Deck 17: Invasive Mechanical Ventilation of the Neonate and Pediatric Patient
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Invasive Mechanical Ventilation of the Neonate and Pediatric Patient
1
Enhanced diffusion in HFV is a function of which of the following factors?
A) Inspiratory flow
B) Plateau pressure
C) Inspiratory time
D) Respiratory frequency
A) Inspiratory flow
B) Plateau pressure
C) Inspiratory time
D) Respiratory frequency
D
The impact of enhanced diffusion, the product of tidal volume and rate, and the relationship between pulmonary units may all vary depending on the HFV technique used, the settings chosen, the patient's lung size, and pathologic conditions.
The impact of enhanced diffusion, the product of tidal volume and rate, and the relationship between pulmonary units may all vary depending on the HFV technique used, the settings chosen, the patient's lung size, and pathologic conditions.
2
Which of the following adjustments should the therapist consider to improve ventilation on a patient undergoing HFV?
A) Increase frequency
B) Increase
C) Increase inspiratory time
D) Decrease frequency
A) Increase frequency
B) Increase
C) Increase inspiratory time
D) Decrease frequency
D
Changes in ventilator rate at a given pressure amplitude cause an inverse change in tidal volume. Thus, when ventilation must be improved, a reduction in breathing frequency improves ventilation because the increased volume output per stroke has a greater impact on ventilation than does the decrease in stroke frequency. The converse is also true. When less ventilation is needed and pressure amplitude is already minimized, increasing breathing frequency will further decrease tidal volume and allow weaning from ventilation.
Changes in ventilator rate at a given pressure amplitude cause an inverse change in tidal volume. Thus, when ventilation must be improved, a reduction in breathing frequency improves ventilation because the increased volume output per stroke has a greater impact on ventilation than does the decrease in stroke frequency. The converse is also true. When less ventilation is needed and pressure amplitude is already minimized, increasing breathing frequency will further decrease tidal volume and allow weaning from ventilation.
3
What frequency defines high-frequency modes of ventilation?
A) >40 breaths per minute
B) >100 breaths per minute
C) >150 breaths per minute
D) >200 breaths per minute
A) >40 breaths per minute
B) >100 breaths per minute
C) >150 breaths per minute
D) >200 breaths per minute
C
Low-frequency ventilation (LFV) is identified as ventilation modes that provide breaths per minutes of <150; high-frequency ventilation (HFV) as modes of ventilation that provide breaths per minute of >150.
Low-frequency ventilation (LFV) is identified as ventilation modes that provide breaths per minutes of <150; high-frequency ventilation (HFV) as modes of ventilation that provide breaths per minute of >150.
4
Which of the following factors need to be considered for HFV ventilator circuits?
I) Time for gas egress during exhalation
II) Circuit compliance
III) Endotracheal tube size
IV) Intrinsic timing mechanisms
A) I and II only
B) I, II, and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I) Time for gas egress during exhalation
II) Circuit compliance
III) Endotracheal tube size
IV) Intrinsic timing mechanisms
A) I and II only
B) I, II, and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During volume-controlled ventilation, which of the following factors influences the peak inspiratory pressure?
A) Pulmonary capillary perfusion
B) Ventilation-perfusion relationships
C) Pulmonary compliance
D) Volume compressed in the ventilatory circuit at end inspiration
A) Pulmonary capillary perfusion
B) Ventilation-perfusion relationships
C) Pulmonary compliance
D) Volume compressed in the ventilatory circuit at end inspiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following forms of mechanical ventilation is the most efficacious method for acquired bronchopleural fistulas?
A) High-frequency jet ventilation (HFJV)
B) High-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV)
C) High-frequency flow interruption (HFFI)
D) Conventional ventilation (CV)
A) High-frequency jet ventilation (HFJV)
B) High-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV)
C) High-frequency flow interruption (HFFI)
D) Conventional ventilation (CV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are indications for HFV?
A) Diffuse, heterogeneous lung disease
B) Existing pulmonary air leak syndrome
C) Severe bronchiolitis
D) PaO2/FiO2 ratio of 300
A) Diffuse, heterogeneous lung disease
B) Existing pulmonary air leak syndrome
C) Severe bronchiolitis
D) PaO2/FiO2 ratio of 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During HFOV manipulation of which of the following components establishes the continuous distending pressure?
A) Gas flow through the pneumotachometer during expiration
B) Peak inspiratory peak-trough pressure gradient
C) Inspiratory valve aperture
D) Bias flow
A) Gas flow through the pneumotachometer during expiration
B) Peak inspiratory peak-trough pressure gradient
C) Inspiratory valve aperture
D) Bias flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following pressure-volume loop was obtained from a patient receiving mechanical ventilation in the pressure support mode. What type of problem does this ventilator graphic represent? 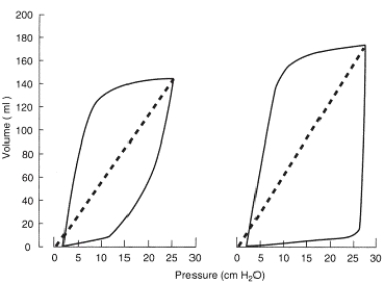
A) Insufficient flow caused by insufficient driving pressure
B) Pressure sensitivity set inappropriately low
C) Excessive tidal volume
D) Increased mechanical dead space

A) Insufficient flow caused by insufficient driving pressure
B) Pressure sensitivity set inappropriately low
C) Excessive tidal volume
D) Increased mechanical dead space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
While checking the ventilator of a pediatric patient, the therapist observes the following volume-time scalar: What action should the therapist take at this time? 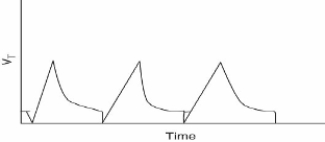
A) Increase the sensitivity setting.
B) Increase the tidal volume and increase the pressure setting.
C) Increase both the inspiratory flow and the pressure setting.
D) Check the patient-ventilator system for the presence of auto-PEEP.

A) Increase the sensitivity setting.
B) Increase the tidal volume and increase the pressure setting.
C) Increase both the inspiratory flow and the pressure setting.
D) Check the patient-ventilator system for the presence of auto-PEEP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the recommended inspiratory time percent setting for HFOV?
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 33%
D) 50%
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 33%
D) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
During high-frequency ventilation, as the diameter of the ETT increases, what happens to the delivered tidal volume under the same pressure settings?
A) It does not change.
B) It increases.
C) It increases only if compliance changes.
D) It decreases.
A) It does not change.
B) It increases.
C) It increases only if compliance changes.
D) It decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following modes of ventilation attempts to maintain a minimum target tidal volume with a constant pressure by manipulating the inspiratory flow?
A) Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
B) Pressure support ventilation (PSV)
C) Volume-assured pressure support (VAPS)
D) Pressure-regulated volume control (PRVC)
A) Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
B) Pressure support ventilation (PSV)
C) Volume-assured pressure support (VAPS)
D) Pressure-regulated volume control (PRVC)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When airway pressure release ventilation is used, what physiologic process occurs as the higher pressure is released and the lower is achieved?
A) Increased functional residual capacity
B) Increased tidal volume
C) Improved oxygenation
D) Exhalation of carbon dioxide
A) Increased functional residual capacity
B) Increased tidal volume
C) Improved oxygenation
D) Exhalation of carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following factors influences the gas volume compressed in the ventilator circuit?
A) Ventilation time constant
B) Water level in the humidifier
C) Location of the exhalation valve
D) Size (inner diameter) of the endotracheal tube
A) Ventilation time constant
B) Water level in the humidifier
C) Location of the exhalation valve
D) Size (inner diameter) of the endotracheal tube

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The therapist is about to mechanically ventilate a neonate with a ventilator that delivers the volume guarantee mode. Which of the ventilator settings does the therapist need to set for this mode?
I) Minute ventilation
II) Tidal volume
III) Inspiratory time
IV) Inspiratory flow
A) I and II only
B) II and IV only
C) I, III, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I) Minute ventilation
II) Tidal volume
III) Inspiratory time
IV) Inspiratory flow
A) I and II only
B) II and IV only
C) I, III, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How is the high-volume strategy achieved when the goal is to deliver a high lung volume to a neonate receiving HFV?
A) By increasing the continuous distending pressure
B) By reducing the peak-trough pressure gradient
C) By increasing the expiratory flow resistance
D) By decreasing the mean airway pressure
A) By increasing the continuous distending pressure
B) By reducing the peak-trough pressure gradient
C) By increasing the expiratory flow resistance
D) By decreasing the mean airway pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
During HFOV, which of the following factors has a direct influence on a neonate's delivered tidal volume?
A) Frequency
B) Oscillatory amplitude
C) Peak inspiratory pressure
D) IPAP and EPAP
A) Frequency
B) Oscillatory amplitude
C) Peak inspiratory pressure
D) IPAP and EPAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is a frequent requirement when employing the low-volume strategy while ventilating a neonatal patient with pulmonary interstitial emphysema by HFV?
A) High inspiratory flow
B) Positive end-expiratory pressure
C) High FiO2
D) Longer inspiratory time
A) High inspiratory flow
B) Positive end-expiratory pressure
C) High FiO2
D) Longer inspiratory time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
On the basis of the following flow/time scalar, which of the following conditions has developed? 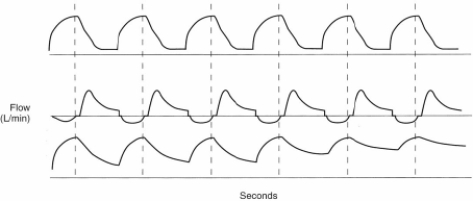
A) Trigger dyssynchrony
B) Excess tidal volume
C) Air trapping
D) Ventilator circuit leak

A) Trigger dyssynchrony
B) Excess tidal volume
C) Air trapping
D) Ventilator circuit leak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How is the radiographic assessment of neonatal lung volume performed?
A) Counting the number of anterior ribs above the diaphragm
B) Counting the number of posterior ribs above the diaphragm
C) Counting the number of posterior ribs below the clavicle
D) Counting the number of anterior ribs below the clavicle
A) Counting the number of anterior ribs above the diaphragm
B) Counting the number of posterior ribs above the diaphragm
C) Counting the number of posterior ribs below the clavicle
D) Counting the number of anterior ribs below the clavicle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The therapist notices that gas exchange has dramatically improved in a neonate undergoing HFOV. However, weaning has not been implemented accordingly. What are the consequences of failing to quickly wean a neonatal patient from HFV?
A) Pulmonary overdistention
B) Pulmonary hypertension
C) Alveolar derecruitment
D) Decreased pulse rate
A) Pulmonary overdistention
B) Pulmonary hypertension
C) Alveolar derecruitment
D) Decreased pulse rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
On the basis of the following pressure-volume loop, what ventilator setting change should the therapist make? 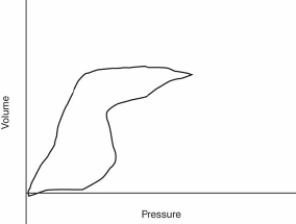
A) Check the inflation pressure on the endotracheal tube cuff.
B) Increase the pressure limit.
C) Increase the delivered tidal volume.
D) Increase the inspiratory flow.

A) Check the inflation pressure on the endotracheal tube cuff.
B) Increase the pressure limit.
C) Increase the delivered tidal volume.
D) Increase the inspiratory flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following actions should a therapist consider in a patient suspected of having an airway obstruction while receiving HFV?
A) Observe the patient's chest wall for movement.
B) Increase conventional ventilation.
C) Increase mean airway pressure on the HFV.
D) Reduce the oscillatory amplitude.
A) Observe the patient's chest wall for movement.
B) Increase conventional ventilation.
C) Increase mean airway pressure on the HFV.
D) Reduce the oscillatory amplitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How is the minute ventilation decreased when a patient is being weaned from HFOV?
A) By decreasing peak pressure
B) By reducing oscillatory amplitude
C) By minimizing
D) By shortening the inspiratory time
A) By decreasing peak pressure
B) By reducing oscillatory amplitude
C) By minimizing
D) By shortening the inspiratory time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why may HFOV be considered a suboptimal ventilation strategy for patients who have either fresh particulate meconium aspiration or bronchopulmonary dysplasia?
A) Ventilation time constants will be decreased.
B) Large increases in tidal volume delivery can occur.
C) Gas trapping may develop.
D) Intrapulmonary shunting becomes likely.
A) Ventilation time constants will be decreased.
B) Large increases in tidal volume delivery can occur.
C) Gas trapping may develop.
D) Intrapulmonary shunting becomes likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The therapist is conducting a ventilator check for a neonate and makes the following notations on the ventilator flow sheet:
PEEP: 5 cm H2O
Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP): 25 cm H2O
Mandatory rate: 15 breaths per minute
FiO2: 0.35
On the basis of these observations, what should the therapist recommend for this neonate?
A) Shunt study
B) Weaning from mechanical ventilation
C) Inhaled nitric oxide
D) High-frequency ventilation
PEEP: 5 cm H2O
Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP): 25 cm H2O
Mandatory rate: 15 breaths per minute
FiO2: 0.35
On the basis of these observations, what should the therapist recommend for this neonate?
A) Shunt study
B) Weaning from mechanical ventilation
C) Inhaled nitric oxide
D) High-frequency ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Over the last 90 minutes, the therapist has obtained three arterial blood samples from an arterial line inserted in a neonate receiving mechanical ventilation and being monitored by capnometry. The PaCO2 values were as follows: (1) 47 mm Hg, (2) 46 mm Hg, and (3) 47 mm Hg. How should the therapist evaluate the following capnogram? 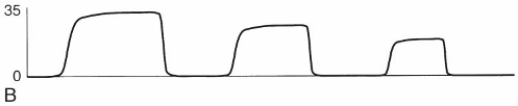
A) Abrupt disconnection from mechanical ventilation
B) Damped waveform caused by severe airflow obstruction
C) Reduced pulmonary blood flow caused by overdistention of the lungs
D) Secretions partially obstructing the sample line leading to the capnometer

A) Abrupt disconnection from mechanical ventilation
B) Damped waveform caused by severe airflow obstruction
C) Reduced pulmonary blood flow caused by overdistention of the lungs
D) Secretions partially obstructing the sample line leading to the capnometer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



