Industrial Average
B) the rate of return on 10 year Treasury bonds
C) some large, mainstream company such as General Electric
D) the Standard & Poor's 500 Index
A) the Dow Jones Industrial Average
B) the rate of return on 10 year Treasury bonds
C) some large, mainstream company such as General Electric
D) the Standard & Poor's 500 Index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following factors comprise the CAPM?
I) dividend yield
II) risk-free rate of return
III) the expected rate of return on the market
IV) risk premium for the firm
A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III and IV only
I) dividend yield
II) risk-free rate of return
III) the expected rate of return on the market
IV) risk premium for the firm
A) I and III only
B) II and IV only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Dow Jones Industrial Average of thirty stocks is customarily used to represent market returns in the CAPM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The CAPM estimates the required rate of return on a stock held as part of a well diversified portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the Capital Asset Pricing Model is depicted graphically, the result is the
A) standard deviation line.
B) coefficient of variation line.
C) security market line.
D) alpha-beta line.
A) standard deviation line.
B) coefficient of variation line.
C) security market line.
D) alpha-beta line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements concerning beta are correct?
I) Stock with high standard deviations of returns will always have high betas.
II) The higher the beta, the higher the expected return.
III) A beta can be positive, negative, or equal to zero.
IV) A beta of 0.35 indicates a lower rate of risk than a beta of 0.50.
A) II and III only
B) I and IV only
C) II, III and IV only
D) I, II, III and IV
I) Stock with high standard deviations of returns will always have high betas.
II) The higher the beta, the higher the expected return.
III) A beta can be positive, negative, or equal to zero.
IV) A beta of 0.35 indicates a lower rate of risk than a beta of 0.50.
A) II and III only
B) I and IV only
C) II, III and IV only
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
MacroN Company has a beta of 1.75. By what percent will the required rate of return on the stock of MacroN Company increase if the expected market rate of return rises by 4%?
A) 7.00%
B) 7.5%
C) 4.75%
D) 5.70%
A) 7.00%
B) 7.5%
C) 4.75%
D) 5.70%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The basic theory linking portfolio risk and return is the Capital Asset Pricing Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Explain what beta measures and how investors can use beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the expected rate of return on AZNG is 12.72, its beta is 1.09 and the market risk premium is 8%, what is the risk-free rate?
A) 4.72%
B) 5.42%
C) 8.72%
D) 4.0%
A) 4.72%
B) 5.42%
C) 8.72%
D) 4.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The stock of NOP, Inc. has a beta of 1.80. The market rate of return is expected to increase by by 3%. Beta predicts that ABC stock should
A) increase in value by 2.4%.
B) increase in value by 5.4%.
C) decrease in value by .8%.
D) increase in value by 1.8%.
A) increase in value by 2.4%.
B) increase in value by 5.4%.
C) decrease in value by .8%.
D) increase in value by 1.8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
OKAY stock has a beta of 0.8. The market as a whole is expected to decline by 12% thereby causing OKAY stock to
A) decline by 9.6%.
B) decline by 12.5%.
C) increase by 9.6%.
D) increase by 12%.
A) decline by 9.6%.
B) decline by 12.5%.
C) increase by 9.6%.
D) increase by 12%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The market rate of return increased by 8% while the rate of return on XYZ stock increased by 4%. The beta of XYZ stock is
A) -2.0.
B) -0.40.
C) 0.50.
D) 2.0.
A) -2.0.
B) -0.40.
C) 0.50.
D) 2.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



