Deck 4: Elasticity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Elasticity
1
Of the following, demand is likely to be the least elastic for
A) pink grapefruit.
B) diamonds.
C) iceberg lettuce.
D) insulin for diabetics.
A) pink grapefruit.
B) diamonds.
C) iceberg lettuce.
D) insulin for diabetics.
insulin for diabetics.
2
The price elasticity of supply is calculated as the
A) percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
B) percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price.
C) quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
D) quantity supplied divided by the per unit cost of production.
A) percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
B) percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price.
C) quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
D) quantity supplied divided by the per unit cost of production.
percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price.
3
When the price of perfume changes from $24 to $26, the quantity supplied increases from 100 jars to 150 jars. What is the elasticity of supply of perfume?
A) 0.04
B) 0.2
C) 25.0
D) 5.0
A) 0.04
B) 0.2
C) 25.0
D) 5.0
5.0
4

The table above gives some data on the supply of roses in a small town. When the price rises from
$15 a dozen to $25 a dozen, the elasticity of supply is
A) 0.80.
B) 5.00.
C) 0.20.
D) 1.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the quantity demanded is 5 units when the price is $1. If the price rises to $2, the quantity demanded falls to 3 units. The price elasticity of demand is
A) 0.5.
B) 2.00.
C) 1.33.
D) 0.75.
A) 0.5.
B) 2.00.
C) 1.33.
D) 0.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The price elasticity of demand can range between
A) zero and infinity.
B) negative one and one.
C) negative infinity and infinity.
D) zero and one.
A) zero and infinity.
B) negative one and one.
C) negative infinity and infinity.
D) zero and one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a price hike of 5 per cent increases the quantity demanded of another good by 2 per cent, the goods must be _______ and the cross elasticity of demand equals _______.
A) substitutes; 2.5
B) complements; 2.5
C) substitutes; 0.40
D) complements; 0.40
A) substitutes; 2.5
B) complements; 2.5
C) substitutes; 0.40
D) complements; 0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the total revenue test, a price cut increases total revenue if demand is
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) elastic.
D) inelastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) elastic.
D) inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a rise in the price of good B increases the quantity demanded of good A,
A) A and B are substitutes.
B) A is a substitute for B, but B is a complement to A.
C) B is a substitute for A, but A is a complement to B.
D) A and B are complements.
A) A and B are substitutes.
B) A is a substitute for B, but B is a complement to A.
C) B is a substitute for A, but A is a complement to B.
D) A and B are complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Microsoft raises the price of its Office software by 10 per cent. As a result, the quantity of personal computers demanded at the current price decreases by 5 per cent. What is the cross elasticity of demand for personal computers with respect to the price of Microsoft Office software?
A) 2.0
B) - 2.0
C) 0.5
D) - 0.5
A) 2.0
B) - 2.0
C) 0.5
D) - 0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A fall in the price of cabbage from $10.50 to $9.50 per carton increases the quantity demanded from 18,800 to 21,200 cartons. The price elasticity of demand is
A) 1.25.
B) 0.80.
C) 8.00.
D) 1.20.
A) 1.25.
B) 0.80.
C) 8.00.
D) 1.20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 10 per cent increase in income has caused a 5 per cent decrease in the quantity demanded. The income elasticity is
A) 2.0.
B) - 2.0.
C) 0.5.
D) - 0.5.
A) 2.0.
B) - 2.0.
C) 0.5.
D) - 0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On most days the price of a rose is $1 and 80 roses are purchased. On Valentine's Day demand increases so that the price of a rose rises to $2 and 320 roses are purchased. Therefore, the price elasticity of
A) supply of roses is about 0.55.
B) demand for roses is about 1.8.
C) supply of roses is about 1.8.
D) demand for roses is about 0.55.
A) supply of roses is about 0.55.
B) demand for roses is about 1.8.
C) supply of roses is about 1.8.
D) demand for roses is about 0.55.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A rise in the price of cabbage from $14 to $18 per carton increases the quantity supplied from 4,000 to 6,000 cartons. The elasticity of supply is
A) 0.8.
B) 1.0.
C) 0.6.
D) 1.6.
A) 0.8.
B) 1.0.
C) 0.6.
D) 1.6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following goods would BEST be described as being in perfectly inelastic supply?
A) Insulin
B) The original portrait of "Whistler's Mother"
C) Pepsi Max
D) CDs by Rihanna
A) Insulin
B) The original portrait of "Whistler's Mother"
C) Pepsi Max
D) CDs by Rihanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A straight- line demand curve with negative slope intersects the horizontal axis at 200 tonnes per week. The point on the demand curve at which the price elasticity of demand is 1 corresponds to a quantity demanded
A) of 200 tonnes.
B) of 100 tonnes.
C) of zero tonnes.
D) that would be negative if a negative quantity demanded were possible.
A) of 200 tonnes.
B) of 100 tonnes.
C) of zero tonnes.
D) that would be negative if a negative quantity demanded were possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The income elasticity of demand is largest for
A) shelter.
B) clothing.
C) luxuries.
D) food.
A) shelter.
B) clothing.
C) luxuries.
D) food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following leads a good to have a high elasticity of supply?
I. The good must be produced using unique resources.
II. The good is produced using commonly available resources.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II
I. The good must be produced using unique resources.
II. The good is produced using commonly available resources.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
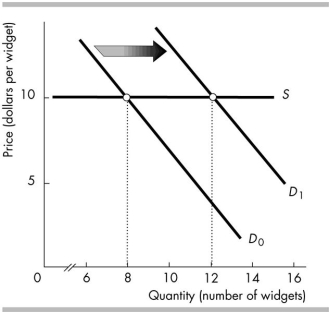
The increase in the demand for widgets, shown in the figure above, is the result of an increase in the price of McBoover devices. Therefore,
A) widgets are a normal good.
B) McBoover devices are a normal good.
C) widgets and McBoover devices are substitutes.
D) widgets and McBoover devices are complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Because of an increase in the price of leather, the price of a pair of women's dress shoes increased by 12 per cent. If the price elasticity of demand for women's dress shoes is 0.85, which of the following will happen?
A) The number of pairs of women's dress shoes demanded will decrease by 10.2 per cent.
B) Total expenditure on women's dress shoes will decrease.
C) Total revenue from the sale of women's dress shoes will decrease.
D) None of the above
A) The number of pairs of women's dress shoes demanded will decrease by 10.2 per cent.
B) Total expenditure on women's dress shoes will decrease.
C) Total revenue from the sale of women's dress shoes will decrease.
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Demand is perfectly inelastic when
A) the good in question has perfect substitutes.
B) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in price.
C) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in quantity demanded.
D) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in the total revenue from sales.
A) the good in question has perfect substitutes.
B) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in price.
C) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in quantity demanded.
D) shifts of the supply curve result in no change in the total revenue from sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If, when income increases by 2 per cent and the price does not change, the quantity of airplane travel demanded increases by 6 per cent, the income elasticity of demand for airplane travel is
A) 3.00.
B) 0.
C) negative.
D) 0.33.
A) 3.00.
B) 0.
C) negative.
D) 0.33.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The price elasticity of demand is equal to the _______ in the _______ divided by the _______ in the _______.
A) percentage change; quantity demanded; percentage change; price
B) change; price; change; quantity demanded
C) change; quantity demanded; change; price
D) percentage change; price; percentage change; quantity demanded
A) percentage change; quantity demanded; percentage change; price
B) change; price; change; quantity demanded
C) change; quantity demanded; change; price
D) percentage change; price; percentage change; quantity demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
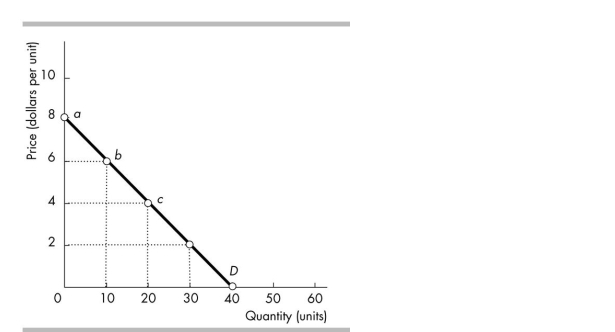
In the above figure, at which point on the demand curve is the price elasticity of demand equal to 1?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) It is impossible to say at which point the elasticity equals one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Demand is inelastic when a price _______ results in total revenue _______.
A) rise; decreasing
B) rise; increasing
C) fall; remaining the same
D) fall; increasing
A) rise; decreasing
B) rise; increasing
C) fall; remaining the same
D) fall; increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the supply of a good is elastic, that means that when price increases,
A) the quantity supplied will increase by a smaller percentage than the price increased.
B) supply will increase.
C) the quantity supplied will decrease.
D) the quantity supplied will increase by a greater percentage than the price increased.
A) the quantity supplied will increase by a smaller percentage than the price increased.
B) supply will increase.
C) the quantity supplied will decrease.
D) the quantity supplied will increase by a greater percentage than the price increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If Sam wants to increase her total revenue from her sales of flowers and she knows that the demand for flowers is price elastic, she should
A) raise her price because she knows that the percentage decrease in the quantity demanded will be smaller than the percentage increase in price.
B) lower her price to increase the demand and shift the demand curve rightward.
C) raise her price because she knows that the quantity demanded will also increase.
D) lower her price because she knows that the percentage increase in the quantity demanded will be greater than the percentage decrease in price.
A) raise her price because she knows that the percentage decrease in the quantity demanded will be smaller than the percentage increase in price.
B) lower her price to increase the demand and shift the demand curve rightward.
C) raise her price because she knows that the quantity demanded will also increase.
D) lower her price because she knows that the percentage increase in the quantity demanded will be greater than the percentage decrease in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the cross elasticity of demand between coffee and tea is positive, an increase in the price of tea will shift the demand curve for
A) tea leftward.
B) coffee leftward.
C) tea rightward.
D) coffee rightward.
A) tea leftward.
B) coffee leftward.
C) tea rightward.
D) coffee rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Supply is elastic if
A) the slope of the supply curve is positive.
B) the good in question is a normal good.
C) a 1 per cent change in price leads to a larger percentage change in quantity supplied.
D) a 1 per cent change in price leads to a smaller percentage change in quantity supplied.
A) the slope of the supply curve is positive.
B) the good in question is a normal good.
C) a 1 per cent change in price leads to a larger percentage change in quantity supplied.
D) a 1 per cent change in price leads to a smaller percentage change in quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a 6 per cent decrease in the price leads to a 5 per cent increase in the quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand is
A) 1.20.
B) 0.60.
C) 0.30.
D) 0.83.
A) 1.20.
B) 0.60.
C) 0.30.
D) 0.83.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price elasticity is between 0 and 1, demand is
A) unit elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
A) unit elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Joan's income has just risen from $940 per week to $1,060 per week. As a result, she decides to purchase 12 per cent more lettuce per week. The income elasticity of Joan's demand for lettuce is
A) 1.00.
B) 1.33.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.90.
A) 1.00.
B) 1.33.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The income elasticity of demand for bicycles is +10, which implies that bicycles are
A) an inferior good.
B) a normal good.
C) a complement good for motorbikes.
D) a substitute good for motorbikes.
A) an inferior good.
B) a normal good.
C) a complement good for motorbikes.
D) a substitute good for motorbikes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a 5 per cent change in the price of a good leads to a 10 per cent change in the quantity supplied, then the supply of the good is _______ and the elasticity of supply is _______.
A) inelastic; 0.5
B) elastic; 2.0
C) elastic; 0.5
D) inelastic; 2.0
A) inelastic; 0.5
B) elastic; 2.0
C) elastic; 0.5
D) inelastic; 2.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the price of oil is $60 per barrel, the quantity of oil supplied is 70 million barrels per day. If the price is $40 per barrel, the quantity of oil supplied is 69 million barrels per day. This implies that the
A) demand for oil is inelastic.
B) supply of oil is inelastic.
C) demand for oil is elastic.
D) supply of oil is elastic.
A) demand for oil is inelastic.
B) supply of oil is inelastic.
C) demand for oil is elastic.
D) supply of oil is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
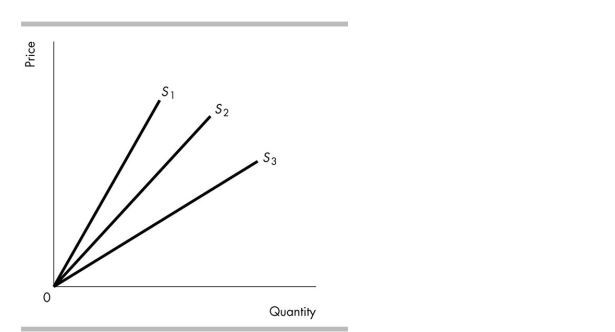
In the above figure, the price elasticity of supply at any given quantity is
A) equal to one on each of the three supply curves.
B) equal to zero on each of the three supply curves.
C) highest along S3, next highest along S2, and lowest along S1.
D) highest along S1, next highest along S2, and lowest along S3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a 20 per cent increase in the price of a used car results in a 10 per cent decrease in the quantity of used cars demanded, then the demand for used cars is
A) inelastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) elastic.
A) inelastic.
B) unit elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The income elasticity of demand is
A) positive for a normal good and negative for an inferior good.
B) always positive.
C) negative for a normal good and positive for an inferior good.
D) always negative.
A) positive for a normal good and negative for an inferior good.
B) always positive.
C) negative for a normal good and positive for an inferior good.
D) always negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A supply curve that is horizontal reflects a supply that
A) is unit elastic.
B) has a zero elasticity.
C) is elastic.
D) is inelastic.
A) is unit elastic.
B) has a zero elasticity.
C) is elastic.
D) is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the cross elasticity of demand between goods X and Y is positive and between goods X and Z is negative, then X and Y are _______ and X and Z are _______.
A) price inelastic; income elastic
B) substitutes; complements
C) price inelastic; complements
D) complements; substitutes
A) price inelastic; income elastic
B) substitutes; complements
C) price inelastic; complements
D) complements; substitutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The income elasticity of demand for vacations is 5. If incomes increase by 3 per cent next year, the quantity of vacations demanded at today's price will increase by _______ per cent.
A) 5
B) 15
C) 5/3
D) 3
A) 5
B) 15
C) 5/3
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An important determinant of the price elasticity of supply is
A) the time period firms have to adjust to a new price.
B) how well consumers like the commodity.
C) the proportion of the consumer's total budget spent on the good.
D) whether the good is a durable or a nondurable.
A) the time period firms have to adjust to a new price.
B) how well consumers like the commodity.
C) the proportion of the consumer's total budget spent on the good.
D) whether the good is a durable or a nondurable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A normal good is defined as a good for which the demand curve
A) shifts rightward as income increases.
B) slopes downward to the right.
C) is perfectly price elastic.
D) shifts leftward as income increases.
A) shifts rightward as income increases.
B) slopes downward to the right.
C) is perfectly price elastic.
D) shifts leftward as income increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
On a straight- line downward- sloping demand curve, the maximum elasticity of demand occurs
A) at its vertical intercept.
B) at its midpoint.
C) where it intersects the supply curve.
D) at its horizontal intercept.
A) at its vertical intercept.
B) at its midpoint.
C) where it intersects the supply curve.
D) at its horizontal intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The price elasticity of demand measures
A) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in demand.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in price.
C) how often the price of a good changes.
D) the slope of a budget curve.
A) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in demand.
B) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in price.
C) how often the price of a good changes.
D) the slope of a budget curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The price elasticity of demand is defined as the magnitude of the
A) percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
B) change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price.
C) change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded.
D) percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
A) percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
B) change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price.
C) change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded.
D) percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The income elasticity of demand is the percentage change in _______ divided by the percentage change in _______.
A) income; the price
B) the quantity demanded; income
C) the price; income
D) income; the quantity demanded
A) income; the price
B) the quantity demanded; income
C) the price; income
D) income; the quantity demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a 5 per cent increase in the price of good A leads to a 4 per cent decrease in the demand for good B, then
A) both goods are normal goods.
B) the goods are substitutes.
C) the goods are complements.
D) only one good is a normal good.
A) both goods are normal goods.
B) the goods are substitutes.
C) the goods are complements.
D) only one good is a normal good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose tennis shoes cost $50 per pair and firms supply 50,000 pairs of shoes. If the price decreases to $45 and firms decide to supply 48,000, the elasticity of supply equals
A) 0.39.
B) 0.04.
C) 2.63.
D) 0.0025.
A) 0.39.
B) 0.04.
C) 2.63.
D) 0.0025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Goods or services for which a greater proportion of income is spent on the items generally have a more elastic demand.
B) The longer the time that has elapsed since a price change, the more elastic the demand.
C) Goods or services that have few close substitutes generally have a less elastic demand.
D) A narrowly defined good or service generally has a less elastic demand.
A) Goods or services for which a greater proportion of income is spent on the items generally have a more elastic demand.
B) The longer the time that has elapsed since a price change, the more elastic the demand.
C) Goods or services that have few close substitutes generally have a less elastic demand.
D) A narrowly defined good or service generally has a less elastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Marvin loves chocolate truffles. As the price of a chocolate truffle increases from $1 to $2 to $3, Marvin continues to buy a dozen chocolate truffles every week. Marvin's demand for chocolate truffles is _______.
A) elastic
B) illustrated by a horizontal demand curve
C) unit elastic
D) perfectly inelastic
A) elastic
B) illustrated by a horizontal demand curve
C) unit elastic
D) perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The demand for bus rides is a downward- sloping straight- line demand curve. The price elasticity of demand for bus rides
A) decreases as the price of a bus ride falls.
B) is the same no matter what the price of a bus ride.
C) decreases as the price of a bus ride rises.
D) increases as the price of a bus ride falls.
A) decreases as the price of a bus ride falls.
B) is the same no matter what the price of a bus ride.
C) decreases as the price of a bus ride rises.
D) increases as the price of a bus ride falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The price elasticity of demand for new cars is 1.2. Hence, a 10 per cent price increase will
A) decrease the quantity of new cars demanded by 1.2 per cent.
B) increase consumer expenditure on new cars by 1.2 per cent.
C) increase consumer expenditure on new cars by 12 per cent.
D) decrease the quantity of new cars demanded by 12 per cent.
A) decrease the quantity of new cars demanded by 1.2 per cent.
B) increase consumer expenditure on new cars by 1.2 per cent.
C) increase consumer expenditure on new cars by 12 per cent.
D) decrease the quantity of new cars demanded by 12 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A straight- line demand curve with negative slope intersects the horizontal axis at 100 tonnes per week. At the midpoint on the demand curve (corresponding to 50 tonnes per week) the price elasticity of demand is
A) 1.0.
B) 0.5.
C) 0.
D) unknown without more information.
A) 1.0.
B) 0.5.
C) 0.
D) unknown without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A shift of the supply curve of DVDs raises the price of a DVD from $9.50 to $10.50 and reduces the quantity demanded from 41 million to 39 million DVDs a month. The price elasticity of demand for DVDs is
A) 0.5.
B) $2 per 2 million DVDs a month.
C) 2.0.
D) 2 million DVDs a month per dollar.
A) 0.5.
B) $2 per 2 million DVDs a month.
C) 2.0.
D) 2 million DVDs a month per dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
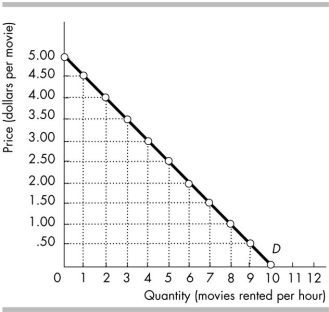
The above figure shows the demand curve for movie rentals from Blockbuster. If Blockbuster raised its price from $2.50 to $3.00 per movie, between these two prices the price elasticity of demand equals
A) 2.0.
B) 0.8.
C) 1.2.
D) 0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If your demand for a good is _______, then a 1 per cent fall in its price will lead you to _______ your expenditure on the good.
A) unit elastic; increase
B) inelastic; increase
C) inelastic; decrease
D) elastic; decrease
A) unit elastic; increase
B) inelastic; increase
C) inelastic; decrease
D) elastic; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a 5 per cent increase in the price results in a 9 per cent increase in quantity supplied, the elasticity of supply is
A) 1.20.
B) 0.30.
C) 0.55.
D) 1.80.
A) 1.20.
B) 0.30.
C) 0.55.
D) 1.80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When the price of a movie ticket increases from $5 to $7, the quantity of tickets demanded decreases from 600 to 400 a day. What is the price elasticity of demand for movie tickets?
A) 0.83
B) 1.20
C) 2.32
D) 1.00
A) 0.83
B) 1.20
C) 2.32
D) 1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Because product X has a very small, positive income elasticity of demand, it is likely that product X
Is a
A) product with many good complements.
B) luxury.
C) necessity.
D) product with many good substitutes.
Is a
A) product with many good complements.
B) luxury.
C) necessity.
D) product with many good substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The cross elasticity of demand between Coca- Cola and Pepsi- Cola is _______ so that Coke and Pepsi are _______.
A) negative; substitutes
B) negative; normal goods
C) positive; complements
D) positive; substitutes
A) negative; substitutes
B) negative; normal goods
C) positive; complements
D) positive; substitutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
As the price of mobile phones fell during the last decade, consumers' total expenditures on mobile phones increased. If the demand curve for mobile phones did not shift, this fact means that the demand for mobile phones
A) is elastic.
B) must have shifted leftward.
C) is inelastic.
D) must be upward- sloping.
A) is elastic.
B) must have shifted leftward.
C) is inelastic.
D) must be upward- sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Deb's income has just risen from $950 per week to $1,050 per week. As a result, she decides to increase the number of movies she attends each month by 5 per cent. Her demand for movies is
A) represented by a vertical line.
B) income elastic.
C) income inelastic.
D) represented by a horizontal line.
A) represented by a vertical line.
B) income elastic.
C) income inelastic.
D) represented by a horizontal line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Blue pens and black pens are close substitutes. The cross elasticity of demand for black pens with respect to the price of blue pens is
A) zero.
B) negative.
C) equal to 1.
D) positive.
A) zero.
B) negative.
C) equal to 1.
D) positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A decrease in the supply of sugar increases the price of sugar from $1.00 a packet to $1.25 a packet. The quantity demanded decreases from 100 packets a day to 80 packets a day. The price elasticity of demand for sugar is _______.
A) 0.5
B) 0.75
C) 1.25
D) 1.0
A) 0.5
B) 0.75
C) 1.25
D) 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
To maximise its revenue,
A) a firm facing elastic demand should always raise its price.
B) a firm should always charge the highest price possible regardless of the elasticity of demand.
C) a firm facing inelastic demand should always raise its price.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
A) a firm facing elastic demand should always raise its price.
B) a firm should always charge the highest price possible regardless of the elasticity of demand.
C) a firm facing inelastic demand should always raise its price.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The price elasticity of demand for furniture is estimated at 1.3. This value means a one per cent increase in the
A) quantity of furniture demanded will decrease the price of furniture by 1.3 per cent.
B) price of furniture will increase the quantity of furniture demanded by 1.3 per cent.
C) price of furniture will decrease the quantity of furniture demanded by 1.3 per cent.
D) quantity of furniture demanded will increase the price of furniture by 1.3 per cent.
A) quantity of furniture demanded will decrease the price of furniture by 1.3 per cent.
B) price of furniture will increase the quantity of furniture demanded by 1.3 per cent.
C) price of furniture will decrease the quantity of furniture demanded by 1.3 per cent.
D) quantity of furniture demanded will increase the price of furniture by 1.3 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the supply curve is vertical then supply is
A) relatively elastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
A) relatively elastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
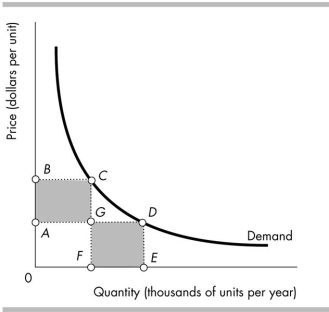
The elasticity of demand along the demand curve shown in the above figure is constant and equal to 1. Thus,
A) area 0BCF equals area FGDE.
B) area 0BCF equals area 0AGF.
C) area 0BCF equals area 0ADE.
D) area ABCG equals area 0AGF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The price elasticity of demand for purses is measured in
A) dollars.
B) dollars per purse.
C) purses.
D) None of the above answers is correct because there are no units for elasticity of demand.
A) dollars.
B) dollars per purse.
C) purses.
D) None of the above answers is correct because there are no units for elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The elasticity of supply equals _______ if the supply curve is vertical.
A) 1
B) 0
C) infinity
D) - 1
A) 1
B) 0
C) infinity
D) - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The income elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the
A) quantity of a good demanded to changes in income.
B) quantity of a good demanded to changes in its price.
C) consumer's income to a change in the price of the goods he or she consumes.
D) quantity of a good demanded to changes in another good's price.
A) quantity of a good demanded to changes in income.
B) quantity of a good demanded to changes in its price.
C) consumer's income to a change in the price of the goods he or she consumes.
D) quantity of a good demanded to changes in another good's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
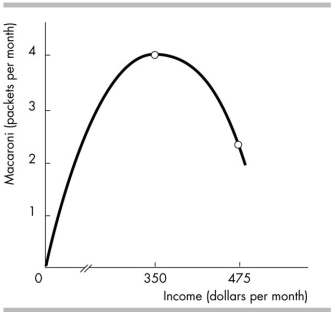
The figure shows the relationship between Moira's income and the quantity of macaroni that she demands. When income is less than $350 per month, macaroni
A) is a normal good.
B) has many substitutes.
C) has negative income elasticity.
D) is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
As time passes after a change in the price, the supply of a good or service
A) becomes less elastic.
B) initially becomes more elastic and then becomes less elastic.
C) initially becomes less elastic and then becomes more elastic.
D) becomes more elastic.
A) becomes less elastic.
B) initially becomes more elastic and then becomes less elastic.
C) initially becomes less elastic and then becomes more elastic.
D) becomes more elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The price elasticity of demand is 5.0 if a 10 per cent increase in the price results in a _______ decrease in the quantity demanded.
A) 10 per cent
B) 50 per cent
C) 5 per cent
D) 2 per cent
A) 10 per cent
B) 50 per cent
C) 5 per cent
D) 2 per cent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the price of a burger decreases by 5 per cent and as a result the quantity of burgers demanded increases by 8 per cent, the price elasticity of demand equals
A) 0.40.
B) 0.625.
C) 1.60.
D) 0.60.
A) 0.40.
B) 0.625.
C) 1.60.
D) 0.60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the demand for a good is elastic, the price elasticity of demand is
A) less than zero.
B) between 0 and 1.
C) greater than 1.
D) equal to 1.
A) less than zero.
B) between 0 and 1.
C) greater than 1.
D) equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
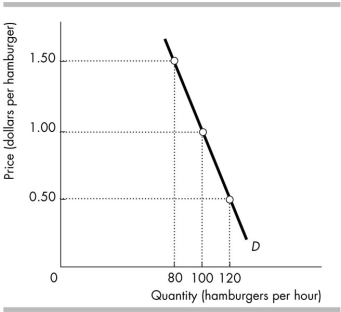
The above figure illustrates the demand for hamburgers. When the price is $1 a hamburger, the elasticity of demand is _______ and a 1 per cent increase in the price will _______ the quantity of hamburgers demanded by _______ per cent.
A) 1.00; decrease; 0.40
B) 2.50; increase; 2.50
C) 5.00; decrease; 5.00
D) 0.40; decrease; 0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The concept of elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of the
A) quantity supplied to a change in the price.
B) quantity demanded to a change in the quantity supplied.
C) quantity supplied to a change in the quantity demanded.
D) price to a change in the quantity supplied.
A) quantity supplied to a change in the price.
B) quantity demanded to a change in the quantity supplied.
C) quantity supplied to a change in the quantity demanded.
D) price to a change in the quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The income elasticity of demand for restaurant meals is 1.61. So,
A) if income increases by 16.1 per cent, the quantity demanded of restaurant meals will increase by 10 per cent.
B) if income increases by 10 per cent, the quantity demanded of restaurant meals will increase by 16.1 per cent.
C) restaurant meals are an income elastic normal good.
D) Both answers B and C are correct.
A) if income increases by 16.1 per cent, the quantity demanded of restaurant meals will increase by 10 per cent.
B) if income increases by 10 per cent, the quantity demanded of restaurant meals will increase by 16.1 per cent.
C) restaurant meals are an income elastic normal good.
D) Both answers B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



