Deck 3: Interdependence and the Gains From Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Interdependence and the Gains From Trade
1
One reason trade benefits both parties is that it allows each to specialise in what they do better.
True
2
A constant trade-off in the production of two goods implies that the production possibility frontier will be a curve rather than a straight line.
False
3
The producer who has the smaller opportunity cost of producing a good is said to have a comparative advantage in producing that good.
True
4
People's motivation to trade comes from the goods or services they expect to get in return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
It takes Barbara four hours to make a pie and four hours to make a shirt. It takes Gary two hours to make a pie and five hours to make a shirt. Barbara should specialise in making shirts and Gary should specialise in making pies. Then they should trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The principle of absolute advantage explains the gains from trade and why economic interdependence occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Rusty can edit two pages in one minute, and can type 80 words in one minute. Emily can edit one page in one minute and can type 100 words in one minute. Rusty has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in editing and Emily has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in typing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Trade is not based on absolute advantage; rather it is based on comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose it takes Jean four hours to catch 10 fish and one hour to collect one kilogram of mushrooms. It takes Lee four hours to catch 10 fish and 30 minutes to collect 1 kg of mushrooms. Lee should specialise in catching fish and Jean should specialise in collecting mushrooms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If trade is not possible, then each person's production possibility frontier is the same as each person's consumption possibility frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Shaquille can score 32 points or produce 12 rebounds in one game. Karl can score three points or produce one rebound in one game. Shaquille has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in both scoring and rebounding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose Aaron can build a table in three days and clean a house in one hour, while Jack can clean a house in three hours but it only takes him one day to build a table. Jack has an absolute advantage over Aaron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If one country can produce all goods more cheaply than another, there is no reason to trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As long as two people have different opportunity costs, each can gain from trade by being able to obtain a good at a price lower than his or her opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For a country producing two goods, the opportunity cost of one good will be the inverse of the opportunity cost of the other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two individuals or two nations can benefit from trade even if one country has an absolute advantage over the other in producing all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Comparative advantage will always occur when two parties have different opportunity costs in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Differences in opportunity cost and comparative advantage allow for gains from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Trade allows a country to pivot outwards its production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lee can pick 30 apples in one hour. He can pick 60 kiwifruit in half an hour. The opportunity cost to Lee of picking one apple is four kiwifruit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
David Ricardo developed the theory of imports and exports, as we know them today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In order to have a linear production possibilities frontier (one that is not bowed out), it must be that:
A) there are no trade-offs
B) the trade-off between two goods is constant
C) the trade-off between two goods is increasing
D) the trade-off between two goods is decreasing
A) there are no trade-offs
B) the trade-off between two goods is constant
C) the trade-off between two goods is increasing
D) the trade-off between two goods is decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Goods produced abroad and sold domestically are called exports and goods produced domestically and sold abroad are called imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Table 3-1. For the potato farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat is:
A) eight hours of labour
B) four hours of labour
C) 2 kg of potatoes
D) 1/2 kg of potatoes
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Table 3-1. For the potato farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat is:
A) eight hours of labour
B) four hours of labour
C) 2 kg of potatoes
D) 1/2 kg of potatoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The reason most people provide you with goods and services is because:
A) their beliefs make them feel charitable to you
B) they want to be your friend
C) they will receive something they want in return
D) they are not as good at bargaining as you are
A) their beliefs make them feel charitable to you
B) they want to be your friend
C) they will receive something they want in return
D) they are not as good at bargaining as you are

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Table 3-1. For the cattle farmer, the opportunity cost of one kg of potatoes is:
A) four hours of labour
B) two hours of labour
C) 1/4 kg of meat
D) 4 kg of meat
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Table 3-1. For the cattle farmer, the opportunity cost of one kg of potatoes is:
A) four hours of labour
B) two hours of labour
C) 1/4 kg of meat
D) 4 kg of meat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Adam Smith discusses that countries should be self-sufficient in his 1776 book An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
According to Table 3-1:
A) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in meat
B) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in neither goods
C) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in meat, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes
D) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in neither goods, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.According to Table 3-1:
A) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in meat
B) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in neither goods
C) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in meat, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes
D) the cattle farmer has a comparative advantage in neither goods, and the potato farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The conclusions of Adam Smith and David Ricardo on the gains from trade are no longer valid due to the increase of barriers to trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A Korean worker can produce 10 cars per month or grow 1500 kg of wheat per month and an American worker can produce four cars or 1700 kg of rice per month. Korea and the US can both gain if Korea makes more cars and exports them to the US in exchange for imports of increased output of Australian rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a country imports goods from overseas, it will always suffer a reduction in welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A country's consumption possibilities frontier can be moved outside its production possibilities frontier:
A) by producing a greater variety of goods and services
B) by allocating resources differently
C) through trade
D) by lowering unemployment in the country
A) by producing a greater variety of goods and services
B) by allocating resources differently
C) through trade
D) by lowering unemployment in the country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If it takes Australian workers fewer hours to produce every good than it takes Malaysian workers, Australia cannot gain from trade with Malaysia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
International trade may make some individuals in a nation better off, while other individuals are made worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A person is able to obtain goods at prices that are less than that person's opportunity cost because each person concentrates on the activity for which he or she has the lower opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The central argument for free trade has changed a lot in the past two centuries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A butcher can produce only sausages, and a farmer can produce only potato chips. The butcher and the farmer like both foods. They:
A) cannot gain from trade under any circumstances
B) could gain from trade under certain circumstances, but not always
C) could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food
D) could gain from trade only if they were indifferent between sausages and potato chips
A) cannot gain from trade under any circumstances
B) could gain from trade under certain circumstances, but not always
C) could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food
D) could gain from trade only if they were indifferent between sausages and potato chips

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Table 3-1. For the potato farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes is:
A) eight hours of labour
B) 1/2 kg of meat
C) 2 kg of meat
D) four hours of labour
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Table 3-1. For the potato farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes is:
A) eight hours of labour
B) 1/2 kg of meat
C) 2 kg of meat
D) four hours of labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Table 3-1. For the cattle farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat is:
A) five hours of labour
B) one hour of labour
C) 1/4 kg of potatoes
D) 4 kg of potatoes
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Table 3-1. For the cattle farmer, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat is:
A) five hours of labour
B) one hour of labour
C) 1/4 kg of potatoes
D) 4 kg of potatoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The principle of comparative advantage was developed in Adam Smith's 1817 book Principles of Political Economy and Taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Table 3-2
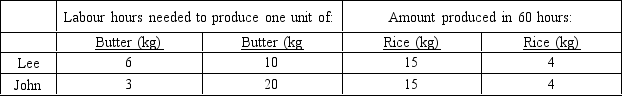
According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has a comparative advantage in rice
B) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
C) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
D) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in rice

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has a comparative advantage in rice
B) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
C) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
D) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. The opportunity cost of 1 kg of butter for John is:
A) 3/2 kg of rice
B) 4/3 kg of rice
C) 3/4 kg of rice
D) 2/3 kg of rice

Refer to Table 3-2. The opportunity cost of 1 kg of butter for John is:
A) 3/2 kg of rice
B) 4/3 kg of rice
C) 3/4 kg of rice
D) 2/3 kg of rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Comparative advantage is based on:
A) capital costs
B) labour costs
C) dollar price
D) opportunity costs
A) capital costs
B) labour costs
C) dollar price
D) opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Graph 3-1. For Robinson Crusoe, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of coconuts is:
A) 2 kg of fish
B) 1/2 kg of fish
C) 4 kg of fish
D) 1/4 kg of fish
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Graph 3-1. For Robinson Crusoe, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of coconuts is:
A) 2 kg of fish
B) 1/2 kg of fish
C) 4 kg of fish
D) 1/4 kg of fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. The opportunity cost of 1 kg of butter for Lee is:
A) 3/2 kg of rice
B) 4/3 kg of rice
C) 3/4 kg of rice
D) 2/3 kg of rice

Refer to Table 3-2. The opportunity cost of 1 kg of butter for Lee is:
A) 3/2 kg of rice
B) 4/3 kg of rice
C) 3/4 kg of rice
D) 2/3 kg of rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Table 3-2

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in butter, and John specialising in rice
B) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in butter, and John specialising in butter
C) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in rice, and John specialising in butter
D) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in rice, and John specialising in rice

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in butter, and John specialising in rice
B) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in butter, and John specialising in butter
C) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in rice, and John specialising in butter
D) Lee and John both could benefit by Lee specialising in rice, and John specialising in rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Mark can cook dinner in 30 minutes and wash the laundry in 20 minutes while his housemate John can cook dinner in 15 minutes and wash the laundry in 30 minutes. How should they allocate their work?
A) Mark should cook dinner based on his comparative advantage
B) John should cook dinner based on his absolute advantage
C) John should cook dinner based on his comparative advantage
D) Mark should do the laundry based on his absolute advantage
A) Mark should cook dinner based on his comparative advantage
B) John should cook dinner based on his absolute advantage
C) John should cook dinner based on his comparative advantage
D) Mark should do the laundry based on his absolute advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
According to Graph 3-1:
A) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
B) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in coconuts, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
C) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
D) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in neither goods
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.According to Graph 3-1:
A) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
B) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in coconuts, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
C) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
D) Robinson Crusoe has a comparative advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in neither goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Trade is based on:
A) absolute advantage
B) comparative advantage
C) trade subsidies
D) free trade agreements
A) absolute advantage
B) comparative advantage
C) trade subsidies
D) free trade agreements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Table 3-2

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has an absolute advantage in both goods
B) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
C) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
D) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in both goods

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has an absolute advantage in both goods
B) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
C) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
D) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Table 3-2

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
B) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has an absolute advantage in rice
C) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in neither good
D) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has an absolute advantage in neither good

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in butter
B) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has an absolute advantage in rice
C) Lee has a comparative advantage in rice, and John has an absolute advantage in neither good
D) Lee has a comparative advantage in butter, and John has an absolute advantage in neither good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Absolute advantage is found by:
A) comparing opportunity costs
B) calculating the dollar cost of production
C) comparing the productivity of one nation to that of another
D) first determining which country has a comparative advantage
A) comparing opportunity costs
B) calculating the dollar cost of production
C) comparing the productivity of one nation to that of another
D) first determining which country has a comparative advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Graph 3-1. For Friday, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of coconuts is:
A) 2/3 kg of fish
B) 3 kg of fish
C) 1 kg of fish
D) 2 kg of fish
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Graph 3-1. For Friday, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of coconuts is:
A) 2/3 kg of fish
B) 3 kg of fish
C) 1 kg of fish
D) 2 kg of fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Table 3-2

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
B) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
C) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in neither good
D) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has a comparative advantage in rice

According to Table 3-2:
A) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
B) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in butter
C) Lee has an absolute advantage in rice, and John has a comparative advantage in neither good
D) Lee has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and John has a comparative advantage in rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
According to Graph 3-1:
A) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in coconuts, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
B) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
C) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
D) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.According to Graph 3-1:
A) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in coconuts, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish
B) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
C) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in fish, and Friday has a comparative advantage in coconuts
D) Robinson Crusoe has an absolute advantage in neither goods, and Friday has a comparative advantage in fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Graph 3-1. For Friday, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of fish is:
A) 1 kg of coconuts
B) 3/2 kg of coconuts
C) 1/3 kg of coconuts
D) 2 kg of fish
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Graph 3-1. For Friday, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of fish is:
A) 1 kg of coconuts
B) 3/2 kg of coconuts
C) 1/3 kg of coconuts
D) 2 kg of fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. For Lee the opportunity cost of 1 kg of rice is:
A) 4/3 kg of butter
B) 3/4 kg of butter
C) 2/3 kg of butter
D) 3/2 kg of butter

Refer to Table 3-2. For Lee the opportunity cost of 1 kg of rice is:
A) 4/3 kg of butter
B) 3/4 kg of butter
C) 2/3 kg of butter
D) 3/2 kg of butter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Trade can benefit society as a whole because it allows:
A) people to specialise in activities in which they have a comparative advantage
B) for a more efficient use of resources
C) for goods to be obtained at a lower opportunity cost
D) all of the above are correct
A) people to specialise in activities in which they have a comparative advantage
B) for a more efficient use of resources
C) for goods to be obtained at a lower opportunity cost
D) all of the above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Graph 3-1
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
Refer to Graph 3-1. For Robinson Crusoe, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of fish is:
A) 2 kg of coconuts
B) 1/2 kg of coconuts
C) 4 kg of coconuts
D) 1/4 kg of coconuts
 These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.
These figures illustrate the production possibilities frontiers for Robinson Crusoe and Friday with 12 hours of labour.Refer to Graph 3-1. For Robinson Crusoe, the opportunity cost of 1 kg of fish is:
A) 2 kg of coconuts
B) 1/2 kg of coconuts
C) 4 kg of coconuts
D) 1/4 kg of coconuts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. For John the opportunity cost of one kg of rice:
A) 3/4 kg of butter
B) 3/2 kg of butter
C) 4/3 kg of butter
D) 2/3 kg of butter

Refer to Table 3-2. For John the opportunity cost of one kg of rice:
A) 3/4 kg of butter
B) 3/2 kg of butter
C) 4/3 kg of butter
D) 2/3 kg of butter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) the US will export cars and Europe will export aeroplanes
B) the US will export aeroplanes and Europe will export cars
C) the US will export cars and Europe will export cars
D) the US will export aeroplanes and Europe will export aeroplanes

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) the US will export cars and Europe will export aeroplanes
B) the US will export aeroplanes and Europe will export cars
C) the US will export cars and Europe will export cars
D) the US will export aeroplanes and Europe will export aeroplanes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Table 3-4
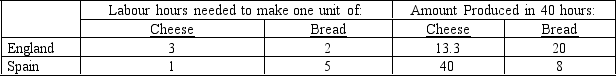
According to Table 3-4, England and Spain could benefit by specialising in _____ respectively:
A) bread and cheese
B) cheese and bread
C) both goods and neither goods
D) neither goods and both goods

According to Table 3-4, England and Spain could benefit by specialising in _____ respectively:
A) bread and cheese
B) cheese and bread
C) both goods and neither goods
D) neither goods and both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, Europe will export what product to the US?
A) cars
B) both aeroplanes and cars
C) aeroplanes
D) Europe should buy both products from the US

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, Europe will export what product to the US?
A) cars
B) both aeroplanes and cars
C) aeroplanes
D) Europe should buy both products from the US

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one car for Europe is:
A) four aeroplanes
B) three aeroplanes
C) 1/3 aeroplane
D) 1/4 aeroplane

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one car for Europe is:
A) four aeroplanes
B) three aeroplanes
C) 1/3 aeroplane
D) 1/4 aeroplane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one aeroplane for Europe is:
A) four cars
B) three cars
C) 1/3 car
D) 1/4 car

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one aeroplane for Europe is:
A) four cars
B) three cars
C) 1/3 car
D) 1/4 car

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. If Europe and the US trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) all individuals in both countries will gain
B) both countries can have more aeroplanes and cars
C) Europe will specialise in cars and the US will specialise in aeroplanes
D) both countries will consume on their own production possibilities frontier

Refer to Table 3-3. If Europe and the US trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) all individuals in both countries will gain
B) both countries can have more aeroplanes and cars
C) Europe will specialise in cars and the US will specialise in aeroplanes
D) both countries will consume on their own production possibilities frontier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Table 3-4

According to Table 3-4:
A) England has a comparative advantage in bread, and Spain has a comparative advantage in cheese
B) England has a comparative advantage in cheese, and Spain has a comparative advantage in bread
C) England has a comparative advantage in both goods, and Spain has a comparative advantage in neither goods
D) England has a comparative advantage in neither goods, and Spain has a comparative advantage in both goods

According to Table 3-4:
A) England has a comparative advantage in bread, and Spain has a comparative advantage in cheese
B) England has a comparative advantage in cheese, and Spain has a comparative advantage in bread
C) England has a comparative advantage in both goods, and Spain has a comparative advantage in neither goods
D) England has a comparative advantage in neither goods, and Spain has a comparative advantage in both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Table 3-4

According to Table 3-4:
A) England has an absolute advantage in bread, and Spain has an absolute advantage in cheese
B) England has an absolute advantage in cheese, and Spain has an absolute advantage in bread
C) England has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Spain has an absolute advantage in neither goods
D) Neither England nor Spain has an absolute advantage

According to Table 3-4:
A) England has an absolute advantage in bread, and Spain has an absolute advantage in cheese
B) England has an absolute advantage in cheese, and Spain has an absolute advantage in bread
C) England has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Spain has an absolute advantage in neither goods
D) Neither England nor Spain has an absolute advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one aeroplane for the US is:
A) four cars
B) three cars
C) 1/3 car
D) 1/4 car

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one aeroplane for the US is:
A) four cars
B) three cars
C) 1/3 car
D) 1/4 car

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one car for the US is:
A) four aeroplanes
B) three aeroplanes
C) 1/3 aeroplane
D) 1/4 aeroplane

Refer to Table 3-3. The opportunity cost of one car for the US is:
A) four aeroplanes
B) three aeroplanes
C) 1/3 aeroplane
D) 1/4 aeroplane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of bread in England is:
A) 2/3 unit of cheese
B) two units of cheese
C) one unit of cheese
D) 1/2 unit of cheese

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of bread in England is:
A) 2/3 unit of cheese
B) two units of cheese
C) one unit of cheese
D) 1/2 unit of cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of cheese in England is:
A) four units of bread
B) two units of bread
C) 1/2 unit of bread
D) 1.5 units of bread

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of cheese in England is:
A) four units of bread
B) two units of bread
C) 1/2 unit of bread
D) 1.5 units of bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. If Europe and the US trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) all individuals in both countries will gain
B) car producers in Europe and aeroplane producers in the US will gain
C) some individuals within each society will be made worse off
D) one country will be better off and the other country will be worse off

Refer to Table 3-3. If Europe and the US trade according to the principle of comparative advantage:
A) all individuals in both countries will gain
B) car producers in Europe and aeroplane producers in the US will gain
C) some individuals within each society will be made worse off
D) one country will be better off and the other country will be worse off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. If England reduced the labour hours needed for it to produce cheese by 2.5 hours, it would:
A) have a comparative advantage over Spain in the production of cheese
B) have an absolute advantage over Spain in the production of both goods
C) have a comparative advantage over Spain in the production of both goods
D) have an absolute advantage over Spain in the production of cheese but not in the production of bread

Refer to Table 3-4. If England reduced the labour hours needed for it to produce cheese by 2.5 hours, it would:
A) have a comparative advantage over Spain in the production of cheese
B) have an absolute advantage over Spain in the production of both goods
C) have a comparative advantage over Spain in the production of both goods
D) have an absolute advantage over Spain in the production of cheese but not in the production of bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of bread in Spain is:
A) one unit of cheese
B) five units of cheese
C) 1/5 unit of cheese
D) 1/3 unit of cheese

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of bread in Spain is:
A) one unit of cheese
B) five units of cheese
C) 1/5 unit of cheese
D) 1/3 unit of cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Table 3-3

According to Table 3-3, the US and Europe could benefit by specialising in _____ respectively.
A) aeroplanes and aeroplanes
B) cars and aeroplanes
C) aeroplanes and cars
D) neither goods and cars

According to Table 3-3, the US and Europe could benefit by specialising in _____ respectively.
A) aeroplanes and aeroplanes
B) cars and aeroplanes
C) aeroplanes and cars
D) neither goods and cars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. If England and Spain trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, England will export which product to Spain:
A) bread
B) cheese
C) both cheese and bread
D) England cannot benefit from trade with Spain

Refer to Table 3-4. If England and Spain trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, England will export which product to Spain:
A) bread
B) cheese
C) both cheese and bread
D) England cannot benefit from trade with Spain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of cheese in Spain is:
A) one unit of bread
B) five units of bread
C) 1/5 unit of bread
D) 1/3 unit of bread

Refer to Table 3-4. The opportunity cost of one unit of cheese in Spain is:
A) one unit of bread
B) five units of bread
C) 1/5 unit of bread
D) 1/3 unit of bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 3-4

Refer to Table 3-4. If England and Spain trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, Spain will export which product to England?
A) bread
B) both bread and cheese
C) cheese
D) Spain cannot benefit from trade with England

Refer to Table 3-4. If England and Spain trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, Spain will export which product to England?
A) bread
B) both bread and cheese
C) cheese
D) Spain cannot benefit from trade with England

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, the US will export what product to Europe?
A) cars
B) both aeroplanes and cars
C) aeroplanes
D) the US should buy both products from Europe

Refer to Table 3-3. If the US and Europe trade according to the principle of comparative advantage, the US will export what product to Europe?
A) cars
B) both aeroplanes and cars
C) aeroplanes
D) the US should buy both products from Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



