Deck 12: Analysis of Variance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Analysis of Variance
1
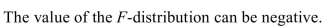
False
2
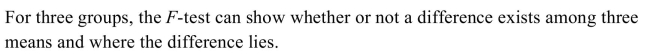
True
3
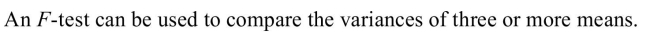
False
4
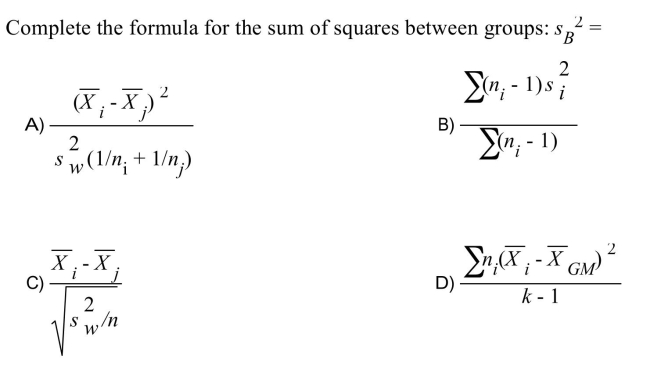

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In an Analysis of Variance Summary Table, if the Mean Square Between = 14 and the Mean Square Within = 27, then the null hypothesis of the groups having the same mean
Is
A) cannot be determined without knowing the Degrees of Freedom (between and within).
B) accepted because 14 < 27.
C) cannot be determined without knowing the Sums of Squares (between and within).
D) rejected because 14 < 27.
Is
A) cannot be determined without knowing the Degrees of Freedom (between and within).
B) accepted because 14 < 27.
C) cannot be determined without knowing the Sums of Squares (between and within).
D) rejected because 14 < 27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In an Analysis of Variance Summary Table, if the Mean Square Between = 41 and the Mean Square Within = 27, then the null hypothesis of the groups having the same mean
Is
A) rejected because 41 > 27.
B) cannot be determined without knowing the Sums of Squares (between and within).
C) accepted because 41 > 27.
D) cannot be determined without knowing the Degrees of Freedom (between and within).
Is
A) rejected because 41 > 27.
B) cannot be determined without knowing the Sums of Squares (between and within).
C) accepted because 41 > 27.
D) cannot be determined without knowing the Degrees of Freedom (between and within).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The variance is made by computing the variance using all
the data and is not affected by differences in the means.
the data and is not affected by differences in the means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
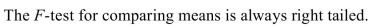

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
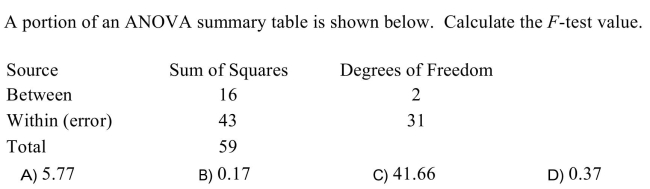

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
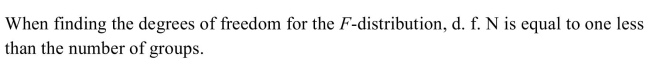

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

A) 15
B) 30
C) 6
D) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

A) F = 0.91
B) F = 3.46
C) F = 1.32
D) F = 2.39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A researcher is comparing 4 groups to test if they have the same means. There are data values altogether. The degrees of freedom for the Between (dfB) and the degrees of
Freedom for the Within (dfW) are
A) dfB = 4, dfW = 63
B) dfB = 3, dfW = 60
C) dfB = 60, dfW = 63
D) dfB = 3, dfW = 63
Freedom for the Within (dfW) are
A) dfB = 4, dfW = 63
B) dfB = 3, dfW = 60
C) dfB = 60, dfW = 63
D) dfB = 3, dfW = 63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

A) The variances of the populations must be equal.
B) The samples must be independent of each other.
C) The sample sizes must be equal.
D) The populations from which the samples were obtained must be normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When there is one independent variable, the analysis of variance is called a
ANOVA.
ANOVA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If there is no difference in the means, the variance
will be approximately equal to the within-group variance.
will be approximately equal to the within-group variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The between-group variance and the within-group variance are sometimes referred to as
A) mean squares.
B) main effects.
C) interaction effects.
D) an ANOVA summary table.
A) mean squares.
B) main effects.
C) interaction effects.
D) an ANOVA summary table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
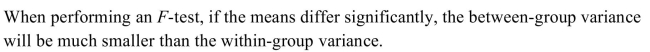

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
ANOVA is an abbreviation for the following term:
A) Scheffé test
B) Tukey test
C) analysis of variance
D) variance
A) Scheffé test
B) Tukey test
C) analysis of variance
D) variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

A) dfN = 35, dfD = 20
B) dfN = 29, dfD = 2
C) dfN = 20, dfD = 35
D) dfN = 2, dfD = 29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
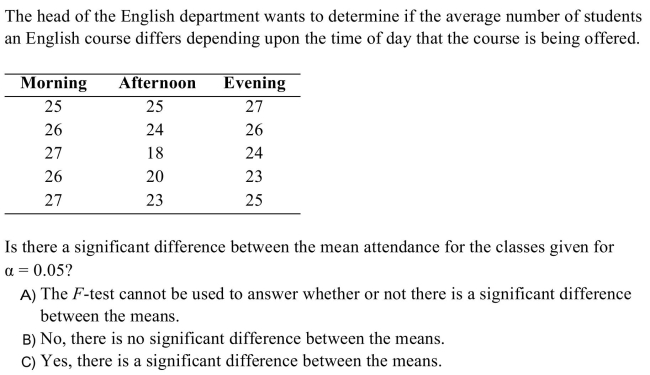

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

A) 0.158
B) 0.031
C) 3.900
D) 0.062

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The test can be used after the analysis of variance has been
completed to make pairwise comparisons between means when groups have the
same sample size.
completed to make pairwise comparisons between means when groups have the
same sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
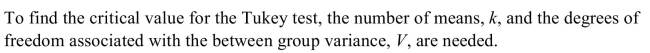

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In order to conduct the Scheffé test, one must compare the means two at a time using all
possible combinations of means.
possible combinations of means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
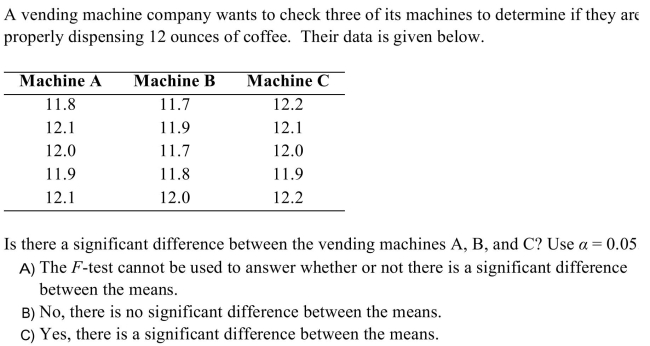

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
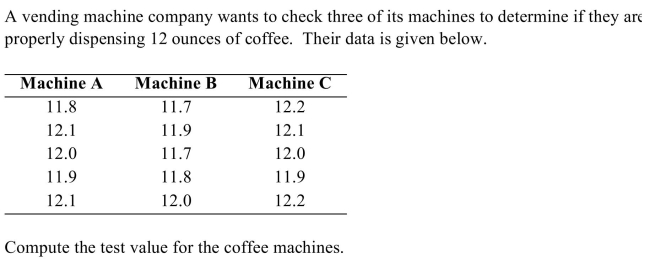
A) 5.06
B) 2.25
C) 4.86
D) 6.62

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The test to detect where the difference is among the means can
be used even if the sample sizes are not equal.
be used even if the sample sizes are not equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
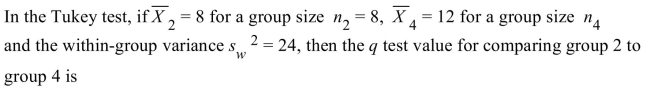
A) -0.17
B) -0.01
C) -0.82
D) -2.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
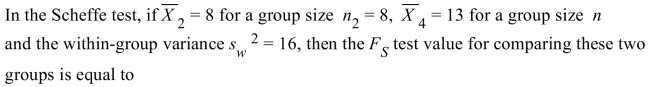
A) -1.25
B) 3.91
C) 6.25
D) 1.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
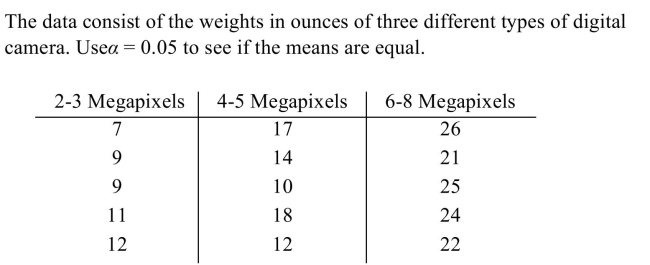

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume that the conclusion from an ANOVA is that the null hypothesis is rejected, in other words that the 8 population means (from equal sized samples) are not all equal. We
Should expect that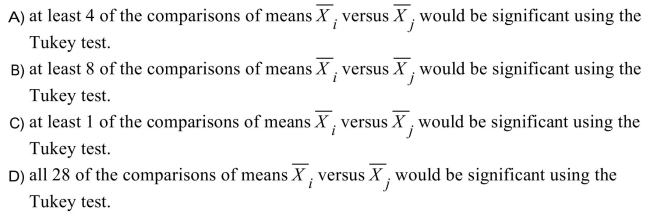
Should expect that
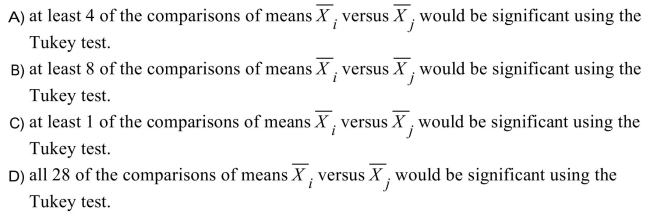

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
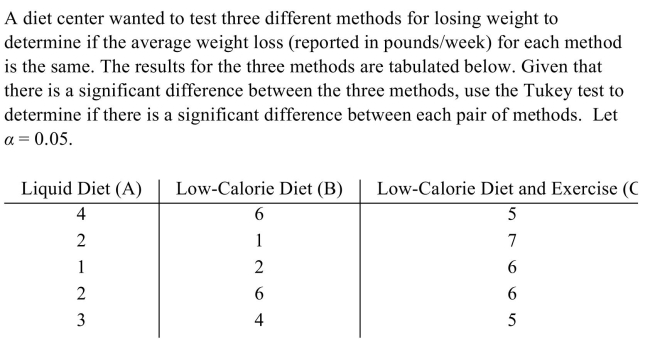

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
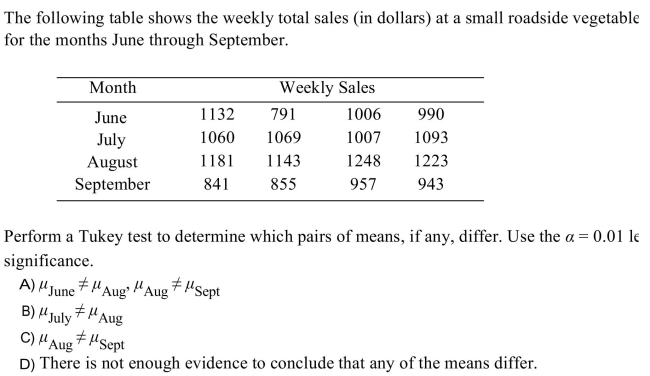

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
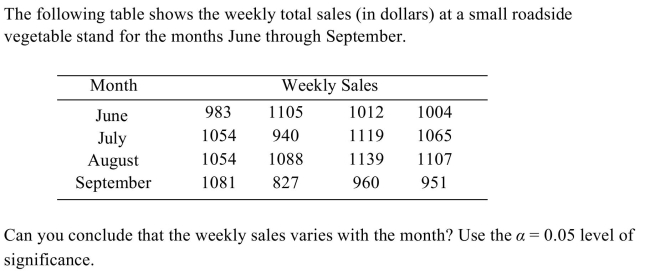
A) No
B) Yes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assume that the conclusion from an ANOVA is that the null hypothesis is rejected, in other words that the 5 population means are not all equal. We should expect that 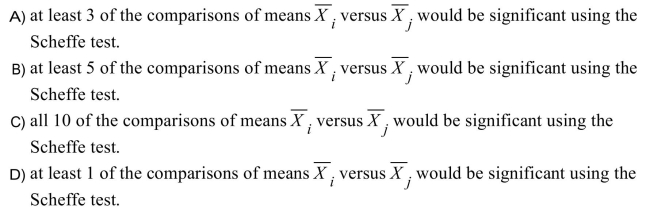
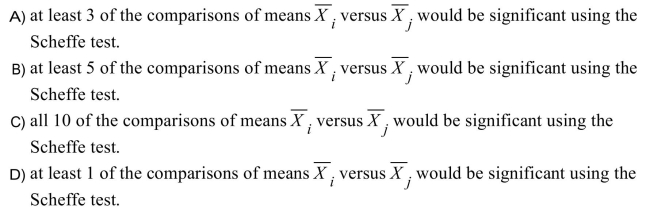

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following assumptions does not apply to the two-way ANOVA?
A) The means of the populations must be equal.
B) The populations from which the samples were obtained must be normally or approximately normally distributed.
C) The samples must be independent of each other.
D) The groups must be equal in sample size.
A) The means of the populations must be equal.
B) The populations from which the samples were obtained must be normally or approximately normally distributed.
C) The samples must be independent of each other.
D) The groups must be equal in sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
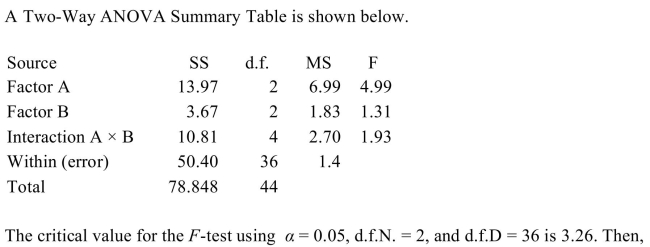
A) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor A and the Interaction (A ×
B) effect should be rejected.
B) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor A should be rejected.
C) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor B should be rejected.
D) all of the null hypotheses should be accepted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
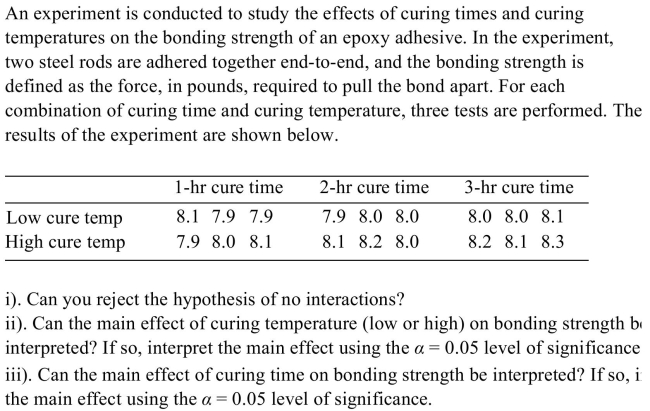

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
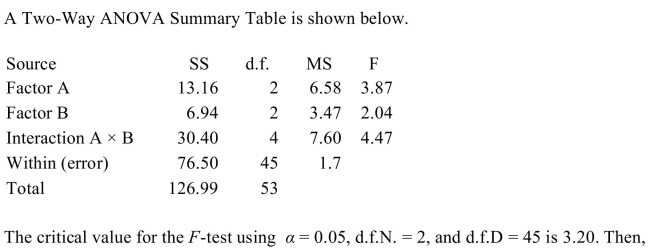
A) all of the null hypotheses should be accepted.
B) effect should be rejected.
B) the null hypothesis concerning Factor A should be rejected.
C) the null hypothesis concerning Factor B should be rejected.
D) the null hypothesis concerning Factor A and the Interaction (A ×

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45

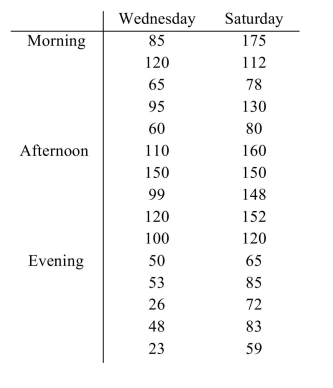

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
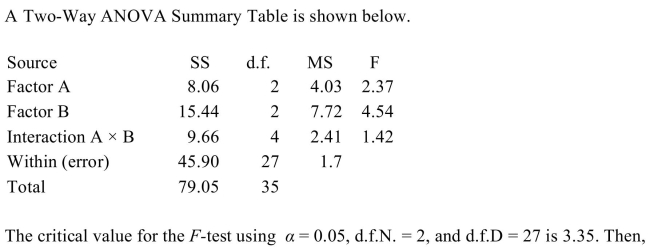
A) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor A should be rejected.
B) effect should be rejected.
B) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor B should be rejected.
C) all of the null hypotheses should be accepted.
D) only the null hypothesis concerning Factor A and the Interaction (A ×

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In 2-way ANOVA, each independent variable investigated could have two or
more different treatments or .
more different treatments or .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
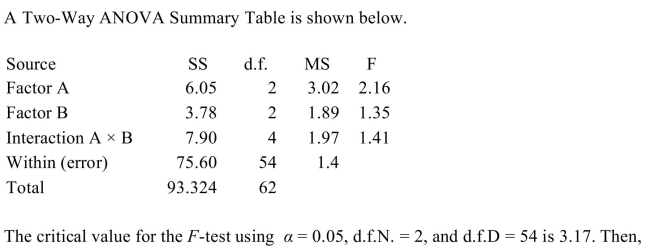
A) The null hypothesis concerning Factor A should be rejected
B) The null hypothesis concerning Factor A and the Interaction (A ×
B) effect should be rejected
C) The null hypothesis concerning Factor B should be rejected
D) All of the null hypotheses should be accepted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In 2-way ANOVA, effects of the independent variables are also referred to as the
.
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a two-way ANOVA design, variable A has four levels and variable B has two
levels. There are eight data values in each cell. What is the d.f.N. for factor B?
levels. There are eight data values in each cell. What is the d.f.N. for factor B?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For a disordinal interaction, the main effects can be interpreted independently of each
other.
other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
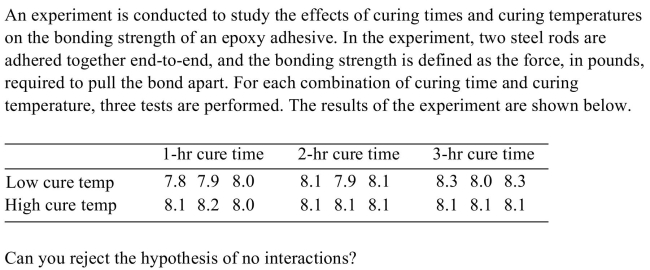
A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A researcher is performing a two-way ANOVA using two factors. The first factor has levels and the second factor has 3 levels. In the ANOVA Summary Table, the degrees of
Freedom for the first and second factors will be
A) 7 d.f. for the first factor and 3 d.f. for the second factor
B) 8 d.f. for the first factor and 4 d.f. for the second factor
C) 6 d.f. for the first factor and 2 d.f. for the second factor
D) 21 d.f. for the first factor and 21 d.f. for the second factor
Freedom for the first and second factors will be
A) 7 d.f. for the first factor and 3 d.f. for the second factor
B) 8 d.f. for the first factor and 4 d.f. for the second factor
C) 6 d.f. for the first factor and 2 d.f. for the second factor
D) 21 d.f. for the first factor and 21 d.f. for the second factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
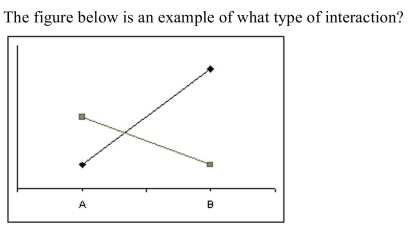
A) disordinal interaction
B) polar interaction
C) cardinal interaction
D) ordinal interaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a two-way ANOVA procedure, variable A has four levels and variable B has two
levels. The d.f.N. for factor A × B would be 3.
levels. The d.f.N. for factor A × B would be 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Independent variables can also be called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
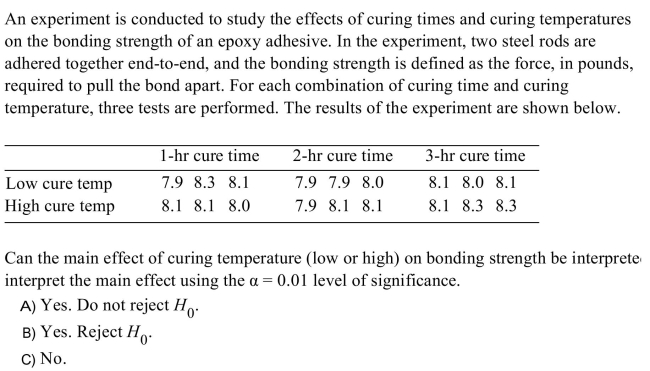

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A researcher is performing a two-way ANOVA using two factors. The first factor has levels and the second factor has 9 levels. In the ANOVA Summary Table, the degrees of
Freedom for the interaction between the first and second factors will be
A) 32
B) 27
C) 24
D) 36
Freedom for the interaction between the first and second factors will be
A) 32
B) 27
C) 24
D) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
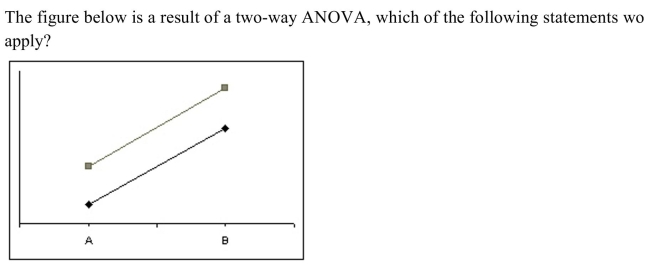
A) The graph does not give any indication of whether or not there is an interaction effect.
B) The main effects should not be interpreted without considering the interaction effect.
C) There is no significant interaction effect.
D) There is a significant interaction effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
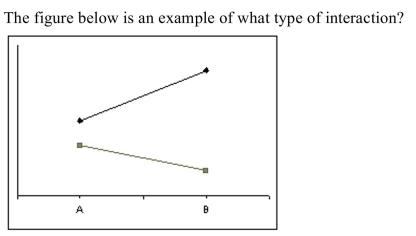
A) disordinal interaction
B) ordinal interaction
C) cardinal interaction
D) There is no interaction because the lines do not cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
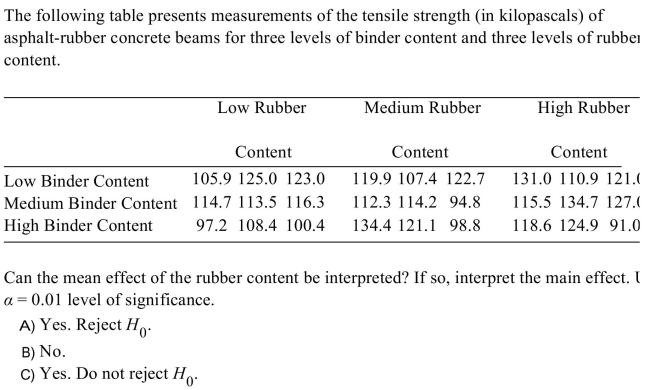

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
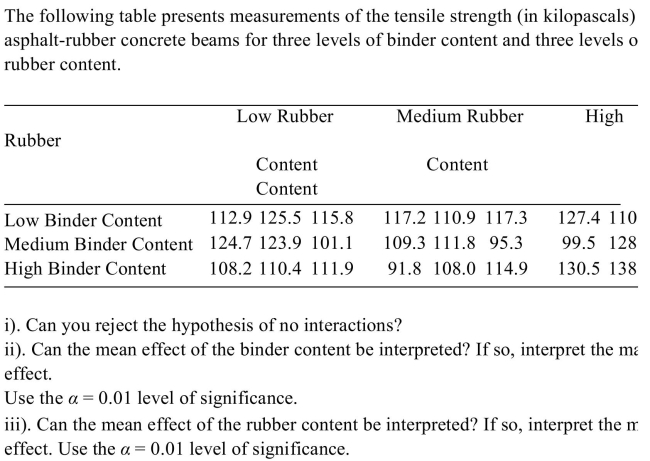

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
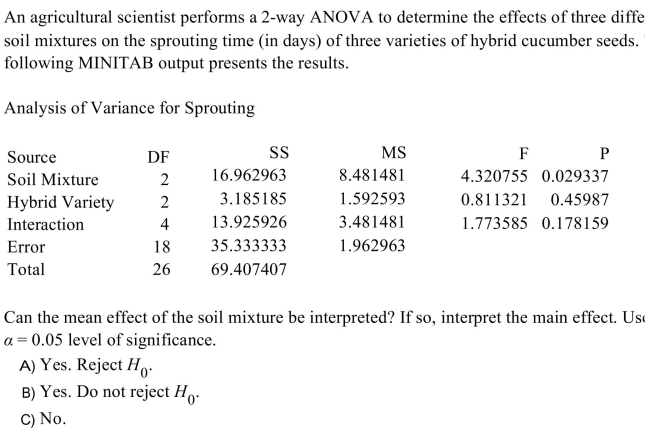

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
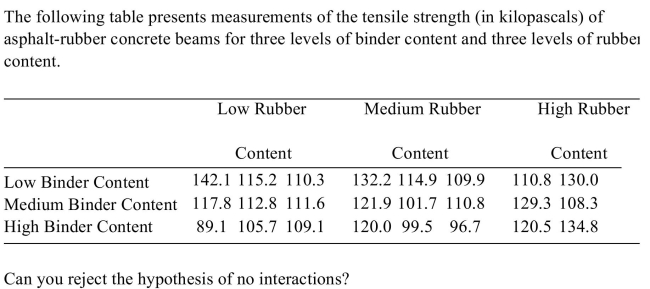
A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
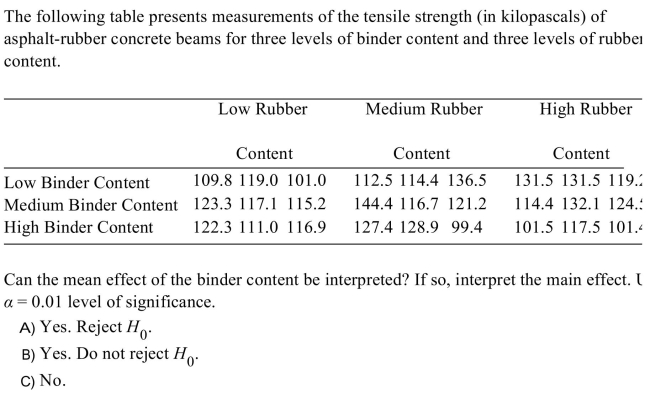

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
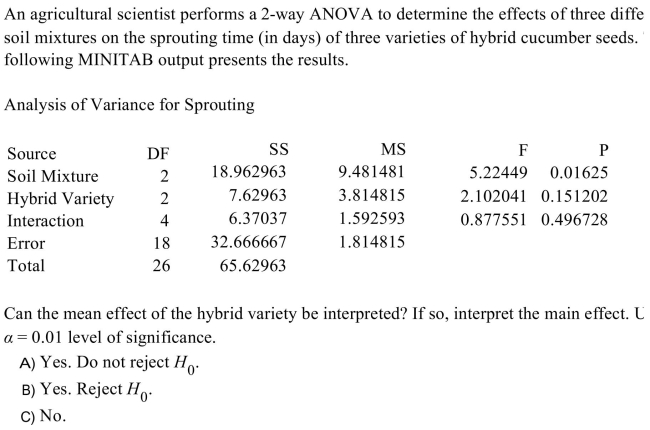

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
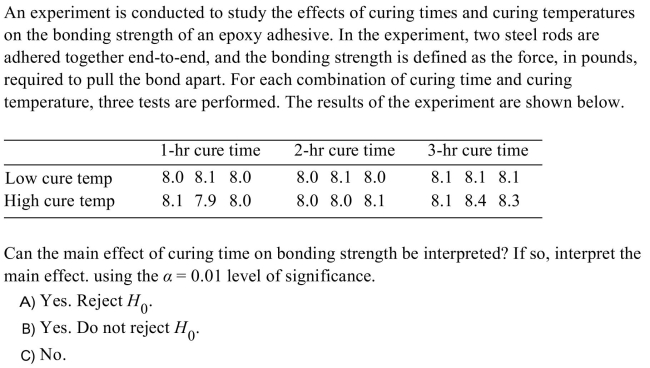

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
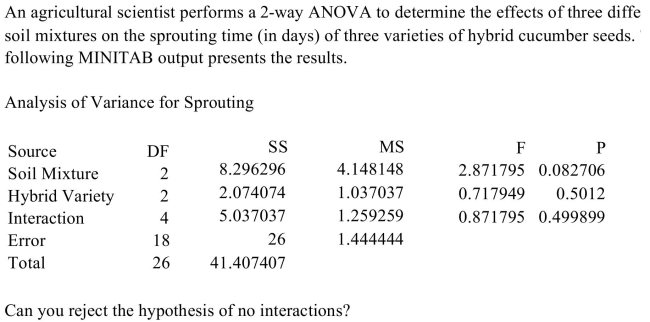
A) No
B) Yes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



