Deck 13: Statistical Quality Control
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Statistical Quality Control
1
An example of assignable variation in a production system may be that workers are not identically trained.
True
2
To obtain a 99.7 percent confidence level in a p-chart, we would use a value of 3 for "z."
True
3
Measurement by attributes means taking a sample, measuring the attribute in question, and determining the level of quality in the population from which the sample was drawn.
False
4
Genichi Taguchi's view of the cost of quality is that variance is a discontinuous function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Process control is concerned with monitoring quality after the product or service has been produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Acceptance sampling is performed on goods that already exist to determine what percentage of items conforms to specifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Statistical process control involves testing random samples of output from a process to determine whether the process is producing items within a preselected range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
It is impossible to have zero variability in production processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The value for "z" used in quality control charts is based on the degree of confidence you want to have in the resulting UCL and LCL values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Attributes are those quality characteristics that are classified as either conforming or not conforming to specification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A p-chart has upper and lower control limits expressed as lines on the chart. As long as the sample values fall between these two lines, there is no need to investigate process behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In acceptance sampling, the value for the acceptance number (c) is determined by the interaction of the acceptable quality level (AQL), the lot tolerance percent defective (LTPD), the probability of rejecting a high-quality lot (alpha), and the probability of accepting a low-quality lot (beta).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In acceptance sampling, the number of units in the sample (n) is determined by the interaction of the acceptable quality level (AQL), the lot tolerance percent defective (LTPD), the probability of rejecting a high-quality lot (alpha), and the probability of accepting a low-quality lot (beta).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the fraction defective is 0.12 based on a sample size of 16, the standard deviation used in the p-chart is about 0.08.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The p-chart is only useful for sampling that deals with continuous variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The capability index is used to gauge economic changes in service systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Variation that is inherent in a production process itself is called assignable variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Variation that is inherent in a production process itself is called common variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An example of assignable variation in a production system may be that a machine is not adjusted properly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the fraction defective is 0.4 based on a sample size of 100, the standard deviation used in the p-chart is about 0.10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
LTPD in acceptance sampling stands for lot tolerance for parts defective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For R-charts, the typical sample size is 10-15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The probability associated with rejecting a high-quality lot is denoted in acceptance sampling with the Greek letter alpha.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In monitoring process quality, we might use which of the following statistics?
A) Absolute values
B) Percentage deviation from tolerance centers
C) "k" values for the sample mean
D) Logarithmic control intervals
E) Difference between the highest and lowest value in a sample
A) Absolute values
B) Percentage deviation from tolerance centers
C) "k" values for the sample mean
D) Logarithmic control intervals
E) Difference between the highest and lowest value in a sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The capability index (Cpk) calculates the percentage of items being produced within specifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The capability index (Cpk) indicates the position of the mean and tails of a process's variance relative to design specifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You have just used the capability index (Cpk) formulas to compute the two values "min [1.5, 1]." Which of the following is the proper interpretation of these numbers?
A) The true capability index value is 1.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) The true capability index value is between 1.5 and 1.
A) The true capability index value is 1.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) The true capability index value is between 1.5 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Greek letter alpha is associated with consumer's risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You have just used the capability index (Cpk) formulas to compute the two values "min [2, 2.5]." Which of the following is the proper interpretation of these numbers?
A) The true capability index value is 2.5.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) The true capability index value is between 2 and 2.5.
A) The true capability index value is 2.5.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) The true capability index value is between 2 and 2.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In sampling variables, the actual measurements of the variable observed are used regardless of whether the unit is good or bad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The producer's risk associated with rejecting a high-quality lot is denoted in acceptance sampling with the Greek letter beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sampling plans are generally displayed graphically through the use of operating characteristic (OC) curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Total, 100 percent inspection can never be cost justified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You have just used the capability index (Cpk) formulas to compute the two values "min [1, 1]." Which of the following is the proper interpretation of these numbers?
A) The true capability index value is exactly 1.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) The true capability index value is exactly 1.
B) The mean of the production process has shifted to the left of the design limits.
C) The mean of the production process has shifted to the right of the design limits.
D) The mean has not shifted at all.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Designers establish specifications that solely define the target value only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
One hundred percent inspection is justified when the cost of inspection is low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Standard practice in statistical process control for variables is to set control limits so that 95 percent of the sample means will fall within the UCL and the LCL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
AQL stands for accepting questionable lots in production quality management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The probability associated with accepting a low-quality lot is denoted in acceptance sampling with the Greek letter alpha.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A rule of thumb for p-charts is to use a sample size of at least 250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You want to determine the control lines for a p-chart for quality control purposes. If the total number of defects from all samples is 560, the number of samples is 70, and the sample size is 80, which of the following would be the standard deviation used in developing the control lines?
A) 0.9000
B) 0.4556
C) 0.0335
D) 0.0011
E) 0.0112
A) 0.9000
B) 0.4556
C) 0.0335
D) 0.0011
E) 0.0112

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You want to determine the control lines for a p-chart for quality control purposes. If the total number of defects from all samples is 2,500, the number of samples is 100, and the sample size is 500, which of the following would be the standard deviation used in developing the control lines?
A) 0.4900
B) 0.2499
C) 0.0707
D) 0.000315
E) 0.000975
A) 0.4900
B) 0.2499
C) 0.0707
D) 0.000315
E) 0.000975

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If there are 12 total defects from 10 samples, each sample consisting of 100 individual items in a production process, which of the following is the fraction defective that can be used in a p-chart for quality control purposes?
A) 12
B) 1.2
C) 0.12
D) 0.012
E) 0.0012
A) 12
B) 1.2
C) 0.12
D) 0.012
E) 0.0012

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You want to develop a three-sigma R-chart. You know the average range is 5 based on several samples of size 10. Which of the following is the resulting UCL?
A) 20.9
B) 8.9
C) 7.02
D) 5
E) 3.1
A) 20.9
B) 8.9
C) 7.02
D) 5
E) 3.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You are going to develop an R-chart based on range statistics, and you are using a sample size of 9 for your charting purposes. Which of the following is the lower control limit D3 factor for the chart?
A) 0.08
B) 0.14
C) 0.18
D) 0.22
E) 0.29
A) 0.08
B) 0.14
C) 0.18
D) 0.22
E) 0.29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You are going to develop an X-bar chart based on range statistics, and you are using a sample size of 12 for your charting purposes. Which of the following is the A2 factor for the X-bar chart?
A) 0.37
B) 0.31
C) 0.27
D) 0.22
E) 0.18
A) 0.37
B) 0.31
C) 0.27
D) 0.22
E) 0.18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Quality control charts usually have a central line and upper and lower control limit lines. Which of the following is a reason that the process being monitored with the chart should be investigated?
A) A single point falls above or below the control limits.
B) Behavior is normal.
C) A large number of plots are on or near the central line.
D) There is no real trend in any direction.
E) There is a change in raw materials or operators.
A) A single point falls above or below the control limits.
B) Behavior is normal.
C) A large number of plots are on or near the central line.
D) There is no real trend in any direction.
E) There is a change in raw materials or operators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Quality control charts usually have a central line and upper and lower control limit lines. Which of the following is not a reason that the process being monitored with the chart should be investigated?
A) A large number of plots are close to the upper or lower control lines.
B) The behavior of the plots is erratic.
C) A single point falls above or below the control limits.
D) There is a change in raw materials or operators.
E) There is a run of five above the central line.
A) A large number of plots are close to the upper or lower control lines.
B) The behavior of the plots is erratic.
C) A single point falls above or below the control limits.
D) There is a change in raw materials or operators.
E) There is a run of five above the central line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For which of the following should we use an R-chart to monitor process quality?
A) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
B) Tire pressures in an auto assembly plant
C) Vehicles passing emissions inspection
D) Computer software errors
E) Number of units with missing operations
A) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
B) Tire pressures in an auto assembly plant
C) Vehicles passing emissions inspection
D) Computer software errors
E) Number of units with missing operations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For which of the following should we use an R-chart to monitor process quality?
A) Weighing trucks at a highway inspection station to determine if they are overloaded
B) Deciding whether an airliner has sufficient fuel for its trip
C) Student grades measured from 1 to 100
D) Determining whether vehicles from a motor pool will run
E) Determining the accuracy of a forecast of "snow"
A) Weighing trucks at a highway inspection station to determine if they are overloaded
B) Deciding whether an airliner has sufficient fuel for its trip
C) Student grades measured from 1 to 100
D) Determining whether vehicles from a motor pool will run
E) Determining the accuracy of a forecast of "snow"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You are developing an X-bar chart based on sample means. You know the standard deviation of the sample means is 4, the desired confidence level is 99 percent, and the average of the sample means is 20. Which of the following is your LCL?
A) 36
B) 24
C) 9.68
D) 16.79
E) 30.32
A) 36
B) 24
C) 9.68
D) 16.79
E) 30.32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
You want to determine the upper control line for a p-chart for quality control purposes. You take several samples of a size of 100 items in your production process. From the samples, you determine the fraction defective is 0.05 and the standard deviation is 0.01. If the desired confidence level is 99.7 percent, which of the following is the resulting UCL value for the line?
A) 0.39
B) 0.08
C) 0.06
D) 0.05
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 0.39
B) 0.08
C) 0.06
D) 0.05
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You want to develop a three-sigma R-chart. You know the average range is 12 based on several samples of size 6. Which of the following is the resulting LCL?
A) 20.0
B) 18.3
C) 7.02
D) 5.6
E) 0.0
A) 20.0
B) 18.3
C) 7.02
D) 5.6
E) 0.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For which of the following should we use a p-chart to monitor process quality?
A) The dimensions of brick entering a kiln
B) Lengths of boards cut in a mill
C) The weight of fluid in a container
D) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
E) Temperatures in a classroom
A) The dimensions of brick entering a kiln
B) Lengths of boards cut in a mill
C) The weight of fluid in a container
D) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
E) Temperatures in a classroom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For which of the following should we use a p-chart to monitor process quality?
A) Defective electrical switches
B) Errors in the length of a pencil
C) Weight errors in cans of soup
D) Temperature of entrees in a restaurant
E) Letter grades on a final examination
A) Defective electrical switches
B) Errors in the length of a pencil
C) Weight errors in cans of soup
D) Temperature of entrees in a restaurant
E) Letter grades on a final examination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You are developing an X-bar chart based on sample means. You know the standard deviation of the sample means is 4, the desired confidence level is 99.7 percent, and the average of the sample means is 24. Which of the following is your UCL?
A) 36
B) 24
C) 12
D) 4
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 36
B) 24
C) 12
D) 4
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If there are 40 total defects from 8 samples, each sample consisting of 200 individual items in a production process, which of the following is the fraction defective that can be used in a p-chart for quality control purposes?
A) 2.5
B) 0.25
C) 0.025
D) 0.0025
E) 0.00025
A) 2.5
B) 0.25
C) 0.025
D) 0.0025
E) 0.00025

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
You want to determine the control lines for a p-chart for quality control purposes. If the desired confidence level is 99 percent, which of the following values for "z" would you use in computing the UCL and LCL?
A) 0.99
B) 2
C) 2.58
D) 3
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 0.99
B) 2
C) 2.58
D) 3
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
You want to determine the lower control line for a p-chart for quality control purposes. You take several samples of a size of 50 items in your production process. From the samples, you determine the fraction defective is 0.006 and the standard deviation is 0.001. If the desired confidence level is 99.7 percent, which of the following is the resulting LCL value for the line?
A) 0.0
B) 0.002
C) 0.003
D) 0.004
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) 0.0
B) 0.002
C) 0.003
D) 0.004
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For which of the following should we use an X-bar chart based on sample means to monitor process quality?
A) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
B) Tire pressures in an auto assembly plant
C) Vehicles passing emissions inspection
D) Computer software errors
E) Number of units with missing operations
A) Grades in a freshman "pass/fail" course
B) Tire pressures in an auto assembly plant
C) Vehicles passing emissions inspection
D) Computer software errors
E) Number of units with missing operations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider a sampling plan with n = 40 and c = 1 and given Acceptable quality level (AQL), Lot tolerance percent defective (LTPD), producer's risk (α) and consumer's risk (β). Suppose that c is increased to 2, keeping AQL and LTPD unchanged, consumer's risk (β) will
A) Always decrease
B) Always increase
C) Sometime decrease
D) Stay the same
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Always decrease
B) Always increase
C) Sometime decrease
D) Stay the same
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Other things remaining the same, and assuming thatis smaller than USL and larger than LSL, if the standard deviation (σ) of the process decreases, process capability index (Cpk) of the process will
I. Stay the same
II. Will always increase
III. Will always decrease
IV. Will sometimes increase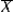
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) Either II or III
E) IV
I. Stay the same
II. Will always increase
III. Will always decrease
IV. Will sometimes increase
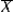
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) Either II or III
E) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
You are going to develop an R-chart based on range statistics, and you are using a sample size of 15 for your charting purposes. Which of the following is the upper control limit D4 factor for the chart?
A) 1.65
B) 1.70
C) 1.76
D) 1.87
E) 1.92
A) 1.65
B) 1.70
C) 1.76
D) 1.87
E) 1.92

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider a sampling plan with n = 40 and c = 1 and given Acceptable quality level (AQL), Lot tolerance percent defective (LTPD), producer's risk (α) and consumer's risk (β). Suppose that c is increased to 2, keeping AQL and LTPD unchanged, producer's risk (α) will
A) Always decrease
B) Always increase
C) Sometime decrease
D) Stay the same
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Always decrease
B) Always increase
C) Sometime decrease
D) Stay the same
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



