Deck 11: Respiratory Insufficiency, Respiratory Failure and Ventilatory Management Protocols
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Respiratory Insufficiency, Respiratory Failure and Ventilatory Management Protocols
1
Which of the following are contraindications for noninvasive ventilation?
1) Facial and head trauma
2) Community-acquired pneumonia
3) Copious, viscous sputum
4) Severe upper GI bleeding
A)1
B)2, 3
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 3, 4
1) Facial and head trauma
2) Community-acquired pneumonia
3) Copious, viscous sputum
4) Severe upper GI bleeding
A)1
B)2, 3
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 3, 4
1, 3, 4
2
What is the primary pathophysiologic mechanism in alveolar hypoventilation?
A) Decreased minute ventilation
B) Increased ventilation/perfusion ratio
C) Decreased venous admixture
D) Decreased inspired oxygen pressure
A) Decreased minute ventilation
B) Increased ventilation/perfusion ratio
C) Decreased venous admixture
D) Decreased inspired oxygen pressure
Decreased minute ventilation
3
Which of the following are causes of hypercapnic respiratory?
1) Impending ventilatory failure
2) Apnea
3) Severe refractory hypoxemia
4) Acute ventilatory failure
A)1, 3
B)1, 2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3
1) Impending ventilatory failure
2) Apnea
3) Severe refractory hypoxemia
4) Acute ventilatory failure
A)1, 3
B)1, 2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3
1, 2, 4
4
What VD/VT ratio range would you expect to see in a patient receiving mechanical ventilation?
A) 20% and 40%
B) 30% and 50%
C) 40% and 60%
D) 50% and 70%
A) 20% and 40%
B) 30% and 50%
C) 40% and 60%
D) 50% and 70%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You are the respiratory therapist managing an adult male patient receiving mechanical ventilation as a result of hypoxemic respiratory failure. The patient has a pressure time index of 0.16, and rapid shallow breath index of 95, and the cuff-leak test demonstrated the patient could breathe when it was deflated. What would your recommendations to the physician be regarding weaning this patient based on this data?
A) Do not attempt to wean.
B) Attempt to wean.
C) Reattempt a spontaneous breathing trial to see if RSBI improves before weaning.
D) Cannot determine.
A) Do not attempt to wean.
B) Attempt to wean.
C) Reattempt a spontaneous breathing trial to see if RSBI improves before weaning.
D) Cannot determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What effect would a pulmonary embolism have on the VD/VT and the ratios?
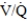
A) The VD/VT would increase and the would decrease.
B) The VD/VT would decrease and the would increase.
C) The VD/VT and the ratios would both increase.
D) The VD/VT and the ratios would both decrease.
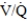
A) The VD/VT would increase and the would decrease.
B) The VD/VT would decrease and the would increase.
C) The VD/VT and the ratios would both increase.
D) The VD/VT and the ratios would both decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are clinical indicators of type I respiratory failure?
1) Decreased PaO2
2) Increased P(A-a)O2
3) Decreased PaO2/FIO2
4) Decreased
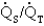
A)1, 2
B)2, 4
C)1, 2, 3
D)2, 3, 4
1) Decreased PaO2
2) Increased P(A-a)O2
3) Decreased PaO2/FIO2
4) Decreased
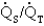
A)1, 2
B)2, 4
C)1, 2, 3
D)2, 3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a critical value for the key clinical indicators in hypercapnic respiratory failure in an adult?
1) pH 7.19
2) Ventilatory rate 35 breaths/min
3) MIP 80 cm H2O
4) VD/VT 35%
A)1, 4
B)2, 3
C)1, 2
D)3, 4
1) pH 7.19
2) Ventilatory rate 35 breaths/min
3) MIP 80 cm H2O
4) VD/VT 35%
A)1, 4
B)2, 3
C)1, 2
D)3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following values is the VD/VT value if the PaCO2 is 40 mm Hg and the is 30 mm Hg?
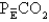
A) 0.25 or 25%.
B) 0.33 or 33%.
C) 0.4 or 40%.
D) Need more information to determine the value.
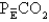
A) 0.25 or 25%.
B) 0.33 or 33%.
C) 0.4 or 40%.
D) Need more information to determine the value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following are abnormal causes of anatomic shunt?
1) Bronchial venous drainage
2) Congenital heart disease
3) Intrapulmonary fistula
4) Vascular lung tumors
A)1, 3
B)1, 2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3
1) Bronchial venous drainage
2) Congenital heart disease
3) Intrapulmonary fistula
4) Vascular lung tumors
A)1, 3
B)1, 2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



