Deck 1: Collecting Data in Reasonable Ways
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Collecting Data in Reasonable Ways
1
If the subjects as well as the person measuring the response are aware ofthe treatment assigned to the subject, only single-blinding is being used.
False
2
Increasing sample size will eliminate bias in a sample.
False
3
A friend who is not taking statistics wonders why anyone would choose to take asample. "Obviously," she says, "you would get better information from a census."In a short paragraph, explain why statisticians might use a sample rather than acensus.
Although we may get better information from a census, it is usually far too costly and time consuming to contact every member of the population.A large random sample will be nearly as good for far less cost.
4
A placebo is designed to be identical in appearance to the treatment ofinterest, but contains no active ingredients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A study is an observational study if the investigator observes the behaviorof a response variable after one or more factors have been manipulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A treatment is a particular combination of values for the explanatoryvariables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Random assignment to treatments will guarantee that treatment groups areexactly alike for experimental purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Response bias occurs when responses are not actually obtained from allindividuals selected for inclusion in the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Stratified sampling does not involve simple random sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the sample size is small relative to the population size, there is littlepractical difference in the results of sampling with replacement andsampling without replacement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a well-designed experiment the treatments are confounded with othervariables whenever possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Variables are extraneous if their effects on the response variable cannot bedistinguished from one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Blocking is used to filter out the effects of some extraneous variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The method of control wherein an extraneous variable is held constant iscalled blocking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A control group provides a baseline for comparison with a treatmentgroup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Random subpopulations of a population are called strata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Random assignment of volunteers to treatments will, on average, result incomparable experimental groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A simple random sample of size n is by definition a sample that is selectedin a manner to guarantee each individual in the population an equal chanceof selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Clusters are non-overlapping subgroups of a population that have beenidentified as homogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Selection bias occurs if only volunteers are used in a study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Six species of wood-pecking birds are known to damage homes. Woodpeckers areprotected by the Federal Migratory Bird Treaty Act, and homeowners must controlthem by nonlethal methods. Over a three-month period, investigators evaluated theuse of mirrors, artificial snakes, and artificial owls as woodpecker deterrents.Homeowners' yards were classified into 4 categories: (1) no trees; (2) lightly woodedyards; (3) wooded yards; and (4) heavily wooded yards. The homes were visited atleast 4 times to establish baseline damage rates (number of new holes per day) beforeusing any deterrent. Deterrents were randomly assigned to the homes in eachcategory and changes in the damage rate were recorded at the end of the experimentaltime period. The design used was a randomized block design.(a) What is the explanatory variable (factor) for this experiment?
b) What is the response variable for this experiment?
(c) After completing the study, someone suggested that amount of rainfall mightaffect woodpecker activity and that homes in areas that receive more rainfallmight show greater damage. Is this something that the investigator should beworried about?
If yes, explain why; if no, explain what aspect of the design of theexperiment eliminates this worry.
b) What is the response variable for this experiment?
(c) After completing the study, someone suggested that amount of rainfall mightaffect woodpecker activity and that homes in areas that receive more rainfallmight show greater damage. Is this something that the investigator should beworried about?
If yes, explain why; if no, explain what aspect of the design of theexperiment eliminates this worry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
We have distinguished two types of studies: observational and experimental. Brieflyexplain the difference between these two types of study. You may use an example tosupport your answer but not as a substitute for an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A consumer group is performing an experiment to evaluate the tartar-fightingproperties of different brands of toothpaste. Three brands of toothpaste are beingcompared in a randomized comparative experiment. (There is no "do-not-brush"control group.) 300 adult volunteers of varying ages (100 for each toothpaste brand)have been randomly assigned to the treatments. The toothpaste for each brand isdelivered in containers that are the same except for the letters, X, Y, and Zprominently displayed. A team of dentists, blind to the identities of the toothpastebrands, will evaluate the levels of tartar on the subjects' teeth after 2 months of use.The subjects have been instructed to brush their teeth as they normally do during thecourse of the experiment.(a) What is the explanatory variable (factor) for this experiment?
(
b) What is the response variable for this experiment?
(c) After the onset of the experiment, it was discovered that a significant number ofvolunteers using Brand Y toothpaste recently enrolled in a short class on healthpractices, and one of the lessons involved instruction in effective brushing techniques.If none of the volunteers using Brands X and Z enrolled in the class, how would thisaffect the consumer group's interpretation of the results of the experiment?
(
b) What is the response variable for this experiment?
(c) After the onset of the experiment, it was discovered that a significant number ofvolunteers using Brand Y toothpaste recently enrolled in a short class on healthpractices, and one of the lessons involved instruction in effective brushing techniques.If none of the volunteers using Brands X and Z enrolled in the class, how would thisaffect the consumer group's interpretation of the results of the experiment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In competitive sports coaches may record athletes' practice sessions to provide moreeffective feedback to the athlete. Some coaches believe video recording may make theathletes more nervous and actually decrease their performance. You have been asked todesign an experiment to address this issue for competitive high school tennis players. Theproportion of successful first serves will be the response variable. The subjects for theexperiment are 60 high school male competitive tennis players of varying ability whohave volunteered for the experiment.
a) Describe the treatment(s) in your experiment
b) The experience levels of the players is one possible confounding variable. In a fewsentences, explain how you would control this variable
c) Can the results of this experiment be generalized to all male tennis players?
Why or why not?
a) Describe the treatment(s) in your experiment
b) The experience levels of the players is one possible confounding variable. In a fewsentences, explain how you would control this variable
c) Can the results of this experiment be generalized to all male tennis players?
Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
We have distinguished two types of studies: observational and experimental. Brieflyexplain the difference between these two types of study. You may use an example tosupport your answer but not as a substitute for an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
River City is seeking to compare the effects of two mosquito sprays, A and B, to beused in the insect control plan for their park system. Consider the following twoplans for a statistical study:• In Plan #1, a simple random sample of plots of park land would be taken from thepopulation of River City parks. Either treatment A or B would be randomlyassigned to each of the plots.• In Plan #2, a simple random sample of plots of park land would be taken from thepopulation of River City park areas that are rarely visited. Either treatment A orB would be randomly assigned to each of the plots.
a) Consider study plan #1:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
b) Consider study plan #2:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
a) Consider study plan #1:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
b) Consider study plan #2:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Bias is a potentially serious problem that can arise in surveys.
a) In a few sentences, explain the concept of bias.
b) What is the distinction between response bias and non-response bias?
a) In a few sentences, explain the concept of bias.
b) What is the distinction between response bias and non-response bias?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Bias is the tendency for samples to differ from the corresponding population in somesystematic way. Some types of bias are: (a) selection bias, (
b) response bias, and/or(c) nonresponse bias. In a few sentences, discuss the differences among thesedifferent types of bias. Examples may illustrate, but not substitute for, a discussion.
b) response bias, and/or(c) nonresponse bias. In a few sentences, discuss the differences among thesedifferent types of bias. Examples may illustrate, but not substitute for, a discussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain how you would determine if a variable is an explanatory variable or anextraneous variable?
Again, you may use an example to support your answer but notas a substitute for an explanation.
Again, you may use an example to support your answer but notas a substitute for an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
After reading the description below, determine whether the study is an observationalor experimental study. Justify your answer with specific references to theinformation in the study."We compared paired daytime and night counts of wild brook trout, browntrout, and rainbow trout made by the same snorkelers in five streamsduring August. Overall, we counted 109 trout in the daytime and 333trout at night. We speculate that trout counted at night were presentduring the daytime but were hidden from view. Biologists should considerthat trout behavior and visibility might vary between daytime and night,even during summer. In some streams, the majority of trout may not beseen during the daytime."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
River City is seeking to compare the effects of two mosquito sprays, A and B, to beused in the insect control plan for their park system. Consider the following twoplans for a statistical study:• In Plan #1, a simple random sample of plots of park land would be taken from thepopulation of River City parks. Either treatments A or B would be randomlyassigned to each of the plots.• In Plan #2, simple random samples of plots of park land would be taken fromeach of four geographic areas in River City. (River City has 4 geographic areas oftown, the NE, NW, SE, and SW quadrants.) Either treatments A or B would berandomly assigned to each of the plots within each geographic area.
a) Consider study plan #1:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
b) Consider study plan #2:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
a) Consider study plan #1:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?
b) Consider study plan #2:i) Would it be appropriate to infer a cause-and-effect relationship if the results ofthe two treatments differ?
Why or why not?
ii) Could the results be generalized to all areas of the park land?
Why or whynot?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A friend who is not taking statistics wonders why anyone would choose to take asample. "Obviously," she says, "you would get better information from a census."In a short paragraph, explain why statisticians might use a sample rather than acensus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The ZZZ chain of motels has a standard method of constructing their buildings tomaximize the ease of parking for its customers. The rooms are arranged in adjacentbuildings, A and B, so that customers can park close to their rooms. The layout forthe 48-room motels is diagrammed below: 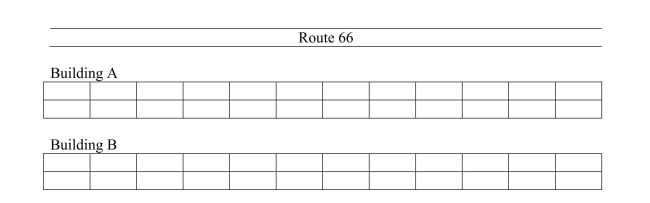 The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. In order to make the directionseasy for the cleaning staff to follow, he elects to use systematic sampling.
The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. In order to make the directionseasy for the cleaning staff to follow, he elects to use systematic sampling.
a) Describe carefully how you would use random numbers to set up the systematicsampling process. (In your description you may assume you have a randomnumber table, but do NOT carry out the procedure you describe.)
b) Write a short paragraph for the cleaning staff that explains how to carry out yourmethod in part (a). The members of the cleaning staff have not taken statistics, sothe use of statistical terminology will not be helpful.
 The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. In order to make the directionseasy for the cleaning staff to follow, he elects to use systematic sampling.
The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. In order to make the directionseasy for the cleaning staff to follow, he elects to use systematic sampling.a) Describe carefully how you would use random numbers to set up the systematicsampling process. (In your description you may assume you have a randomnumber table, but do NOT carry out the procedure you describe.)
b) Write a short paragraph for the cleaning staff that explains how to carry out yourmethod in part (a). The members of the cleaning staff have not taken statistics, sothe use of statistical terminology will not be helpful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The ZZZ chain of motels has a standard method of constructing their buildings tomaximize the ease of parking for its customers. The rooms are arranged in adjacentbuildings, A and B, so that customers can park close to their rooms. The layout forthe 48-room motels is diagrammed below: 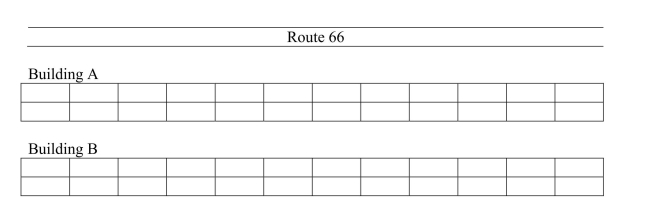 The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. As she tries to decide on anappropriate sampling strategy, the manager realizes the rooms in Building A might benoisier than Building B, and this should be taken into account.
The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. As she tries to decide on anappropriate sampling strategy, the manager realizes the rooms in Building A might benoisier than Building B, and this should be taken into account.
a) What sampling strategy should she use in this situation?
Provide appropriatestatistical justification.
b) Write a short paragraph for the cleaning staff that explains how to carry out yourmethod in part (a). The members of the cleaning staff have not taken statistics.
 The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. As she tries to decide on anappropriate sampling strategy, the manager realizes the rooms in Building A might benoisier than Building B, and this should be taken into account.
The manager wishes to assess customer satisfaction with the motel services. His planis to survey the adults in each of 12 rooms. The cleaning staff will place surveys onthe customers' beds before they check in to the motel. As she tries to decide on anappropriate sampling strategy, the manager realizes the rooms in Building A might benoisier than Building B, and this should be taken into account.a) What sampling strategy should she use in this situation?
Provide appropriatestatistical justification.
b) Write a short paragraph for the cleaning staff that explains how to carry out yourmethod in part (a). The members of the cleaning staff have not taken statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An anthropologist is studying the strength of fragments of pottery ("sherds") found inthree archeological sites in the Phoenix Basin area of Arizona. Her study involvesapplying force to the sherds until they break, so she plans to use only a small sampleof available artifacts. Her data contains the location of the sherd (site), and theweight and thickness of the sherd. A partial list of the data is shown below. 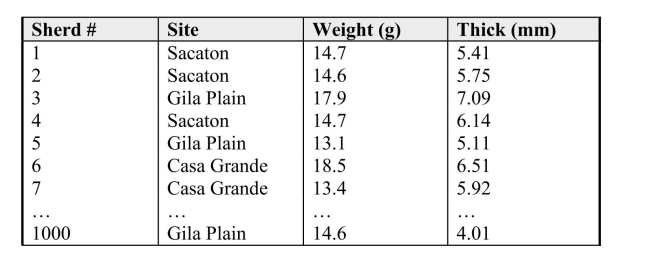 a) Briefly describe a process to select a simple random sample of size n = 20 fromthis list of sherds. You may assume that you have a random number table to workwith, but do NOT carry out the process you describe.
a) Briefly describe a process to select a simple random sample of size n = 20 fromthis list of sherds. You may assume that you have a random number table to workwith, but do NOT carry out the process you describe.
b) Briefly describe how a stratified random sample could be selected with stratacorresponding to archeological sites.
 a) Briefly describe a process to select a simple random sample of size n = 20 fromthis list of sherds. You may assume that you have a random number table to workwith, but do NOT carry out the process you describe.
a) Briefly describe a process to select a simple random sample of size n = 20 fromthis list of sherds. You may assume that you have a random number table to workwith, but do NOT carry out the process you describe.b) Briefly describe how a stratified random sample could be selected with stratacorresponding to archeological sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Two of the basic sampling methods studied in statistics are the simple random sampleand the stratified random sample. How do these methods of sampling differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Bias is a potentially serious problem that can arise in surveys.
a) In a few sentences, explain the concept of bias.
b) What is the distinction between selection bias and non-response bias?
a) In a few sentences, explain the concept of bias.
b) What is the distinction between selection bias and non-response bias?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the following three methods for random sampling: (a) simple randomsampling, (
b) stratified random sampling, and (c) cluster sampling. In a fewsentences, discuss the similarities and differences among these sampling methods.What aspects of the population would lead you to choose each of these methods?
The paragraphs below in questions 2 and 3 present information about a health study.Each gives a hint about possible bias. Decide whether the possible bias is (i) selectionbias, (ii) response bias, or (iii) nonresponse bias, and explain why you chose your answer.
b) stratified random sampling, and (c) cluster sampling. In a fewsentences, discuss the similarities and differences among these sampling methods.What aspects of the population would lead you to choose each of these methods?
The paragraphs below in questions 2 and 3 present information about a health study.Each gives a hint about possible bias. Decide whether the possible bias is (i) selectionbias, (ii) response bias, or (iii) nonresponse bias, and explain why you chose your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Explain how you would determine if a variable is an explanatory variable or aresponse variable?
Again, you may use an example to support your answer but not asa substitute for an explanation.
Again, you may use an example to support your answer but not asa substitute for an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the defining characteristic of a simple random sample?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
One part of the Nurses Health Study focuses on possible causes of skin cancer.Nurses were asked about different behaviors and aspects of their health when theyentered the study. Those nurses subsequently diagnosed with cancer were given thequestionnaires again. Investigators discovered that after the diagnosis the nursestended to report a reduced ability to tan. The investigators concluded that the shift inreporting might be caused by an awareness of their diagnosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After reading the description below, determine whether the study is an observationalor experimental study. Justify your answer with specific references to theinformation in the study."Before expanding the regional airport, children living nearby were determinedto be in one of two aircraft-noise groups (i) aircraft noise at present or (ii)aircraft noise would come with the expansion. Three hundred twenty-sixchildren (mean age = 10.4 years) took part in three data-collection waves, onebefore and two after the expansion of the airports. After the expansion, long-term memory and reading were found to be impaired in the group newlyexposed to aircraft noise."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One part of the Demographic and Health Surveys Program is concerned withmeasures of malnutrition. Investigators measure physical characteristics of children,at different ages. Sadly, in some countries, many children die early, and thus a bias isintroduced in the study because the investigators cannot collect data from thedeceased children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A common classroom practice is to have students exchange their quizzes for grading.This practice is hypothesized to reduce time between quiz and feedback to students,thus resulting in higher achievement. Your history teacher, aware of your statisticalprowess, has asked you to design an experiment to test this theory. You have decidedto use the final exam (not graded by students) as your response measure. Yourhistory teacher has three classes, one early in the morning, one at noon, and one latein the afternoon. Each class contains 30 students.(a) Describe the treatments you will use in your experiment(
b) One possible confounding variable is the time of day; students may be more alertat certain times of the day than at other times. Describe a method that could beused to control this variable. Students have already been assigned their schedules,and these cannot be changed.(c) Do you feel the results of your experiment could be generalized to math classes?
Explain why or why not.
b) One possible confounding variable is the time of day; students may be more alertat certain times of the day than at other times. Describe a method that could beused to control this variable. Students have already been assigned their schedules,and these cannot be changed.(c) Do you feel the results of your experiment could be generalized to math classes?
Explain why or why not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



