Deck 24: Special Topic: Intramolecular Reactions and Neighboring Group Participation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Special Topic: Intramolecular Reactions and Neighboring Group Participation
1
What reagent(s) could be used to perform the following synthesis in one step? 
A) Br2, CCl4
B) HBr, H2O
C) PBr3, HOAc
D) HBr,AIBN
E) MCPBA, NaBr

A) Br2, CCl4
B) HBr, H2O
C) PBr3, HOAc
D) HBr,AIBN
E) MCPBA, NaBr
Br2, CCl4
2
Consider these two similar reactions and their stereochemical outcomes. 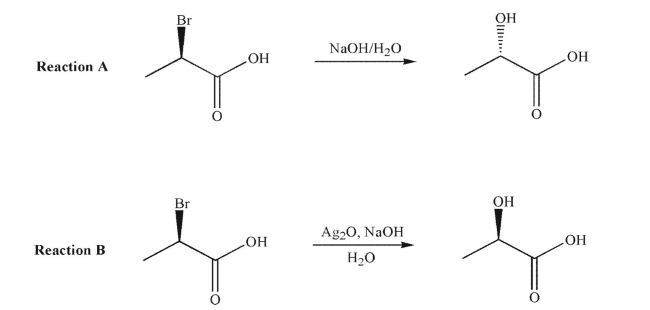 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Reaction A is likely to involve neighboring group participation.
B)Reaction B is likely to involve neighboring group participation.
C)Both reactions are equally likely to involve neighboring group participation.
D)Neither reaction likely involves neighboring group participation.
E)Not enough information is provided to assess these two reactions.
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A)Reaction A is likely to involve neighboring group participation.
B)Reaction B is likely to involve neighboring group participation.
C)Both reactions are equally likely to involve neighboring group participation.
D)Neither reaction likely involves neighboring group participation.
E)Not enough information is provided to assess these two reactions.
Reaction B is likely to involve neighboring group participation.
3
What experimental observation rules out the possibility of a hydride shift occurring in the hydrolysis of 1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane? 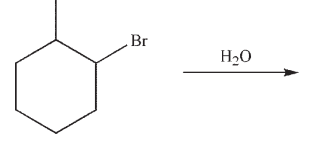
A)The reaction follows second order kinetics.
B)The reaction follows first order kinetics.
C)There is no kinetic isotope effect observed when the hydrogen is exchanged for
deuterium.
D)Changes in solvent polarity have a large effect on the reaction rate.
E)Replacing hydrogen with deuterium results in a change in the rate of reaction.

A)The reaction follows second order kinetics.
B)The reaction follows first order kinetics.
C)There is no kinetic isotope effect observed when the hydrogen is exchanged for
deuterium.
D)Changes in solvent polarity have a large effect on the reaction rate.
E)Replacing hydrogen with deuterium results in a change in the rate of reaction.
There is no kinetic isotope effect observed when the hydrogen is exchanged for
deuterium.
deuterium.
4
The following solvolysis reaction goes through a hydride shift to give the rearranged product.The hydrogen atom that moves is explicitly shown. 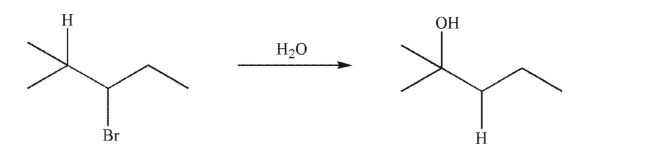 When this hydrogen atom is replaced with a deuterium atom, the rate of reaction slows
When this hydrogen atom is replaced with a deuterium atom, the rate of reaction slows
Considerably.Which of the following conclusions can be drawn correctly from this result?
A)The bromide ion leaves before the hydride shift occurs.
B)The hydride shift occurs, then the bromide ion leaves.
C)The hydride shift occurs at the same time as the bromide ion leaves.
D)These data describe the presence of a kinetic isotope effect.
E)Both c and d are reasonable conclusions.
 When this hydrogen atom is replaced with a deuterium atom, the rate of reaction slows
When this hydrogen atom is replaced with a deuterium atom, the rate of reaction slowsConsiderably.Which of the following conclusions can be drawn correctly from this result?
A)The bromide ion leaves before the hydride shift occurs.
B)The hydride shift occurs, then the bromide ion leaves.
C)The hydride shift occurs at the same time as the bromide ion leaves.
D)These data describe the presence of a kinetic isotope effect.
E)Both c and d are reasonable conclusions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Anchimeric assistance
A)generally slows the rate of a reaction by raising the activation energy for the rate-determining step.
B)is a term for any intramolecular reaction.
C)refers to the involvement of intramolecular assistance in the rate-determining step of a reaction.
D)only involves weak nucleophiles, as long as they are present in the molecule undergoing reaction.
E)may be either intra- or intermolecular, as long as there is a rate acceleration.
A)generally slows the rate of a reaction by raising the activation energy for the rate-determining step.
B)is a term for any intramolecular reaction.
C)refers to the involvement of intramolecular assistance in the rate-determining step of a reaction.
D)only involves weak nucleophiles, as long as they are present in the molecule undergoing reaction.
E)may be either intra- or intermolecular, as long as there is a rate acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why does the following reaction result in a racemic mixture of products? 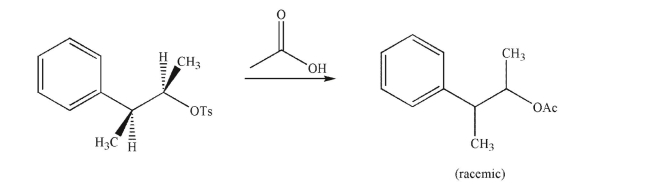
A)The acetic acid reagent is achiral.
B)Once the tosylate ionizes, it leaves a planar carbocation that can be attacked with equal likelihood at either side.
C)The key intermediate is achiral.
D)Both the enantiomeric products are equal in energy.
E)Neighboring group participation diminishes the selectivity of the reaction.

A)The acetic acid reagent is achiral.
B)Once the tosylate ionizes, it leaves a planar carbocation that can be attacked with equal likelihood at either side.
C)The key intermediate is achiral.
D)Both the enantiomeric products are equal in energy.
E)Neighboring group participation diminishes the selectivity of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which product would be expected to form in this reaction? 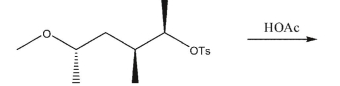
A)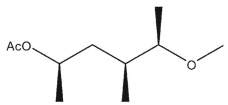
B)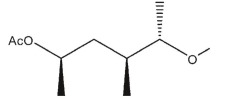
C)a and b
D)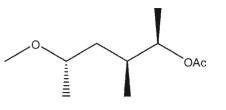
E)b and d

A)

B)

C)a and b
D)

E)b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following bicyclic amines will undergo the fastest rate of methanolysis to form an ether?
A)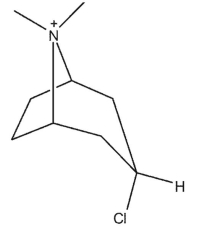
B)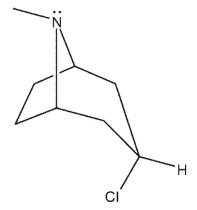
C)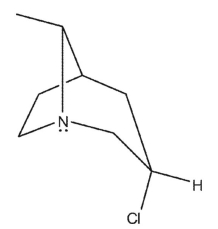
D)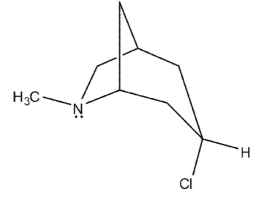
E)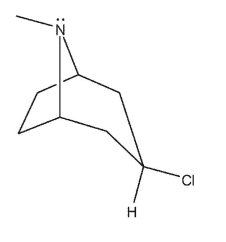
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Predict the product of the reaction conditions shown. 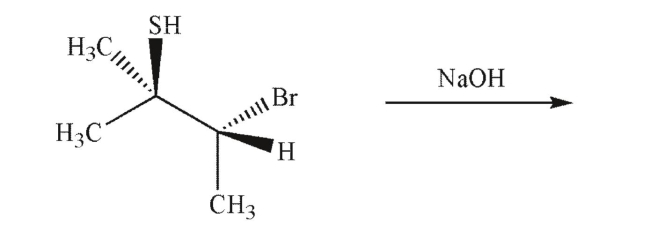


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is an intermediate in the reaction shown? 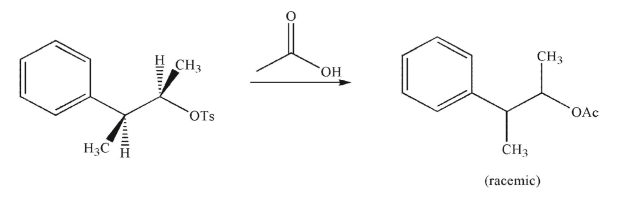
A)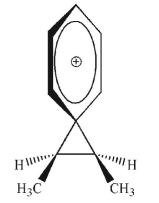
B)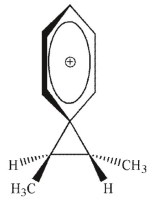
C)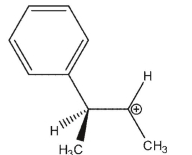
D)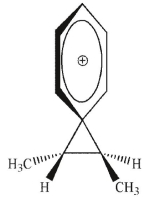
E)both a and c

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of these can participate as neighboring groups?
A)single bonds
B)double bonds
C)heteroatoms
D)all of the above
E)all but a
A)single bonds
B)double bonds
C)heteroatoms
D)all of the above
E)all but a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What would be the expected order for rates of reaction for the following compounds with acetic acid? 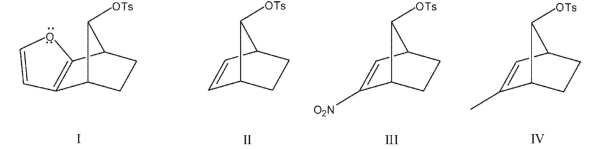
A) I > II > III > IV
B) I > II > IV > III
C) IV > II > I > III
D) IV > I > II > III
E) I > IV > II > III

A) I > II > III > IV
B) I > II > IV > III
C) IV > II > I > III
D) IV > I > II > III
E) I > IV > II > III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Predict the product of the following reaction sequence. 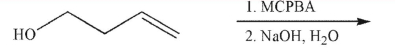
A)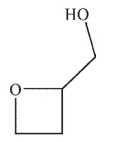
B)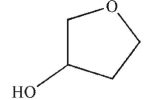
C)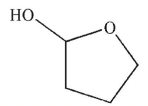
D)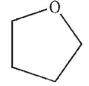
E)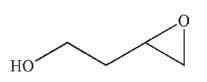

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these observations provides unequivocal evidence of the formation of a nonclassical ion in the following reaction? 
A)retention of exo-stereochemistry in the product ester
B)racemization of the product in the reaction
C)faster reaction for the exo tosylate than the endo-tosylate
D)None of these give unequivocal evidence of a nonclassical cation.
E)a and b both give unequivolcal evidence for a nonclassical cation.

A)retention of exo-stereochemistry in the product ester
B)racemization of the product in the reaction
C)faster reaction for the exo tosylate than the endo-tosylate
D)None of these give unequivocal evidence of a nonclassical cation.
E)a and b both give unequivolcal evidence for a nonclassical cation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not a possible indicator of neighboring group participation in a reaction?
A)An unexpected stereochemical result.
B)Inversion of configuration at a stereogenic center.
C)An unanticipated increase in reaction rate.
D)An atypical rearrangement.
E)both b and d
A)An unexpected stereochemical result.
B)Inversion of configuration at a stereogenic center.
C)An unanticipated increase in reaction rate.
D)An atypical rearrangement.
E)both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following reaction.
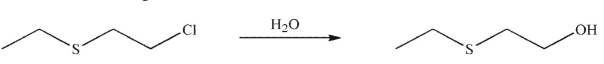
Which of these statements is incorrect?
A) Sulfur displaces chloride ion in an intramolecular SN2 reaction.
B) This reaction is an example of neighboring group participation involving a heteroatom.
C) The reaction goes through an intermediate episulfonium ion.
D) The reaction follows an SN2 mechanism where water displaces chloride ion from the starting material.
E) HCl is produced in the reaction as a by-product.

Which of these statements is incorrect?
A) Sulfur displaces chloride ion in an intramolecular SN2 reaction.
B) This reaction is an example of neighboring group participation involving a heteroatom.
C) The reaction goes through an intermediate episulfonium ion.
D) The reaction follows an SN2 mechanism where water displaces chloride ion from the starting material.
E) HCl is produced in the reaction as a by-product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following reactions would not be considered an example of neighboring group
participation or intramolecular reaction?
A) the formation of a lactone from a γ-hydroxyacid
B) interconversion between D-glucose and D-glucopyranose
C) hydrolysis of a cyclic anhydride to a diacid
D) the conversion of a halohydrin into an epoxide
E) the thermal elimination reaction of an ester
participation or intramolecular reaction?
A) the formation of a lactone from a γ-hydroxyacid
B) interconversion between D-glucose and D-glucopyranose
C) hydrolysis of a cyclic anhydride to a diacid
D) the conversion of a halohydrin into an epoxide
E) the thermal elimination reaction of an ester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Coates’ cation
A) is best described as a rapidly equilibrating set of localized ions.
B) is a three-center, two-electron system.
C) shows more than three signals in its 1H NMR spectrum.
D) is not stable at low temperature.
E) both c and d
A) is best described as a rapidly equilibrating set of localized ions.
B) is a three-center, two-electron system.
C) shows more than three signals in its 1H NMR spectrum.
D) is not stable at low temperature.
E) both c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement best summarizes the stereochemical outcomes of the following two reactions? 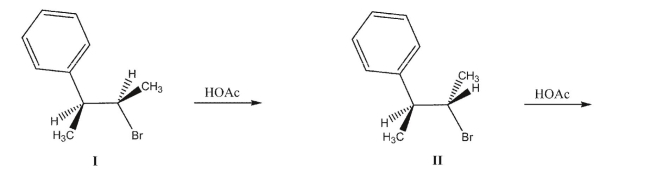
A)Both reactions I and II generate racemic mixtures of products.
B)Both reactions I and II generate achiral products.
C)Reaction I generates a racemic mixture, while reaction II generates an achiral product.
D)Reaction I generates a racemic mixture, while reaction II generates a chiral product.
E)Reaction I generates an achiral product, while reaction II generates a chiral product.

A)Both reactions I and II generate racemic mixtures of products.
B)Both reactions I and II generate achiral products.
C)Reaction I generates a racemic mixture, while reaction II generates an achiral product.
D)Reaction I generates a racemic mixture, while reaction II generates a chiral product.
E)Reaction I generates an achiral product, while reaction II generates a chiral product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following structures have neighboring groups that can assist in substitution reactions? 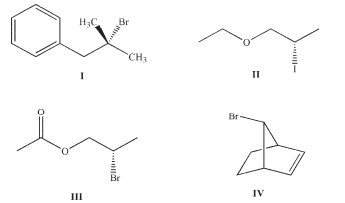
A) I
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV

A) I
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Propose an explanation for the difference in rates and products observed in the following two reactions.
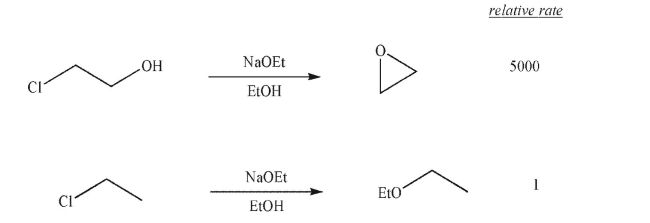


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain why trans-1-chloro-2-phenylcyclohexane A would be expected to undergo hydrolysis in acetic acid much more rapidly than the corresponding cis-isomer B :
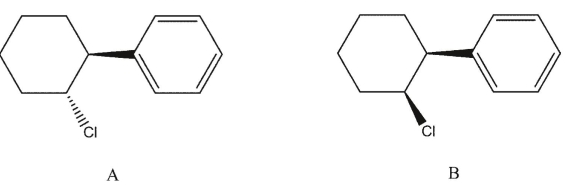


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Structure A reacts faster with nucleophiles than structure B.Explain. 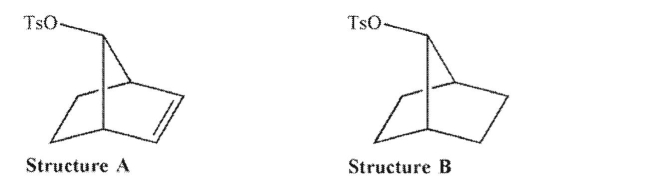


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A carbene in the singlet state is typically portrayed as sp2 hybridized, with a vacant p -orbital and a pair of nonbonding electrons residing in one sp2 hybrid orbital. Using molecular orbital theory, describe how a neighboring 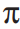 -bond can act as a nucleophile with the carbene in the formation of a cyclopropyl ring.
-bond can act as a nucleophile with the carbene in the formation of a cyclopropyl ring.
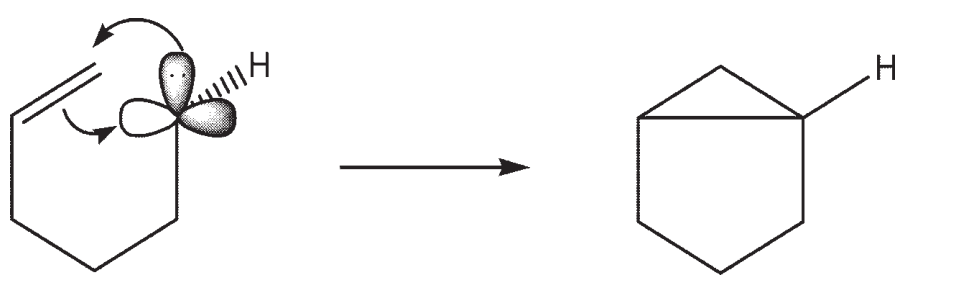
 -bond can act as a nucleophile with the carbene in the formation of a cyclopropyl ring.
-bond can act as a nucleophile with the carbene in the formation of a cyclopropyl ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain why compound A below would be expected to undergo solvolysis more quickly than
compound B: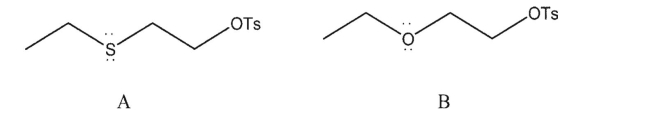
compound B:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the idea of neighboring group participation to rationalize the following stereochemical results. 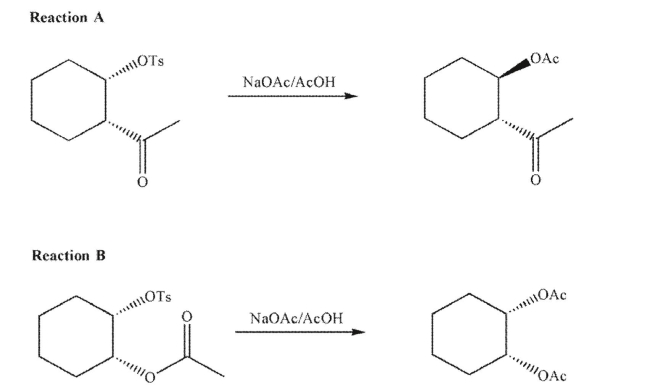


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Neighboring group effects are more strongly observed in trans-2-hydroxycyclopentylsulfonates (Structure A ) than in the corresponding nitroarenesulfonates (Structure B).
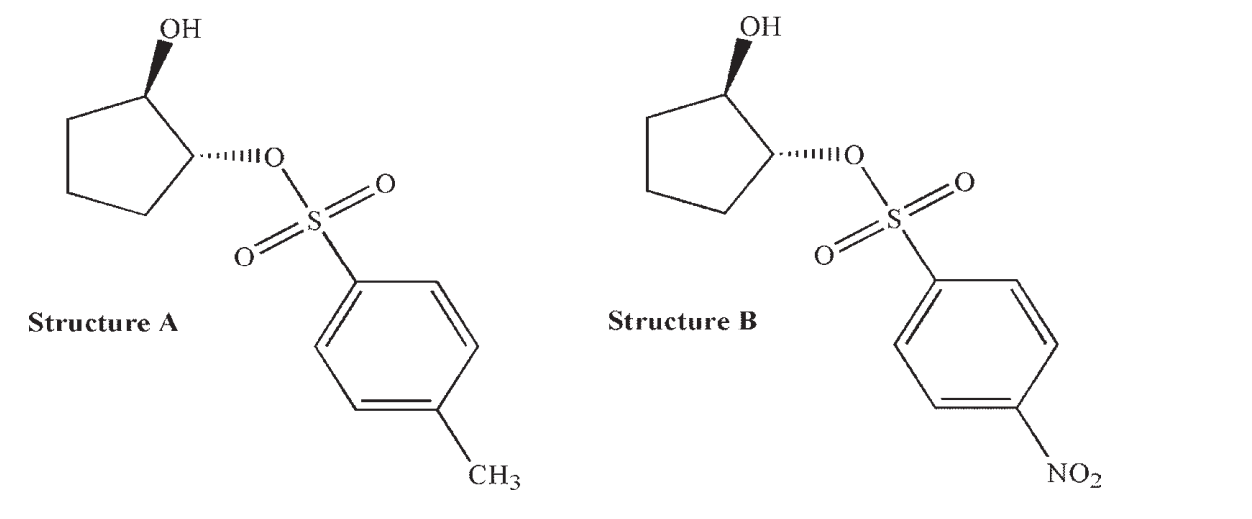
Draw the product you would expect from the reaction of structure A with an acetate ion, and propose an explanation why a neighboring group effect may not be as significant for structure B.

Draw the product you would expect from the reaction of structure A with an acetate ion, and propose an explanation why a neighboring group effect may not be as significant for structure B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How many different 13C NMR signals would you expect to see in the spectrum of the nonclassical norbornyl cation?
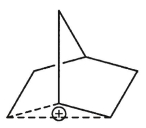


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Draw the mechanism of the following reaction; include all lone pairs involved, curved arrows, and
nonzero formal charges.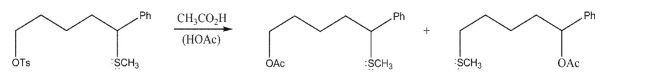
nonzero formal charges.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Predict the product and draw a mechanism for the reaction that occurs under the conditions
shown.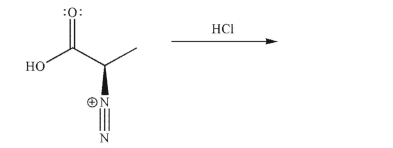
shown.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The syn-tosylate of 7-hydroxynorbornene undergoes hydrolysis 104 times faster than the tosylate of 7-hydroxynorbornane, but produces the rearranged product shown.Draw the mechanism of the hydrolysis reaction. 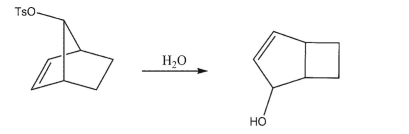


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Propose a mechanism for the following transformation, which is an example from the chemical
literature.Show all necessary lone pairs, curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges.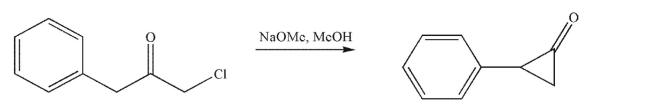
literature.Show all necessary lone pairs, curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of these two compounds is expected to undergo solvolysis in acetic acid at a faster rate? 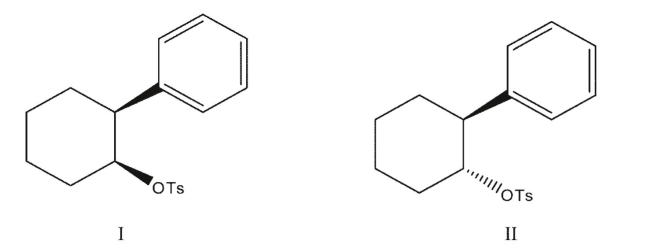


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Draw the mechanism of the following reaction. 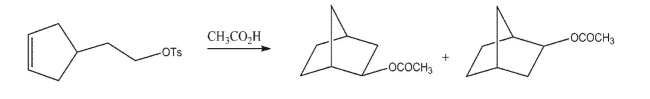


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A reaction called the Payne rearrangement involves neighboring group participation to generate a
rearranged product.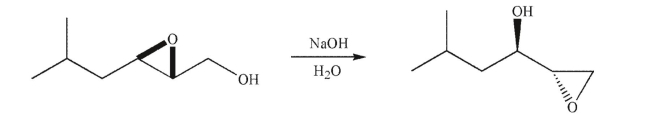 Propose a mechanism for the Payne rearrangement.
Propose a mechanism for the Payne rearrangement.
rearranged product.
 Propose a mechanism for the Payne rearrangement.
Propose a mechanism for the Payne rearrangement.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When the enantiomeric bromohydrins shown are treated with HBr, racemic 2,3-dibromobutane is
the result but not meso-2,3-dibromobutane.Explain these results.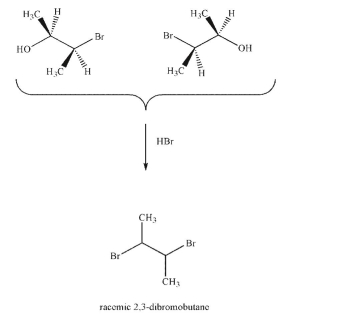
the result but not meso-2,3-dibromobutane.Explain these results.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Draw a mechanism to rationalize the following transformation.Show all necessary lone pairs,
curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges.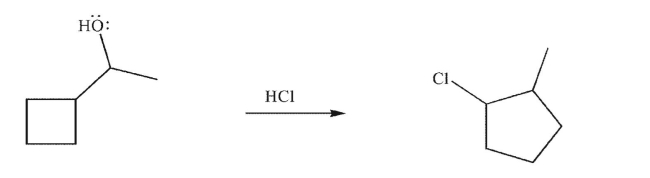
curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Draw a mechanism for the reaction shown.Include all necessary lone pairs, curved arrows, and
nonzero formal charges.
nonzero formal charges.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw a mechanism to illustrate the following transformation.Show all necessary lone pairs,
nonzero formal charges, and curved arrows.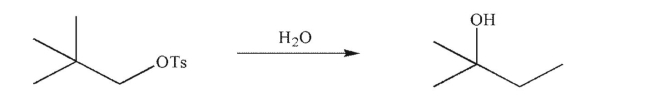
nonzero formal charges, and curved arrows.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Both bromoglucosides X and Y, when dissolved in methanol, give the same product, a methyl
glycoside.Propose an explanation for this result based on neighboring group effects.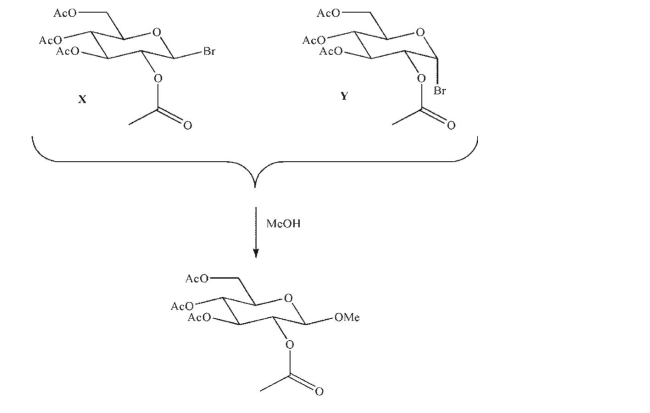
glycoside.Propose an explanation for this result based on neighboring group effects.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



