Deck 3: Cost-Benefit Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cost-Benefit Analysis
1
Using the present value criterion is more reliable than using the internal rate of return and the benefit-cost ratio.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
True
2
The chain-reaction game
A)compounds a bad decision by making more bad decisions, causing unwanted projects to get funded.
B)was cancelled on network TV.
C)counts secondary costs without counting secondary benefits.
D)counts secondary benefits without counting secondary loses.
A)compounds a bad decision by making more bad decisions, causing unwanted projects to get funded.
B)was cancelled on network TV.
C)counts secondary costs without counting secondary benefits.
D)counts secondary benefits without counting secondary loses.
counts secondary benefits without counting secondary loses.
3
Risk is a part of cost-benefit analysis.
A)decided by others whether to be
B)always
C)unable to be calculated as
D)never
A)decided by others whether to be
B)always
C)unable to be calculated as
D)never
always
4
When wages are viewed as benefits instead of costs of a project, it is an example of the
A)dating game.
B)double-counting game.
C)labour game.
D)chain-reaction game.
A)dating game.
B)double-counting game.
C)labour game.
D)chain-reaction game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For certain intangibles that cannot be measured, it is best to
A)leave it to the private sector to decide on value.
B)exclude them from cost benefit analysis, and then calculate how large they must be to reverse the decision.
C)guess.
D)reevaluate using the Hicks-Kaldor criterion.
A)leave it to the private sector to decide on value.
B)exclude them from cost benefit analysis, and then calculate how large they must be to reverse the decision.
C)guess.
D)reevaluate using the Hicks-Kaldor criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The value of a human life
A)can be estimated using probability of death.
B)can be estimated by lost earnings.
C)is an intangible that is hard to value.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)can be estimated using probability of death.
B)can be estimated by lost earnings.
C)is an intangible that is hard to value.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
As long as net returns are positive, the gainers could compensate the losers and still enjoy a net increase in utility. This notion is called
A)the Hicks-Kaldor criterion.
B)a potential Pareto improvement.
C)both of these answers are correct.
D)neither of these answers is correct.
A)the Hicks-Kaldor criterion.
B)a potential Pareto improvement.
C)both of these answers are correct.
D)neither of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For a government to be efficient, a project should be funded
A)until the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost.
B)only when the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost.
C)only when the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit.
D)as long as the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit.
A)until the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost.
B)only when the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost.
C)only when the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit.
D)as long as the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A social rate of discount measures the value society places on consumption that is sacrificed in the future.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Real dollar amounts are essentially the same as nominal dollar amounts.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Money values indexed to a given period are known as
A)inverse.
B)random.
C)real.
D)nominal.
A)inverse.
B)random.
C)real.
D)nominal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the benefit-cost ratio of a project is greater than 1, the project should be considered.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The value that society places on consumption that is sacrificed in the present is called
A)social marginal damages.
B)social rate of discount.
C)social returns.
D)social marginal costs.
A)social marginal damages.
B)social rate of discount.
C)social returns.
D)social marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Inflation favours
A)lenders.
B)borrowers.
C)neither borrowers nor lenders.
D)both borrowers and lenders.
A)lenders.
B)borrowers.
C)neither borrowers nor lenders.
D)both borrowers and lenders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the figure below. If the supply curve returns to its initial level of Sa, the amount of consumer surplus will return to its original level. 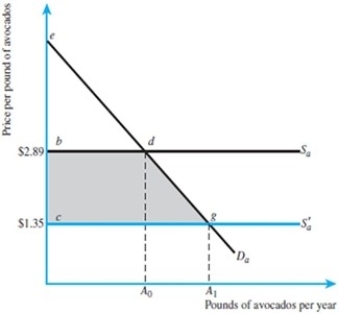
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Counting as benefits of the project the sum of the increase in land value and the present value of net income from farming it is an example of the chain-reaction game.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the benefits or costs of a project are risky, they must be avoided.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Cost-benefit analysis is
A)impossible since benefits and costs are hard to evaluate.
B)used by only the private sector to determine whether certain projects should be undertaken.
C)a set of practical procedures for guiding public expenditure decisions.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)impossible since benefits and costs are hard to evaluate.
B)used by only the private sector to determine whether certain projects should be undertaken.
C)a set of practical procedures for guiding public expenditure decisions.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The systematic study of the costs of the various alternatives should be done to find the cheapest way possible is sometimes called cost-effectiveness analysis.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the private sector, if the net return is positive it should be undertaken regardless of who gains and loses.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the interest rate that should be used to ensure a total balance of $3,000 two years from now if you have a starting balance of $2,000?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The rate at which future money must be discounted is known as the
A)rate of inflation.
B)discount rate.
C)time rate.
D)exposure rate.
A)rate of inflation.
B)discount rate.
C)time rate.
D)exposure rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the figure below. If the demand curve can be characterized by the equation Q = 10 - P, how much of an increase in consumer surplus will occur when the price of avocados falls from $2.89 to
$1.35?
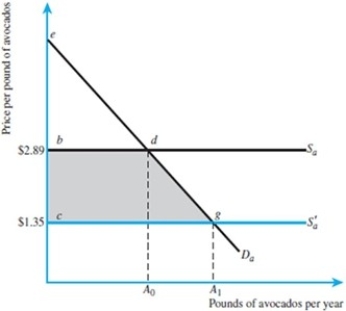
$1.35?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The government has hired you to advise them on the merits of a project that is being proposed. The project is expected to generate benefits of 14 million dollars today, 5 million dollars in one year from today, and 1 million dollars in two years from today. (These are the only years of concern.)The project costs nothing today, but will cost 20 million dollars in two years. Assume the interest rate is 10%. If the benefit-cost ratio is greater than 1, the project should be allowed. What is your policy suggestion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why is it that projects that should not be undertaken are sometimes undertaken?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Compare the following methods to evaluate a project: present value criterion, internal rate of return, and benefit-cost ratio. Which is preferred? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The term "present value" refers to the future value of present day money.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the interest rate is 5 percent, what is the present value of $5,000 five years from now?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Internal rate of return analysis suggests that a project should be undertaken if
A)IRR > discount rate.
B)NPV > 0.
C)discount rate > inflation rate.
D)MB > 0.
A)IRR > discount rate.
B)NPV > 0.
C)discount rate > inflation rate.
D)MB > 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider two projects. The first project pays benefits of $90 today and nothing else. The second project pays nothing today, nothing one year from now, but $100 two years from now. Which project would be preferred if the discount rate were 0%? What if the rate increased to 10%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The shadow price of goods traded in imperfect markets is the underlying social marginal cost.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The term "future value"
A)can be determined by inverting the formula for present value.
B)refers to the present value of future money.
C)includes the shadow prices of all goods used in a project.
D)is not used in modern public finance analysis.
A)can be determined by inverting the formula for present value.
B)refers to the present value of future money.
C)includes the shadow prices of all goods used in a project.
D)is not used in modern public finance analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Some analysts have argued that cost-benefit analysis does not take into account issues involving equity and is nothing more than an efficiency test. Do you agree with this statement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose in a certain city the demand for low-cost housing can be characterized by the equation P = 500 - 2Q, where Q is housing measured in square feet. Further, suppose that supply is characterized by the equation: P = 25 + 3Q.
(A)How much consumer surplus is there?
(B)Suppose that a grant is given so that the supply of housing is increased. This increase changes the supply curve to P = 3Q. How much does consumer surplus change because of the grant?
(A)How much consumer surplus is there?
(B)Suppose that a grant is given so that the supply of housing is increased. This increase changes the supply curve to P = 3Q. How much does consumer surplus change because of the grant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Evaluating of costs and benefits is likely to require
A)only observed prices.
B)only economists as they possess all the technical expertise required.
C)a PhD in economics.
D)ad hoc assumptions.
A)only observed prices.
B)only economists as they possess all the technical expertise required.
C)a PhD in economics.
D)ad hoc assumptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



