Deck 6: Experimental Research: Group Designs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Experimental Research: Group Designs
1
Which is the best example of random assignment of participants in an experiment?
A) Assigning participants systematically to a treatment condition
B) Drawing random numbers to assign participants into experimental groups
C) Using a method that allows for equal and unbiased assignment of participants to groups
D) All of the above
A) Assigning participants systematically to a treatment condition
B) Drawing random numbers to assign participants into experimental groups
C) Using a method that allows for equal and unbiased assignment of participants to groups
D) All of the above
Using a method that allows for equal and unbiased assignment of participants to groups
2
What are the two central features of a pretest-posttest control group design?
A) One group and the dependent variable is posttest scores
B) Two groups and the dependent variable is the pretest scores
C) One group and the effect of the intervention is determined by the change between pretest-posttest
D) Two groups and pretest-posttest scores are compared to assess the change
A) One group and the dependent variable is posttest scores
B) Two groups and the dependent variable is the pretest scores
C) One group and the effect of the intervention is determined by the change between pretest-posttest
D) Two groups and pretest-posttest scores are compared to assess the change
Two groups and pretest-posttest scores are compared to assess the change
3
Posttest-only control groups are not commonly used because:
A) They only require on experimental group
B) They do not control for threats to internal validity
C) Test sensitization problems
D) Pretest is not available
A) They only require on experimental group
B) They do not control for threats to internal validity
C) Test sensitization problems
D) Pretest is not available
Pretest is not available
4
Which treatments are believed to produce more change in multiple-treatment counterbalanced designs?
A) The treatments that are repeated
B) The first treatments
C) The last treatments
D) All are equally effective
A) The treatments that are repeated
B) The first treatments
C) The last treatments
D) All are equally effective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How can posttreatment differences occur between groups even when the treatment has no effect?
A) The subjects in each group revert to their group means that may be different
B) Subjects adopt an apprehensive subject role
C) Demand characteristics
D) There were lapses in treatment integrity
A) The subjects in each group revert to their group means that may be different
B) Subjects adopt an apprehensive subject role
C) Demand characteristics
D) There were lapses in treatment integrity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A Latin square would produce which of the following order sequences?
A)
B)
C)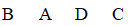
D)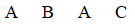
A)

B)

C)
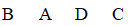
D)
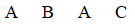

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Factorial designs are preferred because they:
A) Test the influence of the treatment and control conditions
B) Allow for the analysis of multiple treatment and interaction effects
C) Are easier to conduct than other designs like a Solomon four-group design
D) Produce the least amount of reactivity to the experimental manipulation
A) Test the influence of the treatment and control conditions
B) Allow for the analysis of multiple treatment and interaction effects
C) Are easier to conduct than other designs like a Solomon four-group design
D) Produce the least amount of reactivity to the experimental manipulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Posttest-only control groups are used to:
A) To reduce reactivity to a pretest
B) Determine the effect of a treatment on a control group
C) Establish the strength of the posttest measure
D) All of the above
A) To reduce reactivity to a pretest
B) Determine the effect of a treatment on a control group
C) Establish the strength of the posttest measure
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Quasi-experimental designs:
A) Are not true experiments
B) Allow experimenters to control the independent variables, but not the dependent variables
C) Require counter balancing of treatments
D) Do not allow for between-group comparisons
A) Are not true experiments
B) Allow experimenters to control the independent variables, but not the dependent variables
C) Require counter balancing of treatments
D) Do not allow for between-group comparisons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is a typical strategy used to ensure equivalence of experimental groups?
A) Matching subje cts at posttreatment
B) Randomly assigning cases to conditions
C) Post-testing nuisance variables
D) Identify all differences between groups
A) Matching subje cts at posttreatment
B) Randomly assigning cases to conditions
C) Post-testing nuisance variables
D) Identify all differences between groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What type of design allows participants to be given the same treatments but in different orders?
A) Crossover design
B) Multiple-treatment counterbalanced design
C) Combined-order design
D) Both a and b
A) Crossover design
B) Multiple-treatment counterbalanced design
C) Combined-order design
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Regression toward the mean, is related to the test-retest correlation for the measure, as follows:
A) The higher the correlation from one occasion to the next, the more likely there is regression toward the mean for extreme cases
B) The lower the correlation from one occasion to the next, the more likely there is regression toward the mean
C) But only for extreme cases who take the test on both occasions
D) a and c
A) The higher the correlation from one occasion to the next, the more likely there is regression toward the mean for extreme cases
B) The lower the correlation from one occasion to the next, the more likely there is regression toward the mean
C) But only for extreme cases who take the test on both occasions
D) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Generality of experimental results is most dependent upon which factor?
A) Number of participants
B) Representativeness of the participants
C) The effect size
D) Statistically significant differences between groups
A) Number of participants
B) Representativeness of the participants
C) The effect size
D) Statistically significant differences between groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Ceiling and floor effects refer to:
A) The minimum and maximum goals of treatment
B) Limits to the amount of change possible
C) Top and bottom scoring participants
D) A measure with a range of possible scores that is too great to detect an effect
A) The minimum and maximum goals of treatment
B) Limits to the amount of change possible
C) Top and bottom scoring participants
D) A measure with a range of possible scores that is too great to detect an effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why is a Solomon four-group design desirable?
A) It replicates the treatment and control conditions
B) It has high internal validity and high external validity
C) Easier to conduct than many other designs
D) Both b and c
A) It replicates the treatment and control conditions
B) It has high internal validity and high external validity
C) Easier to conduct than many other designs
D) Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



