Deck 14: Available Online: Other Mathematical Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/27
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Available Online: Other Mathematical Systems
1
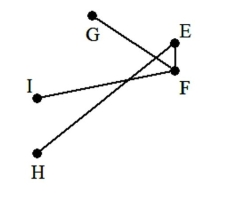
A) The graph is not a tree because two edges overlap.
B) The graph is not a tree because it is disconnected.
C) The graph is not a tree because it contains a circuit.
D) The graph is a tree.
The graph is not a tree because it is disconnected.
2
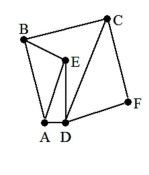
A) F, D, C, B, A, E, D, F
B) E, B, A, D, F, C, E
C) A, E, B, C, F, D, E, A
D) F, D, E, A, B, C, F
F, D, E, A, B, C, F
3
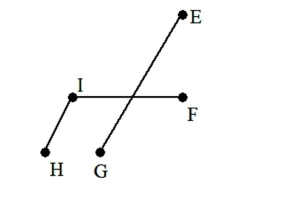
Determine if an Euler path or an Euler circuit exists so that a person who plows the roads does not have to pass over any street twice. If an Euler path or an Euler circuit exists, find one. The intersections of the streets have been labeled for you.
A) Euler path: C-B-A-H-G-I-J-F-E-D-C-F
B) Euler circuit: B-A-H-G-B-C-D-E-F-G-I-J-F-C-B
C) Euler path: B-A-H-G-B-C-D-E-F-G-I-J-F-C
D) neither exists

A) Euler path: C-B-A-H-G-I-J-F-E-D-C-F
B) Euler circuit: B-A-H-G-B-C-D-E-F-G-I-J-F-C-B
C) Euler path: B-A-H-G-B-C-D-E-F-G-I-J-F-C
D) neither exists
Euler path: B-A-H-G-B-C-D-E-F-G-I-J-F-C
4
A) The graph is not a tree because it contains a circuit.
B) The graph is not a tree because two edges overlap.
C) The graph is not a tree because it is disconnected.
D) The graph is a tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
State whether the graph has an Euler path, an Euler circuit, or neither. If it has an Euler path or an Euler circuit, find one.
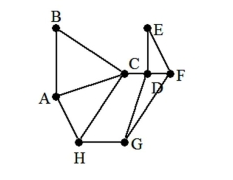
A) Euler path: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, C, A, H
B) Euler circuit: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A
C) Euler path: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A
D) neither

A) Euler path: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, C, A, H
B) Euler circuit: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A
C) Euler path: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A
D) neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Based on the information in the table, use the brute force method to find the shortest routefrom Angleton to all the other cities and back to Angleton.
A) 255 miles
B) 249 miles
C) 215 miles
D) 224 miles
A) 255 miles
B) 249 miles
C) 215 miles
D) 224 miles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
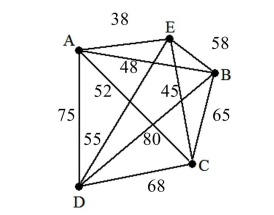
A) 304
B) 238
C) 213
D) 303

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Decide whether the connected graph has an Euler path, an Euler circuit, an Euler circuit butnot an Euler path, or neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path. The graph has 2 odd vertices and 2 even vertices.
A) Euler circuit but not an Euler path
B) Euler path
C) neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path
D) Euler circuit
A) Euler circuit but not an Euler path
B) Euler path
C) neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path
D) Euler circuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Decide whether the connected graph has an Euler path, an Euler circuit, an Euler circuit butnot an Euler path, or neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path. The graph has 4 odd vertices and 5 even vertices.
A) Euler circuit
B) Euler circuit but not an Euler path
C) neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path
D) Euler path
A) Euler circuit
B) Euler circuit but not an Euler path
C) neither an Euler circuit nor an Euler path
D) Euler path

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
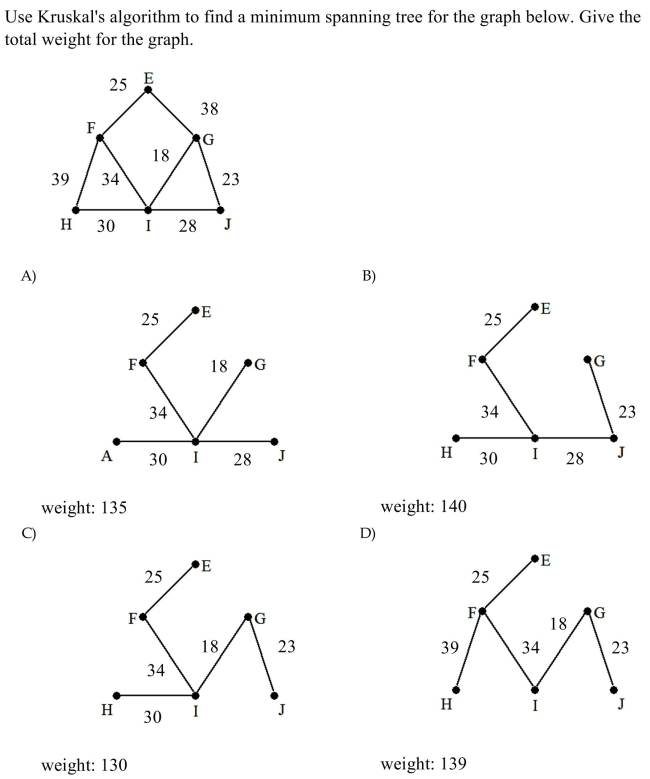

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
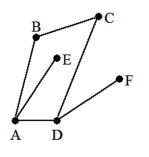
A) B, C
B) A, B, C, D, E, F
C) A, D, E, F
D) A, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
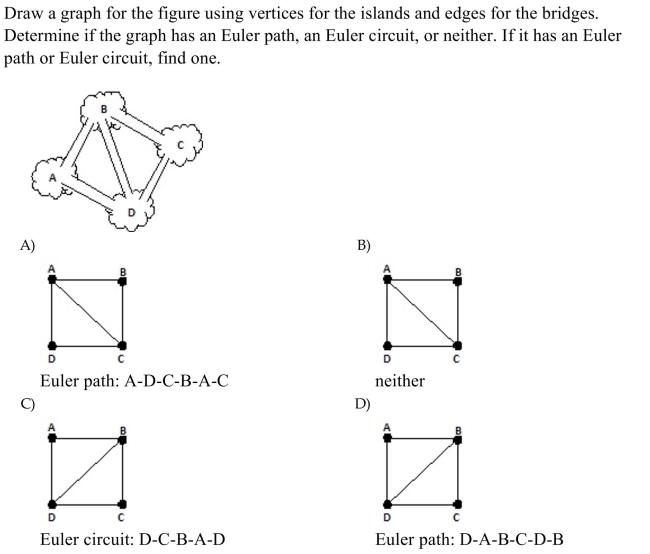

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Find the number of Hamilton circuits if a complete graph has five vertices.
A) 24
B) 32
C) 720
D) 120
A) 24
B) 32
C) 720
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
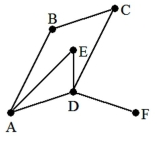
A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Based on the information in the table, use the nearest neighbor method to find an approximation to the shortest route from Angleton to all the other cities and back to Angleton.
A) 243 miles
B) 227 miles
C) 255 miles
D) 258 miles
A) 243 miles
B) 227 miles
C) 255 miles
D) 258 miles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
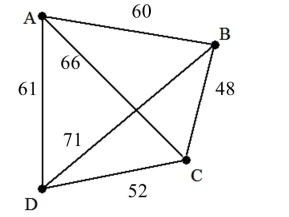
A) 246
B) 209
C) 221
D) 249

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
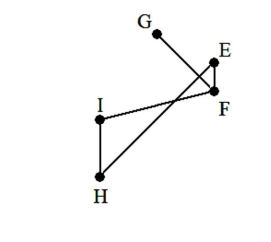
A) The graph is not a tree because it contains a circuit.
B) The graph is a tree.
C) The graph is not a tree because two edges overlap.
D) The graph is not a tree because it is disconnected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
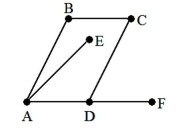
A) C, D, A, B, C
B) C, D, F, C
C) C, D, A, B
D) C, D, F, D, C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
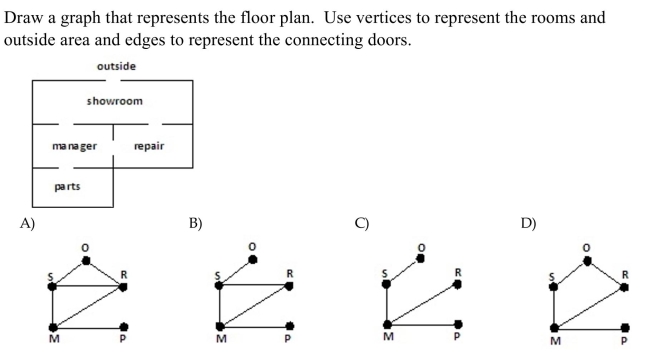

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
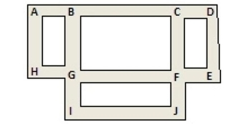
Edges may be removed from the graph that follows so that is becomes a spanning tree. Identify a set of edges that can be removed to accomplish this.
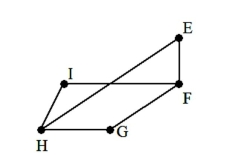
A) EF and EH
B) GH and FG
C) GH and HI
D) HI and FI

A) EF and EH
B) GH and FG
C) GH and HI
D) HI and FI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
State whether the graph has an Euler path, an Euler circuit, or neither. If it has an Euler path or an Euler circuit, find one.
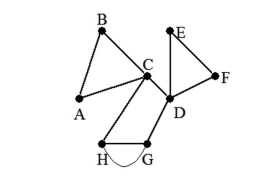
A) neither
B) Euler circuit: A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G, H, C, A
C) Euler path: H, C, A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G
D) Euler path: H, C, A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G, H, G

A) neither
B) Euler circuit: A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G, H, C, A
C) Euler path: H, C, A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G
D) Euler path: H, C, A, B, C, D, E, F, D, G, H, G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
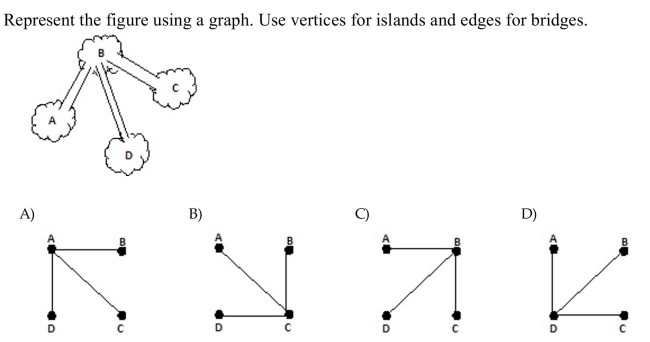

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
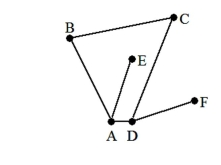
A) F, D, C, B, A, E
B) D, E, A, B, C, D, F
C) F, D, A, B, C, E
D) E, A, D, C, B, A, D, F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At a concert, the production manager needs to run electricity to several lights. The distances in feet are shown. Use a minimum spanning tree to determine the shortest amount of wire that will be needed.
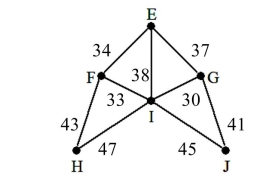
A) 172 feet
B) 176 feet
C) 181 feet
D) 192 feet

A) 172 feet
B) 176 feet
C) 181 feet
D) 192 feet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
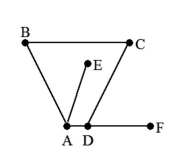
A) AE, BC, DF
B) A, D
C) AE, DF
D) E, F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
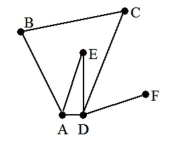
A) A, F
B) A, B, C, D
C) B, C, D, E
D) A, B, C, D, E, F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
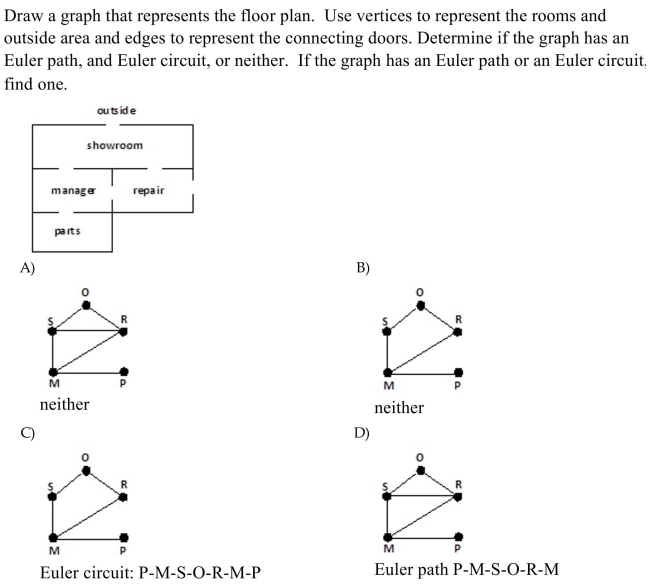

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



