Deck 18: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
Glutamic acid has an isoelectric point of 3.08. At which pH is the cationic form in greatest concentration?
A) 2
B) 3.2
C) 5.6
D) 9.7
A) 2
B) 3.2
C) 5.6
D) 9.7
2
2
Which is the charge on lysine at pH 11?
A) 0
B) +1
C) -1
D) +2
A) 0
B) +1
C) -1
D) +2
-1
3
Which amino acid has a nonpolar side chain?
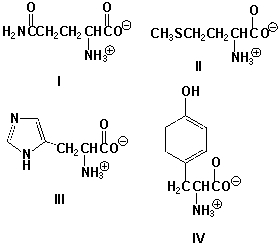
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
II
4
Which is the chemical structure of the tripeptide glutathione (glu-cys-gly)?
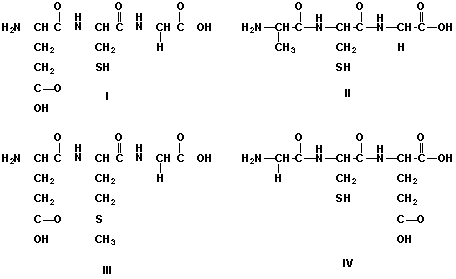
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Lysine has an isoelectric point of 9.74. What charge does tyrosine have at pH 7 and toward which electrode would it migrate during electrophoresis?
A) negative, anode
B) positive, cathode
C) negative, cathode
D) positive, anode
A) negative, anode
B) positive, cathode
C) negative, cathode
D) positive, anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is the order of increasing acidity for the indicated carboxyl groups (least first)?
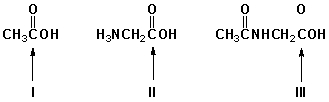
A) I, II, III
B) II, III, I
C) III, II, I
D) I, III, II

A) I, II, III
B) II, III, I
C) III, II, I
D) I, III, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which amino acid has a basic side chain?
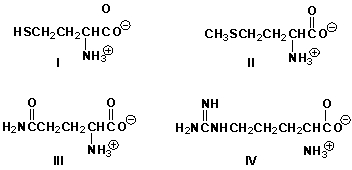
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Isoleucine has pka values of 2.32 (-COOH) and 9.76 (-NH3+). Which is isoleucine's isoelectric point?
A) 3.08
B) 7.64
C) 6.04
D) 9.74
A) 3.08
B) 7.64
C) 6.04
D) 9.74

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tyrosine has an isoelectric point of 5.63. What charge does tyrosine have at pH 7 and toward which electrode would it migrate during electrophoresis?
A) negative, anode
B) positive, cathode
C) negative, cathode
D) positive, anode
A) negative, anode
B) positive, cathode
C) negative, cathode
D) positive, anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which amino acids have protic side chains?
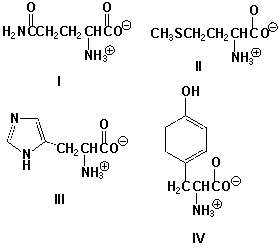
A) I, III
B) II, IV
C) II, III
D) III, IV

A) I, III
B) II, IV
C) II, III
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is the predominant form of lysine in blood plasma at pH 7.4?
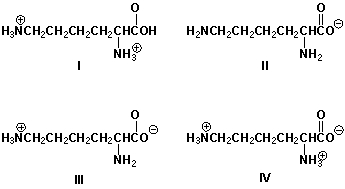
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which describes the isoelectric point of an amino acid?
A) The degree of ionization of the amino acid at pH 7.
B) The pH at which there is no net charge for the amino acid.
C) The degree of ionization of the amino acid at pH 7 in an electric field.
D) The pH at which the amino acid has a maximal charge.
A) The degree of ionization of the amino acid at pH 7.
B) The pH at which there is no net charge for the amino acid.
C) The degree of ionization of the amino acid at pH 7 in an electric field.
D) The pH at which the amino acid has a maximal charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which molecule has an overall positive charge?
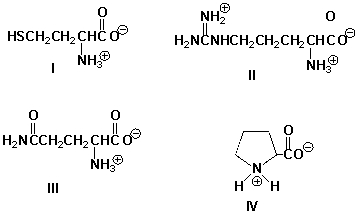
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which is the order of increasing mobility of the molecule toward the cathode (least first)?
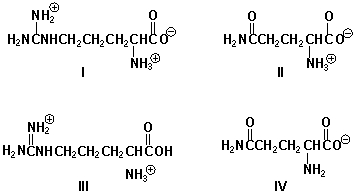
A) III, I, II, IV
B) I, III, II, IV
C) IV, II, I, III
D) III, IV, I, II

A) III, I, II, IV
B) I, III, II, IV
C) IV, II, I, III
D) III, IV, I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which characteristics are correct for a peptide bond in a polypeptide?
I. planar
II. cis
III. trans
IV. tetrahedral
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV
I. planar
II. cis
III. trans
IV. tetrahedral
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Arginine has an isoelectric point of 10.76. At which pH would the predominate form of arginine in solution migrate toward the positive terminal during electrophoresis?
A) 5
B) 7
C) 10.76
D) 12
A) 5
B) 7
C) 10.76
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is the structure of the pentapeptide that gave lys-leu-phe on reaction with cyanogen bromide, and gave fragments met-lys, leu-phe, and arg on reaction with trypsin.
A) arg-met-phen-leu-lys
B) lys-leu-phe-arg-met
C) arg-met-lys-leu-phe
D) met-arg-lys-leu-phe
A) arg-met-phen-leu-lys
B) lys-leu-phe-arg-met
C) arg-met-lys-leu-phe
D) met-arg-lys-leu-phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is the order of increasing basicity for the indicated amino groups (least first)?
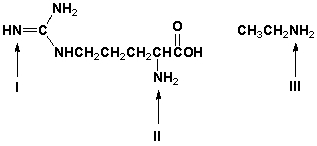
A) I, II, III
B) II, III, I
C) III, II, I
D) I, III, II

A) I, II, III
B) II, III, I
C) III, II, I
D) I, III, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is the charge of lysine at pH 2?
A) 0
B) +1
C) -1
D) +2
A) 0
B) +1
C) -1
D) +2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Aspartic acid has an isoelectric point of 2.98. At which pH would the predominant form of aspartic acid in solution migrate toward the negative electrode during electrophoresis?
A) 1
B) 2.98
C) 4
D) 7
A) 1
B) 2.98
C) 4
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Spider silk is remarkably strong, its tensile strength is superior to that of steel and it is extremely lightweight: a strand of spider-silk long enough to circle the earth would weigh less than 500 g. In a typical spider silk strand, crystalline beta-sheet regions, which are rich in glycine- and alanine, alternate with amorphous segments. The latter are responsible for the sticky or non-sticky properties, depending on the kind of spider silk. Why are glycine and alanine especially suited for the formation of beta-sheet regions?
I. Glycine and alanine are hydrophobic and cause the hydrophobic sticking of neighboring polymer strands.
II. Glycine and alanine feature very little or no steric hindrance for the formation of hydrogen bonds between neighboring protein strands.
III. Glycine and alanine feature very little or no steric hindrance for the formation of hydrogen bonds within a protein strands.
IV. Glycine and alanine are polar. They allow ionic interactions between neighboring polymer chains.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct
I. Glycine and alanine are hydrophobic and cause the hydrophobic sticking of neighboring polymer strands.
II. Glycine and alanine feature very little or no steric hindrance for the formation of hydrogen bonds between neighboring protein strands.
III. Glycine and alanine feature very little or no steric hindrance for the formation of hydrogen bonds within a protein strands.
IV. Glycine and alanine are polar. They allow ionic interactions between neighboring polymer chains.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The structure of a common amino acid with a polar side chain is



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Karl Nessler received the patent for the so-called "hot procedure" for a permanent (hair) in 1906. The hair was treated with a basic solution (NaOH in water, pH approx. 10) and then heated for several hours on the curler. The result was often extremely curly hair. What kind of bonds was/were actually (partially) broken and reformed?
I. hydrogen bonds
II. ionic bonds
III. disulfide-bridges
IV. dipolar bonds
A) I and II are correct
B) I, II and III are correct
C) I, II, and IV are correct
D) all of the above are correct
I. hydrogen bonds
II. ionic bonds
III. disulfide-bridges
IV. dipolar bonds
A) I and II are correct
B) I, II and III are correct
C) I, II, and IV are correct
D) all of the above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Denaturation is a process in which proteins lose their natural shape and order of assembly and, therefore, their biological functions. Which of the following statements is/are true?
I. In quaternary structure denaturation, protein sub-units are dissociated.
II. In tertiary structure denaturation, covalent and ionic bonds are predominantly formed.
III. In tertiary structure denaturation, covalent and ionic bonds are disrupted.
IV. In quaternary structure denaturation, proteins lose all regular repeating patterns, such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct
I. In quaternary structure denaturation, protein sub-units are dissociated.
II. In tertiary structure denaturation, covalent and ionic bonds are predominantly formed.
III. In tertiary structure denaturation, covalent and ionic bonds are disrupted.
IV. In quaternary structure denaturation, proteins lose all regular repeating patterns, such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The tertiary structure of proteins depends primarily on which property of amino acids?
I. disulfide bonds
II. hydrogen bonds
III. amide bonds
IV. polar side chains
A) III, IV
B) I, IV
C) II, III
D) I, II
I. disulfide bonds
II. hydrogen bonds
III. amide bonds
IV. polar side chains
A) III, IV
B) I, IV
C) II, III
D) I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A pentapeptide has the following proportions of amino acids: gly (1), leu (1), val (1), phe (2). Treatment of the pentapeptide with chymotrypsin gave the following fragments: gly-val, leu, phe. Which is the structure of the pentapeptide?
A) phe-phe-gly-val-leu
B) gly-val-phe-leu-phe
C) leu-gly-val-phe-phe
D) phe-leu-gly-val-phe
A) phe-phe-gly-val-leu
B) gly-val-phe-leu-phe
C) leu-gly-val-phe-phe
D) phe-leu-gly-val-phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Denaturation is a process in which proteins lose their natural shape and order of assembly and, therefore, their biological functions. Which of the following statements is/are true?
I. In secondary denaturation, some of the amide-bonds of the proteins´ backbones are hydrolyzed.
II. In secondary structure denaturation, proteins lose all regular repeating pattern, such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
III. In secondary structure denaturation, proteins adopt random-coil conformations.
IV. In secondary structure denaturation, noncovalent dipole-dipole interactions between polar amino acids/side chains and the solvent are disrupted.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct
I. In secondary denaturation, some of the amide-bonds of the proteins´ backbones are hydrolyzed.
II. In secondary structure denaturation, proteins lose all regular repeating pattern, such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
III. In secondary structure denaturation, proteins adopt random-coil conformations.
IV. In secondary structure denaturation, noncovalent dipole-dipole interactions between polar amino acids/side chains and the solvent are disrupted.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Oxytocine is a mammalian hormone that also acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. Among many other functions, it also facilitates birth and breastfeeding. Oxytocine is a small peptide made of nine amino acids (a nonapeptide). The primary sequence is cysteine - tyrosine - isoleucine - glutamine - asparagine - cysteine - proline - leucine - glycine. In its active form oxytocine forms a cyclic structure. Which secondary bond is most suitable to form the cyclic structure?
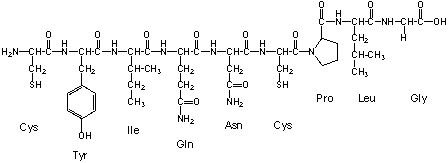
A) a thioester between cysteine and glycine
B) a disulfide bridge between cysteine and cysteine
C) an amide between cysteine and glycine
D) an ester between the phenolic group of tyrosine and glycine

A) a thioester between cysteine and glycine
B) a disulfide bridge between cysteine and cysteine
C) an amide between cysteine and glycine
D) an ester between the phenolic group of tyrosine and glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPa) is a serine endopeptidase. The active site of this peptidase binds the peptide-motif Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala and cleaves the protein/peptide between arginine and serine. What is the sequence of the products of the oligopeptide
Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
After cleavage by uPa?
A) Ala-Gly and Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
B) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg and Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
C) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser and Asp
D) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser and Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
After cleavage by uPa?
A) Ala-Gly and Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
B) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg and Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp
C) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser-Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser and Asp
D) Ala-Gly-Ser-Gly-Arg-Ser and Ala-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ser-Asp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are the differences between polyamides and proteins ?
I. Polyamides are unable to undergo hydrogen bonding between individual polymer chains.
II. Polyamides usually do not have hydroxyl- or thiol-groups as side chains.
III. Proteins and polyamides can be partially crystalline.
IV. Polyamides have a more stable bond between their monomers than proteins have between the individual amino acids.
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) II and IV
D) III and IV
I. Polyamides are unable to undergo hydrogen bonding between individual polymer chains.
II. Polyamides usually do not have hydroxyl- or thiol-groups as side chains.
III. Proteins and polyamides can be partially crystalline.
IV. Polyamides have a more stable bond between their monomers than proteins have between the individual amino acids.
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) II and IV
D) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Serotonin regulates intestinal movements in humans, as well as the human mood, appetite, and some cognitive functions including memory and learning. In the human body, serotonin is synthesized by hydroxylation of the essential amino acid L-tryptophan and subsequent decarboxylation. Complete the following reaction scheme:
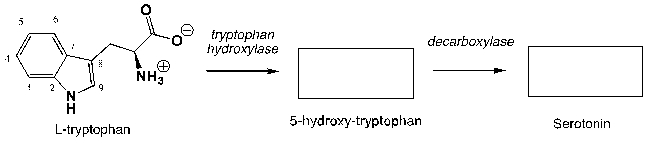


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The structure of a common amino acid with a basic side chain is



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A polypeptide gave the following proportions of amino acids upon hydrolysis: ala (1), gly (1), ile (2), phe (2), ser (1), tyr (2). Edman degradation yields tyrosine phenylthiohydantoin. Partial hydrolysis of the peptide gave a mixture of smaller peptides including: ala-gly, gly-tyr, ile-ile, phe-ile, ser-phe, tyr-ser, tyr-phe, ile-ala. Which is the C-terminal amino acid in the original peptide?
A) tyr
B) ser
C) phe
D) ile
A) tyr
B) ser
C) phe
D) ile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which are true describing the secondary structure of a protein that is an -helix?
I. The helix is coiled counterclockwise.
II. The N-H bond and the C=O bond point outward.
III. Hydrogen bonding is between groups 4 amino acid units apart.
IV. The coil has 3.6 amino acids per turn.
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV
I. The helix is coiled counterclockwise.
II. The N-H bond and the C=O bond point outward.
III. Hydrogen bonding is between groups 4 amino acid units apart.
IV. The coil has 3.6 amino acids per turn.
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The structure of vasopressin is very similar to that of oxytocin (primary sequence of vasopressin: cysteine - tyrosine - phenylalanine - glutamine - asparagine - cysteine - proline - arginine - glycine), which is also a nonapeptide with a disulfide bridge. One of the most important roles of vasopressin is to regulate the body's retention of water; it is released when the body is dehydrated and causes the kidneys to conserve water, thus concentrating the urine, and reducing urine volume. In addition, it has a variety of neurological effects on the brain. What are the differences in the structures of vasopressin and oxytocin?
I. residue #3: isoleucine (oxytocin) vs. phenylalanine (vasopressin)
II. residue #7: isoleucine (oxytocin) vs. phenylalanine (vasopressin)
III. residue #8: leucine (oxytocin) vs. arginine (vasopressin)
IV. residue #4: asparagine (oxytocin) vs. cysteine (vasopressin)
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct
I. residue #3: isoleucine (oxytocin) vs. phenylalanine (vasopressin)
II. residue #7: isoleucine (oxytocin) vs. phenylalanine (vasopressin)
III. residue #8: leucine (oxytocin) vs. arginine (vasopressin)
IV. residue #4: asparagine (oxytocin) vs. cysteine (vasopressin)
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The first known procedures to bend straight hair into curls dates from 3000 B.C.: Hot Curlers made from clay were used. The hair was apparently dry. What kind of bonds was/were actually broken and reformed?
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic bonds
C) disulfide-bridges
D) dipolar bonds
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic bonds
C) disulfide-bridges
D) dipolar bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Draw both L-aspartic acid and D-aspartic acid. Specify the configuration (R or S) at each stereocenter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why will Gly-Met-Gly react with cyanogen bromide, but Gly-Cys-Gly will not react with cyanogen bromide?
I. There would be a highly strained four-membered ring intermediate in the case of cysteine.
II. After the addition of the thiol of cysteine to the cyano-group, a stable thioether will be formed, which does not react any further.
III. After the addition of the thiol of cysteine to the bromo-cation, a stable thioether will be formed, which does not react any further.
IV. Cysteine cannot form a stable bromonium-ion intermediate.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct
I. There would be a highly strained four-membered ring intermediate in the case of cysteine.
II. After the addition of the thiol of cysteine to the cyano-group, a stable thioether will be formed, which does not react any further.
III. After the addition of the thiol of cysteine to the bromo-cation, a stable thioether will be formed, which does not react any further.
IV. Cysteine cannot form a stable bromonium-ion intermediate.
A) I and II are correct
B) II and III are correct
C) I and III are correct
D) II and IV are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The secondary structure of proteins depends primarily on which property of amino acids?
A) disulfide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) amide bonds
D) polar side chains
A) disulfide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) amide bonds
D) polar side chains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The structure of a common amino acid with an acidic side chain is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The isoelectric point of cysteine is ______________.
pKa (COOH) = 2.05, pKa (NH3+) = 10.25, pKa (SH) = 8.00
pKa (COOH) = 2.05, pKa (NH3+) = 10.25, pKa (SH) = 8.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The result of the reaction of the hydrolysis of Leu-Ile-Lys-Cys-Val-Asn-Gln-Tyr with trypsin is __________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The isoelectric point of Glycine is 6.06 (pKa (COOH) = 2.35, pKa (NH3+) = 9.78).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The sequence of a heptapeptide can be deduced from the following experimental results as Thr-Tyr-Cys-Gln-Arg-Trp-His
Edman degradation Thr
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Thr-Tyr-Cys-Gln-Arg
Trp-His
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Thr-Tyr
Cys-Gln-Arg-Trp
His
Edman degradation Thr
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Thr-Tyr-Cys-Gln-Arg
Trp-His
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Thr-Tyr
Cys-Gln-Arg-Trp
His

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Whereas L-cysteine is a building block of peptides and proteins, D-cysteine is a common building block of bacterial membranes. Draw both, L-cysteine and D-cysteine. Which stereocenter has S and which has R configuration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
-Helix and -sheet are examples of protein secondary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The sequence of an octapeptide can be deduced from the following experimental results as Cys-Asn-Met-Tyr-Val-Phe-Lys-Pro.
Edman degradation Cys
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Cys-Asn-Met-Tyr-Val-Phe-Lys
Pro
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Cys-Asn-Met-Tyr
Val-Phe
Lys-Pro
Treatment with Cyanogen Bromide Cys-Asn-Met
Tyr-Val-Phe-Lys-Pro
Edman degradation Cys
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Cys-Asn-Met-Tyr-Val-Phe-Lys
Pro
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Cys-Asn-Met-Tyr
Val-Phe
Lys-Pro
Treatment with Cyanogen Bromide Cys-Asn-Met
Tyr-Val-Phe-Lys-Pro

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The structure of the tripeptide Glu-Gly-Phe is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Arginine is an amino acid with a basic side chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The result of the reaction of the hydrolysis of Ala-Phe-Leu-Tyr-Leu-Pro with chymotrypsin is __________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The sequence of a decapeptide can be deduced from the following experimental results as Leu-Met-Ser-Thr-Trp-His-Phe-Asp-Lys-Glu.
Edman degradation Leu
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Leu-Met-Ser-Thr-Trp-His-Phe-Asp-Lys
Glu
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Leu-Met-Ser-Thr-Trp
His-Phe
Asp-Lys-Glu
Treatment with Cyanogen Bromide Leu-Met
Ser-Thr-Trp-His-Phe-Asp-Lys-Glu
Edman degradation Leu
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Trypsin Leu-Met-Ser-Thr-Trp-His-Phe-Asp-Lys
Glu
Hydrolysis catalyzed by Chymotrypsin Leu-Met-Ser-Thr-Trp
His-Phe
Asp-Lys-Glu
Treatment with Cyanogen Bromide Leu-Met
Ser-Thr-Trp-His-Phe-Asp-Lys-Glu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A major stabilizing factor of protein tertiary structure is disulfide linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Asparagine is an amino acid with an acidic side chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Complete the following mechanism
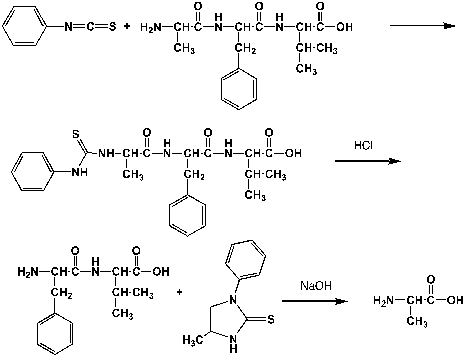


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
At pH 7.05 lysine pI = 9.74) will migrate toward the positive electrode during electrophoresis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The result of the reaction of Asp-Val-Met-Leu-His with cyanogen bromide is _______________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following amino acids react with more than one equivalent of phenylisothiocyanate in an Edman-reaction? Assume that all four are in an N-terminal position.
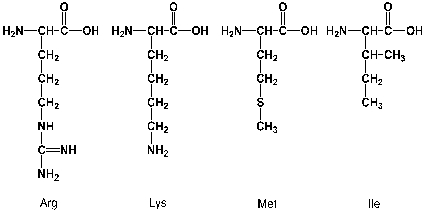


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Complete the following mechanism:





Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The isoelectric point of proline is ______________.
pKa (COOH) = 2.00, pKa (NH3+) = 10.60
pKa (COOH) = 2.00, pKa (NH3+) = 10.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



