Deck 28: Pregnancy and Human Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/97
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Pregnancy and Human Development
1
Estrogen and progesterone maintain the integrity of the uterine lining and prepare the mammary glands to secrete milk. Which of the following structures makes this possible during the first three months of pregnancy?
A) corpus luteum
B) the chorion
C) corona radiata
D) the amnion
A) corpus luteum
B) the chorion
C) corona radiata
D) the amnion
A
2
Which of the following is not assessed as part of the Apgar score?
A) respiration
B) temperature
C) muscle tone
D) heart rate
A) respiration
B) temperature
C) muscle tone
D) heart rate
B
3
Hormones concerned with events of lactation include .
A) oxytocin
B) estrogen
C) hCG
D) progesterone
A) oxytocin
B) estrogen
C) hCG
D) progesterone
A
4
The correct sequence of preembryonic structures is .
A) morula, zygote, blastocyst
B) zygote, blastocyst, morula
C) zygote, morula, blastocyst
D) blastocyst, morula, zygote
A) morula, zygote, blastocyst
B) zygote, blastocyst, morula
C) zygote, morula, blastocyst
D) blastocyst, morula, zygote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Derivatives of the mesoderm include _.
A) glandular derivatives of the digestive tract
B) epithelium of the digestive tract
C) endothelium of blood and lymph vessels
D) all nervous tissue
A) glandular derivatives of the digestive tract
B) epithelium of the digestive tract
C) endothelium of blood and lymph vessels
D) all nervous tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Milk ejection or letdown reflex is stimulated by which of the following hormones associated with pregnancy?
A) inhibin
B) gonadotropin
C) prolactin
D) oxytocin
A) inhibin
B) gonadotropin
C) prolactin
D) oxytocin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The formation of endodermal and ectodermal germ layers occurs at .
A) fertilization
B) gastrulation
C) blastula formation
D) cleavage
A) fertilization
B) gastrulation
C) blastula formation
D) cleavage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which body system of a pregnant woman undergoes the most dramatic physiological changes during pregnancy?
A) urinary system
B) cardiovascular system
C) respiratory system
D) digestive system
A) urinary system
B) cardiovascular system
C) respiratory system
D) digestive system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The result of polyspermy in humans is .
A) multiple births
B) interruption of meiosis
C) a nonfunctional zygote
D) mitotic insufficiency
A) multiple births
B) interruption of meiosis
C) a nonfunctional zygote
D) mitotic insufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Relaxin is a hormone produced by the placenta and ovaries. The function of this hormone is to
)
A) ensure the implantation of the blastula
B) block the pain of childbirth
C) prevent morning sickness
D) relax the pubic symphysis
)
A) ensure the implantation of the blastula
B) block the pain of childbirth
C) prevent morning sickness
D) relax the pubic symphysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
It is impossible for sperm to be functional (able to fertilize the egg) until after .
A) the tail disappears
B) they have been stored in the uterus for several days
C) they become spermatids
D) they undergo capacitation
A) the tail disappears
B) they have been stored in the uterus for several days
C) they become spermatids
D) they undergo capacitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the choices below occurs if fertilization of the ovum occurs and implantation takes place?
A) The corpus luteum degenerates and becomes the corpus albicans.
B) The ovarian cycle begins.
C) Increased levels of FSH will be produced.
D) The corpus luteum is maintained until the placenta takes over its hormone- producing functions.
A) The corpus luteum degenerates and becomes the corpus albicans.
B) The ovarian cycle begins.
C) Increased levels of FSH will be produced.
D) The corpus luteum is maintained until the placenta takes over its hormone- producing functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
During which stage of labor is the fetus delivered?
A) dilation stage
B) expulsion stage
C) gastrula stage
D) placental stage
A) dilation stage
B) expulsion stage
C) gastrula stage
D) placental stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
At which stage of labor is the "afterbirth" expelled?
A) full dilation
B) placental
C) expulsion
D) dystocia
A) full dilation
B) placental
C) expulsion
D) dystocia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Derivatives of the endoderm include .
A) synovial membranes of the joints
B) organs of the urogenital system
C) blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissue
D) epithelium of the respiratory tract
A) synovial membranes of the joints
B) organs of the urogenital system
C) blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissue
D) epithelium of the respiratory tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The decidua basalis is _ .
A) the tissue that surrounds the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo
B) not a maternal contribution to the placenta
C) located between the developing embryo and the myometrium
D) destined to remain in the uterus after the birth of the infant
A) the tissue that surrounds the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo
B) not a maternal contribution to the placenta
C) located between the developing embryo and the myometrium
D) destined to remain in the uterus after the birth of the infant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Proteases and acrosin are enzymes. How do they function in reproduction?
A) They act to break down the protective barriers around the egg, allowing the sperm to penetrate.
B) They neutralize the mucous secretions of the uterine mucosa.
C) They direct the sperm to the egg through chemical messengers.
D) Their function is unknown.
A) They act to break down the protective barriers around the egg, allowing the sperm to penetrate.
B) They neutralize the mucous secretions of the uterine mucosa.
C) They direct the sperm to the egg through chemical messengers.
D) Their function is unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Neural tissue is formed by the _.
A) epiderm
B) ectoderm
C) mesoderm
D) endoderm
A) epiderm
B) ectoderm
C) mesoderm
D) endoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Select the correct statement about fertilization.
A) If estrogen is present, the pathway through the cervical opening is blocked from sperm entry.
B) Both spermatozoa and the ovulated secondary oocyte remain viable for about 72 hours in the female reproductive tract.
C) Millions of sperm cells are destroyed by the vagina's acidic environment.
D) Once inside the uterus, most sperm cells are protected and remain viable.
A) If estrogen is present, the pathway through the cervical opening is blocked from sperm entry.
B) Both spermatozoa and the ovulated secondary oocyte remain viable for about 72 hours in the female reproductive tract.
C) Millions of sperm cells are destroyed by the vagina's acidic environment.
D) Once inside the uterus, most sperm cells are protected and remain viable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What destroys the sperm receptors on the surface of the oocyte?
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) the process of capacitation
C) zonal inhibiting proteins
D) human placental lactogen
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) the process of capacitation
C) zonal inhibiting proteins
D) human placental lactogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The placenta, a vitally important metabolic organ, is made up of a contribution from mother and fetus. Which portion is from the fetus?
A) yolk sac
B) amnion
C) chorion
D) umbilicus
A) yolk sac
B) amnion
C) chorion
D) umbilicus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cardiovascular system of a newborn must be adjusted after the infant takes its first breath. Which of the following is also true?
A) The ductus venosus is disconnected at the severing of the umbilical cord and all visceral blood goes into the vena cava.
B) The foramen ovale between the atria of the fetal heart closes at the moment of birth.
C) The urinary system is activated at birth.
D) The ductus arteriosus constricts and is converted to the ligamentum arteriosum.
A) The ductus venosus is disconnected at the severing of the umbilical cord and all visceral blood goes into the vena cava.
B) The foramen ovale between the atria of the fetal heart closes at the moment of birth.
C) The urinary system is activated at birth.
D) The ductus arteriosus constricts and is converted to the ligamentum arteriosum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which hormone is not produced by the placenta?
A) human placental lactogen
B) human chorionic thyrotropin
C) inhibin
D) relaxin
A) human placental lactogen
B) human chorionic thyrotropin
C) inhibin
D) relaxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not usually considered a teratogen?
A) thalidomide
B) aspirin
C) German measles
D) wine
A) thalidomide
B) aspirin
C) German measles
D) wine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a correct matching of a fetal structure with what it becomes at birth?
A) ductus arteriosus-ligamentum teres
B) foramen ovale-fossa ovalis
C) ductus venosus-ligamentum venosum
D) umbilical arteries-medial umbilical ligament
A) ductus arteriosus-ligamentum teres
B) foramen ovale-fossa ovalis
C) ductus venosus-ligamentum venosum
D) umbilical arteries-medial umbilical ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The dorsal surface cells of the inner cell mass form .
A) the primitive streak
B) one of the fetal membranes
C) a structure called the embryonic disc
D) the notochord
A) the primitive streak
B) one of the fetal membranes
C) a structure called the embryonic disc
D) the notochord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Select the correct statement about the special fetal blood vessels.
A) The fossa ovalis becomes the foramen ovale.
B) The umbilical vein becomes the ligamentum teres.
C) The hepatic portal vein forms from the umbilical artery.
D) The distal parts of the umbilical arteries form the superior vesical arteries.
A) The fossa ovalis becomes the foramen ovale.
B) The umbilical vein becomes the ligamentum teres.
C) The hepatic portal vein forms from the umbilical artery.
D) The distal parts of the umbilical arteries form the superior vesical arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How long is the egg viable and capable of being fertilized after it is ovulated?
A) 12- 24 hours
B) 36- 72 hours
C) 24- 36 hours
D) a full week
A) 12- 24 hours
B) 36- 72 hours
C) 24- 36 hours
D) a full week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is true in reference to what may pass through the placental barriers?
A) nutrients and respiratory gases only
B) respiratory gases, hormones, nutrients, and blood cells
C) nutrients, respiratory gases, wastes, and alcohol
D) hormones, blood cells, and nutrients
A) nutrients and respiratory gases only
B) respiratory gases, hormones, nutrients, and blood cells
C) nutrients, respiratory gases, wastes, and alcohol
D) hormones, blood cells, and nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Shortly after implantation .
A) the embryo gastrulates (within 3 days)
B) myometrical cells cover and seal off the blastocyst
C) maternal blood sinuses bathe the inner cell mass
D) the trophoblast forms two distinct layers
A) the embryo gastrulates (within 3 days)
B) myometrical cells cover and seal off the blastocyst
C) maternal blood sinuses bathe the inner cell mass
D) the trophoblast forms two distinct layers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The trophoblast is mostly responsible for forming the .
A) lining of the endometrium
B) allantois
C) archenteron
D) placental tissue
A) lining of the endometrium
B) allantois
C) archenteron
D) placental tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following events does not occur during the first 8 weeks of development?
A) presence of all body systems
B) myelination of the spinal cord
C) formation of a functional cardiovascular system
D) beginning of ossification
A) presence of all body systems
B) myelination of the spinal cord
C) formation of a functional cardiovascular system
D) beginning of ossification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Muscle tissue is formed by the .
A) mesoderm
B) ectoderm
C) epiderm
D) endoderm
A) mesoderm
B) ectoderm
C) epiderm
D) endoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cleavage as part of embryonic development is distinctive because it involves .
A) cell division by mitosis with little or no growth between successive divisions
B) meiotic cell divisions
C) splitting the cell into two separate cells
D) forming the primary germ layer
A) cell division by mitosis with little or no growth between successive divisions
B) meiotic cell divisions
C) splitting the cell into two separate cells
D) forming the primary germ layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not a germ layer?
A) mesoderm
B) ectoderm
C) epiderm
D) endoderm
A) mesoderm
B) ectoderm
C) epiderm
D) endoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall is called .
A) placenta previa
B) ectopic pregnancy
C) placenta cleavage
D) abrupto placenta
A) placenta previa
B) ectopic pregnancy
C) placenta cleavage
D) abrupto placenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Implantation of the blastocyst is the result of all of the following except .
A) phagocytosis by the trophoblast cells
B) adherence of the trophoblast cells to the endometrium
C) proteolytic enzymes produced by the trophoblast cells
D) settling of the blastocyst onto the prepared uterine lining
A) phagocytosis by the trophoblast cells
B) adherence of the trophoblast cells to the endometrium
C) proteolytic enzymes produced by the trophoblast cells
D) settling of the blastocyst onto the prepared uterine lining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sperm move to the uterine tube through uterine contractions and the energy of their own flagella. What other factor is involved in sperm movement?
A) hormonal attraction to the ova
B) the cilia on the apex of the cells lining the endometrium
C) the increased temperature in the vagina, which stimulates sperm motility
D) reverse peristalsis of the uterus and uterine tubes
A) hormonal attraction to the ova
B) the cilia on the apex of the cells lining the endometrium
C) the increased temperature in the vagina, which stimulates sperm motility
D) reverse peristalsis of the uterus and uterine tubes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which hormone maintains the viability of the corpus luteum?
A) progesterone
B) estrogen
C) human placental lactogen
D) human chorionic gonadotropin
A) progesterone
B) estrogen
C) human placental lactogen
D) human chorionic gonadotropin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Neural tissue develops from the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
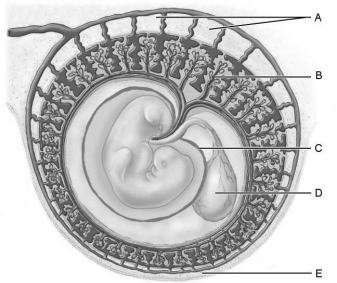 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:Protective water- filled sac surrounding the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
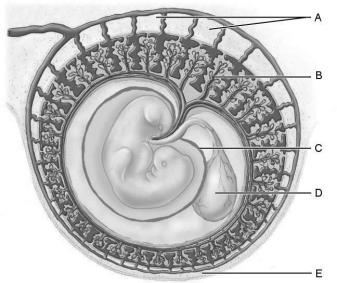 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:The stage of development is the first in which all three germ layers of tissue are evident.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
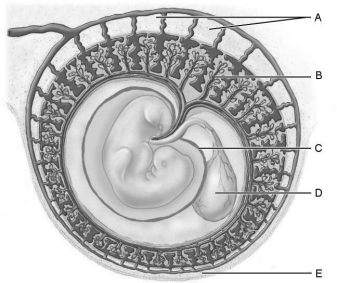 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:After the egg is fertilized, it is called a(n) _.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
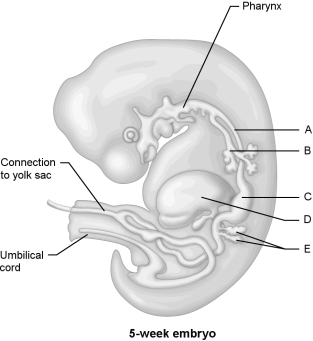 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Describe the events of the oocyte from sperm penetration to first cleavage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The _ cells of the blastocyst will take part in placental formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Briefly describe the events leading to the implantation of the blastocyst in the uterus, including how it is nourished.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:The part of the endometrium destined to be a part of the placenta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At what time in the pregnancy is the placenta fully prepared to fulfill the needs of the developing fetus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Describe the events allowing monospermy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The first axial support for the embryo is called the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
As the newborn suckles, the mother's pituitary produces to assist in producing milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How are the metabolic needs of the implanted embryo provided for?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
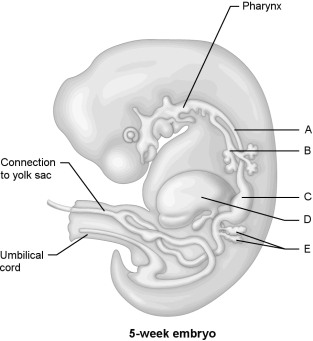 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Pancreas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
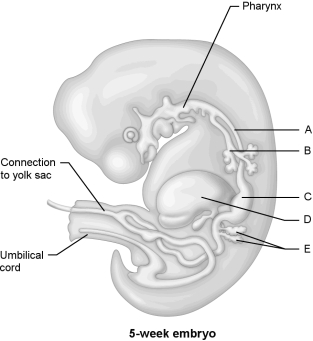 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:The part of the endometrium that surrounds the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When do we begin to call the developing individual a fetus rather than an embryo?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
List four factors that help to precipitate parturition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain what triggers a baby's first breath.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
is a tissue with star- shaped cells that are free to migrate widely throughout the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
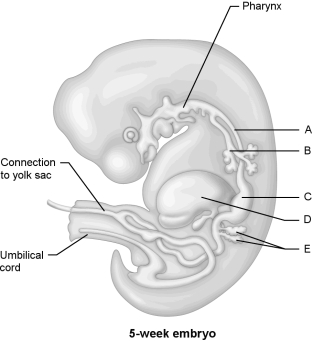 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:The act of giving birth is called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
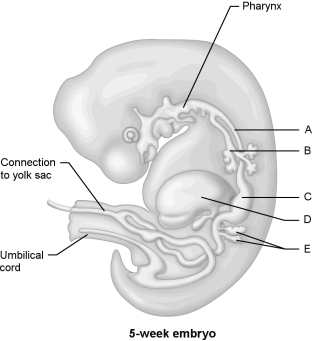 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What embryonic structure is the structural base for the umbilical cord?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The embryo is directly enclosed in and protected by the amnion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In fetal circulation, one way in which blood bypasses the nonaerated lungs is by way of the foramen ovale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The body systems of the developing embryo are present in at least rudimentary form at eight weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The "fluid- filled, hollow ball of cells" stage of development is the blastocyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells, while the morula is a solid ball of cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Surfactant production in premature infants is rarely a factor in providing normal respiratory activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Define Braxton- Hicks contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
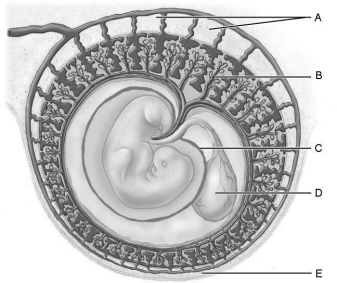 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:Site of early blood cell production, and forms part of the gut (digestive tube).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
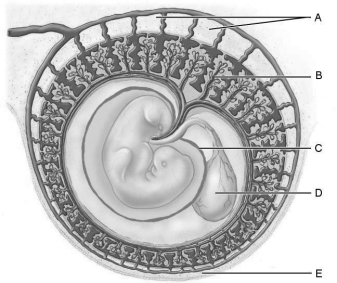 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:Extraembryonic membrane that develops from the trophoblast and some extraembryonic mesoderm, and forms part of the placenta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A zygote is usually formed within the uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:Which cells invade the endometrium, digesting the uterine cells they contact, so that implantation of the blastocyst can occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The period from fertilization through week eight is called the embryonic period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fertilization occurs while the egg is still in the ovarian follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
 Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:
Figure 28.2Using Figure 28.2, match the following:The first "milk" the mother produces is called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Briefly describe the physiological changes occurring in the mother during pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:
Figure 28.1Using Figure 28.1, match the following:Stomach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The embryonic stage lasts until the end of the eighth week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



