Deck 9: Health Care
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Health Care
1
The government can address by providing universal health insurance coverage and charging uniform premiums.
A)asymmetric information
B)adverse selection
C)expected utility
D)commodity egalitarianism
A)asymmetric information
B)adverse selection
C)expected utility
D)commodity egalitarianism
adverse selection
2
In 2014, total spending on health as a percentage of GDP was 4.9 percent.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
False
3
Low-risk individuals prefer zero coverage to social insurance.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
True
4
When people have diminishing marginal utility, they have a preference for
A)risk smoothing.
B)risk pooling.
C)risk premium.
D)risk aversion.
A)risk smoothing.
B)risk pooling.
C)risk premium.
D)risk aversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One reason for increasing health care costs is the aging of the population.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Marginal benefit and marginal cost must to avoid a deadweight loss.
A)never equal
B)decrease at an increasing rate
C)increase at an increasing rate
D)equal
A)never equal
B)decrease at an increasing rate
C)increase at an increasing rate
D)equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Government per capita spending on health has been trending upwards.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When people take less care to avoid risks because they have insurance, this is known as
A)adverse selection.
B)asymmetric information.
C)moral hazard.
D)risk aversion.
A)adverse selection.
B)asymmetric information.
C)moral hazard.
D)risk aversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An actuarially fair insurance premium would charge more than required to cover the expected compensation for the expenses.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The demand for insurance depends on the level of
A)risk premium.
B)risk smoothing.
C)risk pooling.
D)risk aversion.
A)risk premium.
B)risk smoothing.
C)risk pooling.
D)risk aversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the figure below, the value of insurance is $7,000. 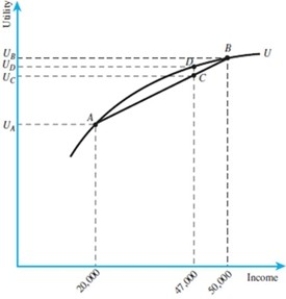
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The proportion of Medicare services, such as drugs, that is not fully insured is called the
A)user fee.
B)risk premium.
C)loading fee.
D)coinsurance rate.
A)user fee.
B)risk premium.
C)loading fee.
D)coinsurance rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Among the OECD countries, which country had the highest total health expenditures as a percent of GDP in 2011?
A)Canada
B)Japan
C)United States
D)Australia
A)Canada
B)Japan
C)United States
D)Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Canada's national healthcare program is governed by the
A)Canada Health Act.
B)Canada Social Transfer.
C)Canada Health Transfer.
D)Constitution Act.
A)Canada Health Act.
B)Canada Social Transfer.
C)Canada Health Transfer.
D)Constitution Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the figure below, $40,000 for certain is as desirable as $47,000 with risk. 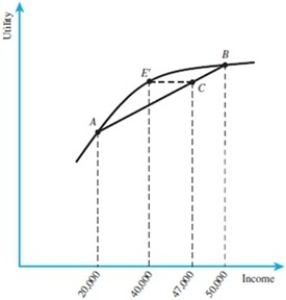
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In 2014, the province with the lowest per capita health expenditures was
A)Alberta.
B)Ontario.
C)Quebec.
D)Newfoundland and Labrador.
A)Alberta.
B)Ontario.
C)Quebec.
D)Newfoundland and Labrador.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Health care markets may be inefficient because of
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)poor information.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)poor information.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Pooling individuals allows insurance companies to risk from a societal point of view.
A)decrease
B)increase
C)do nothing regarding
D)none of these answers is correct.
A)decrease
B)increase
C)do nothing regarding
D)none of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Expected values
A)are weighted by the probability of an outcome occurring.
B)are calculated as the average value.
C)are calculated over all possible outcomes.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)are weighted by the probability of an outcome occurring.
B)are calculated as the average value.
C)are calculated over all possible outcomes.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Social insurance programs are not subject to adverse selection.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that an economist has a utility function U = (Income)0.25. Her income is $65K a year, but there is a 10 percent chance of becoming ill and making only $57K.
(a)What is her expected utility if she does not have insurance?
(b)What is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
(c)How much is she willing to pay for insurance?
(a)What is her expected utility if she does not have insurance?
(b)What is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
(c)How much is she willing to pay for insurance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose there are two drivers, Jermaine and Janet. Jermaine is not a very safe driver. In fact, there is a 7.5% chance that he will have an accident within the next year. Janet is a relatively safe driver. Her chances of having an accident in the next year are only 1%. If Jermaine is involved in an accident, he will cost the insurance company $1,000,000. If Janet is involved in an accident, she will only cost the company $500,000. What is the expected payout that the company can expect from insuring these two?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that the quantity demanded of visits to a doctor per year is given by X = 12 - 0.05P, where X is the number of visits and P is the price the patient pays for a visit.
(a)How many visits would the patient make if he or she had to pay the full price of a visit, $100?
(b)How many visits would the patient make if medical services were free?
(a)How many visits would the patient make if he or she had to pay the full price of a visit, $100?
(b)How many visits would the patient make if medical services were free?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
With increasing costs to the Canadian health system, what are some ways the government could try to mitigate this increase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
It has been suggested in both the Kirby Report and Romanow Report that drugs be included as part of the publicly funded health plan. Do you think this recommendation should be adopted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The difference between the willingness to pay and the actuarially fair premium is known as
A)the loading fee.
B)the expected utility.
C)the level of risk aversion.
D)the risk premium.
A)the loading fee.
B)the expected utility.
C)the level of risk aversion.
D)the risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
We have read that the uninsured and the insured behave differently in regard to medical services. Suppose that the insured have a demand curve that can be written as Q = 100 - P, where Q is the quantity of medical services and P is the price. Suppose further that the uninsured have a demand curve that can be written as Q = 100 - 2P.
(a)At a price of $10 of medical services, how much will each demand?
(b)At a quantity of 50 units, how much will the price be for the insured and uninsured?
(a)At a price of $10 of medical services, how much will each demand?
(b)At a quantity of 50 units, how much will the price be for the insured and uninsured?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Data suggests that wait times in Canada are lower relative to the United States.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We have read in this chapter that people with insurance may be more likely to engage in risky behaviour because they are insured. Does it make sense then that there should be an "insurance tax" on people who engage in these types of activities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



