Deck 20: Iscriminant, Factor and Cluster Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Iscriminant, Factor and Cluster Analysis
1
The objective of a discriminant analysis is to predict the value of the dependent variable based on the values of the fixed independent variables.
False
2
Regression and Discriminant analyses are conceptually similar
False
3
A factor score is a measurement of how closely related each input variable is to a derived factor.
False
4
The group mean, in a discriminant analysis, is known as the centroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Discriminant analysis can only be used for description and not for prediction purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Discriminant analysis and ANOVA are the appropriate statistical techniques for testing the hypotheses that the group means of two or more groups are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Factor loadings are a measurement of the correlations between the factors and the original variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In discriminant analysis, predictors with a large coefficient contribute more to the discriminating power of the function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One rule of thumb in deciding on the number of factors to retain is to include all factors that explain at least 50 percent of the variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Each input variable in a study is termed a factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Each respondent has a factor score on each factor in addition to the respondent's rating on the original variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
One function of factor analysis is to identify underlying constructs in the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The underlying assumption in a discriminant analysis is that the independent variables are assumed to be normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Factor analysis is usefully employed when there is a need to determine the direction of causality between two or three variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Discriminant analysis techniques are used to classify into one of two or more alternate groups based on a set of measurements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Larger values of Wilks lambda indicate that the group means appear to be different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The statistical explanation for discriminant analysis is that of maximizing the between-group variance relative to the within-group variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In discriminant analysis, with 'm' groups and 'p' predictor variables, min p,m-1) gives the number of discriminant functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Factor analysis is usefully employed when it is desirable to combine several questions, thereby creating a new variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A factor is a variable or construct that is not directly observable but needs to be inferred from the input variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Simple Euclidean distance is a common measurement of similarity on a perceptual map.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
It is always advisable to have as many factors as the number of input variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In quick clustering, the first step is to identify the highest entry in each column of a matrix of inter-band inter-product, etc.) correlations. 38.Consider the following data: 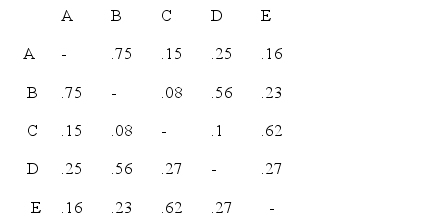 The following is an accurate graphical representation of the data shown above:
The following is an accurate graphical representation of the data shown above: 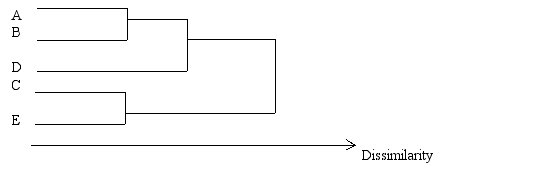
 The following is an accurate graphical representation of the data shown above:
The following is an accurate graphical representation of the data shown above: 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a clustering procedure starts with one cluster and subdivides until all objects are in their own single-object cluster, the procedure is termed top-down hierarchical clustering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The ABC Company is involved in trying to segment its market so that it can better design specific marketing programs directed at each segment.One method of segmenting that it might use is cluster analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Factor loadings and correlations are identical if each variable has its mean subtracted and is divided by its standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
While analyzing and interpreting consumer perception data using factor analysis, a researcher found the factor loading on Factor 1 to be high.However, he could not interpret the factor meaningfully. A probable cause for this situation is computation error or shortsightedness in his interpretation, since a high loading ensures meaningfulness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Varimax searches for a set of factor loadings such that each factor has some loadings close to 0 and some loadings close to -1 or +1. Factor Loadings 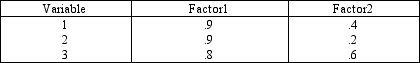


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An attractive feature of varimax rotation is that it may retain the variance explained, while reducing the number of factors in the solution as compared to principal components analysis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
After performing a principal components analysis, a researcher finds that the cumulative variance explained by the solution is 0.56.He can increase the explained variance by performing a varimax rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The basic task in cluster analysis is to uncover competing explanations for a causal phenomenon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A nonhierarchical clustering program is one in which objects are allowed to leave one cluster to join another as clusters are being formed if the clustering criterion will be improved by doing so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The first factor accounts for more of the variation in the data than the second factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The percent of variance explained is a summary measurement indicating how much of the total original variance of all the respondents is represented by the factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In both principal components analysis and varimax rotation, the factors are constrained to be uncorrelated or geometrically perpendicular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The variation in variable 3 is shown to be completely explained by the two-factor solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All factor analysis methods constrain the factors to be uncorrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Rotation of factors changes the interpretation of the factors while retaining the principal component patterns of loadings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Communality is the percent of a variable's variance which contributes to the correlation with other variables or is common to other variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An attractive feature of principal components analysis is the easy interpretability of the factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The analysis technique used to identify variables that contribute to differences in the a prior defined groups is
A)regression.
B)discriminant analysis.
C)conjoint analysis.
D)factor analysis.
E)multidimensional scaling.
A)regression.
B)discriminant analysis.
C)conjoint analysis.
D)factor analysis.
E)multidimensional scaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is true about factor analysis?
A)it is a multivariate data analysis technique.
B)it can be used by researchers to do cluster analysis and multidimensional scaling.
C)it can be used by researchers to identify underlying constructs in the data.
D)it can be used to reduce the number of variables to a more manageable set.
E)all of these are true.
A)it is a multivariate data analysis technique.
B)it can be used by researchers to do cluster analysis and multidimensional scaling.
C)it can be used by researchers to identify underlying constructs in the data.
D)it can be used to reduce the number of variables to a more manageable set.
E)all of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The amount of variance a variable shares with other variables is called
A)communality
B)factor loading
C)factor score
D)none of the above
A)communality
B)factor loading
C)factor score
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following methods of clustering uses the "nearest neighbor" approach ?
A)complete linkage
B)single linkage
C)Ward's method
D)average linkage
A)complete linkage
B)single linkage
C)Ward's method
D)average linkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A major advantage of cluster analysis is the availability of standard statistical tests to ensure that the output does not represent pure randomness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Nonhierarchical clustering will produce tighter clusters due to the fact that an object will be admitted into a cluster only if it improves the clustering criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following:  Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Factor 1 is composed of variables 1 and 2.
B)Factor 1 is composed of variables 1, 2, and 4.
C)Factor 1 is composed of variables 3 and 5.
D)Factor 2 is composed of variables 1, 2, and 4.
E)None of the above
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A)Factor 1 is composed of variables 1 and 2.
B)Factor 1 is composed of variables 1, 2, and 4.
C)Factor 1 is composed of variables 3 and 5.
D)Factor 2 is composed of variables 1, 2, and 4.
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The simple correlation between the independent variable and the discriminant function is represented by
A)discriminant loading
B)structure correlation
C)total correlation matrix
D)centroid
A)discriminant loading
B)structure correlation
C)total correlation matrix
D)centroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In discriminant analysis, with M groups and p predictor variables, the number of discriminant functions is given by
A)m-1, p-1)
B)m-1, p)
C)m, p-1)
D)m, p)
E)none of the above.
A)m-1, p-1)
B)m-1, p)
C)m, p-1)
D)m, p)
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Initial starting points in nonhierarchical clustering is represented by
A)cluster membership
B)cluster seeds
C)cluster centurions
D)none of the above
A)cluster membership
B)cluster seeds
C)cluster centurions
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Factor is observable that is why it is a variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For discrimination to be based on all predictors the most appropriate function estimation method is
A)sequential
B)direct
C)pooled
D)stepwise
A)sequential
B)direct
C)pooled
D)stepwise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which one of the following is not an objective of discriminant analysis?
A)Determining linear combinations of the predictor variables to separate groups
B)Developing procedures for assigning new objects
C)Testing whether significant differences exist between the groups
D)Determining the variables that explain the intergroup differences
E)Predicting the level of the dependent variable when the independent variable is changed.
A)Determining linear combinations of the predictor variables to separate groups
B)Developing procedures for assigning new objects
C)Testing whether significant differences exist between the groups
D)Determining the variables that explain the intergroup differences
E)Predicting the level of the dependent variable when the independent variable is changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
All of the following are true about factor analysis except
A)it is a technique that serves to combine questions, thereby creating new variables.
B)it is an analysis of interdependence technique that analyzes the interdependence between questions, variables, or objects.
C)it is most closely related to multivariate regression and multivariate analysis of variance in the nature of tasks
Performed.
D)it can help the analyst determine which questions, variables, or objects are redundant and what they are measuring.
E)all of these are true
A)it is a technique that serves to combine questions, thereby creating new variables.
B)it is an analysis of interdependence technique that analyzes the interdependence between questions, variables, or objects.
C)it is most closely related to multivariate regression and multivariate analysis of variance in the nature of tasks
Performed.
D)it can help the analyst determine which questions, variables, or objects are redundant and what they are measuring.
E)all of these are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Given multivariate data, cluster analysis techniques seek to identify natural groupings of objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the primary purpose is data reduction one would use
A)cluster analysis
B)factor analysis
C)discriminant analysis
D)conjoint analysis
A)cluster analysis
B)factor analysis
C)discriminant analysis
D)conjoint analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the following data: 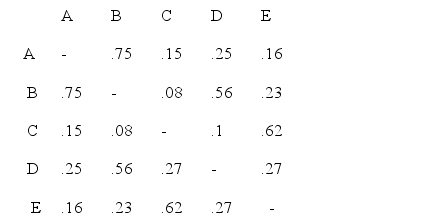 The clusters using the quick cluster technique.identified by the table above are
The clusters using the quick cluster technique.identified by the table above are
A)A, B, and D; and C and E.
B)A, B, and C; and D and E.
C)A and B; and C, D, and E.
D)A, C, and D; and B and E.
E)None of the above.
 The clusters using the quick cluster technique.identified by the table above are
The clusters using the quick cluster technique.identified by the table above areA)A, B, and D; and C and E.
B)A, B, and C; and D and E.
C)A and B; and C, D, and E.
D)A, C, and D; and B and E.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A plot of eigenvalues against the number of factors is called
A)factor loading
B)scree
C)factor score
D)communality
A)factor loading
B)scree
C)factor score
D)communality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When analyzing differences between groups 2 or more.one would use
A)cluster analysis
B)factor analysis
C)discriminant analysis
D)conjoint analysis
A)cluster analysis
B)factor analysis
C)discriminant analysis
D)conjoint analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In factor analysis each subsequent factor accounts for
A)increasing amount of variance in data
B)decreasing amount of variance in data
C)same amount of variance in data
D)none of the above
A)increasing amount of variance in data
B)decreasing amount of variance in data
C)same amount of variance in data
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements are true of the hierarchical approach? I.The approach is relatively easy to read and interpret. II.The output has the logical structure that should theoretically always exist. III.The subsequent analysis is constrained by the first combination or separation of objects. IV.It tends to be more reliable. V.If the program makes a close decision early in the analysis that subsequently proves to be wrong with respect to the clustering criterion, it can be remedied. VI.Split-sample results will tend to look more similar.
A)I and II.
B)I, II, III, V and VI.
C)I, IV, V, and VI.
D)I, II and III.
E)IV, V, and VI.
A)I and II.
B)I, II, III, V and VI.
C)I, IV, V, and VI.
D)I, II and III.
E)IV, V, and VI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The basic assumption of cluster analysis is that 1-It is always possible to group data into well-defined homogeneous groups. 2-The basic measurement of similarity is a valid measurement of proximity between objects. 3-There is theoretical justification for structuring the objects into clusters.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)1 and 2
E)2 and 3
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)1 and 2
E)2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The amount of variance in the original variables that is associated with a factor is represented by
A)factor loading
B)scree
C)factor score
D)eigenvalue
E)cluster seed
A)factor loading
B)scree
C)factor score
D)eigenvalue
E)cluster seed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
.The coefficients that link the factors to the variables are called
A)factor loadings
B)screes
C)factor scores
D)eigenvalues
E)cluster seeds
A)factor loadings
B)screes
C)factor scores
D)eigenvalues
E)cluster seeds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is a valid approach to clustering? 1-"Top-down" hierarchical clustering 2-"Top-down" nonhierarchical clustering 3-Piecewise linear clustering 4-"Bottom-up" nonhierarchical clustering
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)2, 3, and 4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)2, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the data shown below: 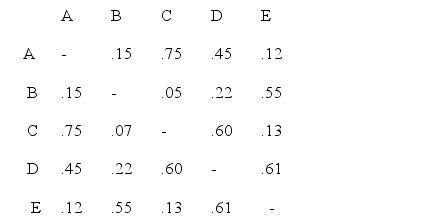 Using the quick clustering technique and a criterion that the average measurement of similarity within clusters be at least 0.60, the following clusters are uncovered for the data shown above:
Using the quick clustering technique and a criterion that the average measurement of similarity within clusters be at least 0.60, the following clusters are uncovered for the data shown above:
A)A, C, and D; and B and E.
B)A and C; and B and E.
C)A and C.
D)A, C, and D.
E)None of the above.
 Using the quick clustering technique and a criterion that the average measurement of similarity within clusters be at least 0.60, the following clusters are uncovered for the data shown above:
Using the quick clustering technique and a criterion that the average measurement of similarity within clusters be at least 0.60, the following clusters are uncovered for the data shown above:A)A, C, and D; and B and E.
B)A and C; and B and E.
C)A and C.
D)A, C, and D.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



