Deck 1: An Introduction to Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: An Introduction to Finance
1
If Canadian households, in aggregate, own real assets with a market value of $3.194 trillion, and also own net financial assets with a market value of $2.344 trillion, the total net assets of Canadian households have a market value of
A)$3.194 trillion
B)$5.538 trillion
C)$-0.850 trillion
D)$0.850 trillion
A)$3.194 trillion
B)$5.538 trillion
C)$-0.850 trillion
D)$0.850 trillion
$5.538 trillion
2
Given the following hypothetical information regarding the real and financial assets in Canada for 2022 (numbers in $ billions):
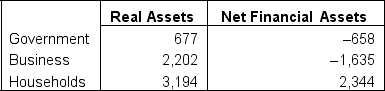
What is the value of the total net assets in Canada for 2022?
A)$5,842 billion
B)$6,086 billion
C)$6,124 billion
D)$6,105 billion

What is the value of the total net assets in Canada for 2022?
A)$5,842 billion
B)$6,086 billion
C)$6,124 billion
D)$6,105 billion
$6,124 billion
3
Which of the following sectors is NOT a user of savings in the economy?
A)business sector
B)household sector
C)government sector
D)banking sector
A)business sector
B)household sector
C)government sector
D)banking sector
household sector
4
In Canada, the primary provider of funds to business and government is (are)
A)international banks.
B)large Canadian banks.
C)the household sector.
D)market intermediaries.
A)international banks.
B)large Canadian banks.
C)the household sector.
D)market intermediaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As of 2018 what was the major proportion of Canadian households' financial assets?
A)stocks and bonds
B)deposits
C)foreign investment
D)claims on retirement and insurance funds
A)stocks and bonds
B)deposits
C)foreign investment
D)claims on retirement and insurance funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following does NOT appear as an item on Canada's balance sheet, as presented in the text?
A)non-residential structures
B)net worth or equity
C)net foreign liabilities
D)net foreign assets
A)non-residential structures
B)net worth or equity
C)net foreign liabilities
D)net foreign assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Finance is the study of how and under what terms
A)savings are allocated between lenders and borrowers.
B)investments are allocated between investors and brokers.
C)institutions with excess money make share purchase decisions.
D)households allocate money between spending and saving.
A)savings are allocated between lenders and borrowers.
B)investments are allocated between investors and brokers.
C)institutions with excess money make share purchase decisions.
D)households allocate money between spending and saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An example of direct intermediation would be
A)an individual borrowing money from a bank.
B)an individual borrowing money from their mother.
C)an individual using a real estate broker to finance their home purchase.
D)a stockbroker selling securities to an individual.
A)an individual borrowing money from a bank.
B)an individual borrowing money from their mother.
C)an individual using a real estate broker to finance their home purchase.
D)a stockbroker selling securities to an individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The three intermediation channels that transfer money from lenders to borrowers are
A)direct, indirect, and financial intermediation.
B)direct, indirect, and monetary intermediation.
C)direct, financial, and monetary intermediation.
D)indirect, financial, and monetary intermediation.
A)direct, indirect, and financial intermediation.
B)direct, indirect, and monetary intermediation.
C)direct, financial, and monetary intermediation.
D)indirect, financial, and monetary intermediation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Human capital is
A)based on only the current skills, but not the education, of a country's citizens.
B)based on only the education, but not the current skills, of a country's citizens.
C)based on the skills and education of citizens and should be included in a country's wealth.
D)difficult to measure and should therefore not be included in a country's wealth.
A)based on only the current skills, but not the education, of a country's citizens.
B)based on only the education, but not the current skills, of a country's citizens.
C)based on the skills and education of citizens and should be included in a country's wealth.
D)difficult to measure and should therefore not be included in a country's wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the following list, which item is a financial asset?
A)land
B)bond
C)building
D)inventory
A)land
B)bond
C)building
D)inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A financial security is
A)a jail term for a financial manager that has committed fraud.
B)a contract that is created only when a new stock is issued to the public.
C)a financial contract created whenever funds are transferred.
D)a contract that is created only when a new bond is first sold.
A)a jail term for a financial manager that has committed fraud.
B)a contract that is created only when a new stock is issued to the public.
C)a financial contract created whenever funds are transferred.
D)a contract that is created only when a new bond is first sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Entities that invest funds on behalf of others and change the nature of the transactions are called
A)brokers.
B)financial intermediaries.
C)dealers.
D)market intermediaries.
A)brokers.
B)financial intermediaries.
C)dealers.
D)market intermediaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Joe has just borrowed $5,000 from his aunt in order to make a down payment on a car.This borrowing transaction is an example of
A)indirect intermediation.
B)direct intermediation.
C)external intermediation.
D)market transaction.
A)indirect intermediation.
B)direct intermediation.
C)external intermediation.
D)market transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is NOT a financial intermediary?
A)chartered banks
B)insurance companies
C)pension funds
D)mutual funds
A)chartered banks
B)insurance companies
C)pension funds
D)mutual funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You are provided with the following hypothetical information regarding the real and financial assets in Canada for 2022 (numbers in $ billions):
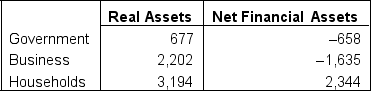
What is the value of the net financial assets owned by non-residents for 2022?
A)$901 billion
B)$51 billion
C)$2,293 billion
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

What is the value of the net financial assets owned by non-residents for 2022?
A)$901 billion
B)$51 billion
C)$2,293 billion
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following items is NOT a real asset?
A)land
B)television
C)bond
D)gold mine
A)land
B)television
C)bond
D)gold mine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT one of the main functions performed by mutual funds?
A)pooling sums of money to make investments
B)paying out premiums to their clients
C)providing professional management expertise
D)acting as a "pass-through" for individuals to invest in the equity and debt markets
A)pooling sums of money to make investments
B)paying out premiums to their clients
C)providing professional management expertise
D)acting as a "pass-through" for individuals to invest in the equity and debt markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the main difference between real assets and financial assets?
A)Real assets are tangible and financial assets are intangible.
B)Real assets have known values, while the values of financial assets are not known.
C)Real assets are intangible and financial assets are tangible.
D)Real assets have unknown values, while the values of financial assets are known.
A)Real assets are tangible and financial assets are intangible.
B)Real assets have known values, while the values of financial assets are not known.
C)Real assets are intangible and financial assets are tangible.
D)Real assets have unknown values, while the values of financial assets are known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Although Canadian banks are involved in almost all areas of the financial system, which of the following is their core activity?
A)stock market investment activity
B)retirement planning
C)wealth management
D)taking deposits and lending funds
A)stock market investment activity
B)retirement planning
C)wealth management
D)taking deposits and lending funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An example of a non-marketable financial asset is a
A)demand deposit.
B)T-bill.
C)commercial paper.
D)common share.
A)demand deposit.
B)T-bill.
C)commercial paper.
D)common share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Who are the biggest borrowers and lenders in Canada, respectively?
A)government and households
B)government and banks
C)banks and mutual funds
D)Crown corporations and banks
A)government and households
B)government and banks
C)banks and mutual funds
D)Crown corporations and banks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How do governments obtain the majority of their short- and long-term financing?
A)T-bills and Canada Savings Bonds
B)T-bills, traditional bonds, and Canada Savings Bonds
C)T-bills, equity, and traditional bonds
D)traditional bonds and Canada Savings Bonds
A)T-bills and Canada Savings Bonds
B)T-bills, traditional bonds, and Canada Savings Bonds
C)T-bills, equity, and traditional bonds
D)traditional bonds and Canada Savings Bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is an existing stock exchange in Canada?
A)Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
B)Montreal Exchange (ME)
C)Vancouver Stock Exchange (VSE)
D)Winnipeg Stock Exchange (WSE)
A)Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
B)Montreal Exchange (ME)
C)Vancouver Stock Exchange (VSE)
D)Winnipeg Stock Exchange (WSE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two examples of marketable assets include
A)savings accounts and demand deposits held at financial institutions.
B)provincial and federal savings bonds.
C)demand deposits and provincial savings bonds.
D)equity securities and T-bills.
A)savings accounts and demand deposits held at financial institutions.
B)provincial and federal savings bonds.
C)demand deposits and provincial savings bonds.
D)equity securities and T-bills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Though they are classified as equity, why are preferred shares also similar to debt?
A)Both carry the same interest rate.
B)Dividends on preferred shares must be paid out before any common share dividends.
C)The voting structures for preferred shares and debt are equivalent.
D)Preferred shares have similar maturity structures to debt.
A)Both carry the same interest rate.
B)Dividends on preferred shares must be paid out before any common share dividends.
C)The voting structures for preferred shares and debt are equivalent.
D)Preferred shares have similar maturity structures to debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is NOT an example of a capital market security?
A)bond
B)debenture
C)common equity
D)T-bill
A)bond
B)debenture
C)common equity
D)T-bill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following was NOT one of the major objectives in the restructuring of the Canadian stock exchanges in 1999 and 2000?
A)to create a Canadian market for NASDAQ-listed companies
B)to combine all futures and options trading on one exchange
C)to make the TSX the official exchange for the trading of Canadian senior stocks
D)to create a single national exchange for trading in junior company stocks
A)to create a Canadian market for NASDAQ-listed companies
B)to combine all futures and options trading on one exchange
C)to make the TSX the official exchange for the trading of Canadian senior stocks
D)to create a single national exchange for trading in junior company stocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following was NOT a reason for the credit crunch of 2008-09?
A)mistrust between financial intermediaries
B)illiquidity of debt markets
C)the arrest of Bernard Madoff
D)bankruptcy of one of the leading financial institutions
A)mistrust between financial intermediaries
B)illiquidity of debt markets
C)the arrest of Bernard Madoff
D)bankruptcy of one of the leading financial institutions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT a component of debt securities?
A)maturity
B)repayment
C)dividends
D)interest payments
A)maturity
B)repayment
C)dividends
D)interest payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following is NOT a function of brokers?
A)Manage money for clients.
B)Make the market work.
C)Charge a fee for their services.
D)Assist with the transaction process.
A)Manage money for clients.
B)Make the market work.
C)Charge a fee for their services.
D)Assist with the transaction process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The main difference between exchanges and dealer/OTC markets is
A)exchanges are a part of the primary market, while dealer and OTC markets are part of the secondary market.
B)transactions in dealer markets are conducted entirely by humans, not electronically.
C)exchanges have a physical location while dealer and OTC markets do not.
D)All of the above are differences between exchanges and dealer markets.
A)exchanges are a part of the primary market, while dealer and OTC markets are part of the secondary market.
B)transactions in dealer markets are conducted entirely by humans, not electronically.
C)exchanges have a physical location while dealer and OTC markets do not.
D)All of the above are differences between exchanges and dealer markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All common shares are comprised of which two components?
A)ownership and voting rights
B)ownership and dividend rights
C)voting and dividend rights
D)dividend and yield rights
A)ownership and voting rights
B)ownership and dividend rights
C)voting and dividend rights
D)dividend and yield rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The exchange that acts as the Canadian national derivatives market and conducts all options and futures trading is called the
A)Montreal Exchange (ME).
B)Winnipeg Commodity Exchange.
C)TSX Venture.
D)Alpha Exchange.
A)Montreal Exchange (ME).
B)Winnipeg Commodity Exchange.
C)TSX Venture.
D)Alpha Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Since March 2000 the Montreal Exchange (ME)has functioned as Canada's national market for
A)hedge funds.
B)publicly traded stocks.
C)derivatives.
D)T-bills.
A)hedge funds.
B)publicly traded stocks.
C)derivatives.
D)T-bills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why can't the Canadian government issue equity?
A)because assets belong to all Canadians
B)it is not listed in the financial markets
C)it has too much debt
D)because expenditures exceed revenues
A)because assets belong to all Canadians
B)it is not listed in the financial markets
C)it has too much debt
D)because expenditures exceed revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Financial markets are usually classified by the type and maturity of the financial assets traded.The two main classifications are as follows:
A)bond market and money market.
B)money market and capital market.
C)bond market and foreign-exchange market.
D)commodity market and capital market.
A)bond market and money market.
B)money market and capital market.
C)bond market and foreign-exchange market.
D)commodity market and capital market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which is the only province where trades in unlisted securities need to be reported?
A)British Columbia
B)Quebec
C)Alberta
D)Ontario
A)British Columbia
B)Quebec
C)Alberta
D)Ontario

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A market where transactions are made directly between large institutions and wealthy individuals that bypass brokers and dealers is an example of
A)the primary market.
B)the secondary market.
C)the third market.
D)the fourth market.
A)the primary market.
B)the secondary market.
C)the third market.
D)the fourth market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Of the following list, who are the dominant players in the money market?
I.individuals
II.corporations
III.governments
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I.individuals
II.corporations
III.governments
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain why primary markets are the key to the wealth creation process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the stock of a listed firm decreases by 50 percent, what does it mean to the shareholders?
A)Their ownership of the firm will decrease by 50 percent.
B)Total value of their holdings decreases by 50 percent.
C)The debt of the firm decreases by 50 percent.
D)nothing
A)Their ownership of the firm will decrease by 50 percent.
B)Total value of their holdings decreases by 50 percent.
C)The debt of the firm decreases by 50 percent.
D)nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain what an auction market is and how it works.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The consolidation of U.S.and global stock markets has
A)been increasing recently, as shown by the merger of the NYSE and Euronext.
B)been decreasing recently, as shown by the decrease in multi-listed stocks.
C)led to lower risk in investments because markets have become less interdependent.
D)led to increased reliance on human interactions in securities trading.
A)been increasing recently, as shown by the merger of the NYSE and Euronext.
B)been decreasing recently, as shown by the decrease in multi-listed stocks.
C)led to lower risk in investments because markets have become less interdependent.
D)led to increased reliance on human interactions in securities trading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is an over-the-counter market? Do all bonds in Canada trade over-the-counter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of global financial markets?
A)They represent important sources of funds for borrowers.
B)They provide diversification benefits to Canadian investors.
C)Canadian companies can list their shares in different markets.
D)The value of Canadian shares becomes more stable.
A)They represent important sources of funds for borrowers.
B)They provide diversification benefits to Canadian investors.
C)Canadian companies can list their shares in different markets.
D)The value of Canadian shares becomes more stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How do financial intermediaries help those with "too much money today" and those with "not enough money today"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are the differences between the primary markets and the secondary markets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which is the world's largest and most famous stock market?
A)New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
B)Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
C)Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)
D)London Stock Exchange (LSE)
A)New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
B)Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
C)Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)
D)London Stock Exchange (LSE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why is the secondary market important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Define and describe the difference between the third and fourth markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The two sectors that are normally regarded as the lowest risk in the financial market are
A)T-bills and loans extended to "PIIGS" countries.
B)demand deposits and loans to countries that have taken austerity measures.
C)household mortgages and government debt.
D)government debt and foreign company borrowings.
A)T-bills and loans extended to "PIIGS" countries.
B)demand deposits and loans to countries that have taken austerity measures.
C)household mortgages and government debt.
D)government debt and foreign company borrowings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The spread of the financial crisis in the autumn of 2008 was NOT increased by
A)linkages between global financial markets.
B)the cross listing of firms in different markets.
C)the consolidation of the global financial system.
D)excessive debt of the government.
A)linkages between global financial markets.
B)the cross listing of firms in different markets.
C)the consolidation of the global financial system.
D)excessive debt of the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



