Deck 10: Pure Competition in the Short Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/160
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Pure Competition in the Short Run
1
In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult?
A)pure monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)pure competition
A)pure monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)pure competition
pure monopoly
2
An industry comprising 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market for a differentiated product, is an example of
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.
monopolistic competition.
3
Which of the following statements applies to a purely competitive producer?
A)It will not advertise its product.
B)In long-run equilibrium, it will earn an economic profit.
C)Its product will have a brand name that elicits customer loyalty.
D)Its product is slightly different from those of its competitors.
A)It will not advertise its product.
B)In long-run equilibrium, it will earn an economic profit.
C)Its product will have a brand name that elicits customer loyalty.
D)Its product is slightly different from those of its competitors.
It will not advertise its product.
4
In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis.For a purely competitive firm, marginal revenue graphs as a
A)straight, upsloping line.
B)straight line, parallel to the vertical axis.
C)straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis.
D)straight, downsloping line.
A)straight, upsloping line.
B)straight line, parallel to the vertical axis.
C)straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis.
D)straight, downsloping line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Price is constant to the individual firm selling in a purely competitive market because
A)the firm's demand curve is downsloping.
B)of product differentiation reinforced by extensive advertising.
C)each seller supplies a negligible fraction of total supply.
D)marginal costs are constant.
A)the firm's demand curve is downsloping.
B)of product differentiation reinforced by extensive advertising.
C)each seller supplies a negligible fraction of total supply.
D)marginal costs are constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis.For a purely competitive firm, total revenue graphs as a
A)straight, upsloping line.
B)straight line, parallel to the vertical axis.
C)straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis.
D)straight, downsloping line.
A)straight, upsloping line.
B)straight line, parallel to the vertical axis.
C)straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis.
D)straight, downsloping line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue
A)may be either greater or less than $5.
B)will also be $5.
C)will be less than $5.
D)will be greater than $5.
A)may be either greater or less than $5.
B)will also be $5.
C)will be less than $5.
D)will be greater than $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An industry comprising a small number of firms, each of which considers the potential reactions of its rivals in making price-output decisions, is called
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a characteristic of pure competition?
A)pricing strategies by firms
B)a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)a larger number of sellers
A)pricing strategies by firms
B)a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)a larger number of sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following industries most closely approximates pure competition?
A)agriculture
B)farm implements
C)clothing
D)steel
A)agriculture
B)farm implements
C)clothing
D)steel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Economists would describe the U.S.automobile industry as
A)purely competitive.
B)an oligopoly.
C)monopolistically competitive.
D)a pure monopoly.
A)purely competitive.
B)an oligopoly.
C)monopolistically competitive.
D)a pure monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An industry comprising a very large number of sellers producing a standardized product is known as
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In which of the following market structures is there clear-cut mutual interdependence with respect to price-output policies?
A)pure monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)pure competition
A)pure monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)pure competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis.For a purely competitive firm,
A)marginal revenue will graph as an upsloping line.
B)the demand curve will lie above the marginal revenue curve.
C)the marginal revenue curve will lie above the demand curve.
D)the demand and marginal revenue curves will coincide.
A)marginal revenue will graph as an upsloping line.
B)the demand curve will lie above the marginal revenue curve.
C)the marginal revenue curve will lie above the demand curve.
D)the demand and marginal revenue curves will coincide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe
A)all industries that produce standardized products.
B)any industry in which there is no nonprice competition.
C)a pure monopoly only.
D)those markets that are not purely competitive.
A)all industries that produce standardized products.
B)any industry in which there is no nonprice competition.
C)a pure monopoly only.
D)those markets that are not purely competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A purely competitive seller is
A)both a "price maker" and a "price taker."
B)neither a "price maker" nor a "price taker."
C)a "price taker."
D)a "price maker."
A)both a "price maker" and a "price taker."
B)neither a "price maker" nor a "price taker."
C)a "price taker."
D)a "price maker."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For a purely competitive seller, price equals
A)average revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)total revenue divided by output.
D)all of these.
A)average revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)total revenue divided by output.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is characteristic of a purely competitive seller's demand curve?
A)Price and marginal revenue are equal at all levels of output.
B)Average revenue is less than price.
C)Its elasticity coefficient is 1 at all levels of output.
D)It is the same as the market demand curve.
A)Price and marginal revenue are equal at all levels of output.
B)Average revenue is less than price.
C)Its elasticity coefficient is 1 at all levels of output.
D)It is the same as the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An industry comprising four firms, each with about 25 percent of the total market for a product, is an example of
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)oligopoly.
C)pure monopoly.
D)pure competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a basic characteristic of pure competition?
A)considerable nonprice competition
B)no barriers to the entry or exit of firms
C)a standardized or homogeneous product
D)a large number of buyers and sellers
A)considerable nonprice competition
B)no barriers to the entry or exit of firms
C)a standardized or homogeneous product
D)a large number of buyers and sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The MR = MC rule can be restated for a purely competitive seller as P = MC because
A)each additional unit of output adds exactly its price to total revenue.
B)the firm's average revenue curve is downsloping.
C)the market demand curve is downsloping.
D)the firm's marginal revenue and total revenue curves will coincide.
A)each additional unit of output adds exactly its price to total revenue.
B)the firm's average revenue curve is downsloping.
C)the market demand curve is downsloping.
D)the firm's marginal revenue and total revenue curves will coincide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the short run, the individual competitive firm's supply curve is that segment of the
A)average variable cost curve lying below the marginal cost curve.
B)marginal cost curve lying above the average variable cost curve.
C)marginal revenue curve lying below the demand curve.
D)marginal cost curve lying between the average total cost and average variable cost curves.
A)average variable cost curve lying below the marginal cost curve.
B)marginal cost curve lying above the average variable cost curve.
C)marginal revenue curve lying below the demand curve.
D)marginal cost curve lying between the average total cost and average variable cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm
A)must lower price to sell more output.
B)can sell as much output as it chooses at the existing price.
C)realizes an increase in total revenue that is less than product price when it sells an extra unit.
D)is selling a differentiated (heterogeneous) product.
A)must lower price to sell more output.
B)can sell as much output as it chooses at the existing price.
C)realizes an increase in total revenue that is less than product price when it sells an extra unit.
D)is selling a differentiated (heterogeneous) product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The fact that a purely competitive firm's total revenue curve is linear and upsloping to the right implies that
A)product price increases as output increases.
B)product price decreases as output increases.
C)product price is constant at all levels of output.
D)marginal revenue declines as more output is produced.
A)product price increases as output increases.
B)product price decreases as output increases.
C)product price is constant at all levels of output.
D)marginal revenue declines as more output is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a valid generalization concerning the relationship between price and costs for a purely competitive seller in the short run?
A)Price must be at least equal to average total cost.
B)Price times quantity produced must be equal to or greater than total variable cost for some level of output or the firm will close down in the short run.
C)Price may be equal to, greater than, or less than average total cost.
D)Price must be equal to or greater than minimum average variable cost for the firm to continue producing.
A)Price must be at least equal to average total cost.
B)Price times quantity produced must be equal to or greater than total variable cost for some level of output or the firm will close down in the short run.
C)Price may be equal to, greater than, or less than average total cost.
D)Price must be equal to or greater than minimum average variable cost for the firm to continue producing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output.It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit.Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output.This corporation
A)should close down in the short run.
B)is maximizing its profits.
C)is realizing a loss of $60.
D)is realizing an economic profit of $40.
A)should close down in the short run.
B)is maximizing its profits.
C)is realizing a loss of $60.
D)is realizing an economic profit of $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping.
B)The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is downsloping, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is perfectly elastic.
C)The demand curves are downsloping for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry.
D)The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry.
A)The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping.
B)The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is downsloping, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is perfectly elastic.
C)The demand curves are downsloping for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry.
D)The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A competitive firm will maximize profits at that output at which
A)total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount.
B)total revenue and total cost are equal.
C)price exceeds average total cost by the largest amount.
D)the difference between marginal revenue and price is at a maximum.
A)total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount.
B)total revenue and total cost are equal.
C)price exceeds average total cost by the largest amount.
D)the difference between marginal revenue and price is at a maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The demand curve in a purely competitive industry is , while the demand curve to a single firm in that industry is .
A)perfectly inelastic; perfectly elastic
B)downsloping; perfectly elastic
C)downsloping; perfectly inelastic
D)perfectly elastic; downsloping
A)perfectly inelastic; perfectly elastic
B)downsloping; perfectly elastic
C)downsloping; perfectly inelastic
D)perfectly elastic; downsloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm
A)lies below the firm's demand curve.
B)is downsloping because price must be reduced to sell more output.
C)is horizontal at the market price.
D)has all of these characteristics.
A)lies below the firm's demand curve.
B)is downsloping because price must be reduced to sell more output.
C)is horizontal at the market price.
D)has all of these characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the short run, a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit will produce
A)where the demand and the ATC curves intersect.
B)where total revenue exceeds total cost by the maximum amount.
C)that output at which economic profits are zero.
D)at any point where the total revenue and total cost curves intersect.
A)where the demand and the ATC curves intersect.
B)where total revenue exceeds total cost by the maximum amount.
C)that output at which economic profits are zero.
D)at any point where the total revenue and total cost curves intersect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Marginal revenue is the
A)change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
B)change in average revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
C)difference between product price and average total cost.
D)change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
A)change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
B)change in average revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
C)difference between product price and average total cost.
D)change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose you find that the price of your product is less than minimum AVC.You should
A)minimize your losses by producing where P = MC.
B)maximize your profits by producing where P = MC.
C)close down because, by producing, your losses will exceed your total fixed costs.
D)close down because total revenue exceeds total variable cost.
A)minimize your losses by producing where P = MC.
B)maximize your profits by producing where P = MC.
C)close down because, by producing, your losses will exceed your total fixed costs.
D)close down because total revenue exceeds total variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The MR = MC rule applies
A)to firms in all types of industries.
B)only when the firm is a "price taker."
C)only to monopolies.
D)only to purely competitive firms.
A)to firms in all types of industries.
B)only when the firm is a "price taker."
C)only to monopolies.
D)only to purely competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a firm is maximizing profit, it will necessarily be
A)maximizing profit per unit of output.
B)maximizing the difference between total revenue and total cost.
C)minimizing total cost.
D)maximizing total revenue.
A)maximizing profit per unit of output.
B)maximizing the difference between total revenue and total cost.
C)minimizing total cost.
D)maximizing total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A competitive firm in the short run can determine the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output by equating
A)price and average total cost.
B)price and average fixed cost.
C)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
D)price and marginal revenue.
A)price and average total cost.
B)price and average fixed cost.
C)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
D)price and marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Firms seek to maximize
A)per unit profit.
B)total revenue.
C)total profit.
D)market share.
A)per unit profit.
B)total revenue.
C)total profit.
D)market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A firm reaches a break-even point (normal profit position) where
A)marginal revenue cuts the horizontal axis.
B)marginal cost intersects the average variable cost curve.
C)total revenue equals total variable cost.
D)total revenue and total cost are equal.
A)marginal revenue cuts the horizontal axis.
B)marginal cost intersects the average variable cost curve.
C)total revenue equals total variable cost.
D)total revenue and total cost are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For a purely competitive firm, total revenue
A)is price times quantity sold.
B)increases by a constant absolute amount as output expands.
C)graphs as a straight upsloping line from the origin.
D)has all of these characteristics.
A)is price times quantity sold.
B)increases by a constant absolute amount as output expands.
C)graphs as a straight upsloping line from the origin.
D)has all of these characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve is
A)perfectly elastic at the minimum average total cost.
B)upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
C)upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average total cost curve.
D)upsloping only when the industry has constant costs.
A)perfectly elastic at the minimum average total cost.
B)upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
C)upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average total cost curve.
D)upsloping only when the industry has constant costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
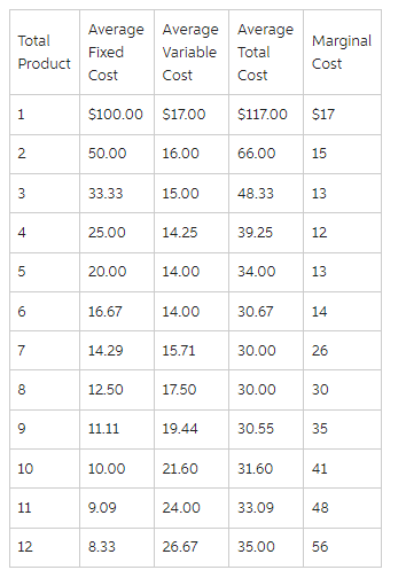
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market.If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce
A)8 units at an economic profit of $16.
B)6 units at an economic profit of $7.98.
C)10 units at an economic profit of $4.
D)7 units at an economic profit of $41.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a firm is confronted with economic losses in the short run, it will decide whether or not to produce by comparing
A)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
B)price and average variable cost.
C)total revenue and total cost.
D)total revenue and total fixed cost.
A)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
B)price and average variable cost.
C)total revenue and total cost.
D)total revenue and total fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
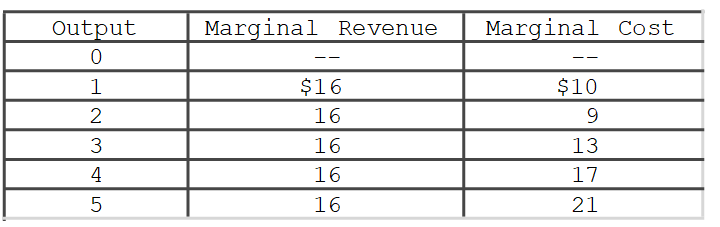
The data in the accompanying table indicates that this firm is selling its output in a(n)
A)monopolistically competitive market.
B)monopolistic market.
C)purely competitive market.
D)oligopolistic market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
On a per-unit basis, economic profit can be determined as the difference between
A)marginal revenue and product price.
B)product price and average total cost.
C)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
D)average fixed cost and product price.
A)marginal revenue and product price.
B)product price and average total cost.
C)marginal revenue and marginal cost.
D)average fixed cost and product price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a purely competitive firm is producing at some output level less than the profit-maximizing output, then
A)price is necessarily greater than average total cost.
B)fixed costs are large relative to variable costs.
C)price exceeds marginal revenue.
D)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
A)price is necessarily greater than average total cost.
B)fixed costs are large relative to variable costs.
C)price exceeds marginal revenue.
D)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based primarily on its
A)AVC curve.
B)ATC curve.
C)AFC curve.
D)MC curve.
A)AVC curve.
B)ATC curve.
C)AFC curve.
D)MC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the short run, a purely competitive firm will always make an economic profit if
A)P = ATC.
B)P > AVC.
C)P = MC.
D)P > ATC.
A)P = ATC.
B)P > AVC.
C)P = MC.
D)P > ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The lowest point on a purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve corresponds to
A)the minimum point on its ATC curve.
B)the minimum point on its AVC curve.
C)the minimum point on its AFC curve.
D)the minimum point on its MC curve.
A)the minimum point on its ATC curve.
B)the minimum point on its AVC curve.
C)the minimum point on its AFC curve.
D)the minimum point on its MC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market.Which of the following tables gives the firm's short- run supply schedule?
A)
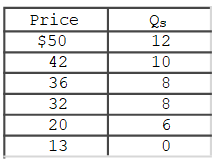
B)
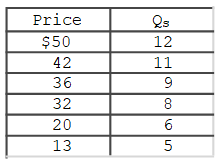
C)
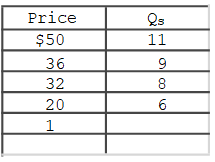
D)
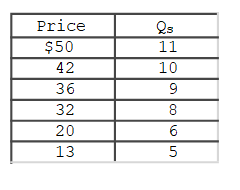

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
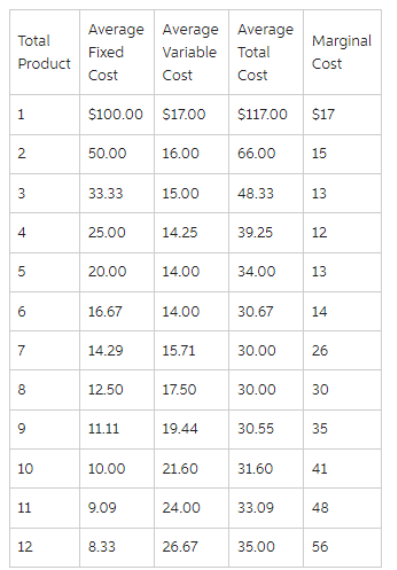
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market.If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce
A)4 units at a loss of $109.
B)4 units at an economic profit of $31.75.
C)8 units at a loss of $48.80.
D)zero units at a loss of $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
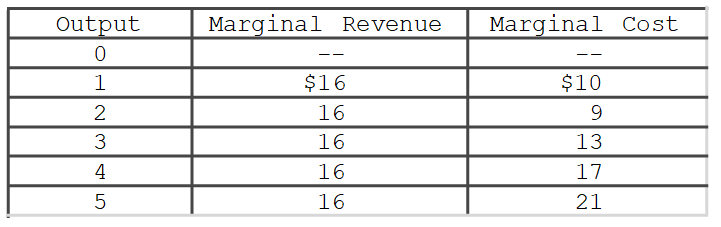
Refer to the data in the accompanying table.If the firm's minimum average variable cost is $10, the firm's profit-maximizing level of output would be
A)2.
B)3.
C)4.
D)5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A purely competitive firm should produce in the short run if its total revenue is sufficient to cover its
A)total variable costs.
B)total costs.
C)total fixed costs.
D)marginal costs.
A)total variable costs.
B)total costs.
C)total fixed costs.
D)marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that at 500 units of output, marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.The firm is selling its output at $5 per unit, and average total cost at 500 units of output is $6.On the basis of this information, we
A)can say that the firm should close down in the short run.
B)can say that the firm can produce and realize an economic profit in the short run.
C)cannot determine whether the firm should produce or shut down in the short run.
D)can assume the firm is not using the most efficient technology.
A)can say that the firm should close down in the short run.
B)can say that the firm can produce and realize an economic profit in the short run.
C)cannot determine whether the firm should produce or shut down in the short run.
D)can assume the firm is not using the most efficient technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
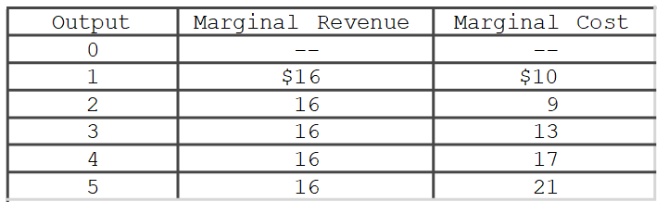
Refer to the data in the accompanying table.Assuming total fixed costs equal to zero, the firm's
A)economic profit is $12.
B)economic profit is $16.
C)loss is $14.
D)economic profit is $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A firm finds that at its MR = MC output, its TC = $1,000, TVC = $800, TFC = $200, and total revenue is $900.This firm should
A)shut down in the short run.
B)produce because the resulting loss is less than its TFC.
C)produce because it will realize an economic profit.
D)liquidate its assets and go out of business.
A)shut down in the short run.
B)produce because the resulting loss is less than its TFC.
C)produce because it will realize an economic profit.
D)liquidate its assets and go out of business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if
A)it cannot produce at an economic profit.
B)price is less than average variable cost at all outputs.
C)price is less than average fixed cost at all outputs.
D)there is no point at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal.
A)it cannot produce at an economic profit.
B)price is less than average variable cost at all outputs.
C)price is less than average fixed cost at all outputs.
D)there is no point at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if product price
A)equals average revenue.
B)is greater than MC.
C)is less than AVC.
D)is less than ATC.
A)equals average revenue.
B)is greater than MC.
C)is less than AVC.
D)is less than ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If at the MC = MR output, AVC exceeds price,
A)new firms will enter this industry.
B)the firm should produce the MC = MR output and realize an economic profit.
C)some firms should shut down in the short run.
D)the firm should expand its plant.
A)new firms will enter this industry.
B)the firm should produce the MC = MR output and realize an economic profit.
C)some firms should shut down in the short run.
D)the firm should expand its plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market.If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will
A)produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40.
B)produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00.
C)shut down in the short run.
D)produce 6 units at a loss of $23.80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a purely competitive firm shuts down in the short run,
A)its loss will be zero.
B)it will realize a loss equal to its total variable costs.
C)it will realize a loss equal to its total fixed costs.
D)it will realize a loss equal to its explicit costs.
A)its loss will be zero.
B)it will realize a loss equal to its total variable costs.
C)it will realize a loss equal to its total fixed costs.
D)it will realize a loss equal to its explicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The short-run supply curve for a purely competitive industry can be found by
A)multiplying the AVC curve of the representative firm by the number of firms in the industry.
B)adding horizontally the AVC curves of all firms.
C)summing horizontally the segments of the MC curves lying above the AVC curve for all firms.
D)adding horizontally the immediate market period supply curves of each firm.
A)multiplying the AVC curve of the representative firm by the number of firms in the industry.
B)adding horizontally the AVC curves of all firms.
C)summing horizontally the segments of the MC curves lying above the AVC curve for all firms.
D)adding horizontally the immediate market period supply curves of each firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the short run, a purely competitive firm will earn a normal profit when
A)P = AVC.
B)P > MC.
C)that firm's MR = market equilibrium price.
D)P = ATC.
A)P = AVC.
B)P > MC.
C)that firm's MR = market equilibrium price.
D)P = ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Oligopoly firms may produce either standardized or differentiated products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a purely competitive firm is maximizing economic profit,
A)it is necessarily maximizing per-unit profit.
B)it may or may not be maximizing per-unit profit.
C)then per-unit profit will be minimized.
D)it is necessarily overallocating resources to its product.
A)it is necessarily maximizing per-unit profit.
B)it may or may not be maximizing per-unit profit.
C)then per-unit profit will be minimized.
D)it is necessarily overallocating resources to its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
(Last Word) Fixed costs for a firm are analogous to
A)the dirt that fills up the financial hole.
B)digging a deeper financial hole by producing when prices are too low.
C)the cost of the shovel needed to fill the financial hole.
D)starting out in a hole that represents economic losses if the firm produces nothing.
A)the dirt that fills up the financial hole.
B)digging a deeper financial hole by producing when prices are too low.
C)the cost of the shovel needed to fill the financial hole.
D)starting out in a hole that represents economic losses if the firm produces nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Assume a purely competitive firm is selling 200 units of output at $3 each.At this output, its total fixed cost is $100 and its total variable cost is $350.This firm
A)is maximizing its profit.
B)is making a profit, but not necessarily the maximum profit.
C)is incurring losses.
D)should shut down in the short run.
A)is maximizing its profit.
B)is making a profit, but not necessarily the maximum profit.
C)is incurring losses.
D)should shut down in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Assume for a competitive firm that MC = AVC at $12, MC = ATC at $20, and MC = MR at $16.This firm will
A)realize a profit of $4 per unit of output.
B)maximize its profit by producing in the short run.
C)minimize its losses by producing in the short run.
D)shut down in the short run.
A)realize a profit of $4 per unit of output.
B)maximize its profit by producing in the short run.
C)minimize its losses by producing in the short run.
D)shut down in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(Consider This) An otherwise unprofitable motel located on a largely abandoned roadway might be able to stay open for several years by
A)increasing its nightly room rates.
B)reducing or eliminating its annual maintenance expenses.
C)charging room rates that exceed marginal revenue.
D)eliminating its fixed costs, including its opportunity costs.
A)increasing its nightly room rates.
B)reducing or eliminating its annual maintenance expenses.
C)charging room rates that exceed marginal revenue.
D)eliminating its fixed costs, including its opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
(Last Word) Temporary shutdowns of firms are most widespread when
A)total fixed costs are rising across the economy.
B)the economy experiences recession.
C)firms have the ability to set prices for their output.
D)wage levels are falling.
A)total fixed costs are rising across the economy.
B)the economy experiences recession.
C)firms have the ability to set prices for their output.
D)wage levels are falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Although individual purely competitive firms can influence the price of their product, these firms as a group cannot influence market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry have no reason to engage in nonprice competition because their products are uniquely different from other sellers in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
(Last Word) Oil wells and seasonal resorts will often shut down temporarily because
A)prices for their output temporarily fall below their average variable costs of production.
B)fixed costs temporarily rise, making production unprofitable.
C)variable costs for pumping oil and operating resorts fluctuate significantly.
D)government regulations require seasonal shutdowns for maintenance purposes.
A)prices for their output temporarily fall below their average variable costs of production.
B)fixed costs temporarily rise, making production unprofitable.
C)variable costs for pumping oil and operating resorts fluctuate significantly.
D)government regulations require seasonal shutdowns for maintenance purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
DASH Airlines is considering the addition of a flight from Red Cloud to David City.The total cost of the flight would be $1,100, of which $800 are fixed costs already incurred.Expected revenues from the flight are $600.DASH should
A)not add this flight, because only flights that cover their full costs are profitable.
B)not add this flight, because it is not profitable at the margin.
C)add this flight, because marginal revenue exceeds marginal costs and total revenue exceeds total variable cost.
D)not add this flight, because total costs exceed total revenue.
A)not add this flight, because only flights that cover their full costs are profitable.
B)not add this flight, because it is not profitable at the margin.
C)add this flight, because marginal revenue exceeds marginal costs and total revenue exceeds total variable cost.
D)not add this flight, because total costs exceed total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The principle that a firm should produce up to the point where the marginal revenue from the sale of an extra unit of output is equal to the marginal cost of producing it is known as the
A)output-maximizing rule.
B)profit-maximizing rule.
C)shut-down rule.
D)break-even rule.
A)output-maximizing rule.
B)profit-maximizing rule.
C)shut-down rule.
D)break-even rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a profit-seeking competitive firm is producing its profit-maximizing output and its total fixed costs fall by 25 percent, the firm should
A)use more labor and less capital to produce a larger output.
B)not change its output.
C)reduce its output.
D)increase its output.
A)use more labor and less capital to produce a larger output.
B)not change its output.
C)reduce its output.
D)increase its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The Ajax Manufacturing Company is selling in a purely competitive market.Its output is 100 units, which sell at $4 each.At this level of output, total cost is $600, total fixed cost is $100, and marginal cost is $4.The firm should
A)reduce output to about 80 units.
B)expand its production.
C)continue to produce 100 units.
D)produce zero units of output.
A)reduce output to about 80 units.
B)expand its production.
C)continue to produce 100 units.
D)produce zero units of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The term imperfect competition refers to every market structure besides pure competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Consider This) An unprofitable motel will stay open in the short run if
A)price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average variable cost.
B)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
C)price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average fixed cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds price.
A)price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average variable cost.
B)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
C)price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average fixed cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a purely competitive firm is producing at the P = MC output and realizing an economic profit, at that output
A)marginal revenue is less than price.
B)marginal revenue exceeds ATC.
C)ATC is being minimized.
D)total revenue equals total cost.
A)marginal revenue is less than price.
B)marginal revenue exceeds ATC.
C)ATC is being minimized.
D)total revenue equals total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In contrast to American firms, Japanese firms frequently make lifetime employment commitments to their workers and agree not to lay them off when product demand is weak.Other things being equal, we would expect Japanese firms to
A)face more elastic product demand curves than American firms.
B)have relatively greater variable costs than American firms.
C)discontinue production at higher product prices than would American firms.
D)continue to produce in the short run at lower prices than would American firms.
A)face more elastic product demand curves than American firms.
B)have relatively greater variable costs than American firms.
C)discontinue production at higher product prices than would American firms.
D)continue to produce in the short run at lower prices than would American firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



