Deck 9: Analytical Chemistry: Spectroscopy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Analytical Chemistry: Spectroscopy
1
What type of compound corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 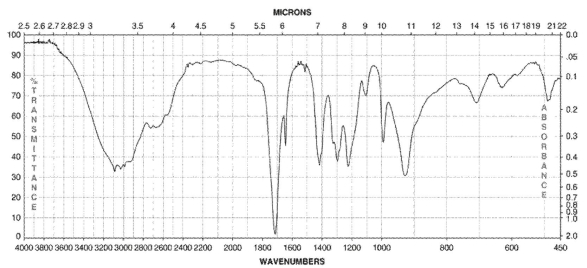
A) ketone
B) carboxylic acid
C) amine
D) alcohol
E) alkane

A) ketone
B) carboxylic acid
C) amine
D) alcohol
E) alkane
carboxylic acid
2
Which set of m/z values is most likely to be observed in the mass spectrum of the ketone below?

A) 100,57,43
B) 100,86,72
C) 100,85,29
D) 57,43,30
E) 102,100,85

A) 100,57,43
B) 100,86,72
C) 100,85,29
D) 57,43,30
E) 102,100,85
100,57,43
3
As conjugation increases across a series of molecules, which of the following statements is true?
I. The HOMO-LUMO gap becomes smaller.
II. The number of possible UV transitions increases.
III. Molecules absorb light at shorter wavelengths.
IV. Molecules absorb light of higher energy.
A) I
B) I, II
C) I, III
D) I, II, IV
E) I, II, III, IV
I. The HOMO-LUMO gap becomes smaller.
II. The number of possible UV transitions increases.
III. Molecules absorb light at shorter wavelengths.
IV. Molecules absorb light of higher energy.
A) I
B) I, II
C) I, III
D) I, II, IV
E) I, II, III, IV
I, II
4
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 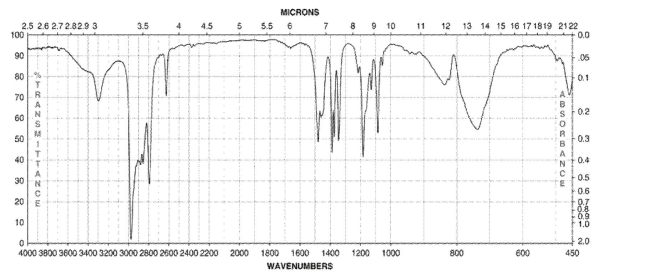
A)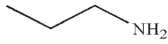
B)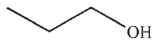
C)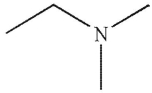
D)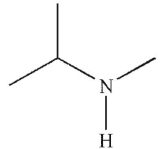
E)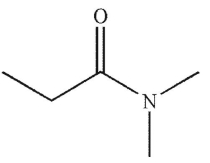

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is true?
A) All nuclei are NMR active.
B) Only nuclei with nonzero spins are NMR active.
C) Only nuclei with spins of 1/2 are NMR active.
D) A nucleus with a spin of 3/2 , such as 11B , is not NMR active.
E) The spin value of a nucleus is not related to whether it will be NMR active.
A) All nuclei are NMR active.
B) Only nuclei with nonzero spins are NMR active.
C) Only nuclei with spins of 1/2 are NMR active.
D) A nucleus with a spin of 3/2 , such as 11B , is not NMR active.
E) The spin value of a nucleus is not related to whether it will be NMR active.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At a field strength of 90 MHz , the resonance frequency of a particular proton is 216 Hz . What is the resonance frequency of this proton at a field strength of 600 MHz ?
A) 2.4 Hz
B) 216 Hz
C) 600 Hz
D) 1440 Hz
E) 33 Hz
A) 2.4 Hz
B) 216 Hz
C) 600 Hz
D) 1440 Hz
E) 33 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the stationary phase in gas chromatography?
A)helium or hydrogen gas
B)a high-molecular-weight polymer
C)an organic solvent
D)the sample
E)either a or b
A)helium or hydrogen gas
B)a high-molecular-weight polymer
C)an organic solvent
D)the sample
E)either a or b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement about shielding is false?
A)Hydrogens that are deshielded experience a net magnetic field that is greater than the applied magnetic field.
B)Hydrogens that are shielded experience a net magnetic field that is less than the applied magnetic field.
C)The net magnetic field experienced by the hydrogens in a given molecule is uniform throughout the molecule.
D)As an external magnetic field is applied, electrons in a molecule circulate and create a magnetic field that opposes the external field.
E)Electron-withdrawing groups exert deshielding effects on nearby hydrogens.
A)Hydrogens that are deshielded experience a net magnetic field that is greater than the applied magnetic field.
B)Hydrogens that are shielded experience a net magnetic field that is less than the applied magnetic field.
C)The net magnetic field experienced by the hydrogens in a given molecule is uniform throughout the molecule.
D)As an external magnetic field is applied, electrons in a molecule circulate and create a magnetic field that opposes the external field.
E)Electron-withdrawing groups exert deshielding effects on nearby hydrogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these is not an observed transition when a ground state ethylene molecule absorbs energy?
A)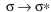
B)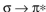
C)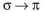
D)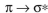
E)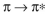
A)
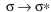
B)
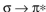
C)
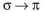
D)
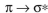
E)
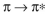

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which m/z value(s) most likely indicates an alkyl chloride?
A) an M peak at 98
B) a base peak at 85 and an M peak at 142
C) a base peak that is 15 mass units lower than the parent ion
D) an M peak at 106 and a peak at 108 that is three times as intense
E) an M peak at 150 and a peak of roughly equal intensity at 152
A) an M peak at 98
B) a base peak at 85 and an M peak at 142
C) a base peak that is 15 mass units lower than the parent ion
D) an M peak at 106 and a peak at 108 that is three times as intense
E) an M peak at 150 and a peak of roughly equal intensity at 152

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Protons generate their own tiny magnetic fields.
B) When no external magnetic field is applied, the two spin states for a proton are equal in energy.
C) In the NMR experiment, radio frequency energy is applied to change the orientation of nuclear spin ("flip" the spin).
D) The presence of an external magnetic field causes a random orientation of the nuclear spins in the atoms in a molecule.
E) Alignment of nuclear spin with an external magnetic field is more favorable than alignment against the field.
A) Protons generate their own tiny magnetic fields.
B) When no external magnetic field is applied, the two spin states for a proton are equal in energy.
C) In the NMR experiment, radio frequency energy is applied to change the orientation of nuclear spin ("flip" the spin).
D) The presence of an external magnetic field causes a random orientation of the nuclear spins in the atoms in a molecule.
E) Alignment of nuclear spin with an external magnetic field is more favorable than alignment against the field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 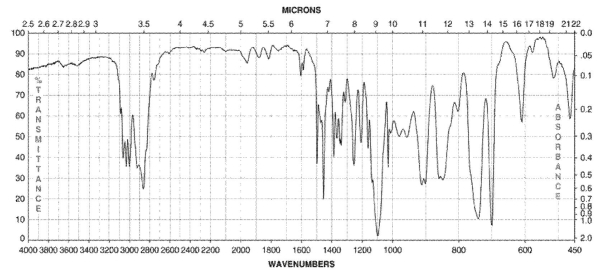
A)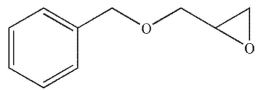
B)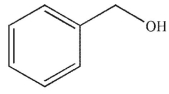
C)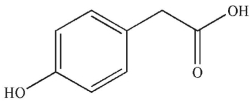
D)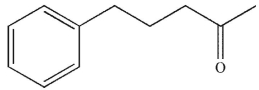
E) none of these compounds

A)

B)

C)

D)

E) none of these compounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements about IR spectroscopy is true?
A) All molecular vibrations can be detected.
B) Absorption of infrared light is associated with both electronic transitions and molecular vibrations.
C) Only vibrations of multiple bonds are observed.
D) For a vibration to be IR active, it must produce a net change in the molecule's dipole moment.
E) Symmetrical vibrations are observed in the IR spectrum, but unsymmetrical vibrations are not.
A) All molecular vibrations can be detected.
B) Absorption of infrared light is associated with both electronic transitions and molecular vibrations.
C) Only vibrations of multiple bonds are observed.
D) For a vibration to be IR active, it must produce a net change in the molecule's dipole moment.
E) Symmetrical vibrations are observed in the IR spectrum, but unsymmetrical vibrations are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 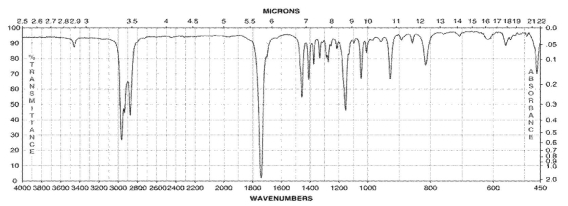
A)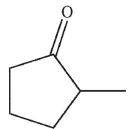
B)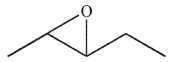
C)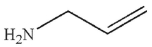
D)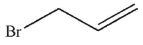
E)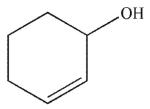

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 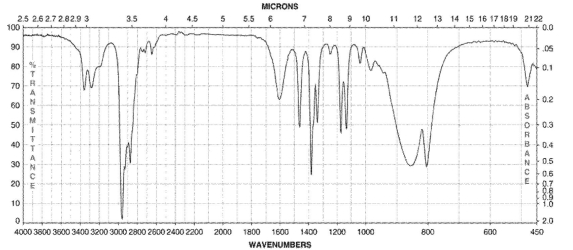
A)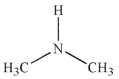
B)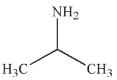
C)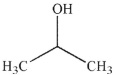
D)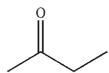
E)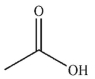

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why are peaks for 13C not observed in a spectrum for 1H ?
A) .13C nuclei are not NMR active.
B) The gyromagnetic ratios for 13C and 1H are similar, so signals generated by these two nuclei are separated from each other.
C) The gyromagnetic ratios for 13C and 1H are sufficiently different that signals generated by these two nuclei are separated from one another.
D) The field strength of the magnet used differs for 13C NMR vs. 1H NMR.
E) The reference substance used in a 13C NMR experiment is different than that used in 1H NMR experiment.
A) .13C nuclei are not NMR active.
B) The gyromagnetic ratios for 13C and 1H are similar, so signals generated by these two nuclei are separated from each other.
C) The gyromagnetic ratios for 13C and 1H are sufficiently different that signals generated by these two nuclei are separated from one another.
D) The field strength of the magnet used differs for 13C NMR vs. 1H NMR.
E) The reference substance used in a 13C NMR experiment is different than that used in 1H NMR experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these molecules do you expect to have the largest value of 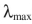 ?
?
A) ethylene
B) 1,3 -butadiene
C) a dodecene (12 double bonds) consisting of isolated alkenes
D) a dodecene (12 double bonds) consisting of fully conjugated alkenes
E) benzene
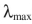 ?
?A) ethylene
B) 1,3 -butadiene
C) a dodecene (12 double bonds) consisting of isolated alkenes
D) a dodecene (12 double bonds) consisting of fully conjugated alkenes
E) benzene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is true?
A) In a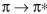 transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
longer wavelength.
B) In a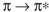 transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
shorter wavelength.
C) In a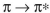 transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
shorter wavelength.
D) In a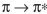 transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
longer wavelength.
E) The HOMO-LUMO gap is related only to energy and not to wavelength.
A) In a
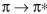 transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy andlonger wavelength.
B) In a
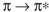 transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy and
transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to lower energy andshorter wavelength.
C) In a
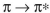 transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
transition, a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy andshorter wavelength.
D) In a
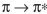 transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy and
transition, a larger HOMO-LUMO gap corresponds to higher energy andlonger wavelength.
E) The HOMO-LUMO gap is related only to energy and not to wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Chemical shift is
A)the area under a given signal.
B)the total number of neighbors that a given hydrogen has.
C)the location of a signal along the x-axis, reported in ppm.
D)the number of peaks into which a signal is split.
E)the distance between the individual "lines" in a signal, reported in Hz.
A)the area under a given signal.
B)the total number of neighbors that a given hydrogen has.
C)the location of a signal along the x-axis, reported in ppm.
D)the number of peaks into which a signal is split.
E)the distance between the individual "lines" in a signal, reported in Hz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the IR spectrum shown here? 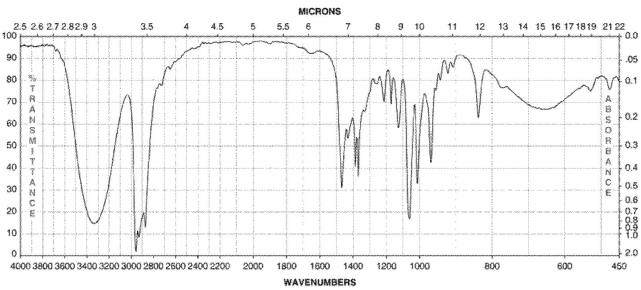
A)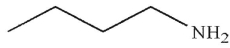
B)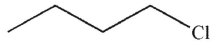
C)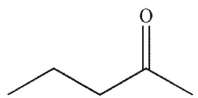
D)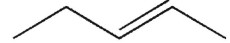
E)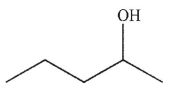

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the mobile and stationary phases in gas chromatography and explain how a mixture of
compounds is separated in this experiment.
compounds is separated in this experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A compound with the following constitution was subjected to mass spectrometry.
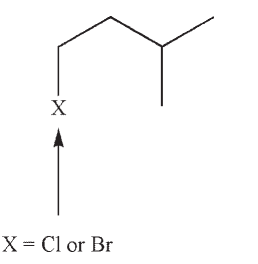
Suggest structures for the ions that correspond to m/z , and 70. Does this spectrum represent the bromo compound or the chloro compound? Explain your reasoning.
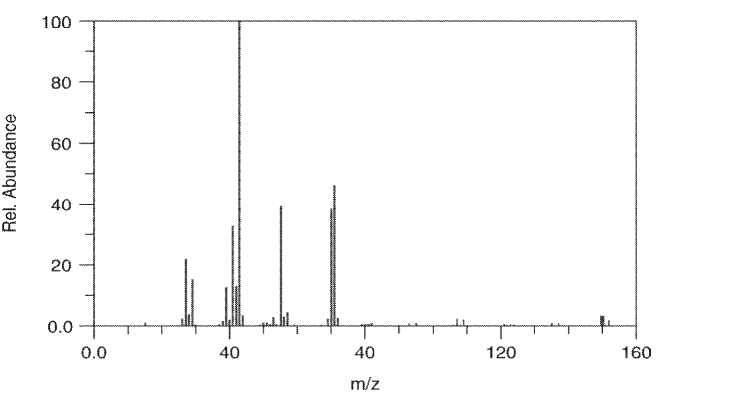

Suggest structures for the ions that correspond to m/z , and 70. Does this spectrum represent the bromo compound or the chloro compound? Explain your reasoning.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which molecule might plausibly have a signal around 124 ppm in a 13C spectrum?
A)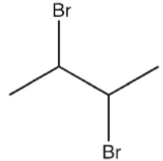
B)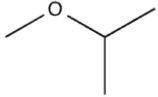
C)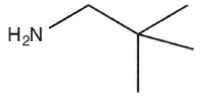
D)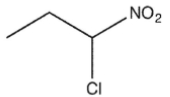
E)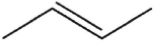
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What do you expect to be the relative integration value of the signal generated by HA protons in the 1H NMR spectrum for this molecule?
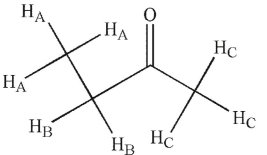
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The compound shown here was subjected to mass spectrometry. What structure gives rise the peak in its mass spectrum with m / z= 92 ?
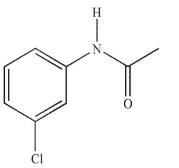


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
To which structure does this 1H NMR spectrum correspond?
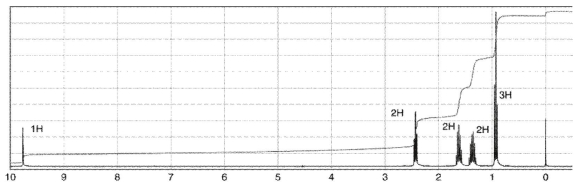
A)
B)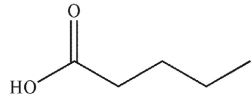
C)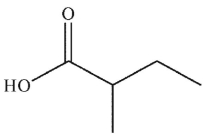
D)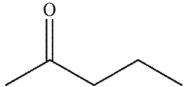
E)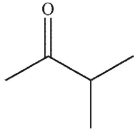

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Only hydrogens that are attached to the same carbon atom are said to be "coupled."
B)Only hydrogens that are attached to adjacent carbon atoms are said to be "coupled."
C)The coupling constant, J, is a measure of the chemical shift for a particular hydrogen or group of hydrogen atoms.
D)The magnitude of the coupling constant, J, depends on the dihedral angle between two hydrogens on adjacent carbons.
E)The coupling constant, J, is independent of the dihedral angle between hydrogens on adjacent carbons.
A)Only hydrogens that are attached to the same carbon atom are said to be "coupled."
B)Only hydrogens that are attached to adjacent carbon atoms are said to be "coupled."
C)The coupling constant, J, is a measure of the chemical shift for a particular hydrogen or group of hydrogen atoms.
D)The magnitude of the coupling constant, J, depends on the dihedral angle between two hydrogens on adjacent carbons.
E)The coupling constant, J, is independent of the dihedral angle between hydrogens on adjacent carbons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To which structure does this 1H NMR spectrum correspond?
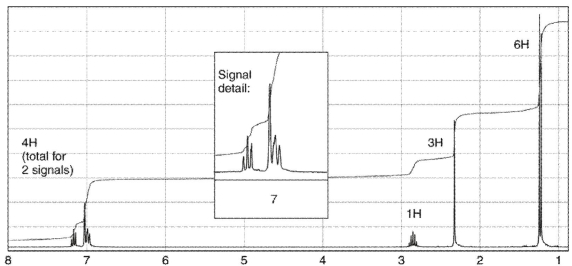
A)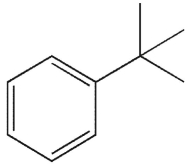
B)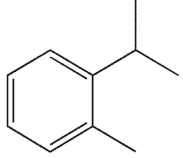
C)
D)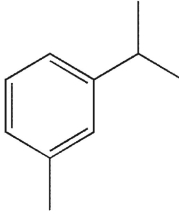
E)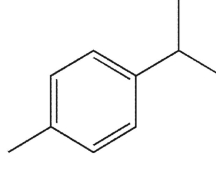

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To which structure does this 1H NMR spectrum correspond?
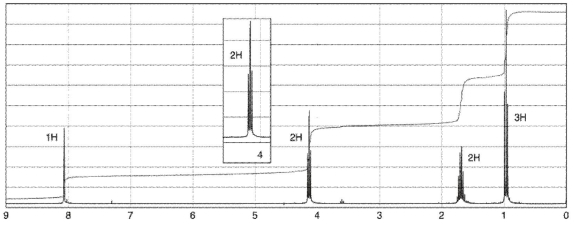
A)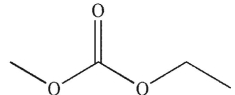
B)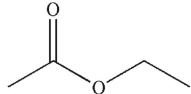
C)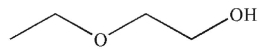
D)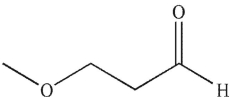
E)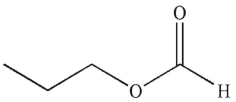

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which molecule might plausibly have a signal around 197 ppm in a 13C spectrum?
A)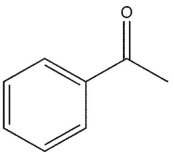
B)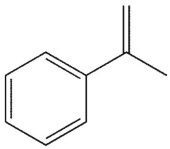
C)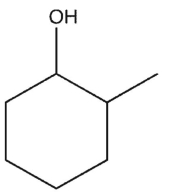
D)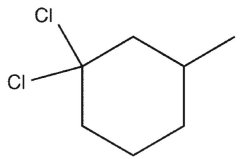
E)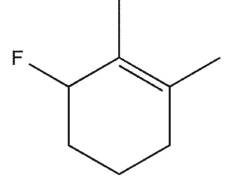
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A common fragmentation pattern of cyclohexene derivatives is a reverse Diels-Alder reaction, where the charged fragment that results is often the diene.Indicate at least two peaks (with m/z values) you would expect to see in the mass spectrum for the compound shown here, and the
structures that correspond to these peaks.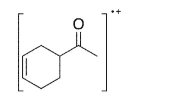
structures that correspond to these peaks.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Draw the products of McLafferty rearrangement of the following compound.
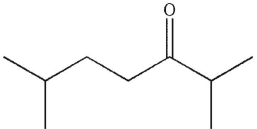


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which hydrogen would have a signal farthest downfield in the 1H NMR spectrum for this molecule?
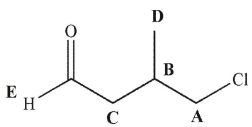
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Explain why there is always an M + 1 peak in a mass spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which hydrogen would have a signal farthest upfield in the 1H NMR spectrum for this molecule?
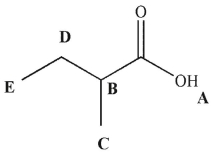
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What would be the effect on the 1H NMR spectrum of adding a drop of D2O to a sample of the molecule shown here?
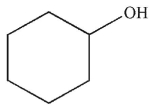
A) Adding the D2O will cause more hydrogen bonding and will change the chemical shift of the hydroxyl proton.
B) Adding the D2O will cause less hydrogen bonding and will change the chemical shift of the hydroxyl proton.
C) A new signal for D2O will appear in the 1H NMR spectrum.
D) A deuterium atom will exchange for the hydroxyl proton and the signal in the 1H NMR spectrum will disappear.
E) Adding D2O will have no effect on the 1H NMR spectrum.

A) Adding the D2O will cause more hydrogen bonding and will change the chemical shift of the hydroxyl proton.
B) Adding the D2O will cause less hydrogen bonding and will change the chemical shift of the hydroxyl proton.
C) A new signal for D2O will appear in the 1H NMR spectrum.
D) A deuterium atom will exchange for the hydroxyl proton and the signal in the 1H NMR spectrum will disappear.
E) Adding D2O will have no effect on the 1H NMR spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How many "lines" do you expect in the signal for HA? 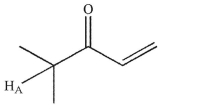
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)7
E)There is insufficient information to answer the question.

A)2
B)3
C)6
D)7
E)There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following compounds corresponds to the 1H NMR spectrum shown here?
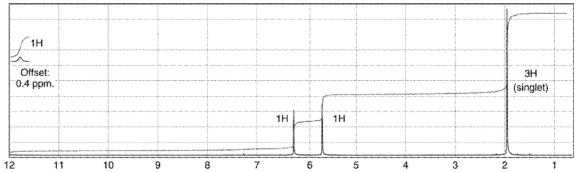
A)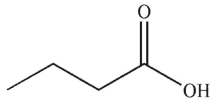
B)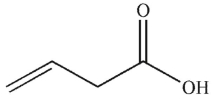
C)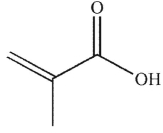
D)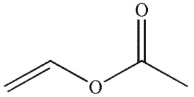
E)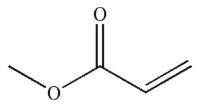

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The molecule shown here was analyzed by mass spectrometry. What structure gives rise to the peak in the mass spectrum with m/z=81 ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
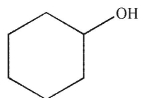
Which structure matches the 1H NMR spectrum shown here?
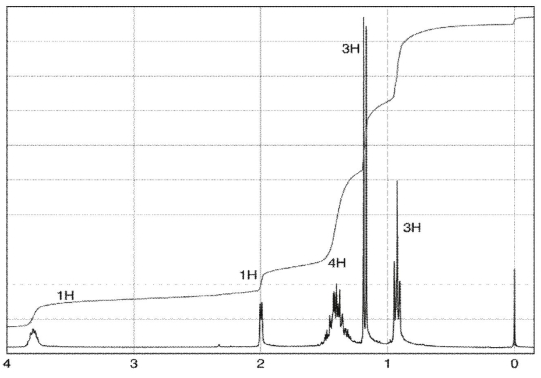
A)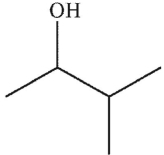
B)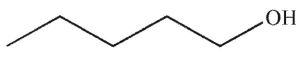
C)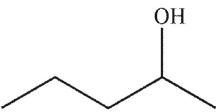
D)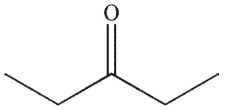
E)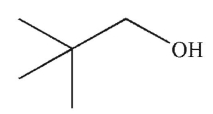

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Are the two hydrogens indicated homotopic, enantiotopic, or diastereotopic? 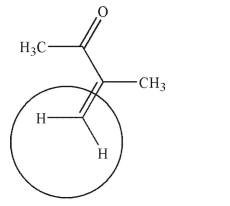


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The compound shown here exhibits a peak at m/z =70 . Explain why.
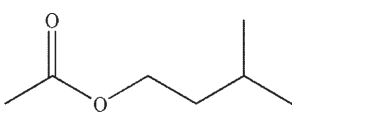


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Are the two hydrogens indicated homotopic, enantiotopic, or diastereotopic? 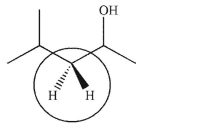


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Predict the splitting pattern of the indicated hydrogen in the following molecule. 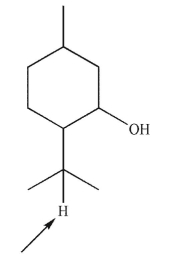


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following compounds corresponds to this 1H NMR spectrum?
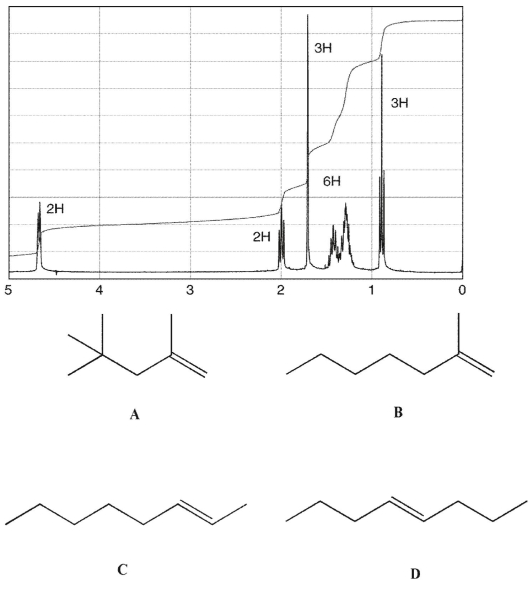


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which carbon in the molecule below will give a singlet even in the off resonance decoupled 13C spectrum?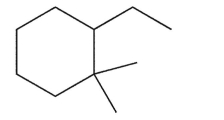


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Predict the splitting pattern of the indicated hydrogen in the following structure. 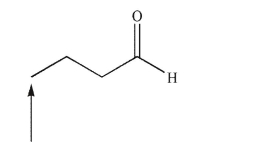


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match the three compounds shown here to the three IR spectra. 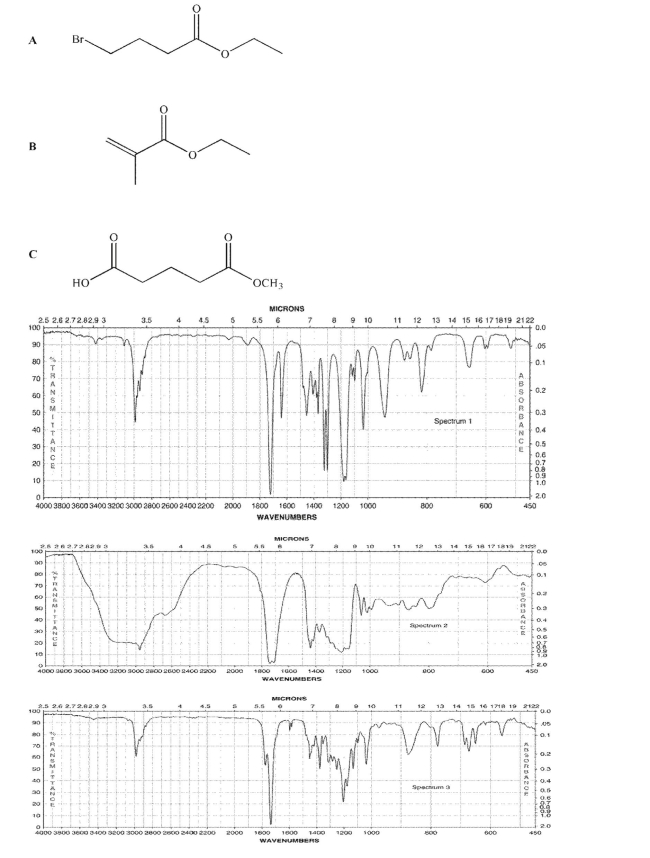


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match each of these 1H NMR spectra to the correct compound. Then assign each signal in both spectra to the corresponding hydrogen(s).
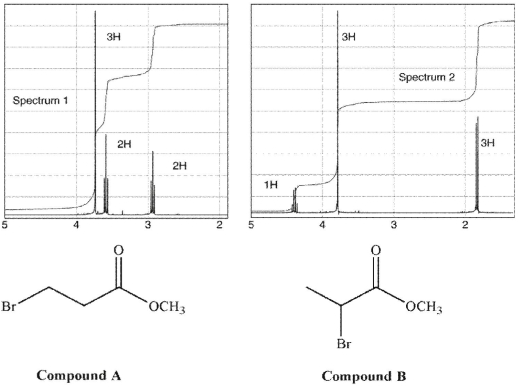


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Explain why chemical shifts are reported in parts per million (ppm).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
β-carotene absorbs light at 453 nm and 483 nm. Calculate the energy, in kcal/mol , corresponding to each of these wavelengths of light. Recall that
E=Nhc/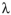 , where N=6.022X1023molecules/mol, h=1.583x10-37 kcal•s/molecule, and c=3.00x 1017nm/s.
, where N=6.022X1023molecules/mol, h=1.583x10-37 kcal•s/molecule, and c=3.00x 1017nm/s.
E=Nhc/
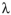 , where N=6.022X1023molecules/mol, h=1.583x10-37 kcal•s/molecule, and c=3.00x 1017nm/s.
, where N=6.022X1023molecules/mol, h=1.583x10-37 kcal•s/molecule, and c=3.00x 1017nm/s. 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which carbon in this molecule will have a 13C signal around 205 \ppm ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a solution with an absorbance of 0.350 is diluted in half, what will be the absorbance of the new solution, assuming the same cell is used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The indole side chain of tryptophan (the amino acid blamed for postfeast sleepiness at Thanksgiving) has a molar absorbtivity of about 5,500 M-1cm-1 at 280 nm . What absorbance do you expect for a 100 micromolar solution of tryptophan if measured in a 1cm cell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A compound with four degrees of unsaturation has the molecular formula C10H14O . Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.
Hint: The chemical shift for an OH signal can vary considerably.
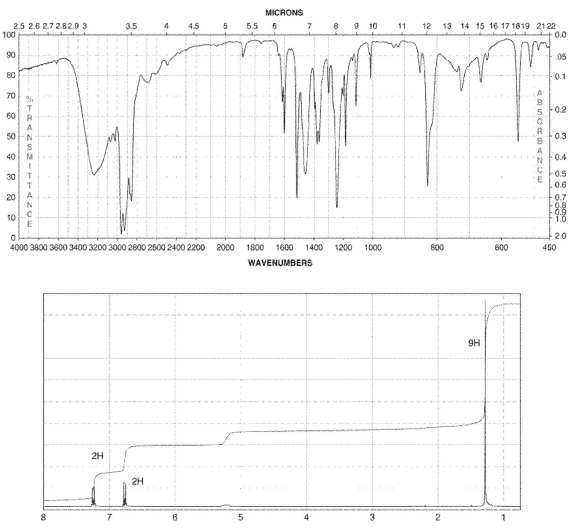
Hint: The chemical shift for an OH signal can vary considerably.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following compounds corresponds to this 1H NMR spectrum?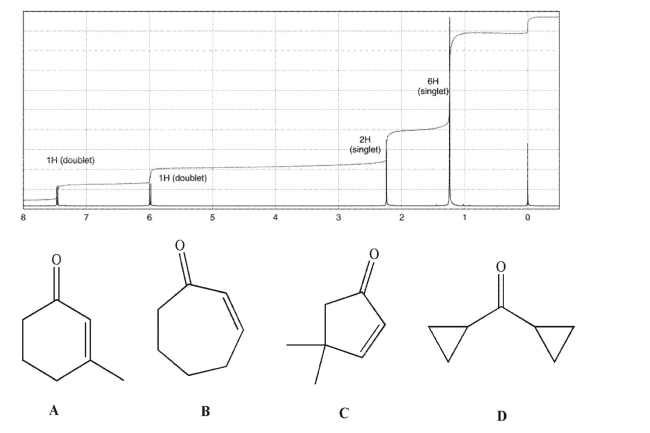


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Are the two hydrogens indicated homotopic, enantiotopic, or diastereotopic? 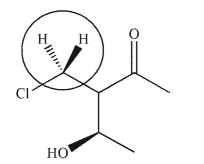


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two constitutional isomers of phenolphthalein are shown below.One of them is colorless, while
the other is responsible for the characteristic pinkish hue desperately sought by beginning students
learning titration techniques.Identify which is the pink isomer, and explain how you know.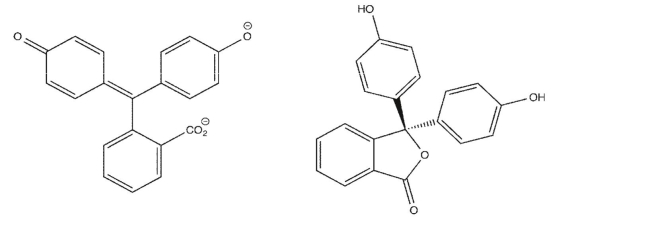
the other is responsible for the characteristic pinkish hue desperately sought by beginning students
learning titration techniques.Identify which is the pink isomer, and explain how you know.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which carbon in this molecule will have a 13C signal around 73/ppm ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
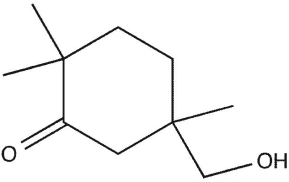
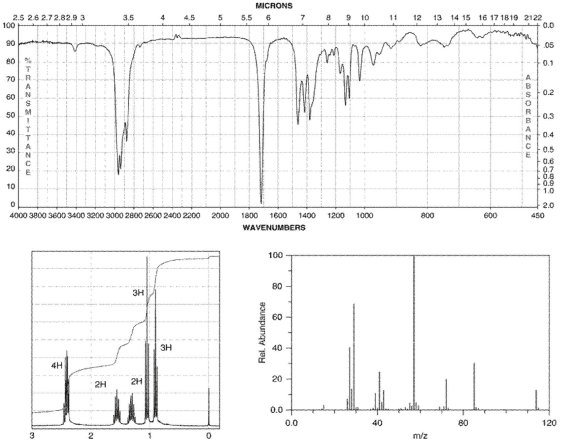
The IR, 1H NMR, and mass spectra for a compound with molecular formula 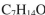 are shown. The molecular ion is at
are shown. The molecular ion is at 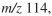 and the base peak is at
and the base peak is at  Determine the structure of the compound.
Determine the structure of the compound.
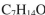 are shown. The molecular ion is at
are shown. The molecular ion is at 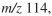 and the base peak is at
and the base peak is at  Determine the structure of the compound.
Determine the structure of the compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A compound with one degree of unsaturation has the molecular formula C4H8O3. Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
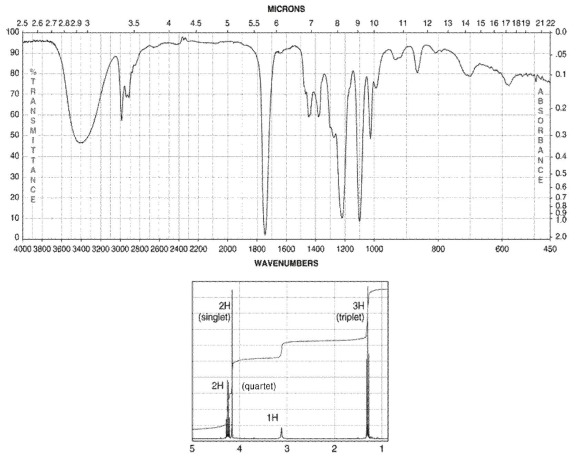
A compound with three degrees of unsaturation has the molecular formula C7H10O. Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.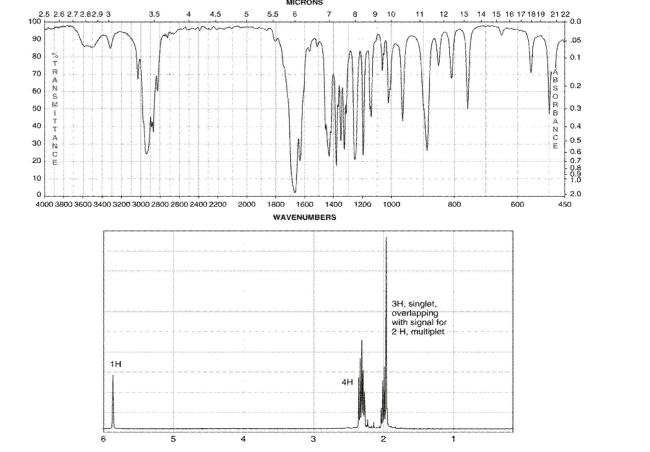


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A compound with zero degrees of unsaturation has the molecular formula C6H14O. Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.
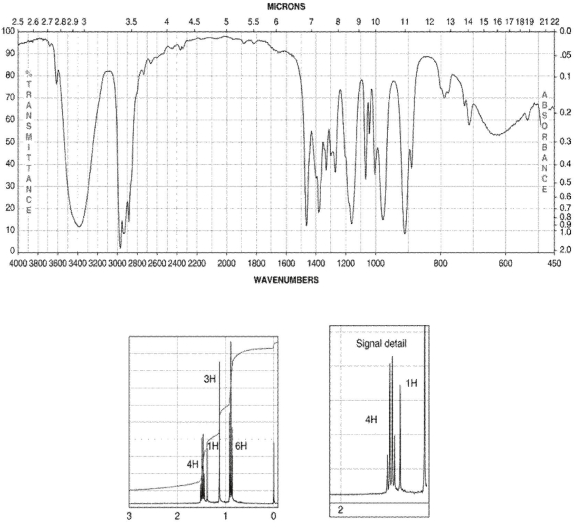


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A compound with four degrees of unsaturation has the molecular formula C10H15NO.
Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.
Hint: The chemical shift for an OH signal can vary considerably.
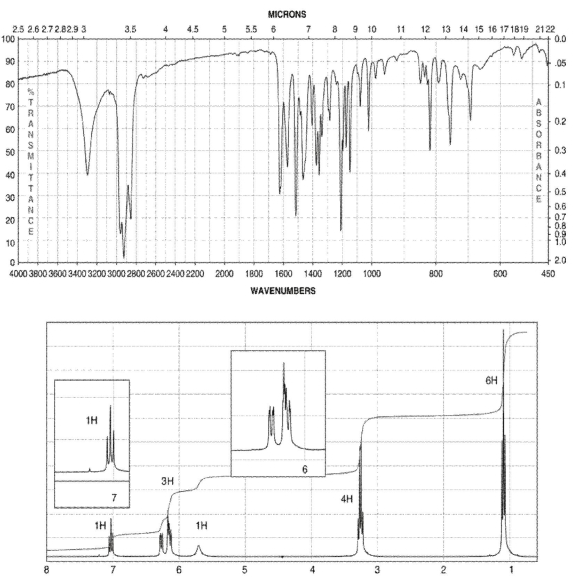
Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.
Hint: The chemical shift for an OH signal can vary considerably.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A compound with five degrees of unsaturation has the molecular formula C8H9NO.
Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.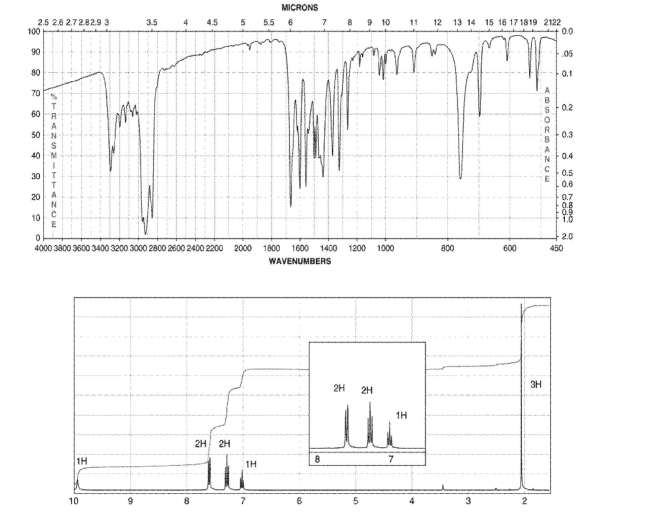
Its IR and 1H NMR spectra are shown. Draw the structure of the compound.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



