Deck 6: Samples and Populations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Samples and Populations
1
When increasing the level of confidence from 95% to 99%, we:
A)lose confidence but gain precision.
B)lose precision but gain confidence that our answer interval is accurate.
C)lose precision and lose confidence that our answer interval is accurate.
D)none of the above.
A)lose confidence but gain precision.
B)lose precision but gain confidence that our answer interval is accurate.
C)lose precision and lose confidence that our answer interval is accurate.
D)none of the above.
lose precision but gain confidence that our answer interval is accurate.
2
The standard deviation of a sampling distribution of means is:
A)equal to the population standard deviation.
B)greater than the population standard deviation.
C)less than the population standard deviation.
D)none of the above.
A)equal to the population standard deviation.
B)greater than the population standard deviation.
C)less than the population standard deviation.
D)none of the above.
less than the population standard deviation.
3
A sample is usually:
A)a little larger than the population.
B)smaller than the population.
C)more tedious and expensive to obtain than the entire population.
D)not reflective of the population.
A)a little larger than the population.
B)smaller than the population.
C)more tedious and expensive to obtain than the entire population.
D)not reflective of the population.
smaller than the population.
4
Research that analyzes a portion of an entire population is carried out on a(n):
A)sample.
B)population.
C)census.
D)sur vey.
A)sample.
B)population.
C)census.
D)sur vey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The standard error of the mean:
A)is the same as the sample standard deviation.
B)is the same as the population standard deviation.
C)is the standard deviation of a theoretical sampling distribution.
D )is equal to the sample size minus 1.
A)is the same as the sample standard deviation.
B)is the same as the population standard deviation.
C)is the standard deviation of a theoretical sampling distribution.
D )is equal to the sample size minus 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The social researcher taking a random sample usually uses:
A)a hat with slips of paper.
B)a lottery ping-pong ball picker.
C)an actuarial table.
D)a table of random numbers.
A)a hat with slips of paper.
B)a lottery ping-pong ball picker.
C)an actuarial table.
D)a table of random numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Pollsters sometimes refer to sampling error as the:
A)mistake.
B)mu.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)m argin of error.
A)mistake.
B)mu.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)m argin of error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When increasing our level of confidence from 95% to 99%, the interval:
A)grows.
B)shrinks.
C)remains the same.
D)none of the above
A)grows.
B)shrinks.
C)remains the same.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The greater the degrees of freedom, the __________ the sample size and the __________ The t distribution approximates the normal distribution.
A)smaller; more closely
B)larger; more closely
C)larger; less closely
D )smaller; less closely
A)smaller; more closely
B)larger; more closely
C)larger; less closely
D )smaller; less closely

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When estimating a population mean, the degrees of freedom, df, is:
A)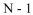
B)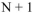
C)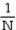
D)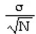
A)
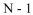
B)
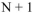
C)
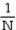
D)
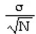

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The difference between the sample mean and the population mean is called:
A)mean variance.
B)sample variance.
C)sampling error.
D)po pulation variance.
A)mean variance.
B)sample variance.
C)sampling error.
D)po pulation variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true of the sampling distribution of means?
A)The sampling distribution of means approximates the normal curve.
B)The mean of a sampling distribution of means is equal to the population mean.
C)The standard deviation of a sampling distribution of means is smaller than the standard
Deviation of the population.
D)all of the above
A)The sampling distribution of means approximates the normal curve.
B)The mean of a sampling distribution of means is equal to the population mean.
C)The standard deviation of a sampling distribution of means is smaller than the standard
Deviation of the population.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Regardless of how well the sampling plan has been designed, with the researcher's best Intentions, no cheating, and no mistakes, a difference between the sample mean and the Population mean known as ______ will almost always be present.
A)measurement mishap
B)sampling error
C)human error
D)si gma erroneous
A)measurement mishap
B)sampling error
C)human error
D)si gma erroneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In using a table of random numbers:
A)always disregard numbers that come up a second time.
B)always disregard numbers that are higher than needed.
C)always include your one favorite number.
D)a and b
A)always disregard numbers that come up a second time.
B)always disregard numbers that are higher than needed.
C)always include your one favorite number.
D)a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The mean of a sampling distribution of means is:
A)equal to the population mean.
B)greater than the population mean.
C)less than the population standard deviation.
D)none of the above.
A)equal to the population mean.
B)greater than the population mean.
C)less than the population standard deviation.
D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A frequency distribution of a large number of random sample means which have been Drawn from the same population is called:
A)the standard error of measurement.
B)the sampling error.
C)the sampling distribution of means.
D)the standard error of the means.
A)the standard error of measurement.
B)the sampling error.
C)the sampling distribution of means.
D)the standard error of the means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Researchers deal with an extra amount of uncertainty in estimating the standard error of The mean with this distribution:
A)normal
B)z
C)asymmetrical
D)t
A)normal
B)z
C)asymmetrical
D)t

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The process of using a table of random numbers:
A)inevitably leads to calculation errors.
B)yields a representative sample.
C)yields a non-representative sample.
D)pr oduces researcher-introduced bias.
A)inevitably leads to calculation errors.
B)yields a representative sample.
C)yields a non-representative sample.
D)pr oduces researcher-introduced bias.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The researcher strives to give every member of the population an equal chance of being
Drawn via:
A)biasing.
B)non-random sampling.
C)random sampling.
D)pers onal judgement.
Drawn via:
A)biasing.
B)non-random sampling.
C)random sampling.
D)pers onal judgement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Through the sampling process, social researchers seek to generalize from a small group to a larger group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The question below refers to the following situation:
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data are as follows:
The unbiased estimate of the standard error of the mean is __________.
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data are as follows:

The unbiased estimate of the standard error of the mean is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The question below refers to the following situation:
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data
are as follows:
The 99% confidence interval with 14 degrees of freedom is 2.977 according to the t Table.
Therefore, the values of this confidence interval are __________.
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data
are as follows:

The 99% confidence interval with 14 degrees of freedom is 2.977 according to the t Table.
Therefore, the values of this confidence interval are __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The question below refers to the following situation:
A random sample of 500 registered voters in a city shows that 53% of the voters support higher taxes to help fund public schools.
Estimate the population proportion with a 95% confidence interval.
A random sample of 500 registered voters in a city shows that 53% of the voters support higher taxes to help fund public schools.
Estimate the population proportion with a 95% confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Holding sample size constant, the social researcher must choose between greater precisionnor greater confidence of being correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The question below refers to the following data: 
Using t-scores, calculate the 99% confidence interval. (Find the t-values in Table C of
Appendix C.)

Using t-scores, calculate the 99% confidence interval. (Find the t-values in Table C of
Appendix C.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following equation is called the __________. 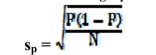
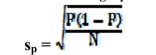

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Unfortunately, sampling error cannot be calculated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The question below refers to the following data: 
Using t-scores, calculate the 95% confidence interval. (Find the t-values in Table C of
Appendix C.)

Using t-scores, calculate the 95% confidence interval. (Find the t-values in Table C of
Appendix C.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The question below refers to the following situation:
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.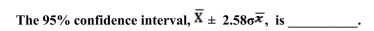
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.
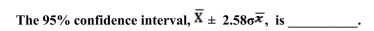

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The question below refers to the following situation:
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data are as follows:
The 95% confidence interval with 14 degrees of freedom is 2.145 according to the t Table.
Therefore, the values of this confidence interval are __________.
A researcher interested in school violence investigates the extent to which conflict occurs in schools. She obtains a weekly count of witnessed arguments from 15 students. The data are as follows:

The 95% confidence interval with 14 degrees of freedom is 2.145 according to the t Table.
Therefore, the values of this confidence interval are __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The question below refers to the following situation:
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.The standard error of the mean is __________.
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.The standard error of the mean is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
h a standard deviation of .3. 
Without using t-scores, calculate the 99% confidence interval.

Without using t-scores, calculate the 99% confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The question below refers to the following situation:
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.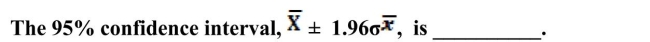
An education researcher is interested in studying student performance on the SAT. The researcher takes a random sample of 200 students and calculates a sample mean of 1600 and a sample standard deviation of 90.
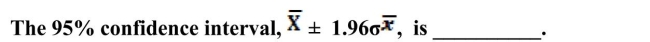

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Compared with the 95% confidence interval, the 99% confidence interval is more narrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The question below refers to the following situation:
A random sample of 500 registered voters in a city shows that 53% of the voters support higher taxes to help fund public schools.
The standard error of the proportion is __________.
A random sample of 500 registered voters in a city shows that 53% of the voters support higher taxes to help fund public schools.
The standard error of the proportion is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The question below refers to the following data: 
Estimate the standard error of the mean.

Estimate the standard error of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The question below refers to the following situation:
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction:
Estimate the standard error of the mean.
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction:

Estimate the standard error of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
h a standard deviation of .3. 
Estimate the standard error of the mean.

Estimate the standard error of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
h a standard deviation of .3. 
Without using t-scores, calculate the 95% confidence interval.

Without using t-scores, calculate the 95% confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the standard error of the mean when analyzing the IQs of 25 adults, given that the population standard deviation of adult IQ is 10?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The question below refers to the following situation:
A random sample of 175 people surveyed were asked whether or not they always stop
completely at stop signs. Seventy-five percent responded that they do not.
Estimate the population proportion with a 95% confidence interval.
A random sample of 175 people surveyed were asked whether or not they always stop
completely at stop signs. Seventy-five percent responded that they do not.
Estimate the population proportion with a 95% confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The question below refers to the following situation:
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction: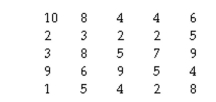
Calculate the 99% confidence interval (use the t-score method; you can find t-values in
Table C of Appendix C):
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction:

Calculate the 99% confidence interval (use the t-score method; you can find t-values in
Table C of Appendix C):

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The question below refers to the following situation:
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction: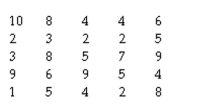
Calculate the 95% confidence interval (use the t-score method; you can find t-values in
Table C of Appendix C):
Given the following raw scores on a standard 10-point scale of student satisfaction:

Calculate the 95% confidence interval (use the t-score method; you can find t-values in
Table C of Appendix C):

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The question below refers to the following situation:
A random sample of 175 people surveyed were asked whether or not they always stop
completely at stop signs. Seventy-five percent responded that they do not.
What is the standard error of the proportion?
A random sample of 175 people surveyed were asked whether or not they always stop
completely at stop signs. Seventy-five percent responded that they do not.
What is the standard error of the proportion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



