Deck 17: Blood
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Blood
1
Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis?
A) an increased number of RBCs
B) decreased tissue demand for oxygen
C) moving to a lower altitude
D) hypoxia of EPO- producing cells
A) an increased number of RBCs
B) decreased tissue demand for oxygen
C) moving to a lower altitude
D) hypoxia of EPO- producing cells
D
2
Which of the following is not a structural characteristic that contributes to erythrocyte gas transport functions?
A) produces energy anaerobically
B) mitotically active
C) biconcave shape
D) hemoglobin containing- sack
A) produces energy anaerobically
B) mitotically active
C) biconcave shape
D) hemoglobin containing- sack
B
3
A lack of intrinsic factor, leading to a deficiency of vitamin B12 and causing an appearance of large pale cells called macrocytes, is characteristic of .
A) aplastic anemia
B) pernicious anemia
C) sickle- cell anemia
D) polycythemia
A) aplastic anemia
B) pernicious anemia
C) sickle- cell anemia
D) polycythemia
B
4
Which of the following is not a distribution function of blood?
A) transport of metabolic wastes from cells
B) transport of hormones to their target organs
C) delivery of oxygen to body cells
D) transport of salts to maintain blood volume
A) transport of metabolic wastes from cells
B) transport of hormones to their target organs
C) delivery of oxygen to body cells
D) transport of salts to maintain blood volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All of the following conditions impair coagulation except .
A) liver disease
B) vascular spasm
C) vitamin K deficiency
D) severe hypocalcemia
A) liver disease
B) vascular spasm
C) vitamin K deficiency
D) severe hypocalcemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the statements below is an incorrect or false statement?
A) Blood typing for the Kell, Lewis, and Duffy factors is always done before a blood transfusion.
B) Unique to the ABO blood group is the presence in the plasma of preformed antibodies.
C) Transfusion of incompatible blood can be fatal.
D) When a transfusion reaction occurs, the oxygen- carrying capacity of the transfused blood cells is disrupted and the clumping of RBCs in small vessels hinders blood flow to tissues beyond those points.
A) Blood typing for the Kell, Lewis, and Duffy factors is always done before a blood transfusion.
B) Unique to the ABO blood group is the presence in the plasma of preformed antibodies.
C) Transfusion of incompatible blood can be fatal.
D) When a transfusion reaction occurs, the oxygen- carrying capacity of the transfused blood cells is disrupted and the clumping of RBCs in small vessels hinders blood flow to tissues beyond those points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When can erythroblastosis fetalis not possibly happen in the child of an Rh negative mother?
A) if the child is type O positive
B) if the father is Rh+
C) if the father is Rh-
D) if the child is Rh+
A) if the child is type O positive
B) if the father is Rh+
C) if the father is Rh-
D) if the child is Rh+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Blood reticulocyte counts provide information regarding .
A) rate of erythrocyte formation
B) rate of platelet formation
C) WBC ability to defend the body against disease
D) clotting ability of the blood
A) rate of erythrocyte formation
B) rate of platelet formation
C) WBC ability to defend the body against disease
D) clotting ability of the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the average normal pH range of blood?
A) 8.35- 8.45
B) 7.35- 7.45
C) 4.65- 4.75
D) 7.75- 7.85
A) 8.35- 8.45
B) 7.35- 7.45
C) 4.65- 4.75
D) 7.75- 7.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not a cause of bleeding disorders?
A) a defect in the clotting cascade
B) vitamin K deficiency
C) excess secretion of platelet- derived growth factor (PDGF)
D) thrombocytopenia, a condition of decreased circulating platelets
A) a defect in the clotting cascade
B) vitamin K deficiency
C) excess secretion of platelet- derived growth factor (PDGF)
D) thrombocytopenia, a condition of decreased circulating platelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a phase of hemostasis?
A) vascular spasm
B) coagulation
C) fibrinolysis
D) platelet plug formation
A) vascular spasm
B) coagulation
C) fibrinolysis
D) platelet plug formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following can be expected with polycythemia except .
A) high blood pressure
B) increased blood volume
C) high hematocrit
D) low blood viscosity
A) high blood pressure
B) increased blood volume
C) high hematocrit
D) low blood viscosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which sequence is correct for the following events?
1) fibrinogen -fibrin
2) clot retraction
3) formation of thromboplastin
4) prothrombin -thrombin
A) 3, 2, 1, 4
B) 3, 4, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 3, 4
D) 4, 3, 1, 2
1) fibrinogen -fibrin
2) clot retraction
3) formation of thromboplastin
4) prothrombin -thrombin
A) 3, 2, 1, 4
B) 3, 4, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 3, 4
D) 4, 3, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
James has a hemoglobin measurement of 16 g/100 ml blood. This is .
A) within the normal range
B) normal only if James is an infant
C) abnormally low
D) above normal
A) within the normal range
B) normal only if James is an infant
C) abnormally low
D) above normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When neither anti- A serum nor anti- B serum clot on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is type .
A) A
B) AB
C) B
D) O
A) A
B) AB
C) B
D) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the choices below is the parent cell for all formed elements of blood?
A) normoblast
B) hemocytoblast
C) polymorphonuclear cell
D) megakaryocyte
A) normoblast
B) hemocytoblast
C) polymorphonuclear cell
D) megakaryocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The slowest step in the clotting process is .
A) production of fibrin strands
B) binding fibrin strands
C) release of PF3
D) formation of prothrombin activator
A) production of fibrin strands
B) binding fibrin strands
C) release of PF3
D) formation of prothrombin activator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a protective function of blood?
A) prevention of blood loss
B) maintenance of body temperature
C) maintenance of normal pH in body tissue
D) maintenance of adequate fluid volume
A) prevention of blood loss
B) maintenance of body temperature
C) maintenance of normal pH in body tissue
D) maintenance of adequate fluid volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which blood type is generally called the universal donor?
A) A
B) O
C) B
D) AB
A) A
B) O
C) B
D) AB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Platelets .
A) have multiple nuclei
B) have a life span of about 120 days
C) are the precursors of leukocytes
D) stick to the damaged area of a blood vessel and help seal the break
A) have multiple nuclei
B) have a life span of about 120 days
C) are the precursors of leukocytes
D) stick to the damaged area of a blood vessel and help seal the break

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Blood volume restorers include all of the following except .
A) albumin
B) dextran
C) packed cells
D) saline solutions
A) albumin
B) dextran
C) packed cells
D) saline solutions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
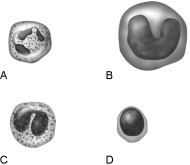 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:How many polypeptide chains make up hemoglobin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The plasma protein that is the major contributor to osmotic pressure is .
A) alpha globulin
B) fibrinogen
C) gamma globulin
D) albumin
A) alpha globulin
B) fibrinogen
C) gamma globulin
D) albumin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The special type of hemoglobin present in fetal red blood cells is .
A) hemoglobin A
B) hemoglobin F
C) hemoglobin B
D) hemoglobin S
A) hemoglobin A
B) hemoglobin F
C) hemoglobin B
D) hemoglobin S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What organ in the body regulates erythrocyte production?
A) brain
B) pancreas
C) liver
D) kidney
A) brain
B) pancreas
C) liver
D) kidney

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true about blood plasma?
A) It is the same as serum but without the clotting proteins.
B) It contains about 20 dissolved components.
C) It is about 90% water.
D) The main protein component is hemoglobin.
A) It is the same as serum but without the clotting proteins.
B) It contains about 20 dissolved components.
C) It is about 90% water.
D) The main protein component is hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
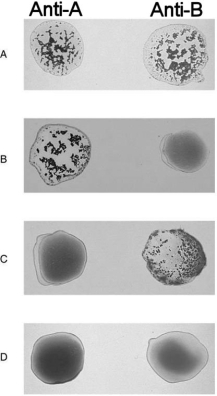 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Universal donor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not a functional characteristic of WBCs?
A) diapedesis
B) positive chemotaxis
C) ameboid motion
D) granulosis
A) diapedesis
B) positive chemotaxis
C) ameboid motion
D) granulosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Explain why blood is classified as a connective tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Fred's blood was determined to be AB positive. What does this mean?
A) There are no antibodies to A, to B, or to Rh antigens in the plasma.
B) He can only receive blood from a donor who is AB positive.
C) Antibodies to A and B are present in the red cells.
D) His blood lacks Rh factor.
A) There are no antibodies to A, to B, or to Rh antigens in the plasma.
B) He can only receive blood from a donor who is AB positive.
C) Antibodies to A and B are present in the red cells.
D) His blood lacks Rh factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Select the incorrect statement regarding blood cell formation.
A) Lymphocytes are formed from lymphoblasts.
B) Platelets are formed from myeloblasts.
C) Erythrocytes are formed from normoblasts.
D) Eosinophils are formed from myeloblasts,
A) Lymphocytes are formed from lymphoblasts.
B) Platelets are formed from myeloblasts.
C) Erythrocytes are formed from normoblasts.
D) Eosinophils are formed from myeloblasts,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following would not be a possible cause of sickling of red blood cells in someone with sickle- cell anemia?
A) malaria and travel at high altitude
B) vigorous exercise
C) sleeping in a well- ventilated room
D) travel at high altitude
A) malaria and travel at high altitude
B) vigorous exercise
C) sleeping in a well- ventilated room
D) travel at high altitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements does not describe blood?
A) Blood varies from bright red to a dark red color.
B) Blood is denser and more viscous than water.
C) Blood carriers body cells to injured areas for repair
D) Blood pH is normally between 7.34 - 7.45.
A) Blood varies from bright red to a dark red color.
B) Blood is denser and more viscous than water.
C) Blood carriers body cells to injured areas for repair
D) Blood pH is normally between 7.34 - 7.45.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
No visible cytoplasmic granules are present in .
A) neutrophils
B) eosinophils
C) monocytes
D) basophils
A) neutrophils
B) eosinophils
C) monocytes
D) basophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Blood is a .
A) homogeneous compound
B) suspension
C) heterogeneous compound
D) colloid
A) homogeneous compound
B) suspension
C) heterogeneous compound
D) colloid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Most common white blood cell found in whole blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:List the most common causes of bleeding disorders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Thromboembolic disorders _ .
A) include embolus formation, a clot moving within the circulatory system
B) are caused by vitamin K deficiency
C) result in uncontrolled bleeding
D) include thrombus formation, a clot in a broken blood vessel
A) include embolus formation, a clot moving within the circulatory system
B) are caused by vitamin K deficiency
C) result in uncontrolled bleeding
D) include thrombus formation, a clot in a broken blood vessel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is characteristic of all leukocytes?
A) They are nucleated.
B) They are the most numerous of the formed elements in blood.
C) They are phagocytic.
D) They have cytoplasmic granules.
A) They are nucleated.
B) They are the most numerous of the formed elements in blood.
C) They are phagocytic.
D) They have cytoplasmic granules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An individual who is blood type AB negative can .
A) receive any blood type in moderate amounts except that with the Rh antigen
B) donate to types A, B, and AB, but not to type O
C) donate to all blood types in moderate amounts
D) receive types A, B, and AB, but not type O
A) receive any blood type in moderate amounts except that with the Rh antigen
B) donate to types A, B, and AB, but not to type O
C) donate to all blood types in moderate amounts
D) receive types A, B, and AB, but not type O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
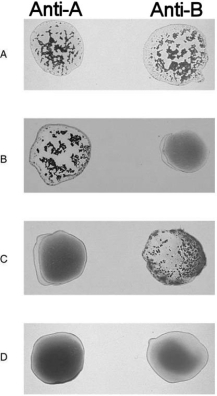 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Type A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:The term that describes blood disorders in which blood oxygen levels ae inadequate to support normal metabolism is .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:The rarest leukocyte is the _ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
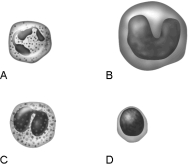 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:The universal recipient blood type is .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
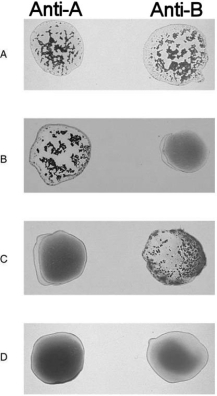 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:What is the buffy coat found in centrifuged whole blood?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:When monocytes migrate into the interstitial spaces, they are called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Type O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When are whole blood transfusions routinely given?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
List the general factors that limit normal clot growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
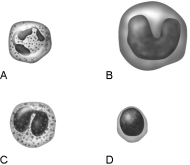 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Main bacteria killer during acute infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Why is iron not stored or transported in its free form? In what form(s) is it stored or transported in blood?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
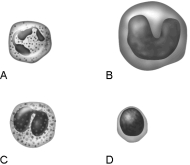 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Monocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Where and how is iron stored in the body?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:List the granulocytes and describe the appearance of their granules in a typical blood smear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
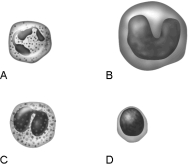 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Becomes a macrophage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
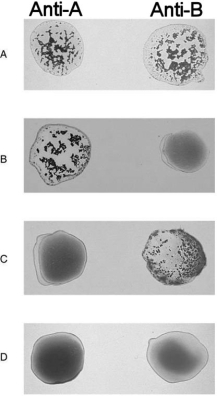 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Type B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:What determines whether blood is bright red or a dull, dark red?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
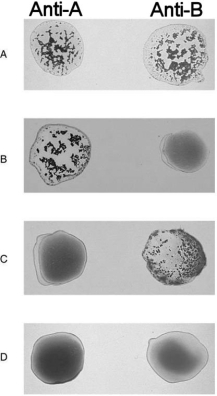 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Universal recipient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Mounts an immune response by direct cell attack or via antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:A(n) is a committed granular leukocyte stem cell that produces neutrophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Diapedesis is the process by which red blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The immediate response to blood vessel injury is clotting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Hemoglobin is made up of the protein heme and the red pigment globin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
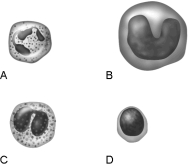 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Kills parasitic worms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Lymphocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Why are the two pathways of blood clotting referred to as the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
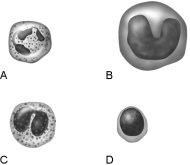 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Eosinophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The process of fibrinolysis disposes of bacteria when healing has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
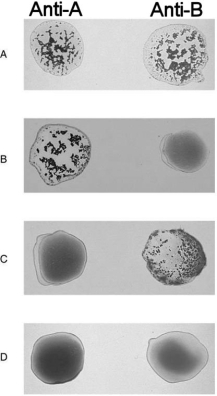 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:The formed element can kill parasitic worms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Myelocytic leukemia involves a cancerous condition of lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
is the stage of development in the life of an erythrocyte during which the nucleus is ejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:
Figure 17.2Using Figure 17.2, match the following:Type AB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Each hemoglobin molecule can transport two molecules of oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Leukocytes move through the circulatory system by amoeboid motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and are the most numerous of all white blood cell types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
 Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:
Figure 17.1Using Figure 17.1, match the following:Neutrophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why is hemoglobin enclosed in erythrocytes rather than existing free in plasma?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
All lymphocytes are leukocytes, but not all leukocytes are lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
White blood cells are produced through the action of colony- stimulating factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



