Deck 12: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
1
Identify the intermediate in the following two-step reaction. Cr2+(aq)+ Sn4+(aq)⇌ Cr3+(aq)+ Sn3+(aq)Cr2+(aq)+ Sn3+(aq)→ Cr3+(aq)+ Sn2+(aq)
A)Sn3+(aq)
B)Sn4+(aq)
C)Sn2+(aq)
D)Cr2+(aq)
E)Cr3+(aq)
A)Sn3+(aq)
B)Sn4+(aq)
C)Sn2+(aq)
D)Cr2+(aq)
E)Cr3+(aq)
Sn3+(aq)
2
Which of the following statements regarding catalysts is incorrect?
A)A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by giving the reaction an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy.
B)Catalysts need not be present in large amounts because they are regenerated during the reaction.
C)Enzymes act as catalysts in our bodies.
D)In a chemical reaction, the catalyst is shown on the reactant side of the equation.
E)The shape of an active site on an enzyme is unique, allowing it to react with only one substrate.
A)A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by giving the reaction an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy.
B)Catalysts need not be present in large amounts because they are regenerated during the reaction.
C)Enzymes act as catalysts in our bodies.
D)In a chemical reaction, the catalyst is shown on the reactant side of the equation.
E)The shape of an active site on an enzyme is unique, allowing it to react with only one substrate.
In a chemical reaction, the catalyst is shown on the reactant side of the equation.
3
Which of the following changes will increase the fraction of collisions that are effective collisions?
A)increasing the temperature
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants
C)decreasing the concentration of the reactants
D)increasing the surface area of the reactants
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)increasing the temperature
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants
C)decreasing the concentration of the reactants
D)increasing the surface area of the reactants
E)All of these choices are correct.
increasing the temperature
4
Factors that influence reaction rates include all of the following except the
A)magnitude of the equilibrium constant.
B)reaction temperature.
C)presence of a catalyst.
D)size of solid reactant particles.
E)concentration of reactants.
A)magnitude of the equilibrium constant.
B)reaction temperature.
C)presence of a catalyst.
D)size of solid reactant particles.
E)concentration of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The rate of a reaction can be increased by all of the following except
A)increasing the temperature.
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants.
C)increasing the surface area of the reactants.
D)adding a catalyst.
E)increasing the volume of the reaction vessel.
A)increasing the temperature.
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants.
C)increasing the surface area of the reactants.
D)adding a catalyst.
E)increasing the volume of the reaction vessel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A catalyst speeds up a chemical reaction by
A)providing an alternate reaction pathway.
B)increasing the activation energy.
C)shifting the equilibrium.
D)increasing the heat of the reaction.
E)decreasing the heat of the reaction.
A)providing an alternate reaction pathway.
B)increasing the activation energy.
C)shifting the equilibrium.
D)increasing the heat of the reaction.
E)decreasing the heat of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following will not increase the rate of a reaction?
A)decreasing the temperature
B)decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C)decreasing the surface area of the reactants
D)removing a catalyst
E)All of these will not increase the rate of a reaction.
A)decreasing the temperature
B)decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C)decreasing the surface area of the reactants
D)removing a catalyst
E)All of these will not increase the rate of a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements regarding catalysts is incorrect?
A)A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by giving the reaction an alternate pathway with lower activation energy.
B)A catalyst is formed temporarily in an early step of a reaction.
C)Most enzyme catalysts are large protein molecules.
D)In a chemical equation the catalyst is shown above the reaction arrow of the equation.
E)The shape of an active site on an enzyme is unique, allowing it to react with only one substrate.
A)A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by giving the reaction an alternate pathway with lower activation energy.
B)A catalyst is formed temporarily in an early step of a reaction.
C)Most enzyme catalysts are large protein molecules.
D)In a chemical equation the catalyst is shown above the reaction arrow of the equation.
E)The shape of an active site on an enzyme is unique, allowing it to react with only one substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify any intermediates in the following three-step reaction: H2C=CH2 + H3O+ → H3C=CH2+ + H2O
H3C=CH2+ + H2O → CH3CH2OH2+
CH3CH2OH2+ + H2O → CH3CH2OH + H3O+
A)H3O+ is an intermediate.
B)H3C=CH2+ is an intermediate.
C)H3C=CH2+, CH3CH2OH2+, and H2O are intermediates.
D)CH3CH2OH2+ is an intermediate.
E)H2O is an intermediate.
H3C=CH2+ + H2O → CH3CH2OH2+
CH3CH2OH2+ + H2O → CH3CH2OH + H3O+
A)H3O+ is an intermediate.
B)H3C=CH2+ is an intermediate.
C)H3C=CH2+, CH3CH2OH2+, and H2O are intermediates.
D)CH3CH2OH2+ is an intermediate.
E)H2O is an intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a chemical reaction at constant temperature, the addition of a catalyst
A)affects the equilibrium constant.
B)increases the average kinetic energy of the reactants.
C)provides an alternate reaction pathway with a different activation energy.
D)decreases the energy released in the chemical reaction.
E)increases the concentration of the products at equilibrium.
A)affects the equilibrium constant.
B)increases the average kinetic energy of the reactants.
C)provides an alternate reaction pathway with a different activation energy.
D)decreases the energy released in the chemical reaction.
E)increases the concentration of the products at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify any intermediates or catalysts in the following two-step reaction: Cu2+ + H2 → CuH+ + H+ CuH+ + H+ + H2C=CH2 → Cu2+ + H3C-CH3
A)CuH+ is an intermediate.
B)Cu2+ is a catalyst, H+ is an intermediate.
C)Cu2+ is a catalyst, CuH+ is an intermediate.
D)Cu2+ is a catalyst, CuH+ and H+ are intermediates.
E)CuH+ and H+ are catalysts, Cu2+ is an intermediate.
A)CuH+ is an intermediate.
B)Cu2+ is a catalyst, H+ is an intermediate.
C)Cu2+ is a catalyst, CuH+ is an intermediate.
D)Cu2+ is a catalyst, CuH+ and H+ are intermediates.
E)CuH+ and H+ are catalysts, Cu2+ is an intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify the intermediate(s)in the following two-step reaction. O3(g)⇌ O2(g)+ O(g)O(g)+ O3(g)→ 2O2(g)
A)O(g)
B)O3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)O2(g)and O(g)
A)O(g)
B)O3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)O2(g)and O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following changes will increase the average kinetic energy of the reactants?
A)increasing the surface area of the reactants
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants
C)adding a catalyst
D)increasing the temperature
E)none of these choices
A)increasing the surface area of the reactants
B)increasing the concentration of the reactants
C)adding a catalyst
D)increasing the temperature
E)none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to collision theory, the increase in the rate constant with increasing temperature is due mostly to the fact that
A)the activation energy decreases with increasing temperature.
B)the fraction of the collisions having sufficient energy to react increases with increasing temperature.
C)the pressure of the reactants increases with increasing temperature.
D)the heat change for most reactions is negative.
E)the fraction of the collisions that have the proper orientation for reaction increases with increasing temperature.
A)the activation energy decreases with increasing temperature.
B)the fraction of the collisions having sufficient energy to react increases with increasing temperature.
C)the pressure of the reactants increases with increasing temperature.
D)the heat change for most reactions is negative.
E)the fraction of the collisions that have the proper orientation for reaction increases with increasing temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify an intermediate in the following two-step reaction. Sn2+ + Fe3+ → Sn3+ + Fe2+ Sn3+ + Fe3+ → Sn4+ + Fe2+
A)Sn2+
B)Fe3+
C)Sn3+
D)Fe2+
E)Sn4+
A)Sn2+
B)Fe3+
C)Sn3+
D)Fe2+
E)Sn4+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the images shows the molecules in a proper orientation for an effective collision for the following reaction? 2HI(g)→ H2(g)+ I2(g) 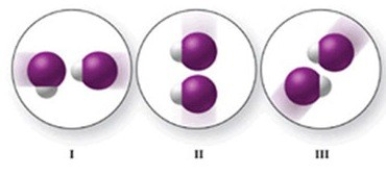
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II
E)II and III

A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II
E)II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the intermediate(s)in the following three-step reaction. Cl2(g)⇌ 2Cl(g)CHCl3(g)+ Cl(g)→ HCl(g)+ CCl3(g)CCl3(g)+ Cl(g)→ CCl4(g)
A)CHCl3(g)
B)HCl(g)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl(g)
E)Cl(g)and CCl3(g)
A)CHCl3(g)
B)HCl(g)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl(g)
E)Cl(g)and CCl3(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify any intermediates or catalysts in the following two-step reaction: H2O2 + 2Br− + 2H+→ 2H2O + Br2 H2O2 + Br2 → 2H+ + O2 + 2Br−
A)H2O2 is an intermediate.
B)H2O2 is a catalyst, Br− is an intermediate.
C)Br− is a catalyst, Br2 is an intermediate.
D)H+ is a catalyst.
E)Br− and H+ are catalysts, Br2 is an intermediate.
A)H2O2 is an intermediate.
B)H2O2 is a catalyst, Br− is an intermediate.
C)Br− is a catalyst, Br2 is an intermediate.
D)H+ is a catalyst.
E)Br− and H+ are catalysts, Br2 is an intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify any intermediates or catalysts in the following two-step reaction: S2O82− + I− → 2SO42− + I+ I+ + I− → I2
A)S2O82− is an intermediate.
B)S2O82− is a catalyst.
C)I− is a catalyst.
D)I+ is an intermediate.
E)SO42− is a catalyst.
A)S2O82− is an intermediate.
B)S2O82− is a catalyst.
C)I− is a catalyst.
D)I+ is an intermediate.
E)SO42− is a catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The kinetics of a reaction is studied at 25ºC and at 50ºC. Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be lower than the rate at 25ºC, since the molecules will be moving too fast to collide effectively.
B)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be twice that of the rate at 25ºC, since the temperature has doubled.
C)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be greater than the rate at 25ºC, since the activation energy will be lower at the higher temperature.
D)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be greater than the rate at 25ºC, since a greater fraction of the molecules will possess sufficient energy to react at the higher temperature.
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be lower than the rate at 25ºC, since the molecules will be moving too fast to collide effectively.
B)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be twice that of the rate at 25ºC, since the temperature has doubled.
C)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be greater than the rate at 25ºC, since the activation energy will be lower at the higher temperature.
D)The rate of the reaction at 50ºC will be greater than the rate at 25ºC, since a greater fraction of the molecules will possess sufficient energy to react at the higher temperature.
E)None of these statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a chemical system has reached equilibrium
A)the forward and reverse reactions have stopped.
B)the rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
C)the rate of the forward reaction is less than the rate of the reverse reaction.
D)the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
E)the equilibrium constant has reached a minimum.
A)the forward and reverse reactions have stopped.
B)the rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
C)the rate of the forward reaction is less than the rate of the reverse reaction.
D)the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
E)the equilibrium constant has reached a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify the catalyst in the following three-step process for the decomposition of ozone. O3(g)⇌ O2(g)+ O(g)NO(g)+ O3(g)→ NO2(g)+ O2(g)O(g)+ NO2(g)→ O2(g)+ NO(g)
A)O(g)
B)O3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)NO(g)
E)NO2(g)
A)O(g)
B)O3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)NO(g)
E)NO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given that the following reaction is exothermic, which of the following sets of changes would cause the following system at equilibrium to shift to increase the number of N2O4(g)molecules? 2NO2(g)⇌ N2O4(g)What observation would indicate that the reaction is at equilibrium in a closed container?
A)Increasing container volume and increasing temperature
B)Increasing container volume and decreasing temperature
C)Decreasing container volume and increasing temperature
D)Decreasing container volume and decreasing temperature
E)Changing volume or temperature will not affect the number of gas molecules present at equilibrium
A)Increasing container volume and increasing temperature
B)Increasing container volume and decreasing temperature
C)Decreasing container volume and increasing temperature
D)Decreasing container volume and decreasing temperature
E)Changing volume or temperature will not affect the number of gas molecules present at equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Activated complexes are
A)stable molecules that are formed during an early step of a reaction, and consumed in a later step.
B)materials which act to increase the rate of a reaction without themselves being consumed.
C)substances which form during a reaction that have a definite, well-known structure.
D)short-lived, high-energy chemical species that are produced during a reaction.
E)a molecular species with normal chemical bonds that is produced during a reaction.
A)stable molecules that are formed during an early step of a reaction, and consumed in a later step.
B)materials which act to increase the rate of a reaction without themselves being consumed.
C)substances which form during a reaction that have a definite, well-known structure.
D)short-lived, high-energy chemical species that are produced during a reaction.
E)a molecular species with normal chemical bonds that is produced during a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the following reaction carried out in a sealed container: 2SO3(g)⇌ 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)A state of equilibrium cannot be reached if the container initially contains
A)SO3 only.
B)O2 only.
C)SO2 and O2 only.
D)SO3 and O2 only.
E)SO3 , SO2 and O2.
A)SO3 only.
B)O2 only.
C)SO2 and O2 only.
D)SO3 and O2 only.
E)SO3 , SO2 and O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For the reaction, CoO(s)+ H2(g)⇌ Co(s)+ H2O(g), at 550°C, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 67. The equilibrium constant expression is
A)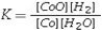
B)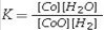
C)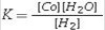
D)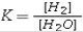
E)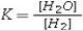
A)
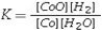
B)
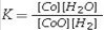
C)
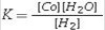
D)
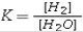
E)
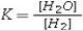

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify the catalyst in the following three-step reaction. NO(g)+ O2(g)→ NO3(g)NO3(g)+ NO(g)→ 2NO2(g)NO2(g)+ SO2(g)→ NO(g)+ SO3(g)
A)SO2(g)
B)NO3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)NO(g)
E)NO2(g)
A)SO2(g)
B)NO3(g)
C)O2(g)
D)NO(g)
E)NO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following reaction carried out in a sealed container: N2(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ 2NH3(g)A state of equilibrium cannot be reached if the container initially contains
A)NH3 only.
B)N2 only.
C)NH3 and N2 only.
D)NH3, N2, and H2.
A)NH3 only.
B)N2 only.
C)NH3 and N2 only.
D)NH3, N2, and H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In order to write the equilibrium constant expression for a reaction, you must
A)know the mechanism for the reaction.
B)know the rate of the forward and reverse reactions.
C)know the concentrations of all reactants and products.
D)have the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
E)know the conditions of pressure, temperature, and concentration for the system.
A)know the mechanism for the reaction.
B)know the rate of the forward and reverse reactions.
C)know the concentrations of all reactants and products.
D)have the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
E)know the conditions of pressure, temperature, and concentration for the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: H2(g)+ I2(g)⇌ 2HI(g)
A)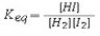
B)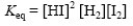
C)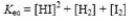
D)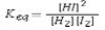
E)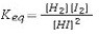
A)
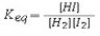
B)
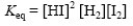
C)
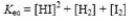
D)
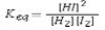
E)
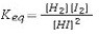

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium at a given temperature: 2NH3(g)+ heat ⇌ N2(g)+ 3H2(g)Which of the following will cause the value of the equilibrium constant for this process to change?
A)Adding more NH3 to the system, with the volume held constant.
B)Increasing the pressure by reducing the volume of the system.
C)Adding an effective catalyst for the process.
D)Raising the temperature of the system.
E)Adding some neon to the system.
A)Adding more NH3 to the system, with the volume held constant.
B)Increasing the pressure by reducing the volume of the system.
C)Adding an effective catalyst for the process.
D)Raising the temperature of the system.
E)Adding some neon to the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH4(g)+ 2H2S(g)⇌ CS2(g)+ 4H2(g)
A)![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_748b_bb3a_49d2f605ee6e_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_9b9c_bb3a_9f95ac826f4c_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_9b9d_bb3a_c5a5f8ec6fc0_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)Keq = [CS2][H2]4 − [CH4][H2S]2
E)Keq = [CS2][H2]4 + [CH4][H2S]2
A)
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_748b_bb3a_49d2f605ee6e_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_9b9c_bb3a_9f95ac826f4c_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>4</sub>(g)+ 2H<sub>2</sub>S(g)⇌ CS<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C) D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> − [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CS<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>4</sup> + [CH<sub>4</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>S]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_9b9d_bb3a_c5a5f8ec6fc0_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)Keq = [CS2][H2]4 − [CH4][H2S]2
E)Keq = [CS2][H2]4 + [CH4][H2S]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the balanced chemical equation that corresponds to the equilibrium constant expression (assuming a homogeneous equilibrium in the gas state)? 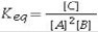
A)A2 + B ⇌ C
B)2A + B ⇌ C
C)C ⇌ A + B
D)C ⇌ A2 + B
E)C ⇌ 2A + B
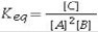
A)A2 + B ⇌ C
B)2A + B ⇌ C
C)C ⇌ A + B
D)C ⇌ A2 + B
E)C ⇌ 2A + B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the balanced chemical equation that corresponds to the equilibrium constant expression (assuming a homogeneous equilibrium in the gas state)? 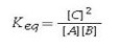
A)A + B ⇌ C
B)2A + 2B ⇌ C
C)C ⇌ A + B
D)A + B ⇌ 2C
E)2C ⇌ A + B
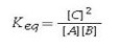
A)A + B ⇌ C
B)2A + 2B ⇌ C
C)C ⇌ A + B
D)A + B ⇌ 2C
E)2C ⇌ A + B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the balanced chemical equation that corresponds to the equilibrium constant expression (assuming a homogeneous equilibrium in the gas state)? 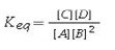
A)A + B2 ⇌ C + D
B)A + 2B ⇌ C + D
C)C + D ⇌ A + B
D)C + D ⇌ A + B2
E)C + D ⇌ A + 2B
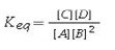
A)A + B2 ⇌ C + D
B)A + 2B ⇌ C + D
C)C + D ⇌ A + B
D)C + D ⇌ A + B2
E)C + D ⇌ A + 2B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the following reaction carried out in a sealed container: N2(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ 2NH3(g)A state of equilibrium can be reached if the container initially contains
A)NH3 only.
B)N2 and H2 only.
C)NH3 and N2 only.
D)NH3, N2, and H2.
E)any of these combinations of reactants and products.
A)NH3 only.
B)N2 and H2 only.
C)NH3 and N2 only.
D)NH3, N2, and H2.
E)any of these combinations of reactants and products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Given that evaporation is an endothermic process, which of the following sets of changes would cause the following system at equilibrium to shift to increase the number of I2 molecules in the gas phase? I2(s)⇌ I2(g)
A)Increasing container volume and increasing temperature
B)Increasing container volume and decreasing temperature
C)Decreasing container volume and increasing temperature
D)Decreasing container volume and decreasing temperature
E)Changing volume or temperature will not affect the number of gas molecules present at equilibrium
A)Increasing container volume and increasing temperature
B)Increasing container volume and decreasing temperature
C)Decreasing container volume and increasing temperature
D)Decreasing container volume and decreasing temperature
E)Changing volume or temperature will not affect the number of gas molecules present at equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH3(g)+ 3O2(g)⇌ 2N2(g)+ 6H2O(g)
A)Keq =![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_c2ae_bb3a_e576f631efe9_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq =![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_e9bf_bb3a_5dc74ba01a6c_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)Keq =![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_e9c0_bb3a_b7017905157c_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)Keq = [N2]2[H2O]6 − [NH3]4[O2]3
E)Keq = [N2]2[H2O]6 + [NH3]4[O2]3
A)Keq =
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_c2ae_bb3a_e576f631efe9_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq =
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_e9bf_bb3a_5dc74ba01a6c_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)Keq =
![<strong>Select the correct equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ 2N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 6H<sub>2</sub>O(g)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = B)K<sub>eq</sub> = C)K<sub>eq</sub> = D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>− [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup> E)K<sub>eq</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>6 </sup>+ [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>4</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39bd_e9c0_bb3a_b7017905157c_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)Keq = [N2]2[H2O]6 − [NH3]4[O2]3
E)Keq = [N2]2[H2O]6 + [NH3]4[O2]3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following reaction carried out in a sealed container: 2SO3(g)⇌ 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)A state of equilibrium can be reached if the container initially contains
A)SO3 only.
B)SO2 and O2 only.
C)SO3 and O2 only.
D)SO3, SO2, and O2.
E)any of these combinations of reactants and products.
A)SO3 only.
B)SO2 and O2 only.
C)SO3 and O2 only.
D)SO3, SO2, and O2.
E)any of these combinations of reactants and products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The graph shows the change in concentrations of the reactant and product as a reaction proceeds. At what point is equilibrium first reached? 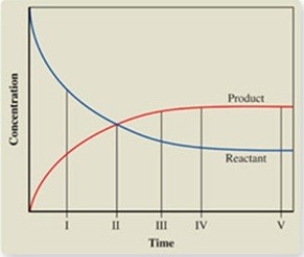
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which equilibrium constant represents a reaction that is reactant favored?
A)Keq = 0.025
B)Keq = 5.2
C)Keq = 8.4 x 10-5
D)Keq = 6.3 x 105
E)not enough information
A)Keq = 0.025
B)Keq = 5.2
C)Keq = 8.4 x 10-5
D)Keq = 6.3 x 105
E)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the reaction CO(g)+ H2O(g)⇌CO2(g)+ H2(g), represented by the following diagram: 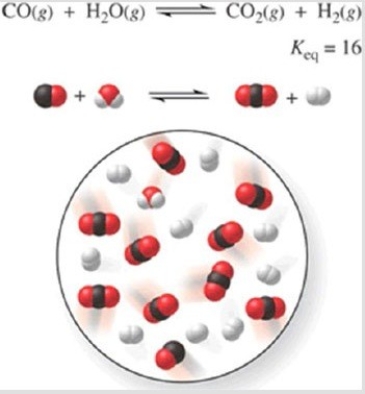 What is the composition of this system when the reaction reaches equilibrium?
What is the composition of this system when the reaction reaches equilibrium?
A)3 CO, 3 H2O, 7 CO2, 7 H2
B)1 CO, 1 H2O, 4 CO2, 4 H2
C)2 CO, 2 H2O, 8 CO2, 8 H2
D)8 CO, 8 H2O, 2 CO2, 2 H2
E)4 CO, 6 H2O, 4 CO2, 6 H2
 What is the composition of this system when the reaction reaches equilibrium?
What is the composition of this system when the reaction reaches equilibrium?A)3 CO, 3 H2O, 7 CO2, 7 H2
B)1 CO, 1 H2O, 4 CO2, 4 H2
C)2 CO, 2 H2O, 8 CO2, 8 H2
D)8 CO, 8 H2O, 2 CO2, 2 H2
E)4 CO, 6 H2O, 4 CO2, 6 H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.200 at a given temperature 2HI(g)⇌ H2(g)+ I2(g)Find the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction: H2(g)+ I2(g)⇌ 2HI(g)
A)0.200
B)0.0400
C)5.00
D)0.500
E)-0.200
A)0.200
B)0.0400
C)5.00
D)0.500
E)-0.200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The reaction S2Cl2(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2SCl2(g)has an equilibrium constant of K = 8. The image shows a partially reacted system. What is the composition of this system when the reaction reaches equilibrium? 
A)1 S2Cl2, 3 Cl2, 10 SCl2
B)2 S2Cl2, 4 Cl2, 8 SCl2
C)3 S2Cl2, 5 Cl2, 6 SCl2
D)4 S2Cl2, 6 Cl2, 4 SCl2
E)5 S2Cl2, 7 Cl2, 2 SCl2

A)1 S2Cl2, 3 Cl2, 10 SCl2
B)2 S2Cl2, 4 Cl2, 8 SCl2
C)3 S2Cl2, 5 Cl2, 6 SCl2
D)4 S2Cl2, 6 Cl2, 4 SCl2
E)5 S2Cl2, 7 Cl2, 2 SCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the following reaction at a specific temperature: 2HI(g)⇌ H2(g)+ I2(g)If [HI] = 0.447 M, [H2] = 0.200 M, and [I2] = 0.200 M at equilibrium, calculate the value of the equilibrium constant under these conditions.
A)0.200
B)0.0400
C)0.0895
D)0.407
E)0.0447
A)0.200
B)0.0400
C)0.0895
D)0.407
E)0.0447

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 4.0 at a given temperature: A ⇌ 2B What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2B ⇌ A?
A)4.0
B)0.25
C)16
D)0.062
E)-4.0
A)4.0
B)0.25
C)16
D)0.062
E)-4.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following reaction at a specific temperature: 2HI(g)⇌ H2(g)+ I2(g)If [HI] = 1.17 M, [H2] = 1.37 M, and [I2] = 0.100 M at equilibrium, calculate the value of the equilibrium constant under these conditions.
A)1.17
B)1.26
C)0.100
D)10.0
E)8.54
A)1.17
B)1.26
C)0.100
D)10.0
E)8.54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For a given reaction, which of the following statements can be made about the value of the equilibrium constant?
A)It always remains the same.
B)It increases when the concentration of one of the products is increased.
C)It increases when the concentration of one of the reactants is increased.
D)It changes when temperature is changed.
E)It can be changed by addition of a catalyst.
A)It always remains the same.
B)It increases when the concentration of one of the products is increased.
C)It increases when the concentration of one of the reactants is increased.
D)It changes when temperature is changed.
E)It can be changed by addition of a catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the following reaction at a specific temperature: CO2(g)+ H2(g)CO(g)+ H2O(g)If [CO2] = 3.60 M, [H2] = 4.00 M, [CO] = 1.18 M, and [H2O] = 2.40 M at equilibrium, calculate the value of the equilibrium ⇌ instant under these conditions.
A)0.471
B)0.197
C)5.08
D)2.12
E)0.444
A)0.471
B)0.197
C)5.08
D)2.12
E)0.444

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 224 at a given temperature: N2(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ 2NH3(g)If [N2] = 10.0 M, [H2] = 10.0 M, and [NH3] = 10.0 M, determine if the reaction is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is correct for a reaction in which Keq << 1?
A)The forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction.
B)The reverse reaction is faster than the forward reaction.
C)There are more products than reactants at equilibrium.
D)There are more reactants than products at equilibrium.
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)The forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction.
B)The reverse reaction is faster than the forward reaction.
C)There are more products than reactants at equilibrium.
D)There are more reactants than products at equilibrium.
E)None of these statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 16 at a given temperature: CO(g)+ H2O(g)⇌ CO2(g)+ H2(g)If [CO] = 4.0 M, [H2O] = 4.0 M, [CO2] = 4.0 M, and [H2] = 4.0 M, determine if the reaction is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.200 at a given temperature: 2HI(g)⇌ H2(g)+ I2(g)If [HI] = 0.200 M, [H2] = 0.200 M, and [I2] = 0.200 M, determine if the reaction is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium, it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 16 at a given temperature: CO(g)+ H2O(g)⇌ CO2(g)+ H2(g)Find the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction: H2(g)+ CO2(g)⇌ CO(g)+ H2O(g)
A)16
B)4.0
C)8.0
D)0.062
E)-16
A)16
B)4.0
C)8.0
D)0.062
E)-16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider the reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: S2Cl2(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2SCl2(g)Keq = 4  Examine the figure, and determine if the system is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
Examine the figure, and determine if the system is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium; it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium; it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.
 Examine the figure, and determine if the system is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?
Examine the figure, and determine if the system is at equilibrium. If it is not, in which direction will it proceed to reach equilibrium?A)The reaction is at equilibrium.
B)The reaction is not at equilibrium; it will shift to the left.
C)The reaction is not at equilibrium; it will shift to the right.
D)It is not possible to tell if the reaction is at equilibrium.
E)To reach equilibrium, the value of Keq must change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which equilibrium constant represents a reaction that is product favored?
A)Keq = 0.025
B)Keq = 5.2
C)Keq = 8.4 x 10-5
D)Keq = 6.3 x 105
E)not enough information
A)Keq = 0.025
B)Keq = 5.2
C)Keq = 8.4 x 10-5
D)Keq = 6.3 x 105
E)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 16 at a given temperature: 2A ⇌ B What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction B ⇌ 2A?
A)5.0
B)25
C)0.20
D)0.040
E)-5.0
A)5.0
B)25
C)0.20
D)0.040
E)-5.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 224 at a given temperature: N2(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ 2NH3(g)Find the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction: 2NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3H2(g)
A)224
B)0.00446
C)448
D)5.02 x 104
E)-224
A)224
B)0.00446
C)448
D)5.02 x 104
E)-224

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is correct for a reaction in which Keq >> 1?
A)The forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction.
B)The reverse reaction is faster than the forward reaction.
C)There are more products than reactants at equilibrium.
D)There are more reactants than products at equilibrium.
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)The forward reaction is faster than the reverse reaction.
B)The reverse reaction is faster than the forward reaction.
C)There are more products than reactants at equilibrium.
D)There are more reactants than products at equilibrium.
E)None of these statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the following reaction at a specific temperature: CO2(g)+ H2(g)⇌ CO(g)+ H2O(g)If [CO2] = 1.80 M, [H2] = 2.00 M, [CO] = 0.590 M, and [H2O] = 1.20 M at equilibrium, calculate the value of the equilibrium constant under these conditions.
A)0.471
B)0.197
C)5.08
D)2.12
E)0.444
A)0.471
B)0.197
C)5.08
D)2.12
E)0.444

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For the reaction CO(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)+ H2O(g)q = −206 kJ What conditions favor maximum conversion of reactants to products?
A)low pressure and low temperature
B)removal of H2(g)and low temperature
C)high pressure and high temperature
D)high pressure and low temperature
E)low pressure and high temperature
A)low pressure and low temperature
B)removal of H2(g)and low temperature
C)high pressure and high temperature
D)high pressure and low temperature
E)low pressure and high temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the following reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: FeO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Fe(s)+ CO2(g)Keq = 0.67 If the equilibrium concentration of CO is measured at 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of CO2?
A)0.50 M
B)1.2 M
C)0.34 M
D)0.27 M
E)1.3 M
A)0.50 M
B)1.2 M
C)0.34 M
D)0.27 M
E)1.3 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb2+(aq)+ 2Cl-(aq)⇌ PbCl2(s)
A)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0883_bb3a_6f2355152c0d_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq = [Pb2+][ Cl−]2
C)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_2f94_bb3a_4be2fcccf2bd_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_2f95_bb3a_070936fd99c8_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_56a6_bb3a_0f5318516639_TB8309_11.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0883_bb3a_6f2355152c0d_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq = [Pb2+][ Cl−]2
C)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_2f94_bb3a_4be2fcccf2bd_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_2f95_bb3a_070936fd99c8_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_56a6_bb3a_0f5318516639_TB8309_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl2(s)⇌ Pb2+(aq)+ 2Cl-(aq)
A)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_e16f_bb3a_03608466c482_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq = [Pb2+][ Cl−]2
C)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_e170_bb3a_591da9770813_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0881_bb3a_950e4ee55e5e_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0882_bb3a_c1f8ae1fac21_TB8309_11.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_e16f_bb3a_03608466c482_TB8309_11.jpg)
B)Keq = [Pb2+][ Cl−]2
C)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_e170_bb3a_591da9770813_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0881_bb3a_950e4ee55e5e_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: PbCl<sub>2</sub>(s)⇌ Pb<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A) B)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Pb<sup>2+</sup>][ Cl<sup>−</sup>]<sup>2</sup> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_0882_bb3a_c1f8ae1fac21_TB8309_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH3NH2(g)+ H2O(l)⇌ CH3NH3+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
A)Keq = [CH3NH3+][OH−]
B)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_7db7_bb3a_853c7221d461_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_7db8_bb3a_878125d23c5d_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_a4c9_bb3a_d30e5f6e5c47_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_a4ca_bb3a_0b51db2ed1ac_TB8309_11.jpg)
A)Keq = [CH3NH3+][OH−]
B)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_7db7_bb3a_853c7221d461_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_7db8_bb3a_878125d23c5d_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_a4c9_bb3a_d30e5f6e5c47_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_a4ca_bb3a_0b51db2ed1ac_TB8309_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
A)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_934c_bb3a_174a7ecba510_TB8309_00.jpg)
B)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_934d_bb3a_570ef91e9d3b_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)Keq = [O2]
D)Keq = [Hg]2[O2]
E)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_ba5e_bb3a_037640760a69_TB8309_11.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_934c_bb3a_174a7ecba510_TB8309_00.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_934d_bb3a_570ef91e9d3b_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)Keq = [O2]
D)Keq = [Hg]2[O2]
E)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: 2HgO(s)⇌ 2Hg(l)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) B) C)K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>] D)K<sub>eq</sub> = [Hg]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c1_ba5e_bb3a_037640760a69_TB8309_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consider the following system at equilibrium: CH4(g)+ 2H2O(g)⇌ CO2(g)+ 4H2(g)What change will cause the equilibrium to shift to form more H2?
A)increase [H2]
B)decrease [H2O]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [CH4]
E)decrease [CO2]
A)increase [H2]
B)decrease [H2O]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [CH4]
E)decrease [CO2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider the reaction 3Fe(s)+ 4H2O(g)⇌ 4H2(g)+ Fe3O4(s)If the total pressure is increased by reducing the volume,
A)the equilibrium constant increases.
B)no change occurs.
C)more Fe(s)is produced.
D)more H2(g)is produced.
E)more H2O(g)is produced.
A)the equilibrium constant increases.
B)no change occurs.
C)more Fe(s)is produced.
D)more H2(g)is produced.
E)more H2O(g)is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consider the following system at equilibrium: NO(g)+ SO3(g)⇌ NO2(g)+ SO2(g)What change will cause the equilibrium to shift to form more NO?
A)increase [SO3]
B)decrease [SO2]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [NO2]
E)decrease [SO3]
A)increase [SO3]
B)decrease [SO2]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [NO2]
E)decrease [SO3]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the following reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: FeO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Fe(s)+ CO2(g)Keq = 0.67 If the equilibrium concentration of CO is measured at 0.15 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of CO2?
A)0.10 M
B)1.2 M
C)0.15 M
D)0.52 M
E)0.22 M
A)0.10 M
B)1.2 M
C)0.15 M
D)0.52 M
E)0.22 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which one of the following changes has no effect on the position of the equilibrium?
A)concentration change
B)volume change
C)pressure change
D)temperature change
E)addition of a catalyst
A)concentration change
B)volume change
C)pressure change
D)temperature change
E)addition of a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consider the following system at equilibrium: NO(g)+ SO3(g)⇌ NO2(g)+ SO2(g)What change will cause the equilibrium to shift to form more SO2?
A)decrease [NO]
B)increase [NO2]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [NO2]
E)decrease [SO3]
A)decrease [NO]
B)increase [NO2]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)decrease [NO2]
E)decrease [SO3]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the following system at equilibrium: CH4(g)+ 2H2O(g)⇌ CO2(g)+ 4H2(g)What change will cause the equilibrium to shift to form more CH4?
A)decrease [H2]
B)increase [H2O]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)increase [CH4]
E)decrease [CO2]
A)decrease [H2]
B)increase [H2O]
C)decrease the volume of the reaction vessel
D)increase [CH4]
E)decrease [CO2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider the following reaction: N2(g)+ 3H2(g)⇌ 2NH3(g)+ heat Which conditions would favor maximum conversion of the reactants to the products?
A)high temperature and high pressure
B)low pressure; temperature is not important
C)high temperature and low pressure
D)low temperature and high pressure
E)low temperature and low pressure
A)high temperature and high pressure
B)low pressure; temperature is not important
C)high temperature and low pressure
D)low temperature and high pressure
E)low temperature and low pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The position of equilibrium would not be appreciably affected by changes in the volume of the container for
A)NiO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Ni(s)+ CO2(g).
B)BaCO3(s)⇌ BaO(s)+ CO2(g).
C)2H2O(g)⇌ 2H2(g)+ O2(g).
D)2CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
E)PCl5(s)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g).
A)NiO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Ni(s)+ CO2(g).
B)BaCO3(s)⇌ BaO(s)+ CO2(g).
C)2H2O(g)⇌ 2H2(g)+ O2(g).
D)2CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
E)PCl5(s)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider the following system at equilibrium: CH4(g)+ 2H2O(g)⇌ CO2(g)+ 4H2(g)What change will cause the equilibrium to shift to form more CO2?
A)increase [H2]
B)decrease [H2O]
C)decrease [CH4]
D)increase [CH4]
E)decrease [H2]
A)increase [H2]
B)decrease [H2O]
C)decrease [CH4]
D)increase [CH4]
E)decrease [H2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Consider the following reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: H2O(g)+ Cl2O(g)⇌ 2HOCl(g)Keq = 0.090 If the equilibrium concentration of HOCl is measured at 0.20 M, what are the equilibrium concentrations of H2O and Cl2O, assuming that they are equal?
A)0.67
B)0.20
C)0.87
D)0.44
E)0.49
A)0.67
B)0.20
C)0.87
D)0.44
E)0.49

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH3NH3+(aq)+ OH-(aq)⇌ CH3NH2(g)+ H2O(l)
A)Keq = [CH3NH3+][OH−]
B)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_cbdb_bb3a_b7e793ddf377_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ec_bb3a_f927b68cf1f2_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ed_bb3a_a989e6b3971a_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ee_bb3a_65f2d12a7d1e_TB8309_11.jpg)
A)Keq = [CH3NH3+][OH−]
B)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_cbdb_bb3a_b7e793ddf377_TB8309_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ec_bb3a_f927b68cf1f2_TB8309_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ed_bb3a_a989e6b3971a_TB8309_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction: CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub><sup>+</sup>(aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)⇌ CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</strong> A)K<sub>eq</sub> = [CH<sub>3</sub>NH3<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>] B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8309/11eb6911_39c2_f2ee_bb3a_65f2d12a7d1e_TB8309_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: H2O(g)+ Cl2O(g)⇌ 2HOCl(g)Keq = 0.090 If the equilibrium concentration of HOCl is measured at 0.15 M, what are the equilibrium concentrations of H2O and Cl2O, assuming that they are equal?
A)0.15 M
B)0.090 M
C)0.50 M
D)0.25 M
E)0.60 M
A)0.15 M
B)0.090 M
C)0.50 M
D)0.25 M
E)0.60 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the following reaction and the value of its equilibrium constant: FeO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Fe(s)+ CO2(g)Keq = 0.67 If the equilibrium concentration of CO is measured at 0.40 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of CO2?
A)0.40 M
B)1.1 M
C)0.67 M
D)0.27 M
E)1.7 M
A)0.40 M
B)1.1 M
C)0.67 M
D)0.27 M
E)1.7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



