Deck 28: Growth, Capital Accumulation, and the Economics of Ideas: Catching up Vs the Cutting Edge
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/145
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Growth, Capital Accumulation, and the Economics of Ideas: Catching up Vs the Cutting Edge
1
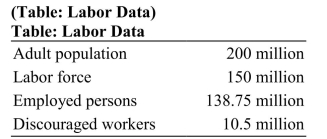 According to the accompanying labor data, the unemployment rate is _________ and the labor force participation rate is __________.
According to the accompanying labor data, the unemployment rate is _________ and the labor force participation rate is __________.A) 7 percent; 60.4 percent
B) 0.7 percent; 99.3 percent
C) 5.6 percent; 69.4 percent
D) 7.5 percent; 75 percent
D
2
What is the unemployment rate for a nation with 6 million employed and 2 million unemployed?
A) 10 percent
B) 15 percent
C) 20 percent
D) 25 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 15 percent
C) 20 percent
D) 25 percent
D
3
An unemployed person is best defined as an adult who
A) does not have a job but is looking for work.
B) is working fewer hours than she wants to.
C) is a full-time homemaker or a full-time student and is therefore not working.
D) has given up looking for work after being laid off for a long period of time.
A) does not have a job but is looking for work.
B) is working fewer hours than she wants to.
C) is a full-time homemaker or a full-time student and is therefore not working.
D) has given up looking for work after being laid off for a long period of time.
A
4
Which of the following best defines a nation's labor force?
A) the total number of persons between the ages of 16 and 65
B) the total number of employed and unemployed persons
C) the total number of persons working full time and part time
D) the total number of persons who are willing and able to work but cannot find a job
A) the total number of persons between the ages of 16 and 65
B) the total number of employed and unemployed persons
C) the total number of persons working full time and part time
D) the total number of persons who are willing and able to work but cannot find a job

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Adults who do not have a job but who are looking for work are
A) unemployed.
B) not part of the labor force.
C) unwilling to accept employment.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) unemployed.
B) not part of the labor force.
C) unwilling to accept employment.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When workers lose their jobs and become officially unemployed, the number of people in the labor force
A) remains constant.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) becomes difficult to predict.
A) remains constant.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) becomes difficult to predict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following individuals can be counted as unemployed?
A) Hannah and Harold, who are serving time for armed robbery
B) Jason and Jill, who have not looked for work for the last two years
C) Stewart and Susan, who are currently housed in a mental institution
D) None of these answers is correct.
A) Hannah and Harold, who are serving time for armed robbery
B) Jason and Jill, who have not looked for work for the last two years
C) Stewart and Susan, who are currently housed in a mental institution
D) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A country has 24 million people in the labor force and 21.5 million of them are employed. What is the unemployment rate in this country?
A) 10.4 percent
B) 2.5 percent
C) 89.6 percent
D) 21.5 percent
A) 10.4 percent
B) 2.5 percent
C) 89.6 percent
D) 21.5 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The percentage of adults in the labor force is the
A) unemployment rate.
B) employment rate.
C) labor force participation rate.
D) work force participation rate.
A) unemployment rate.
B) employment rate.
C) labor force participation rate.
D) work force participation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why is the unemployment rate considered to be an incomplete indicator of the health of the labor market? I. because it does not measure how well people are matched to the jobs they do II. because the definition of discouraged workers is not clear III. because it does not correctly define the adult population
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The labor force includes persons who are I. in prison. II. recently laid off and have given up looking for work. III. unemployed.
A) II only
B) III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) II only
B) III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following individuals can be counted as part of the labor force?
A) someone who retired four months ago
B) someone who is collecting unemployment benefits
C) someone who just celebrated a fifteenth birthday
D) someone who is on active military duty in Afghanistan
A) someone who retired four months ago
B) someone who is collecting unemployment benefits
C) someone who just celebrated a fifteenth birthday
D) someone who is on active military duty in Afghanistan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When workers lose their jobs and become officially unemployed, the unemployment rate
A) remains constant.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) becomes difficult to predict.
A) remains constant.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) becomes difficult to predict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following individuals can be counted as unemployed?
A) a woman who works only part time
B) a temp worker, who is currently responding to job advertisements from the newspaper
C) a man who was laid off from an auto manufacturing plant in Detroit
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) a woman who works only part time
B) a temp worker, who is currently responding to job advertisements from the newspaper
C) a man who was laid off from an auto manufacturing plant in Detroit
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the term for workers who have given up looking for a job but would still like one?
A) jobless workers
B) discouraged workers
C) laid off workers
D) discarded workers
A) jobless workers
B) discouraged workers
C) laid off workers
D) discarded workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following individuals can be counted as unemployed?
A) Darren, a ten-year-old child
B) Moesha, a full-time college student
C) Nazma, a stay-at-home mom
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) Darren, a ten-year-old child
B) Moesha, a full-time college student
C) Nazma, a stay-at-home mom
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of an unemployed person?
A) a retiree working as a volunteer in a hospital
B) a worker who is willing to work more hours if available
C) a recent college graduate looking for her first job
D) a full-time student working part time at night
A) a retiree working as a volunteer in a hospital
B) a worker who is willing to work more hours if available
C) a recent college graduate looking for her first job
D) a full-time student working part time at night

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a country, where both the labor force participation rate and the unemployment rate are very low, which of the following answers explains why this may be the case?
A) A large percentage of the population consists of children.
B) A large percentage of the population is aging and thus has retired.
C) A large percentage of the population is unemployed.
D) None of these answers is correct.
A) A large percentage of the population consists of children.
B) A large percentage of the population is aging and thus has retired.
C) A large percentage of the population is unemployed.
D) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What population categories go into the formula for the unemployment rate?
A) unemployed and employed
B) civilian, military, and unemployed
C) adults not in labor force, employed, and unemployed
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) unemployed and employed
B) civilian, military, and unemployed
C) adults not in labor force, employed, and unemployed
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The labor force is made up of
A) institutionalized people, the military, and employed workers.
B) employed and unemployed workers.
C) unemployed workers, employed workers, and students over 16.
D) all adult non-institutionalized civilians.
A) institutionalized people, the military, and employed workers.
B) employed and unemployed workers.
C) unemployed workers, employed workers, and students over 16.
D) all adult non-institutionalized civilians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Oil shocks, the shift from manufacturing to service jobs, and the use of new technologies are reasons for _____unemployment.
A) frictional
B) cyclical
C) structural
D) permanent
A) frictional
B) cyclical
C) structural
D) permanent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a nonrecession year, the majority of U.S. unemployment is:
A) frictional.
B) structural.
C) cyclical.
D) recurrent.
A) frictional.
B) structural.
C) cyclical.
D) recurrent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When not in a recession, the largest fraction of unemployment in the United States lasts
A) less than 5 weeks.
B) between 5 and 14 weeks.
C) between 15 and 26 weeks.
D) more than 27 weeks.
A) less than 5 weeks.
B) between 5 and 14 weeks.
C) between 15 and 26 weeks.
D) more than 27 weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Creative destruction occurs at the level of the
A) firm.
B) industry.
C) entire economy.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) firm.
B) industry.
C) entire economy.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Discouraged workers are people who
A) have given up looking for work but would still like to work.
B) are willing and able to work but cannot find a job.
C) are looking for a job that pays more than they are currently earning.
D) are working for fewer hours than they want to.
A) have given up looking for work but would still like to work.
B) are willing and able to work but cannot find a job.
C) are looking for a job that pays more than they are currently earning.
D) are working for fewer hours than they want to.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Several years ago, the rising popularity of Barnes & Noble and Borders shifted workers from independent bookshops to larger chains. What type of unemployment was associated with this reallocation of the work force?
A) frictional unemployment
B) technological substitution
C) creative destruction
D) structural unemployment
A) frictional unemployment
B) technological substitution
C) creative destruction
D) structural unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Following the great recession in 2010, the largest fraction of unemployment in the United States had lasted:
A) less than 5 weeks.
B) between 5 and 14 weeks.
C) between 15 and 26 weeks.
D) more than 27 weeks.
A) less than 5 weeks.
B) between 5 and 14 weeks.
C) between 15 and 26 weeks.
D) more than 27 weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Someone who recently moved to Florida because of its warmer climate will need to spend some time looking for a new job. This is an example of
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) underemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) underemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is one of the causes of frictional unemployment?
A) uneducated work force
B) willingness to take lower level jobs
C) scarcity of information
D) overabundance of job vacancies
A) uneducated work force
B) willingness to take lower level jobs
C) scarcity of information
D) overabundance of job vacancies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why has technology lowered frictional unemployment over time? I. Many people who used to be frictionally unemployed are now employed in the technology sector. II. The Internet has made it easier and faster for people to search for jobs that require their particular skill sets. III. The Internet has made posting jobs easier and faster for employers.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A worker repairing VHS cassette-tape players was laid off because most of his customers have started using DVD players. This worker is now
A) a discouraged worker.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) structurally unemployed.
A) a discouraged worker.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) structurally unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, unemployment includes I. discouraged workers. II. workers who are overqualified for their work. III. workers who have a part-time job but want a full-time job.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Frictional unemployment is caused by:
A) creative destruction.
B) recessions.
C) the transformation of the United States into a service economy.
D) the changing seasons of the year.
A) creative destruction.
B) recessions.
C) the transformation of the United States into a service economy.
D) the changing seasons of the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the textbook, Joseph Schumpeter's "creative destruction" results in
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) underemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) underemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The short-term unemployment caused by the ordinary difficulties of matching employee to employer is called
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Frictional unemployment is best defined as
A) long-term unemployment caused by changing features of an economy.
B) short-term unemployment caused by difficulties of matching employees to employers.
C) unemployment caused by cyclical conditions of an economy.
D) a normal level of unemployment caused by high wages.
A) long-term unemployment caused by changing features of an economy.
B) short-term unemployment caused by difficulties of matching employees to employers.
C) unemployment caused by cyclical conditions of an economy.
D) a normal level of unemployment caused by high wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Discouraged workers and underemployed workers are examples of
A) workers not included in the unemployment rate.
B) populations that cause higher unemployment taxes.
C) users of unemployment insurance.
D) poor national employment planning.
A) workers not included in the unemployment rate.
B) populations that cause higher unemployment taxes.
C) users of unemployment insurance.
D) poor national employment planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The persistent, long-term unemployment caused by long-lasting shocks or permanent features of an economy is called
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Individuals who have given up looking for work but still would take a job are considered
A) unemployed workers.
B) displaced workers.
C) discouraged workers.
D) part of the labor force.
A) unemployed workers.
B) displaced workers.
C) discouraged workers.
D) part of the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The presence of discouraged workers causes the measured unemployment rate to be
A) correctly stated.
B) overstated.
C) understated.
D) either overstated, understated, or correctly stated.
A) correctly stated.
B) overstated.
C) understated.
D) either overstated, understated, or correctly stated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the average wage is $9 in country X and $8 in country Y and both countries have similar elasticities of labor supply and demand, then a minimum wage of $4 in both countries will tend to
A) make unemployment higher in country X than in country Y.
B) make unemployment higher in country Y than in country X.
C) make unemployment the same in both countries.
D) have no effect in either country.
A) make unemployment higher in country X than in country Y.
B) make unemployment higher in country Y than in country X.
C) make unemployment the same in both countries.
D) have no effect in either country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Structural unemployment is more persistent in France than in the United States because
A) French workers have less incentive to quickly seek a new position since their unemployment benefits are much higher.
B) France's labor regulations require a mandatory waiting period before a worker can reapply for a new job.
C) American workers have many more job opportunities than French workers.
D) Labor unions are weaker in France than they are in the United States.
A) French workers have less incentive to quickly seek a new position since their unemployment benefits are much higher.
B) France's labor regulations require a mandatory waiting period before a worker can reapply for a new job.
C) American workers have many more job opportunities than French workers.
D) Labor unions are weaker in France than they are in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Legal and cultural issues contribute significantly to what category of unemployment?
A) structural
B) cyclical
C) short-term
D) frictional
A) structural
B) cyclical
C) short-term
D) frictional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
(Figure: Labor Supply and Demand) Figure: Labor Supply and Demand 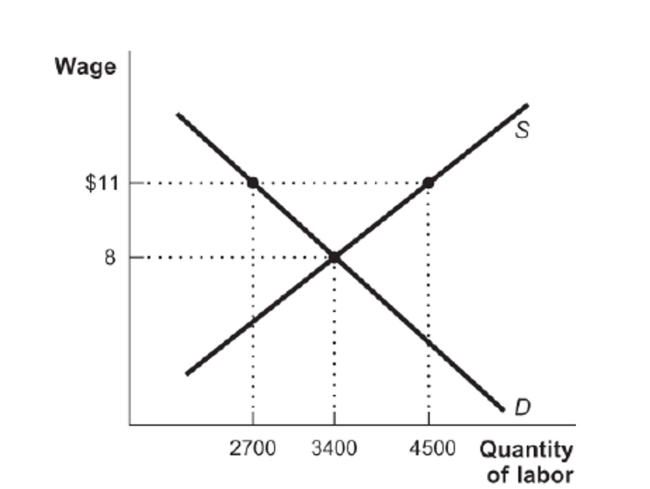 What is the unemployment rate caused by the labor union's action of increasing its wage demands to $11 an hour?
What is the unemployment rate caused by the labor union's action of increasing its wage demands to $11 an hour?
A) 66.7 percent
B) 75.6 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 60 percent
 What is the unemployment rate caused by the labor union's action of increasing its wage demands to $11 an hour?
What is the unemployment rate caused by the labor union's action of increasing its wage demands to $11 an hour?A) 66.7 percent
B) 75.6 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 60 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
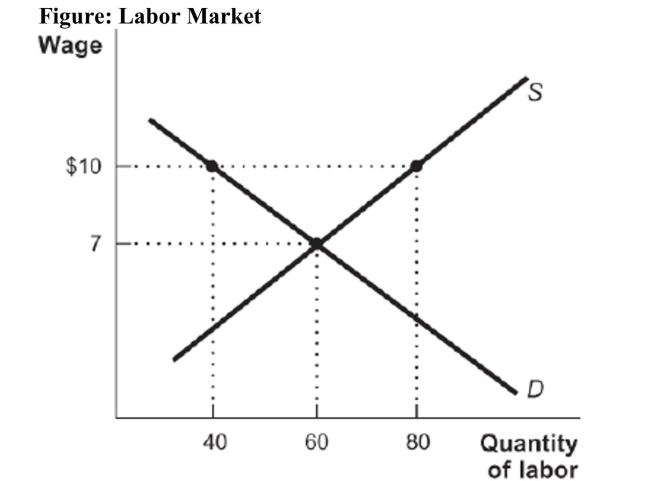 Reference: Ref 11-1 (Figure: Labor Market) Refer to the figure. What is the number of people who are employed at the market clearing wage? How many people end up unemployed due to the implementation of a $10 minimum wage?
Reference: Ref 11-1 (Figure: Labor Market) Refer to the figure. What is the number of people who are employed at the market clearing wage? How many people end up unemployed due to the implementation of a $10 minimum wage?A) 40 thousand; 20 thousand
B) 40 thousand; 40 thousand
C) 60 thousand; 40 thousand
D) 60 thousand; 20 thousand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Both __________ and _________ reduce the quantity of labor demanded.
A) minimum wages; unemployment benefits
B) minimum wages; union wages
C) union wages; unemployment benefits
D) retraining programs; union wages
A) minimum wages; unemployment benefits
B) minimum wages; union wages
C) union wages; unemployment benefits
D) retraining programs; union wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
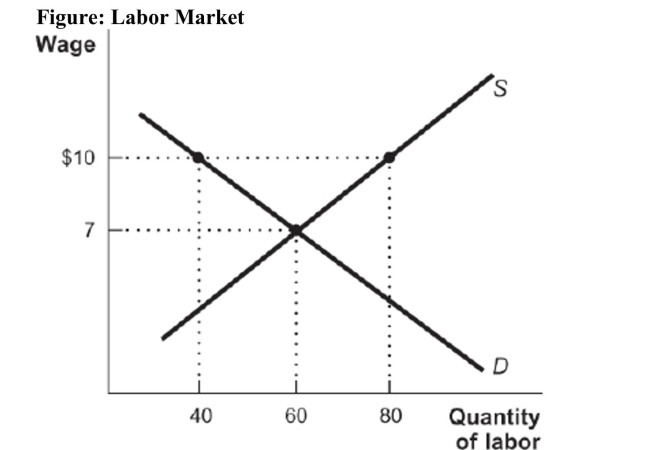 Reference: Ref 11-1 (Figure: Labor Market) Refer to the figure. What is the unemployment rate in this market as a result of the implementation of a $10 minimum wage?
Reference: Ref 11-1 (Figure: Labor Market) Refer to the figure. What is the unemployment rate in this market as a result of the implementation of a $10 minimum wage?A) 20 percent
B) 50 percent
C) 100 percent
D) 25 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following programs could help overcome structural unemployment?
A) worker retraining
B) limitations to unemployment benefits
C) job search assistance programs
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) worker retraining
B) limitations to unemployment benefits
C) job search assistance programs
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An increase in unemployment benefits tends to
A) lower the incentive to search for a job and raise frictional unemployment.
B) lower the incentive to search for a job and lower frictional unemployment.
C) raise the incentive to search for a job and raise frictional unemployment.
D) raise the incentive to search for a job and lower frictional unemployment.
A) lower the incentive to search for a job and raise frictional unemployment.
B) lower the incentive to search for a job and lower frictional unemployment.
C) raise the incentive to search for a job and raise frictional unemployment.
D) raise the incentive to search for a job and lower frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following elements reduces structural unemployment?
A) the enhancement of worker retraining programs
B) the extension of unemployment benefits
C) the growth of labor unions
D) the existence of employment protection laws
A) the enhancement of worker retraining programs
B) the extension of unemployment benefits
C) the growth of labor unions
D) the existence of employment protection laws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A minimum wage is
A) an employment protection law.
B) a labor market price ceiling.
C) the equilibrium wage in an unskilled labor market.
D) None of these answers is correct.
A) an employment protection law.
B) a labor market price ceiling.
C) the equilibrium wage in an unskilled labor market.
D) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Compared to the United States, unemployment rates in Western Europe tend to be
A) lower because of more labor regulations.
B) lower because of fewer labor regulations.
C) higher because of more labor regulations.
D) higher because of fewer labor regulations.
A) lower because of more labor regulations.
B) lower because of fewer labor regulations.
C) higher because of more labor regulations.
D) higher because of fewer labor regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following tend to increase unemployment?
A) unemployment benefits
B) minimum wages
C) labor unions
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) unemployment benefits
B) minimum wages
C) labor unions
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following raises structural unemployment? I. higher union membership II. more unemployment benefits III. higher minimum wages
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following elements increases structural unemployment?
A) active labor market policies
B) bonuses for early employment
C) job-search assistance programs
D) employment protection laws
A) active labor market policies
B) bonuses for early employment
C) job-search assistance programs
D) employment protection laws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Higher unemployment benefits tend to
A) increase the unemployment rate.
B) reduce the unemployment rate.
C) have no impact on the unemployment rate.
D) increase, decrease, or leave the unemployment rate unchanged. It's not possible to tell without further information.
A) increase the unemployment rate.
B) reduce the unemployment rate.
C) have no impact on the unemployment rate.
D) increase, decrease, or leave the unemployment rate unchanged. It's not possible to tell without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Countries in Western Europe have
A) higher minimum wages than the United States.
B) higher median wages than the United States.
C) higher unemployment rates than the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) higher minimum wages than the United States.
B) higher median wages than the United States.
C) higher unemployment rates than the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The United States' shift toward more of a service economy and less of a manufacturing economy has caused an increase in
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
France, Germany, Italy, and Spain have experienced ______ unemployment compared to the United States since 1980.
A) less
B) more
C) the same
D) None of these answers is correct. Germany experienced less unemployment, while the other nations experienced more.
A) less
B) more
C) the same
D) None of these answers is correct. Germany experienced less unemployment, while the other nations experienced more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a national government improves its unemployment benefits, its unemployment rate will most likely
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) follow the global trend, regardless of national policy.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) follow the global trend, regardless of national policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
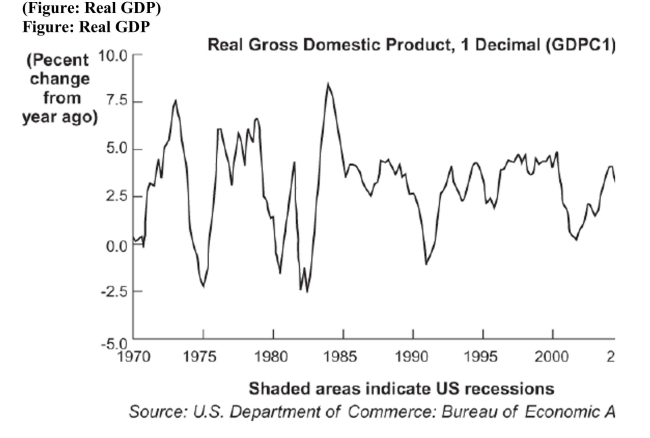 Refer to the figure. Given this view of the real business cycle for the United States over the time period 1970 to 2008, when would you expect cyclical unemployment to have been the highest?
Refer to the figure. Given this view of the real business cycle for the United States over the time period 1970 to 2008, when would you expect cyclical unemployment to have been the highest?A) 1972
B) 1982
C) 1985
D) 2000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What does the World Bank's "rigidity of employment index" provide for us?
A) a summary of the average length of unemployment of over a five-year period
B) a measure of the effects of shrinking manufacturing firms in developed nations
C) a summary of firms costs for hiring, firing, and adjusting employment hours
D) a measure of the available government assistance for workers seeking employment
A) a summary of the average length of unemployment of over a five-year period
B) a measure of the effects of shrinking manufacturing firms in developed nations
C) a summary of firms costs for hiring, firing, and adjusting employment hours
D) a measure of the available government assistance for workers seeking employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Keynesian explanation for cyclical unemployment is
A) that labor is reallocated across different industries.
B) the same as that for frictional and structural unemployment.
C) that wage demands are too high relative to falling prices.
D) that it is a normal response to real shocks in the economy.
A) that labor is reallocated across different industries.
B) the same as that for frictional and structural unemployment.
C) that wage demands are too high relative to falling prices.
D) that it is a normal response to real shocks in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements about the employment-at- will doctrine is TRUE?
A) The doctrine helps raise labor hiring and firing costs, leading to lower unemployment rates.
B) The doctrine helps raise labor hiring and firing costs, leading to higher unemployment rates.
C) The doctrine helps lower labor hiring and firing costs, leading to lower unemployment rates.
D) The doctrine helps lower labor hiring and firing costs, leading to higher unemployment rates.
A) The doctrine helps raise labor hiring and firing costs, leading to lower unemployment rates.
B) The doctrine helps raise labor hiring and firing costs, leading to higher unemployment rates.
C) The doctrine helps lower labor hiring and firing costs, leading to lower unemployment rates.
D) The doctrine helps lower labor hiring and firing costs, leading to higher unemployment rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Unemployment correlated with the business cycle is called
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Comparing current real GDP growth to _______ will give a good indication of the change in the unemployment rate.
A) nominal GDP growth
B) average real GDP growth
C) real growth rates for the past two years
D) None of these answers is correct.
A) nominal GDP growth
B) average real GDP growth
C) real growth rates for the past two years
D) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examples of active labor market policies include I. job-retraining programs. II. job-search assistance. III. early re-employment bonuses.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Employment protection laws tend to I. increase the duration of unemployment. II. increase labor market flexibility. III. increase the job security of workers.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During recessions the unemployment rate
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains relatively constant.
D) fluctuates randomly.
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) remains relatively constant.
D) fluctuates randomly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What allows an employee to quit at any time and an employer to fire at any time for any reason?
A) employment-at-will
B) contractual autonomy
C) right-to-hire
D) termination sovereignty
A) employment-at-will
B) contractual autonomy
C) right-to-hire
D) termination sovereignty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Job search programs and work tests for unemployed workers are likely to be sponsored by
A) firms.
B) unions.
C) governments.
D) workers.
A) firms.
B) unions.
C) governments.
D) workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In 2005, immigrant youth rioted in Paris and throughout France giving high unemployment as one of their main reasons. Who were their most vocal opponents?
A) the workers with the most seniority at their jobs
B) university students
C) corporate executives and managers
D) older unemployed workers from rural regions
A) the workers with the most seniority at their jobs
B) university students
C) corporate executives and managers
D) older unemployed workers from rural regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Long-term unemployment tends to be higher when the government I. raises job security. II. raises hiring and firing costs. III. lowers restrictions for firms to adjust work hours.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following best describes the effects of a major labor union that maintains a union wage above the market equilibrium wage?
A) The quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied, and the unemployment rate increases.
B) The quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied, and the unemployment rate decreases.
C) The quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded, and the unemployment rate increases.
D) The quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded, and the unemployment rate decreases.
A) The quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied, and the unemployment rate increases.
B) The quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied, and the unemployment rate decreases.
C) The quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded, and the unemployment rate increases.
D) The quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded, and the unemployment rate decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why does unemployment rise during recessions? I. because of labor reallocation among affected industries in response to real economic shocks II. because wages do not fall as fast as prices, and firms cannot afford to employ as many workers III. because of increases in aggregate demand
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Higher GDP growth
A) decreases the unemployment rate.
B) increases the unemployment rate.
C) leaves the unemployment rate unchanged.
D) makes the unemployment rate fluctuate randomly.
A) decreases the unemployment rate.
B) increases the unemployment rate.
C) leaves the unemployment rate unchanged.
D) makes the unemployment rate fluctuate randomly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What type of laws affects young, minority, and unemployed workers most negatively?
A) employment-at-will
B) employment protection
C) constructive discharge
D) fair labor
A) employment-at-will
B) employment protection
C) constructive discharge
D) fair labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which one of the following reasons explains why the French at- will employment proposal for the younger population failed?
A) Elitist French youth viewed at-will employment as an infringement of their rights.
B) Riots among the immigrant youth got the government to reconsider.
C) High unemployment among immigrant youth made the proposal intractable.
D) France did not want to adopt the same laws that the United States follows.
A) Elitist French youth viewed at-will employment as an infringement of their rights.
B) Riots among the immigrant youth got the government to reconsider.
C) High unemployment among immigrant youth made the proposal intractable.
D) France did not want to adopt the same laws that the United States follows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What problem do employment protection laws create?
A) They encourage workers to change jobs more frequently.
B) They are costly for governments to maintain.
C) Employers have difficulty keeping qualified workers.
D) Employers are reluctant to hire new workers.
A) They encourage workers to change jobs more frequently.
B) They are costly for governments to maintain.
C) Employers have difficulty keeping qualified workers.
D) Employers are reluctant to hire new workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which one of the following statements regarding the rigidity of employment index discussed in the text is NOT correct?
A) The U.S. labor market experiences more rigidity, thus ranking higher, than most European countries.
B) Countries that rank higher on the index tend to have more long-term unemployment.
C) Countries that rank higher on the index tend to have less flexible and dynamic labor markets.
D) The index ranks countries based on a summary of hiring and firing costs as well as the ease of work hour adjustments.
A) The U.S. labor market experiences more rigidity, thus ranking higher, than most European countries.
B) Countries that rank higher on the index tend to have more long-term unemployment.
C) Countries that rank higher on the index tend to have less flexible and dynamic labor markets.
D) The index ranks countries based on a summary of hiring and firing costs as well as the ease of work hour adjustments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



