Deck 12: Radical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Radical Reactions
1
What is a radical inhibitor?
A)a chemical species that prevents an initiation step in a radical chain reaction
B)a chemical species that terminates the chain in a radical chain reaction
C)a chemical species that prevents chain termination in a radical chain reaction
D)a chemical species that accelerates one or more propagation steps in a radical chain reaction
E)a chemical species that produces radicals
A)a chemical species that prevents an initiation step in a radical chain reaction
B)a chemical species that terminates the chain in a radical chain reaction
C)a chemical species that prevents chain termination in a radical chain reaction
D)a chemical species that accelerates one or more propagation steps in a radical chain reaction
E)a chemical species that produces radicals
a chemical species that terminates the chain in a radical chain reaction
2
Which of the following transformations is a disproportionation?
A)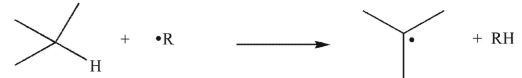
B)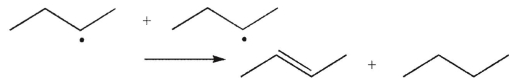
C)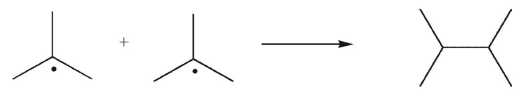
D)
E)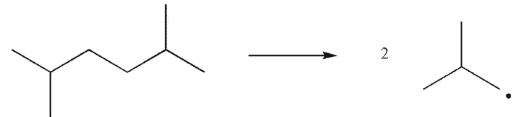
A)
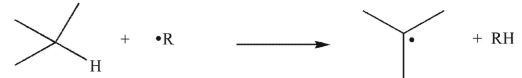
B)

C)

D)

E)
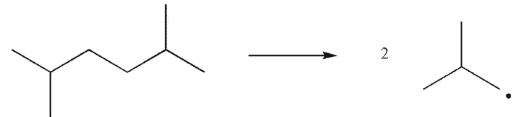

3
Which of the following is least likely to be a radical initiator?
A)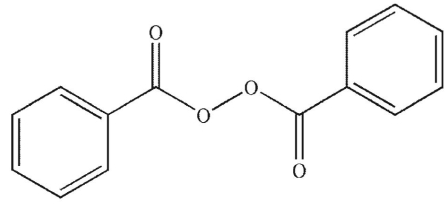
B)
C)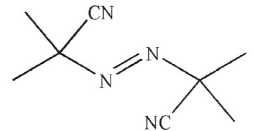
D)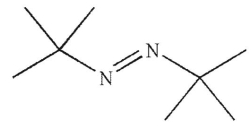
E)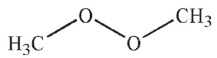
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


4
Which of the following statements about the anti-Markovnikov addition of HX to alkenes is false?
A)The reaction is typically run in the presence of peroxides and/or other radical initiators.
B)The regiochemistry is the result of the formation of the most substituted carbocation in the rate-limiting step.
C)The halogen atom attaches to the less substituted end of the alkene.
D)The reaction is only successful when HBr is used.
E)An alcohol is formed as a byproduct.
A)The reaction is typically run in the presence of peroxides and/or other radical initiators.
B)The regiochemistry is the result of the formation of the most substituted carbocation in the rate-limiting step.
C)The halogen atom attaches to the less substituted end of the alkene.
D)The reaction is only successful when HBr is used.
E)An alcohol is formed as a byproduct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
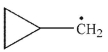
5
Cyclopropylmethyl radical, shown here, decomposes rapidly through a β cleavage process. Which of the following structures is the product of this process?
A)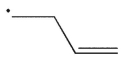
B)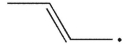
C)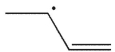
D)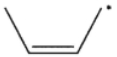
E)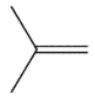

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is the following would not be a valid resonance form for this radical?
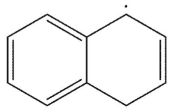
A)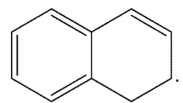
B)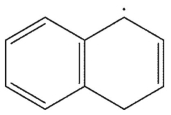
C)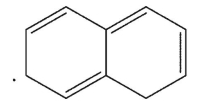
D)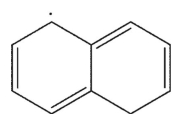
E)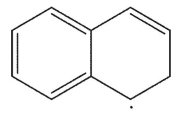

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following do you expect is least likely to act as a radical inhibitor?
A)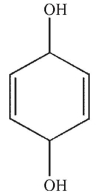
B)
C)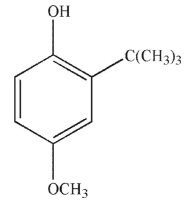
D)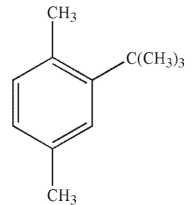
E) All these molecules are equally likely to act as radical inhibitors.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All these molecules are equally likely to act as radical inhibitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The disproportionation product(s) of the alkyl radical shown here will be 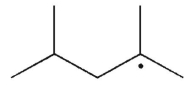
A) two alkanes.
B) an alkane and an alkene.
C) one alkane.
D) one alkene.
E) two alkenes.

A) two alkanes.
B) an alkane and an alkene.
C) one alkane.
D) one alkene.
E) two alkenes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these would not be expected to be a product from radical reaction of the cyclopentyl radical?
A)
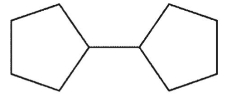
B)
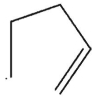
C)

D)
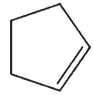
E)
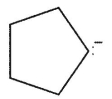
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the indicated C-C bonds requires the least amount of energy to break homolytically?
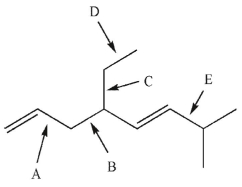
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What orbitals are involved in hyperconjugative stabilization of the radical shown here?
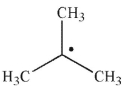
A) filled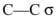 and empty
and empty 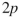
B) filled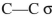 and empty
and empty 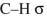
C) filled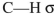 and half-filled
and half-filled 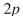
D) filled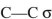 and half-filled
and half-filled 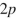
E) filled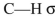 and empty
and empty 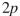

A) filled
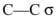 and empty
and empty 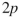
B) filled
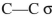 and empty
and empty 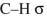
C) filled
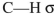 and half-filled
and half-filled 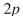
D) filled
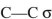 and half-filled
and half-filled 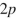
E) filled
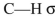 and empty
and empty 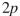

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following monomers will react to provide the polymer shown here?
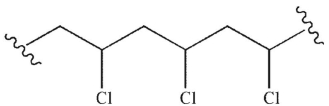
A)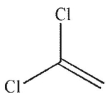
B)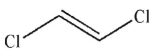
C)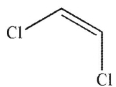
D)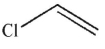
E)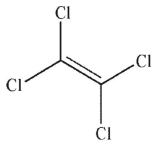

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the most likely stereochemical outcome of the following reaction? 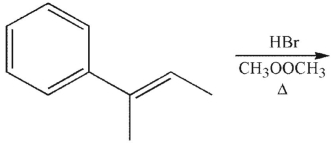
A) an unequal mixture of enantiomers
B) an equal mixture of enantiomers
C) an unequal mixture of diastereomers
D) an equal mixture of diastereomers
E) Choices b and d are equally likely.

A) an unequal mixture of enantiomers
B) an equal mixture of enantiomers
C) an unequal mixture of diastereomers
D) an equal mixture of diastereomers
E) Choices b and d are equally likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following radicals is most stable?
A)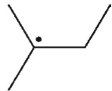
B)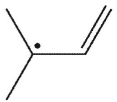
C)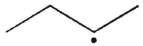
D)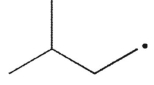
E)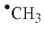
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
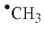

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following methods could not be used to facilitate radical formation?
A)inducing strain in a molecule to weaken sigma bonds
B)treating the molecule with a highly hindered base
C)starting with a molecule that will yield highly stabilized radicals on cleavage
D)starting with a molecule with an exceptionally weak sigma bond
E)treating the starting material with a radical initiator
A)inducing strain in a molecule to weaken sigma bonds
B)treating the molecule with a highly hindered base
C)starting with a molecule that will yield highly stabilized radicals on cleavage
D)starting with a molecule with an exceptionally weak sigma bond
E)treating the starting material with a radical initiator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the name of the process shown here? 
A) disproportionation
B) hydrogen abstraction
C) β cleavage
D) dimerization
E) pyrolysis

A) disproportionation
B) hydrogen abstraction
C) β cleavage
D) dimerization
E) pyrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a termination step in a radical chain reaction?
A)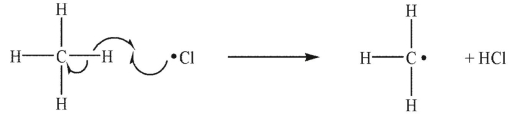
B)
C)
D)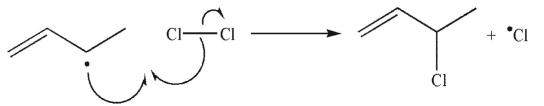
E)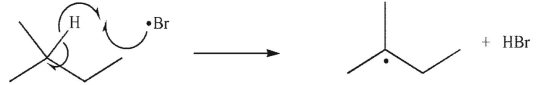
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these would be the expected product of the following reaction?
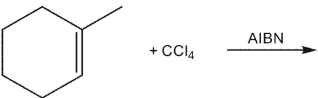
A)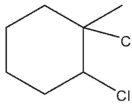
B)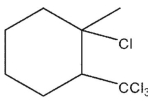
C)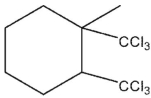
D)
E)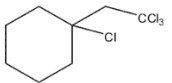

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which  bond is easiest to break homolytically? (For clarity, not all
bond is easiest to break homolytically? (For clarity, not all  bonds in the molecule are shown.)
bonds in the molecule are shown.)
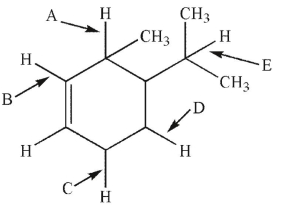
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 bond is easiest to break homolytically? (For clarity, not all
bond is easiest to break homolytically? (For clarity, not all  bonds in the molecule are shown.)
bonds in the molecule are shown.)
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What are the products of β cleavage of the radical species shown?
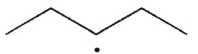
A)
B)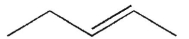
C)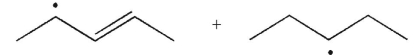
D)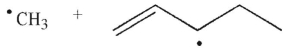
E)

A)

B)

C)
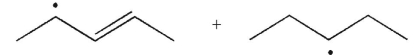
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following concepts should be used to correctly describe the reason for enhanced regioselectivity of photobromination versus photochlorination?
A) relative bond strengths of Cl2 and Br2.
B) energy released on termination steps
C) overall enthalpy of reaction
D) Hammond postulate
E) steric hindrance
A) relative bond strengths of Cl2 and Br2.
B) energy released on termination steps
C) overall enthalpy of reaction
D) Hammond postulate
E) steric hindrance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements about allylic bromination using NBS is false?
A)Molecular bromine concentration must be low.
B)Allylic rearrangements may occur.
C)HBr is required in trace amounts.
D)Symmetrical alkenes are the most suitable substrates for the reaction to avoid mixtures of products.
E)Bromine radical is produced by homolytic cleavage of the N-Br bond in N-bromosuccinimide.
A)Molecular bromine concentration must be low.
B)Allylic rearrangements may occur.
C)HBr is required in trace amounts.
D)Symmetrical alkenes are the most suitable substrates for the reaction to avoid mixtures of products.
E)Bromine radical is produced by homolytic cleavage of the N-Br bond in N-bromosuccinimide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Predict the product of the following reaction.

A)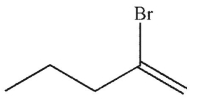
B)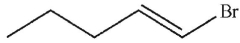
C)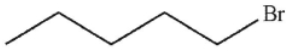
D)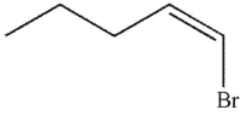
E) both b and d

A)

B)

C)

D)

E) both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a propagation sep?
A)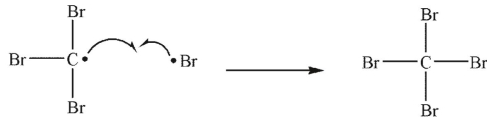
B)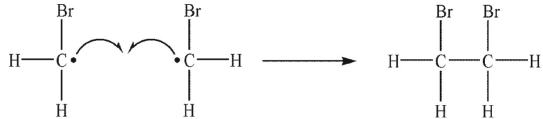
C)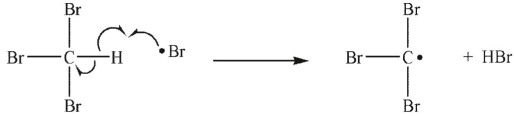
D)
E)
A)
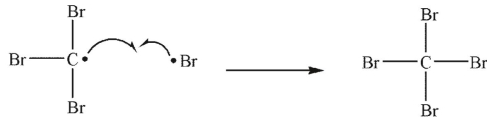
B)
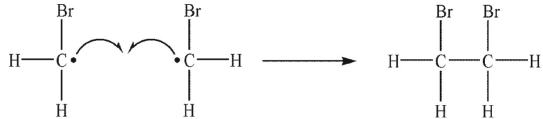
C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Predict the product of the following reaction. 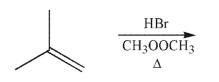


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Draw an arrow-pushing mechanism for the transformation shown here. 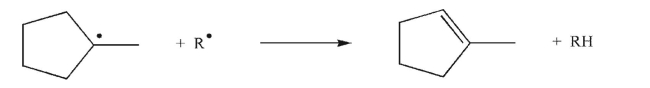


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What would be expected to be the major organic product from the following reaction? 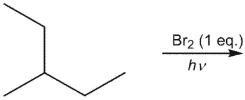
A)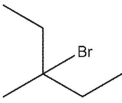
B)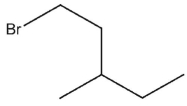
C)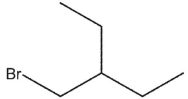
D)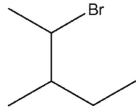
E)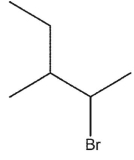

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When a sample of diethyl ether is allowed to stand, over time it reacts with molecular
oxygen to form peroxides.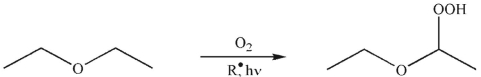
Propose an arrow-pushing mechanism to illustrate the formation of the peroxide from the ether starting material. Use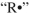 as the initiator. Show all curved arrows and single electrons.
as the initiator. Show all curved arrows and single electrons.
oxygen to form peroxides.

Propose an arrow-pushing mechanism to illustrate the formation of the peroxide from the ether starting material. Use
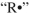 as the initiator. Show all curved arrows and single electrons.
as the initiator. Show all curved arrows and single electrons.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following monobrominated products forms fastest under the conditions shown?
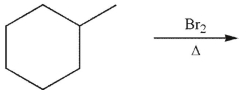
A)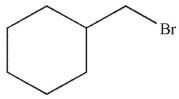
B)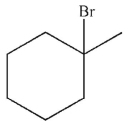
C)
D)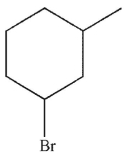
E) All form at equal rates.

A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All form at equal rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following compounds is the product of this reaction? 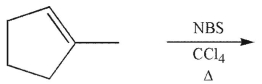
A)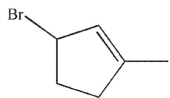
B)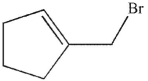
C)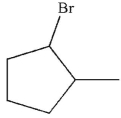
D)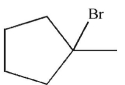
E) Both a and b would be produced.
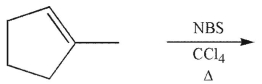
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) Both a and b would be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Predict the most likely products of β cleavage of the radical shown here and draw an arrow-pushing mechanism to illustrate their formation.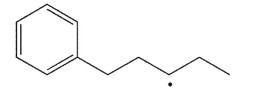


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about rearrangements is false?
A)Hydrogen atom shifts in radicals are not observed.
B)1,2-vinyl group shifts in radicals have been observed.
C)Methyl group shifts in radicals are not observed.
D)Radical rearrangements are disfavored because the transition state for the rearrangement is destabilized.
E)Carbocation rearrangements are favored because the transition state for the rearrangement is stabilized.
A)Hydrogen atom shifts in radicals are not observed.
B)1,2-vinyl group shifts in radicals have been observed.
C)Methyl group shifts in radicals are not observed.
D)Radical rearrangements are disfavored because the transition state for the rearrangement is destabilized.
E)Carbocation rearrangements are favored because the transition state for the rearrangement is stabilized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the stereochemical outcome of the following reaction? 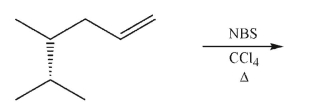
A)Enantiomers are produced in equal amounts.
B)Diastereomers are produced in equal amounts.
C)A single product forms.
D)Enantiomers are produced in unequal amounts.
E)Diastereomers are produced in unequal amounts.

A)Enantiomers are produced in equal amounts.
B)Diastereomers are produced in equal amounts.
C)A single product forms.
D)Enantiomers are produced in unequal amounts.
E)Diastereomers are produced in unequal amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.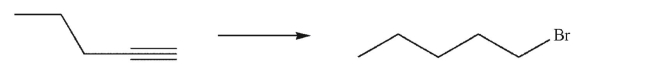
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material. Show the reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For the free radical chloriation of 2-methylbutane, estimate the expected percentage of each product shown.
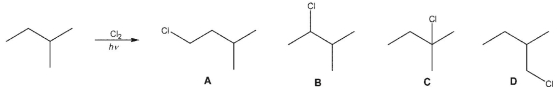
A) A -25 % ; B -17 % ; C -8 % ; D -50 %
B) A-13 % ; B-44 % ; C-17 % ; D-26 %
C) A - 28 % ; B - 14 % ; C - 2 % ; D - 56 %
D) A - 14 % ; B -36 % ; C -23 % ; D -27 %
E) A -28 % ; B -5 % ; C -12 % ; D -55 %

A) A -25 % ; B -17 % ; C -8 % ; D -50 %
B) A-13 % ; B-44 % ; C-17 % ; D-26 %
C) A - 28 % ; B - 14 % ; C - 2 % ; D - 56 %
D) A - 14 % ; B -36 % ; C -23 % ; D -27 %
E) A -28 % ; B -5 % ; C -12 % ; D -55 %

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Unsaturated fats in food react with oxygen to form alkylperoxy radicals.These radicals can then
react further with compounds in the food to degrade its taste.To prevent this process,
preservatives like BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) that act as radical inhibitors are added to some
foods.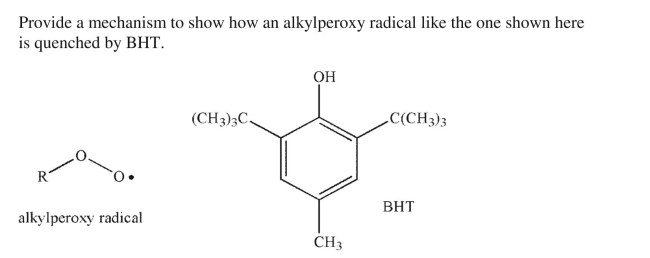
react further with compounds in the food to degrade its taste.To prevent this process,
preservatives like BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) that act as radical inhibitors are added to some
foods.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw the products of the following reaction. 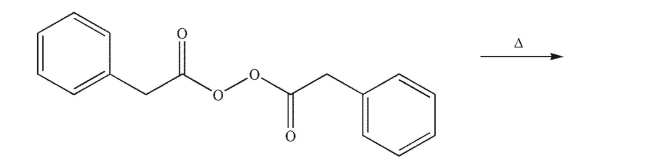


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Predict the major product from addition of two equivalents of HBr in the following reaction.
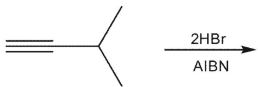
A)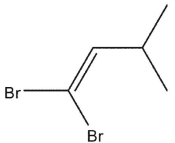
B)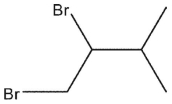
C)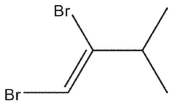
D)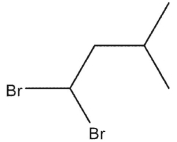
E)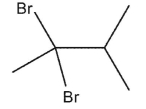

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Draw all the constitutional isomers of the monochloroalkane generated from the free radical
chlorination of methylcyclohexane.Which of the constitutional isomers would also have
stereoisomers?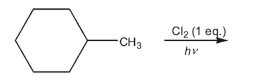
chlorination of methylcyclohexane.Which of the constitutional isomers would also have
stereoisomers?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
S-6-Bromo-1,6-dimethylcyclohexene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the absence of
radical-inducing conditions to produce two major isomers, one of which is optically active; the
other is meso.Draw the stereoisomers that can be produced if the same reaction is performed in
the presence of the radical initiator AIBN.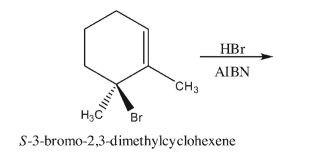
radical-inducing conditions to produce two major isomers, one of which is optically active; the
other is meso.Draw the stereoisomers that can be produced if the same reaction is performed in
the presence of the radical initiator AIBN.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.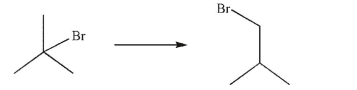
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A chemist would like to prepare a tertiary alcohol via the following reaction sequence.
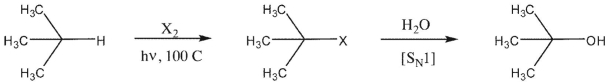
What halogen X should be used to ensure the maximum selectivity for the intermediate haloalkane?

What halogen X should be used to ensure the maximum selectivity for the intermediate haloalkane?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Draw the two organic products formed from the reaction between 3-methylcyclohexene and
N-bromosuccinimide under the conditions shown.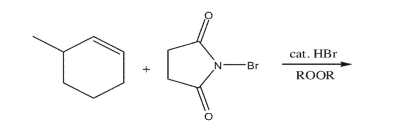
N-bromosuccinimide under the conditions shown.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Draw the stepwise mechanism for the free radical chlorination of cyclobutane to produce
chlorocyclobutane.Identify initiation and propagation steps; give one example of a termination
step.Use single-side curved arrows to show the movement of single electrons.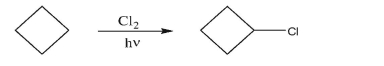
chlorocyclobutane.Identify initiation and propagation steps; give one example of a termination
step.Use single-side curved arrows to show the movement of single electrons.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Anti-Markovnikov addition of HX to an alkene only works with HBr in the presence of peroxides
as a radical initiator.Use the bond dissociation data provided to explain why the reaction fails
with HCl and HI.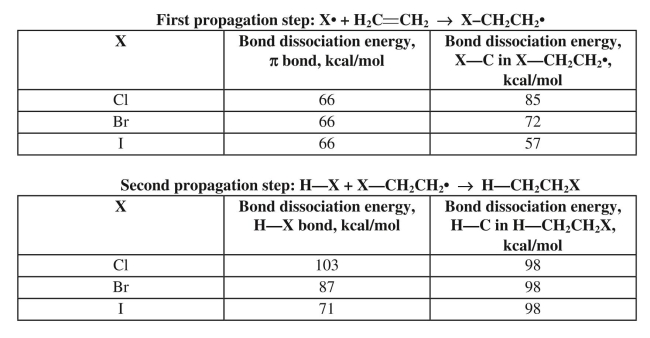
as a radical initiator.Use the bond dissociation data provided to explain why the reaction fails
with HCl and HI.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the principal monobrominated product that would result from the conditions shown? 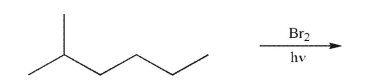


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism for the formation of polystyrene from styrene in the presence of AIBN. 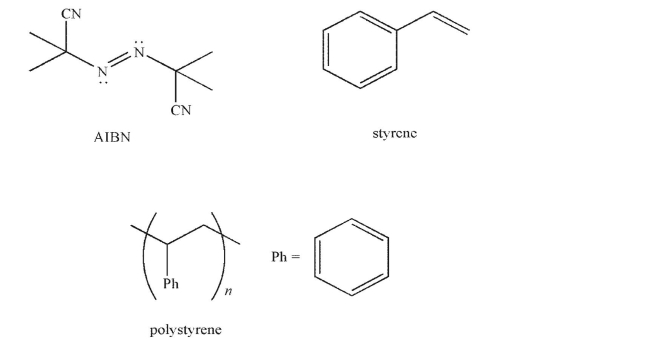


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Predict the product of the following reaction. 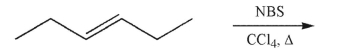


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Draw an arrow-pushing mechanism to show the transformation of dibromomethane to bromoform in
the presence of molecular bromine and bromine radical.
the presence of molecular bromine and bromine radical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Using the bond dissociation energies provided below, draw an energy diagram for the two
propagation steps in the following reaction.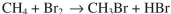
Show the correct relative energies of intermediates, starting materials and products. Estimate the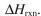
Bond dissociation energies (kcal/mol)
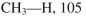
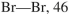
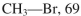
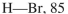
propagation steps in the following reaction.
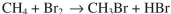
Show the correct relative energies of intermediates, starting materials and products. Estimate the
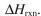
Bond dissociation energies (kcal/mol)
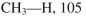
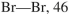
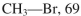
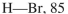

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Provide the structures of all monochlorinated products that would result from the conditions
shown.Assume that all chiral products are formed as racemic mixtures.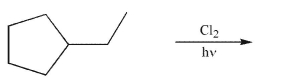
shown.Assume that all chiral products are formed as racemic mixtures.
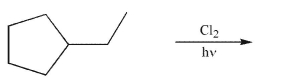

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Predict the product of the following reaction. 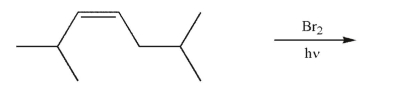


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Draw the products of the following reaction; indicate major and minor products. 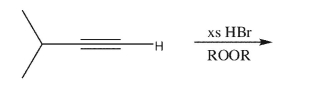
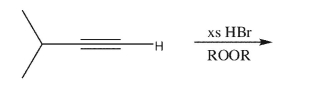

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In a radical chain reaction, termination steps are exothermic, yet propagation steps can be
endothermic.Despite this energetic difference, propagation steps can compete successfully to
continue the chain reaction, resulting in the eventual product.Explain.
endothermic.Despite this energetic difference, propagation steps can compete successfully to
continue the chain reaction, resulting in the eventual product.Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.Explain why the target cannot be made
from the starting material in one step.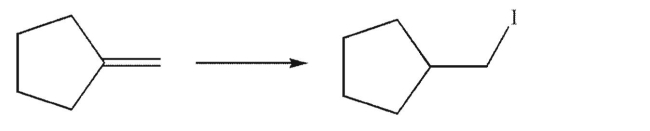
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.Explain why the target cannot be made
from the starting material in one step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Draw the mechanism for the following free radical chain reaction.Clearly indicate initiation and
propagation steps; show one possible termination step.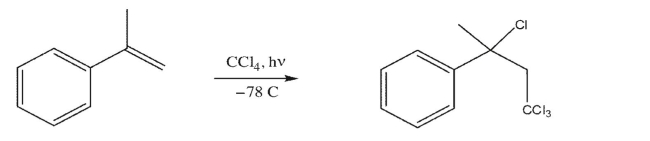
propagation steps; show one possible termination step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.Explain why the first step requires free
radical conditions.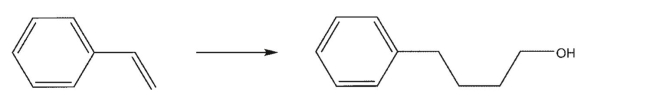
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.Explain why the first step requires free
radical conditions.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Draw the major product of this synthetic sequence. 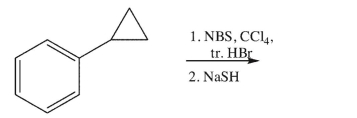
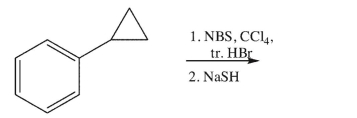

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Predict the major organic product and provide a mechanism to illustrate its formation under the conditions shown.Show all curved arrows, lone pairs, and single electrons, and any nonzero formal charges. 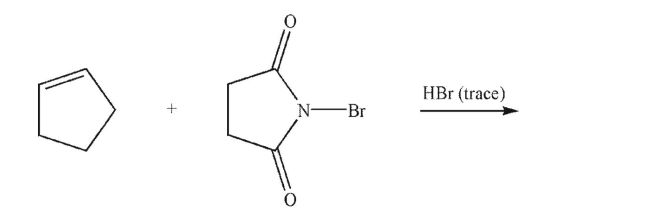


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In an allylic bromination, why is it essential to keep the concentration of molecular bromine relatively low?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.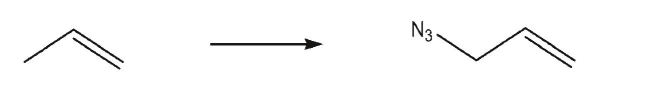
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Devise a multistep synthesis of the target molecule from the given starting material.Show the
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.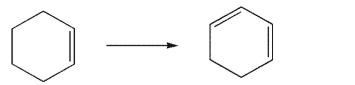
reagents needed for each step and the product of each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Predict the product of the following sequence of reactions. 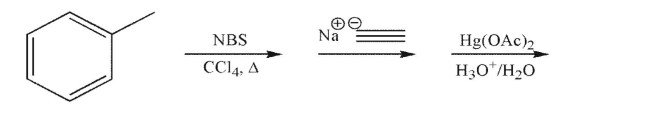


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



