Deck 8: Fiscal Federalism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Fiscal Federalism
1
In the Tiebout model, individuals vote with their
A)feet.
B)ballots.
C)hands.
D)political party.
A)feet.
B)ballots.
C)hands.
D)political party.
feet.
2
The largest share of expenditures on health are made by the government(s).
A)provisional
B)federal
C)state
D)provincial, territorial, and local
A)provisional
B)federal
C)state
D)provincial, territorial, and local
provincial, territorial, and local
3
The Tiebout model assumes that public services are financed by a proportional property tax.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
True
4
Tax effort is normally defined as
A)the economic burden of taxation.
B)the percentage of taxes collected subnationally.
C)the ratio of tax collections to tax capacity.
D)the government's effort to collect taxes.
A)the economic burden of taxation.
B)the percentage of taxes collected subnationally.
C)the ratio of tax collections to tax capacity.
D)the government's effort to collect taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For most federations almost all macroeconomic stabilization comes from governments actively adjusting taxation and spending levels to smooth out slumps and booms.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When did federal transfers as a percentage of provincial and local expenditures reach its peak?
A)1960s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1990s
A)1960s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1990s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A Tiebout model involves
A)perfect information.
B)governments generating no externalities.
C)completely mobile individuals.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)perfect information.
B)governments generating no externalities.
C)completely mobile individuals.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Canada Health Transfer (CHT)and Canada Social Transfer (CST)are matching conditional grants.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Disadvantages of a decentralized system include(s)
A)the lack of ability to redistribute income.
B)intercommunity externalities.
C)forgone scale economies in the provision of public goods.
D)all of these answers are correct.
A)the lack of ability to redistribute income.
B)intercommunity externalities.
C)forgone scale economies in the provision of public goods.
D)all of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Tiebout model perfectly describes the real world.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Equalization is the main program to address fiscal disparities across provinces in Canada.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In 2013-14, all provinces except received equalization payments.
A)Newfoundland and Labrador, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia
B)Newfoundland and Labrador, Ontario and Quebec
C)Ontario and Quebec
D)Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia
A)Newfoundland and Labrador, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia
B)Newfoundland and Labrador, Ontario and Quebec
C)Ontario and Quebec
D)Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and British Columbia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When the federal government gives a grant to a provincial government without restrictions on use, this is known as
A)revenue sharing.
B)a conditional grant.
C)an unconditional grant.
D)an endowment.
A)revenue sharing.
B)a conditional grant.
C)an unconditional grant.
D)an endowment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Net fiscal benefits are
A)when government action is not required to achieve efficiency.
B)the value of publicly provided services minus their cost to the recipient of those services.
C)an economic theory and not present in the real world.
D)all of these answers are correct.
A)when government action is not required to achieve efficiency.
B)the value of publicly provided services minus their cost to the recipient of those services.
C)an economic theory and not present in the real world.
D)all of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Federal transfers as a percentage of federal expenditures are higher now than in the postwar (post World War II)period.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Over the last 100 years, the level of government that has seen the largest increase in its percentage of expenditures is
A)provincial.
B)local.
C)federal.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)provincial.
B)local.
C)federal.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A federal system consists of one level of government to provide public goods and services.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
explores the functions undertaken by different levels of government and the ways in which they relate to each other.
A)Centralization
B)Decentralization
C)Fiscal federalism
D)Federal system
A)Centralization
B)Decentralization
C)Fiscal federalism
D)Federal system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The share of total government expenditures made by subnational governments is called the expenditure centralization ratio.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
percent of Canadians changed their province of residence in 2013-14.
A)10
B)5
C)1
D)20
A)10
B)5
C)1
D)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why is the Tiebout model not a perfect description of the real world? Despite this fact, why does the model perform well, and why is it considered a good depiction of reality?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Advantages of a decentralized system include(s)
A)fostering intergovernmental competition.
B)tailoring government to local tastes.
C)intercommunity externalities.
D)both A and B.
A)fostering intergovernmental competition.
B)tailoring government to local tastes.
C)intercommunity externalities.
D)both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the figure below. Suppose that the initial budget constraint AB is given by the equation G = 150 - c/5, where G is the units of public good and c is consumption. A closed-ended matching grant up to 100 units of public good is proposed. If the slope of line segment AD is -2, write the equation of the new budget constraint after a closed-ended matching grant.
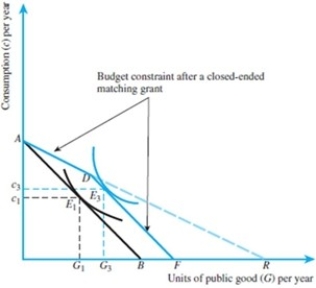


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The flypaper effect causes money to move from the sector it initially hits to stick somewhere else.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
More than half of federal grant outlays go for programs relating to post-secondary education, health, and _.
A)roads
B)defence
C)social assistance
D)international aid
A)roads
B)defence
C)social assistance
D)international aid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Tiebout model can be summarized as individuals voting with their hands.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure below that illustrates a matching grant. Suppose that there is a change to a closed-ended matching grant. Modify the figure below to reflect the change from a matching grant to a closed-end matching grant.
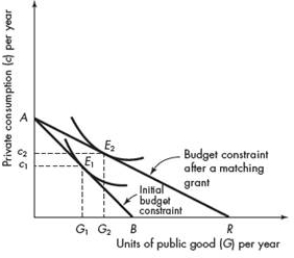


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The measures the dollar cost of the incremental congestion created by each new member to a community.
A)marginal cost of public funds
B)community tax
C)club membership fee
D)marginal congestion cost
A)marginal cost of public funds
B)community tax
C)club membership fee
D)marginal congestion cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In Tiebout's model, the tax can vary across communities.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The federal government and provinces committed to reducing regional economic disparities in the
A)War Measures Act, 1914.
B)British North America Act, 1867.
C)Constitution Act, 1982.
D)Canadian Bill of Rights, 1960.
A)War Measures Act, 1914.
B)British North America Act, 1867.
C)Constitution Act, 1982.
D)Canadian Bill of Rights, 1960.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Equalization is the main vehicle for addressing fiscal disparities across provincial governments. Briefly describe the adjustments introduced to the program in Budget 2007. Do you think these changes to the equalization program were a good idea? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Discuss the disadvantages of a decentralized system. If you were making a recommendations to the government, what are some of the potential issues of a decentralized system you would identify?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Tiebout model offers a quasi-market solution to public good production and community development. What are some drawbacks to this model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A migration response to differences in net fiscal benefits is called fiscally induced migration.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



