Deck 29: Heredity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Heredity
1
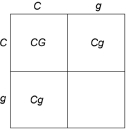 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Given the information in Figure 29.1, if C were an incomplete dominant trait, what would the phenotype ratio be for the offspring?
A) 1:3
B) 1:1:1:1
C) 1:2:1
D) 4:0
C
2
An individual who is heterozygous for a particular trait, yet expresses both alleles of that trait, is an example of _ _.
A) incomplete dominance
B) dominance
C) sex- linked inheritance
D) recessive inheritance
A) incomplete dominance
B) dominance
C) sex- linked inheritance
D) recessive inheritance
A
3
Recessive genes are usually expressed in humans only when .
A) they are coding for genetic diseases
B) they are coding for skin color
C) both alleles are exactly the same, or homozygous
D) the organism is in the embryonic stage
A) they are coding for genetic diseases
B) they are coding for skin color
C) both alleles are exactly the same, or homozygous
D) the organism is in the embryonic stage
C
4
is the most common type of fetal testing.
A) Amniocentesis
B) CVS
C) Blood chemistry
D) A DNA probe
A) Amniocentesis
B) CVS
C) Blood chemistry
D) A DNA probe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Amy's hand was exposed to X rays. A gene in a skin cell of her hand mutated. This mutant gene will .
A) definitely cause skin cancer
B) not form an exact duplicate of itself when the cell divides
C) replicate itself when the cell divides but will not be passed on to Amy's offspring
D) replicate itself and be passed on to Amy's children
A) definitely cause skin cancer
B) not form an exact duplicate of itself when the cell divides
C) replicate itself when the cell divides but will not be passed on to Amy's offspring
D) replicate itself and be passed on to Amy's children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Gene mutations in the sex chromosomes of the human would tend to become visibly expressed
)
A) equally frequently in both sexes
B) more frequently in males
C) in neither males or females
D) more frequently in females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A female infant is born with several hundred oocytes, each one genetically unique. This is due to
)
A) chromosome deletion
B) independent assortment and random crossover
C) recessive inheritance
D) mutation
)
A) chromosome deletion
B) independent assortment and random crossover
C) recessive inheritance
D) mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
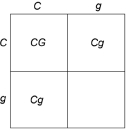 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Which of the following statements is true concerning genetic screening?
A) Screening is illegal in over half of the world.
B) Screening can be done before conception by carrier recognition or during fetal testing.
C) Screening can be done only in the first trimester of pregnancy.
D) Genetic screening is rarely done because it yields very little accurate information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The gene responsible for the condition known as sickle- cell anemia demonstrates _.
A) a recessive genetic disorder
B) a sex- linked genetic disorder
C) incomplete dominance
D) a dominant genetic disorder
A) a recessive genetic disorder
B) a sex- linked genetic disorder
C) incomplete dominance
D) a dominant genetic disorder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
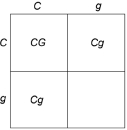 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Given the information in Figure 29.1, what would be the genotype of the offspring designated by the blank square?
A) Gg
B) gg
C) Dg
D) GG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Huntington's disease involves _ .
A) the presence of an extra chromosome
B) hyposecretion of thyroxine
C) degeneration of the basal nuclei of the brain
D) hypersecretion of growth hormone
A) the presence of an extra chromosome
B) hyposecretion of thyroxine
C) degeneration of the basal nuclei of the brain
D) hypersecretion of growth hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Given the information in Figure 29.1, what is the phenotype ratio (assuming C is dominant and there is no incomplete dominance)?
A) 1:2:1
B) 1:3
C) 4:0
D) 1:1:1:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is true concerning environmental influence on genetic expression?
A) Drugs and nutrition can alter normal gene expression.
B) The only time a gene can be influenced by environmental factors is in the second trimester of pregnancy.
C) Environmental factors determine the way in which 90 percent of our genes are expressed.
D) It is impossible to alter in any way the expression of a gene in humans.
A) Drugs and nutrition can alter normal gene expression.
B) The only time a gene can be influenced by environmental factors is in the second trimester of pregnancy.
C) Environmental factors determine the way in which 90 percent of our genes are expressed.
D) It is impossible to alter in any way the expression of a gene in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Dominant alleles are so called because under most circumstances they _ .
A) code for most phenotypic and genotypic expressions of a trait
B) code for genes that are never considered lethal
C) suppress the expression of other alleles
D) code for desired traits only
A) code for most phenotypic and genotypic expressions of a trait
B) code for genes that are never considered lethal
C) suppress the expression of other alleles
D) code for desired traits only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Two alleles expressing exactly the same information for a trait are designated as .
A) homozygous
B) hemizygous
C) heterozygous
D) monogamous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
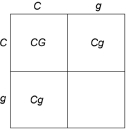 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1Given the information in Figure 29.1, what would the genotype ratio be for the offspring?
A) 4:0
B) 1:2:1
C) 1:1:1:1
D) 1:3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1In meiosis the spermatozoa that are produced are genetically unlike each other and unlike the cell that produces them. This is one reason for the great variation among humans. What causes this effect?
A) chromosome segregation and independent assortment only
B) crossing- over, chromosome segregation, and independent assortment
C) crossing- over and independent assortment only
D) crossing- over and chromosome segregation only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Sex chromosomes of a normal male are .
A) YY
B) XY
C) XX
D) any of these, depending on the father
A) YY
B) XY
C) XX
D) any of these, depending on the father

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Those characteristics that can be determined on superficial inspection of an individual are known as .
A) genotypic
B) polyspermic
C) phenotypic
D) polygenic
A) genotypic
B) polyspermic
C) phenotypic
D) polygenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Figure 29.1
Figure 29.1The main way a recessive allele would be expressed even when only one copy is present would be
)
A) recessive inheritance
B) incomplete dominance
C) sex- linked inheritance
D) dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Inheritance of stature (height) in humans is probably due to .
A) incomplete dominance
B) polygene inheritance
C) polyploidy
D) polymorphism
A) incomplete dominance
B) polygene inheritance
C) polyploidy
D) polymorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
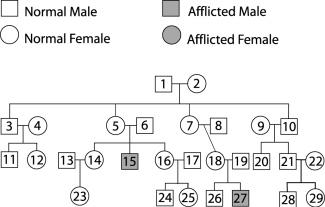 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Color blindness is a(n) trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Define phenocopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The second- generation phenotypes would follow what ratio? (Pair the number with a phenotype in each case.)
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The second- generation phenotypes would follow what ratio? (Pair the number with a phenotype in each case.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An example of multiple- allele inheritance is .
A) hair that seems to have several shades of a color
B) the ABO blood group
C) the appearance of birthmarks on the skin
D) the appearance of freckles on the skin
A) hair that seems to have several shades of a color
B) the ABO blood group
C) the appearance of birthmarks on the skin
D) the appearance of freckles on the skin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
When might amniocentesis be appropriate?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
When might amniocentesis be appropriate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For which of the following are newborn infants not routinely screened at birth?
A) imperforate anus
B) PKU
C) congenital hip dysplasia
D) color blindness
A) imperforate anus
B) PKU
C) congenital hip dysplasia
D) color blindness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Are there any male carriers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The ABO blood type is a good example of a(n) inheritance.
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The ABO blood type is a good example of a(n) inheritance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Two tall red pea plants, when crossed, produced some offspring that were white and dwarf. Assuming that tallness and redness are dominant, what are the genotypes of the parents?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The reason recessive genetic disorders are more frequent than disorders inherited as dominant is that .
A) recessive genetic disorders are limited to persons of the same ethnicity
B) people carrying dominant genetic disorders always die before birth
C) dominant genetic disorders are never expressed in males
D) carriers are not eliminated by the disease before passing the defective alleles on to their offspring
A) recessive genetic disorders are limited to persons of the same ethnicity
B) people carrying dominant genetic disorders always die before birth
C) dominant genetic disorders are never expressed in males
D) carriers are not eliminated by the disease before passing the defective alleles on to their offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Is genetic diversity due entirely to inherited genes on the sex chromosomes?
A) Yes, because the female has two X chromosomes and the male has only one X chromosome.
B) Yes, because genetic diversity is due to the Y influence on the autosomes.
C) Yes, because the male has a Y chromosome.
D) No, because genetic diversity has nothing to do with the sex chromosomes but is due to crossing- over of chromosomes, independent assortment of chromosomes, and segregation of chromosomes.
A) Yes, because the female has two X chromosomes and the male has only one X chromosome.
B) Yes, because genetic diversity is due to the Y influence on the autosomes.
C) Yes, because the male has a Y chromosome.
D) No, because genetic diversity has nothing to do with the sex chromosomes but is due to crossing- over of chromosomes, independent assortment of chromosomes, and segregation of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A couple whose blood types are A (IAi) and B (IBi) may have a child with which of the following blood types?
A) AB only
B) A or B only
C) AB or O only
D) A, B, AB, or O
A) AB only
B) A or B only
C) AB or O only
D) A, B, AB, or O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What were the genotypes of the parental (P1) individuals?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What were the genotypes of the parental (P1) individuals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The X and Y chromosomes are considered the chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What possible genotype(s) could the second- generation, fuzzy- longhaired individuals possess?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What possible genotype(s) could the second- generation, fuzzy- longhaired individuals possess?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A woman has blond hair and brown eyes. This statement is best described as indicating .
A) phenotype
B) allelic pairs
C) recessive traits
D) genotype
A) phenotype
B) allelic pairs
C) recessive traits
D) genotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The second- generation types would have what phenotypes?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The second- generation types would have what phenotypes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A chromosomal aberration in which part of a chromosome is lost is known as .
A) inversion
B) crossing- over
C) translocation
D) deletion
A) inversion
B) crossing- over
C) translocation
D) deletion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
An allele that completely masks the expression of the other alleles is called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When two genes are on the same chromosome, they are considered linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
disease is a disorder of brain lipid metabolism and is an example of a recessive trait.
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
disease is a disorder of brain lipid metabolism and is an example of a recessive trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
How might carriers of deleterious genes be recognized?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
How might carriers of deleterious genes be recognized?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
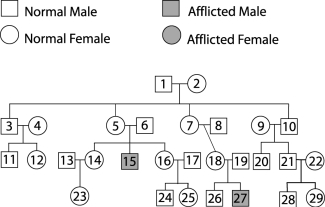 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Identify, by numbers, any other possible carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
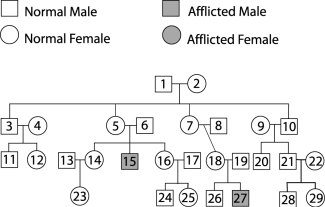 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Removing a sample of the fluid surrounding the fetus for the purpose of studying the chromosomes is a procedure called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
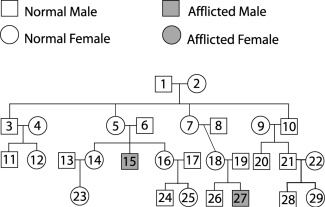 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Is the trait sex- linked?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The 23rd pair of human chromosomes are called chromosomes.
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
The 23rd pair of human chromosomes are called chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
Define karyotype.
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
Define karyotype.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What would the parental gametes be from a cross of two second- generation, straight- shorthaired individuals?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What would the parental gametes be from a cross of two second- generation, straight- shorthaired individuals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Is the trait dominant or recessive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Identify, by numbers, any known carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Hemophilia is an X- linked condition caused by a recessive gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Describe briefly the three mechanisms that lead to genetic variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Are there any afflicted females?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
Observable characteristics expressed by the genes for a trait are called the .
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
Observable characteristics expressed by the genes for a trait are called the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2Use Figure 29.2 to answer the following:
Albinism is a good example of a(n) trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
A cross of two second- generation, straight- shorthaired individuals would yield what phenotype?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
A cross of two second- generation, straight- shorthaired individuals would yield what phenotype?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What is (are) the genotype(s) of the first- generation offspring?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What is (are) the genotype(s) of the first- generation offspring?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What would be the gametes of the first- generation individuals?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What would be the gametes of the first- generation individuals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Among members of the Fuzzy Wuzzy tribe, we will consider two pairs of genes: F = fuzzy hair vs. f = straight hair, and T = long hair vs. t = short hair. A homozygous, straight- shorthaired male marries a homozygous, fuzzy- longhaired female (P1 generation). Their offspring (the F1 generation) intermarry and produce progeny (second generation) of four types:
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What is (are) the phenotype(s) of the first- generation offspring?
fuzzy- longhaired, fuzzy- shorthaired, straight- longhaired, and straight- shorthaired. The results follow a standard dihybrid pattern.
What is (are) the phenotype(s) of the first- generation offspring?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Environmentally produced phenotypes that mimic conditions that may be caused by genetic mutation are called phenocopies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Alleles may code for alternative expressions of a genetic trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The expression of all physical traits is strictly due to the inheritance of specific genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Most genetic disorders are inherited through dominant genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Down syndrome is an example of nondisjunction of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The term lethal dominant gene indicates that the gene causes death only when the individual is homozygous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Genetic segregation implies that the members of the allele pair determining each trait are distributed to different gametes during mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Hereditary characteristics are transmitted to offspring by genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It is possible for a baby to have type O blood if neither parent is type O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Delayed action genes can result in fatal diseases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The same allele can have a different effect depending on which parent it comes from.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Small RNAs control the timing of programmed cell death during development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Normal vision is dictated by autosomal dominant genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Mitochondrial genes are free of errors. As a result, all genetic problems are due exclusively to nuclear genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A Punnett square is a diagram that may be used to figure out the possible combinations of genes for a trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Some segments of the Y chromosome have no counterpart on the X chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Genetic variation results from the crossing over and exchange of chromosomal parts that occur during meiosis II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In incomplete dominance, the heterozygote has a phenotype intermediate between that of homozygous- dominant and homozygous- recessive individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose an XcXc female marries an XcY man. (a) What is the probability of producing a color- blind son? (b) What is the probability of producing a color- blind daughter? (c) What is the probability of producing a daughter who is a carrier for the color- blind gene? (d) What is the probability of having four sons in a row?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In humans, farsightedness is inherited by possession of a dominant gene. If a man who is homozygous for normal vision (aa) marries a woman who is heterozygous for farsightedness, what proportion of their children would be expected to be farsighted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



