Deck 5: The Auditors Legal Liability
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Auditors Legal Liability
1
What is the term used when a failure on the part of a plaintiff to meet certain required standards of care is a factor leading to a loss by the plaintiff?
A) negligence.
B) reasonable foreseeability.
C) contributory negligence.
D) damages.
A) negligence.
B) reasonable foreseeability.
C) contributory negligence.
D) damages.
C
2
Which of these is not a condition that must be met in order for a company to be registered as an authorised audit company?
A) one of the directors of the company must be a registered company auditor.
B) each share in the company must be held and beneficially owned by an individual or the legal personal representatives of an individual.
C) a majority of the votes that may be cast at a general meeting of the company attach to shares in the company that are beneficially owned by individuals who are registered company auditors.
D) the company must not be under external administration.
A) one of the directors of the company must be a registered company auditor.
B) each share in the company must be held and beneficially owned by an individual or the legal personal representatives of an individual.
C) a majority of the votes that may be cast at a general meeting of the company attach to shares in the company that are beneficially owned by individuals who are registered company auditors.
D) the company must not be under external administration.
A
3
The so-called 'deep-pockets' theory in relation to alleged audit failures, refers to:
A) the auditor being the only party left with sufficient funds to indemnify the plaintiff's losses.
A) the gap between the potential liability and the available insurance cover.
B) the requirement to hold a public practice certificate.
C) several widely reported business failures that resulted in significant loss to investors.
A) the auditor being the only party left with sufficient funds to indemnify the plaintiff's losses.
A) the gap between the potential liability and the available insurance cover.
B) the requirement to hold a public practice certificate.
C) several widely reported business failures that resulted in significant loss to investors.
A
4
The correct statement is: Litigation against auditors under the Trade Practices Act:
A) does not require the 'negligence' factors of foreseeability and proximity.
B) under section 52 requires professional service to be rendered with due care and skill.
C) has been ruled out by the Esanda judgment.
D) is specifically excluded.
A) does not require the 'negligence' factors of foreseeability and proximity.
B) under section 52 requires professional service to be rendered with due care and skill.
C) has been ruled out by the Esanda judgment.
D) is specifically excluded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The decision in the Caparo case (1990) reduced the duty of care of auditors to:
A) all users known to the auditor.
B) all users that ought reasonably to have been known to the auditor.
C) the shareholders as a group.
D) all users of the financial statements, except for investors.
A) all users known to the auditor.
B) all users that ought reasonably to have been known to the auditor.
C) the shareholders as a group.
D) all users of the financial statements, except for investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which case laid down the fundamental auditing principles of the 'watchdog' role and the notion of taking reasonable skill and care?
A) Kingston Cotton Mill.
B) London and General Bank.
C) Pacific Acceptance.
D) AWA.
A) Kingston Cotton Mill.
B) London and General Bank.
C) Pacific Acceptance.
D) AWA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which case prompted the development of more specific and comprehensive Auditing Standards in Australia?
A) McKesson and Robbins.
B) Pacific Acceptance.
C) Cambridge Credit.
D) AWA.
A) McKesson and Robbins.
B) Pacific Acceptance.
C) Cambridge Credit.
D) AWA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The judgement in the Pacific Acceptance case was wide-ranging and covered procedures that should exist in a normally competent audit. Which of the following is not accurate concerning procedures listed in the judgement?
A) promptly report fraud or warn of suspicion of fraud whether material or not
B) closely supervise and review the work of inexperienced staff.
C) be very wary about reporting bad news to shareholders always keeping in mind it can affect the value of their investment
D) audit the whole of the year, not just the year-end balances.
A) promptly report fraud or warn of suspicion of fraud whether material or not
B) closely supervise and review the work of inexperienced staff.
C) be very wary about reporting bad news to shareholders always keeping in mind it can affect the value of their investment
D) audit the whole of the year, not just the year-end balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Under the Hedley Byrne principle, auditors' liability to third parties to whom they owe a duty of care:
A) does not exist.
A) is no different from their liability to their clients.
B) is more onerous than their liability to their clients.
B) none of the above.
A) does not exist.
A) is no different from their liability to their clients.
B) is more onerous than their liability to their clients.
B) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Auditors are accountable in law for their professional conduct. This accountability arises under:
A) Common law.
B) Statute law.
C) Tort law.
D) all of the above.
A) Common law.
B) Statute law.
C) Tort law.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The statement that is not reflective of matters that recent cases concerning auditing have emphasised is:
A) assigning appropriately competent and supervised staff to engagements.
B) adequately documenting all audit procedures.
C) adhering to independence guidelines, especially for personal relationships with clients.
D) accepting management representations without corroboration.
A) assigning appropriately competent and supervised staff to engagements.
B) adequately documenting all audit procedures.
C) adhering to independence guidelines, especially for personal relationships with clients.
D) accepting management representations without corroboration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In respect of the provision of auditing services, the auditor will be liable to compensate the plaintiff if:
A) a duty of care is owed to the plaintiff.
B) the audit is negligently performed or the opinion negligently given.
C) the plaintiff has suffered a quantifiable loss as a result of the auditor's negligence.
D) all of the above.
A) a duty of care is owed to the plaintiff.
B) the audit is negligently performed or the opinion negligently given.
C) the plaintiff has suffered a quantifiable loss as a result of the auditor's negligence.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The law regarding the liability by auditors to third parties for financial injury:
A) is still not very clear.
B) has never been tested.
C) does not exist.
D) is very clear.
A) is still not very clear.
B) has never been tested.
C) does not exist.
D) is very clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these is not a characteristic of the current Australian legal environment for auditors?
A) there is a growing concern that auditors are sued following business failure due to their requirement to have professional indemnity insurance.
B) audit firms are not allowed to register as companies
C) recent corporate and accounting failures have contributed to a 'hard insurance market'.
D) the emerging trend of multi-disciplinary practices raises important issues for debate about auditor liability and conflict of interest situations.
A) there is a growing concern that auditors are sued following business failure due to their requirement to have professional indemnity insurance.
B) audit firms are not allowed to register as companies
C) recent corporate and accounting failures have contributed to a 'hard insurance market'.
D) the emerging trend of multi-disciplinary practices raises important issues for debate about auditor liability and conflict of interest situations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following cases did not extend the liability of auditors in regard to the concept of proximity?
A) Shaddock and Associates.
B) Jeb Fasteners.
C) Caparo Industries.
D) Twomax.
A) Shaddock and Associates.
B) Jeb Fasteners.
C) Caparo Industries.
D) Twomax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The term 'privity of contract' refers to:
A) The contractual relationship that exists between two or more contracting parties.
B) The fact that an audit is to be performed in accordance with professional standards.
C) The fact that an auditor appointed to conduct a statutory audit cannot reduce their liability by contract .
D) The mandatory requirement that there must be an engagement letter setting out the terms of the audit contract.
A) The contractual relationship that exists between two or more contracting parties.
B) The fact that an audit is to be performed in accordance with professional standards.
C) The fact that an auditor appointed to conduct a statutory audit cannot reduce their liability by contract .
D) The mandatory requirement that there must be an engagement letter setting out the terms of the audit contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The more exacting auditor responsibility showing the evolving expectations in respect to higher standards of reasonable care was set forth in the:
A) London and General Bank case.
B) Pacific Acceptance case.
C) Kingston Cotton Mills case.
D) Donoghue v Stevenson case.
A) London and General Bank case.
B) Pacific Acceptance case.
C) Kingston Cotton Mills case.
D) Donoghue v Stevenson case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these precautions taken by auditors would avoid or minimise the consequences of litigation?
A) using an engagement letter for all professional services offered by the firm.
B) thoroughly investigating all potential clients before accepting an engagement.
C) ensuring professional pronouncements are fully complied with by the firm.
D) all the above.
A) using an engagement letter for all professional services offered by the firm.
B) thoroughly investigating all potential clients before accepting an engagement.
C) ensuring professional pronouncements are fully complied with by the firm.
D) all the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which case does not appear to support the recent narrowing of the exposure of auditors to third parties?
A) Royal Bank of Scotland.
B) Lowe Lippmann.
C) Esanda Finance.
D) Columbia Coffee.
A) Royal Bank of Scotland.
B) Lowe Lippmann.
C) Esanda Finance.
D) Columbia Coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The passage in the judgment by Cardozo, CJ in the Ultramares case, ' …… a liability in an indeterminate amount for an indeterminate time to an indeterminate class' refers to:
A) an auditor's liability to exercise due care.
B) an auditor's liability to the client.
C) an auditor's liability to third parties.
D) an auditor's statutory liability.
A) an auditor's liability to exercise due care.
B) an auditor's liability to the client.
C) an auditor's liability to third parties.
D) an auditor's statutory liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The outcome in the Hedley Byrne case was:
A) the bank was found liable for the loss.
B) the bank was not found liable as no duty of care was owed.
C) the advertising agency was found to have contributed to the loss.
D) the bank was not found liable due to the disclaimer.
A) the bank was found liable for the loss.
B) the bank was not found liable as no duty of care was owed.
C) the advertising agency was found to have contributed to the loss.
D) the bank was not found liable due to the disclaimer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To determine risks and potential exposure to litigation, professional accountants commonly use an inspection program. An inspection program should be flexible and could contain:
A) routine inspection of all risks.
B) routine inspection of a particular area of risk.
C) inspections as a result of incidents or accidents.
D) all of the above.
A) routine inspection of all risks.
B) routine inspection of a particular area of risk.
C) inspections as a result of incidents or accidents.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
As a result of the rulings in Kingston Cotton Mill and the London and General Bank cases:
A) overall audit quality improved.
B) too literal an interpretation has retarded the development of improved auditing practices.
C) auditors stopped designing procedures that would detect fraud.
D) auditors became more vigilant in the detection of fraud.
A) overall audit quality improved.
B) too literal an interpretation has retarded the development of improved auditing practices.
C) auditors stopped designing procedures that would detect fraud.
D) auditors became more vigilant in the detection of fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In an audit engagement which of the following would be considered to be one stage removed from the privity of contract?
A) the company.
B) the auditor.
C) shareholders.
D) future creditors.
A) the company.
B) the auditor.
C) shareholders.
D) future creditors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Match the case with the ruling:
Cases: Rulings:
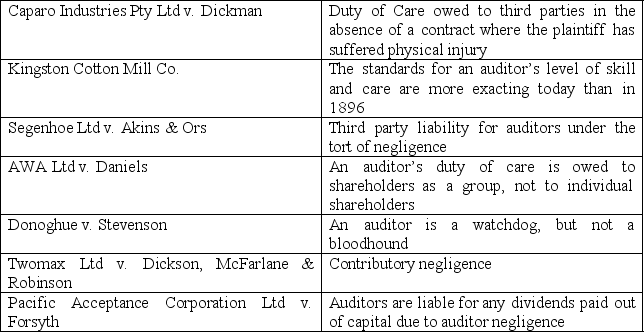
Cases: Rulings:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of these is not a concern of the Australian Government in relation to the level of insurance held by auditors?
A) insurance premiums will reduce in value.
B) consumers may not be able to access appropriate damages in the case of negligence.
C) as auditing is in the public interest any reduction adversely affects the wellbeing of the community.
D) all of the above are a concern
A) insurance premiums will reduce in value.
B) consumers may not be able to access appropriate damages in the case of negligence.
C) as auditing is in the public interest any reduction adversely affects the wellbeing of the community.
D) all of the above are a concern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why has the reaction to the verdict in Caparo Industries generally been unfavourable?
A) it is strongly thought that the loss was not quantifiable.
B) the verdict appears to treat auditors more favourably than it treats other experts on whom third parties rely.
C) the principle of proximity was not sufficiently established
D) it is felt that the auditors were not responsible.
A) it is strongly thought that the loss was not quantifiable.
B) the verdict appears to treat auditors more favourably than it treats other experts on whom third parties rely.
C) the principle of proximity was not sufficiently established
D) it is felt that the auditors were not responsible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The party that is unable to sue the auditors under contract law is:
A) the directors (on behalf of the company).
B) the liquidator.
C) individual shareholders.
D) the receiver.
A) the directors (on behalf of the company).
B) the liquidator.
C) individual shareholders.
D) the receiver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In Australia, the common law concerning the nature and extent of an auditor's duty of care to third parties:
A) was resolved with the verdict in Esanda.
B) follows the ruling in Twomax.
C) has been replaced with statute law.
D) remains complex.
A) was resolved with the verdict in Esanda.
B) follows the ruling in Twomax.
C) has been replaced with statute law.
D) remains complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Segenhoe Ltd, the company claimed that the auditors' negligence caused them to pay a dividend out of capital. What was the outcome of this case?
A) the auditors were found to be liable for the dividends.
A) the shareholders were ordered to return the dividends.
B) the company lost as there was no causal relationship.
C) the company was found to have contributed to the negligence.
A) the auditors were found to be liable for the dividends.
A) the shareholders were ordered to return the dividends.
B) the company lost as there was no causal relationship.
C) the company was found to have contributed to the negligence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The landmark case for the principle of contributory negligence is:
A) Kingston Cotton Mill.
B) Segenhoe Ltd.
C) AWA Ltd.
D) Pacific Acceptance.
A) Kingston Cotton Mill.
B) Segenhoe Ltd.
C) AWA Ltd.
D) Pacific Acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In an audit engagement which of the following would be considered to be two stages removed from the privity of contract?
A) the company.
B) the auditor.
C) shareholders.
D) future creditors.
A) the company.
B) the auditor.
C) shareholders.
D) future creditors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Describe the deep-pockets theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these is not a primary element of a fiduciary relationship?
A) the fiduciary has undertaken to act in the interests of another.
B) the fiduciary is properly certified.
C) the person to whom the fiduciary duty is owed is vulnerable to the fiduciary's abuse of his or her position.
D) all of the above are primary elements of a fiduciary relationship
A) the fiduciary has undertaken to act in the interests of another.
B) the fiduciary is properly certified.
C) the person to whom the fiduciary duty is owed is vulnerable to the fiduciary's abuse of his or her position.
D) all of the above are primary elements of a fiduciary relationship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A. Explain the impact that the Pacific Acceptance case had on existing auditing practice.
B. List four of the procedures or practices that were identified in the ruling as being part of a competent audit.
B. List four of the procedures or practices that were identified in the ruling as being part of a competent audit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of these is not a precaution auditors take to avoid litigation?
A) comply fully with professional pronouncements.
B) never issue a privity letter.
C) maintain adequate professional indemnity cover.
D) all of the above are precautions auditors take to avoid litigation
A) comply fully with professional pronouncements.
B) never issue a privity letter.
C) maintain adequate professional indemnity cover.
D) all of the above are precautions auditors take to avoid litigation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The case of auditor negligence that was unsuccessful as the loss was not quantifiable was:
A) Scott Group Ltd.
B) Shaddock & Associates.
C) JEB Fasteners.
D) Twomax.
A) Scott Group Ltd.
B) Shaddock & Associates.
C) JEB Fasteners.
D) Twomax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The two cases that formed the basis for most subsequent decisions as to the determination of auditor negligence were:
A) Hedley Byrne and AWA.
B) JEB Fasteners and Twomax.
C) Caparo Industries and Esanda.
D) Kingston Cotton Mill and London and General Bank.
A) Hedley Byrne and AWA.
B) JEB Fasteners and Twomax.
C) Caparo Industries and Esanda.
D) Kingston Cotton Mill and London and General Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Name the elements necessary to be successful in a case of negligence and show how these were applied in the case of Twomax Ltd v. Dickson, McFarlane & Robinson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is true regarding damages?
A) damages are only available under tort.
B) damages are available under tort and contract.
C) damages are limited to the audit fees paid.
D) damages are unquantifiable.
A) damages are only available under tort.
B) damages are available under tort and contract.
C) damages are limited to the audit fees paid.
D) damages are unquantifiable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Australian case of Esanda Corporation v. Peat Marwick Hungerfords established the elements that would be necessary for a third party to succeed in an action of negligence against the auditor due to reliance on the audited accounts. Identify what these elements are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain how engagement letters can be used to avoid litigation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why would the courts want to limit the ability of third parties to sue auditors who have been negligent? Are there any arguments that this liability should not be limited?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A. Identify who the parties are in the contractual relationship regarding an audit and what this relationship is termed.
B. Identify who may sue the auditors under contract.
B. Identify who may sue the auditors under contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What were the causes and results of the 'hard insurance market' in Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



