Deck 5: The Sun: the Closest Star
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Sun: the Closest Star
1
How can the density of the Sun be measured?
A) by using the density of hydrogen as measured on Earth
B) by analysing samples of the solar wind
C) by using the amount of area covered by Venus during a transit
D) by using Newton's laws and the Sun's diameter
A) by using the density of hydrogen as measured on Earth
B) by analysing samples of the solar wind
C) by using the amount of area covered by Venus during a transit
D) by using Newton's laws and the Sun's diameter
by using Newton's laws and the Sun's diameter
2
What is the temperature of an object from which no heat energy can be extracted?
A) 0 Kelvin
B) 100 Kelvin
C) 0° Celsius
D) 100° Celsius
A) 0 Kelvin
B) 100 Kelvin
C) 0° Celsius
D) 100° Celsius
0 Kelvin
3
If you know the period and semi-major axis of Venus's orbit, what would you need to calculate the mass of the Sun?
A) Kepler's third law and the mass of Venus
B) Kepler's third law
C) Newton's third law and the mass of Venus
D) Newton's third law
A) Kepler's third law and the mass of Venus
B) Kepler's third law
C) Newton's third law and the mass of Venus
D) Newton's third law
Kepler's third law
4
What does an un-ionized atom always contain?
A) the same number of protons and neutrons
B) the same number of protons and electrons
C) twice as many protons as neutrons
D) twice as many neutrons as protons
A) the same number of protons and neutrons
B) the same number of protons and electrons
C) twice as many protons as neutrons
D) twice as many neutrons as protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the sequence of star colours in order of increasing temperature?
A) red, yellow, blue
B) red, blue, yellow
C) yellow, red, blue
D) blue, yellow, red
A) red, yellow, blue
B) red, blue, yellow
C) yellow, red, blue
D) blue, yellow, red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the definition of Absolute Zero?
A) zero degrees Celsius
B) the temperature at which no thermal energy can be extracted from atoms
C) the temperature at which water freezes
D) the temperature at which molecules split into atoms
A) zero degrees Celsius
B) the temperature at which no thermal energy can be extracted from atoms
C) the temperature at which water freezes
D) the temperature at which molecules split into atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
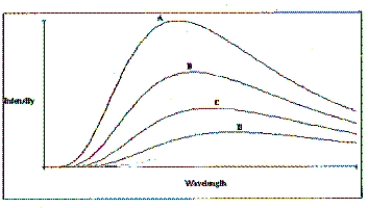
A plot of the continuous spectra of four different stars is shown in the figure. Based on these spectra, which of the stars has the lowest temperature?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
D) Star D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a characteristic of a blackbody?
A) It emits no light.
B) It emits radiation in spectral lines.
C) It emits light in a continuous spectrum.
D) It reflects all light.
A) It emits no light.
B) It emits radiation in spectral lines.
C) It emits light in a continuous spectrum.
D) It reflects all light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Sun emits its maximum intensity of light at about 520 nm. According to Wien's Law, at what wavelength would the maximum intensity be for a star with a surface temperature twice that of the Sun?
A) 260 nm
B) 1040 nm
C) 5800 nm
D) 11600 nm
A) 260 nm
B) 1040 nm
C) 5800 nm
D) 11600 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following contains two or more atoms that are bound together by exchanging or sharing electrons with each other?
A) nucleus
B) ion
C) proton
D) molecule
A) nucleus
B) ion
C) proton
D) molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What makes up the neutral hydrogen atom?
A) one proton and one neutron
B) one proton
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron
D) one proton and one electron
A) one proton and one neutron
B) one proton
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron
D) one proton and one electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which two quantities are needed to calculate density of any object?
A) mass and volume
B) temperature and diameter
C) mass and temperature
D) volume and temperature
A) mass and volume
B) temperature and diameter
C) mass and temperature
D) volume and temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Summer temperatures on Mars can reach 310 K. How would humans deal with such a temperature on Earth?
A) This temperature is so low that a human would freeze to death.
B) This is a Canadian winter temperature; humans could survive with a winter jacket and boots.
C) This is a Canadian summer temperature; humans could be comfortable in shorts and a T-shirt.
D) This temperature is so high that a human would die of heatstroke.
A) This temperature is so low that a human would freeze to death.
B) This is a Canadian winter temperature; humans could survive with a winter jacket and boots.
C) This is a Canadian summer temperature; humans could be comfortable in shorts and a T-shirt.
D) This temperature is so high that a human would die of heatstroke.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The surface temperature of the Sun is about 5800K. Based on this temperature, what is the expected peak wavelength of radiation?
A) orange
B) green
C) yellow
D) red
A) orange
B) green
C) yellow
D) red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The temperature of an object is 273K. What is the temperature in degrees Celsius?
A) 273
B) -273
C) 0
D) 373
A) 273
B) -273
C) 0
D) 373

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two astronomers wish to work together to measure the distance from Earth to the Sun using the transit of Venus. Which of the following instructions should they follow?
A) They should use the same kind of telescope.
B) They should make their measurements from the same location.
C) They should make their measurements at the same time.
D) They should take their measurements 6 months apart.
A) They should use the same kind of telescope.
B) They should make their measurements from the same location.
C) They should make their measurements at the same time.
D) They should take their measurements 6 months apart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Sun emits its maximum intensity of light at about 520 nm. According to Wien's Law, what would the temperature of a star that emits its maximum intensity at 1040 nm be?
A) 1040 K
B) 2900 K
C) 5800 K
D) 10400 K
A) 1040 K
B) 2900 K
C) 5800 K
D) 10400 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following measures the average speed of the particles (atoms or molecules) in a gas?
A) heat
B) composition
C) temperature
D) binding energy
A) heat
B) composition
C) temperature
D) binding energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The temperature of an object is 373K. What is the temperature in degrees Celsius?
A) 100
B) -100
C) 0
D) -373
A) 100
B) -100
C) 0
D) -373

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The temperature of an object is 100K. What is the temperature in degrees Celsius?
A) -273
B) -173
C) 173
D) 273
A) -273
B) -173
C) 173
D) 273

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What state must an atom be in for it to emit a photon?
A) ionized
B) excited
C) ground
D) isotopic
A) ionized
B) excited
C) ground
D) isotopic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is it possible that you could fly a very-well-insulated spaceship through the Sun's photosphere?
A) The photosphere is less than 500 km deep.
B) The photosphere is made of hydrogen gas.
C) The photosphere has a very low temperature.
D) The photosphere has a very low density.
A) The photosphere is less than 500 km deep.
B) The photosphere is made of hydrogen gas.
C) The photosphere has a very low temperature.
D) The photosphere has a very low density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How does gas move within granules on the solar surface?
A) Gas moves upward in the centres of some cells and downward in others; the gas cools as it passes between individual granules.
B) The gas is actually motionless. The dark regions are absorption features from gases in the photosphere.
C) Gas moves upward in the bright cell centres and downward around the darker edges.
D) Gas moves downward in the bright cell centres and upward around the darker edges.
A) Gas moves upward in the centres of some cells and downward in others; the gas cools as it passes between individual granules.
B) The gas is actually motionless. The dark regions are absorption features from gases in the photosphere.
C) Gas moves upward in the bright cell centres and downward around the darker edges.
D) Gas moves downward in the bright cell centres and upward around the darker edges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Where does most of the visible light we see coming from the Sun originate?
A) the chromosphere
B) the photosphere
C) the corona
D) the sunspots
A) the chromosphere
B) the photosphere
C) the corona
D) the sunspots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is found in the centres of granules?
A) hot material rising to the photosphere from below
B) cool material falling from the photosphere to the regions below
C) material that is fainter and hotter than its surroundings
D) material that is brighter and cooler than its surroundings.
A) hot material rising to the photosphere from below
B) cool material falling from the photosphere to the regions below
C) material that is fainter and hotter than its surroundings
D) material that is brighter and cooler than its surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Stefan-Boltzmann law says that hot objects emit energy proportional to the fourth power of their temperature. One star has a temperature of 30,000 K and another star has a temperature of 6,000 K. Compared to the cooler star, how much more energy per second will the hotter star radiate from each square metre of its surface?
A) 5 times as much
B) 25 times as much
C) 625 times as much
D) 1.3×1015 times
A) 5 times as much
B) 25 times as much
C) 625 times as much
D) 1.3×1015 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a set of rules that describes how atoms and subatomic particles behave?
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) the Coulomb force
C) quantum mechanics
D) the binding energy
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) the Coulomb force
C) quantum mechanics
D) the binding energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Sun contains a lot of hot gas, so why do we observe an absorption spectrum rather than an emission spectrum from it?
A) The ionized gas in the photosphere emits a continuous spectrum, which the chromosphere changes into an absorption spectrum.
B) The ionized gas in the photosphere emits an absorption spectrum.
C) The Sun's photosphere is cooler than the layers below it.
D) The Sun's photosphere is hotter than the layers below it.
A) The ionized gas in the photosphere emits a continuous spectrum, which the chromosphere changes into an absorption spectrum.
B) The ionized gas in the photosphere emits an absorption spectrum.
C) The Sun's photosphere is cooler than the layers below it.
D) The Sun's photosphere is hotter than the layers below it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the term for atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons?
A) ions
B) molecules
C) nuclear pairs
D) isotopes
A) ions
B) molecules
C) nuclear pairs
D) isotopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
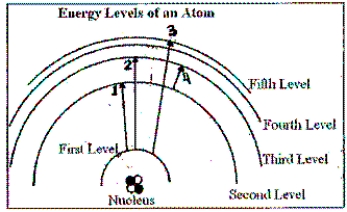
In the diagram, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the greatest energy (shortest wavelength)?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What causes granulation?
A) sunspots
B) rising and sinking gases below the photosphere
C) shock waves in the corona
D) the solar wind flowing away from the corona
A) sunspots
B) rising and sinking gases below the photosphere
C) shock waves in the corona
D) the solar wind flowing away from the corona

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you move an electron from a lower energy level to a higher energy level within an atom, how would you describe that atom?
A) The atom is ionized.
B) The atom is dissociated.
C) The atom is excited.
D) The atom is neutralized.
A) The atom is ionized.
B) The atom is dissociated.
C) The atom is excited.
D) The atom is neutralized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

In the diagram, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the least energy (longest wavelength)?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the binding energy?
A) ionization that occurs within the atom
B) the energy that holds the atom together
C) the energy of quantum effects within the atom
D) the energy that causes excitation of the atom
A) ionization that occurs within the atom
B) the energy that holds the atom together
C) the energy of quantum effects within the atom
D) the energy that causes excitation of the atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is responsible for binding the electrons to the nucleus?
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) Wien's law
C) Coulomb force
D) Balmer series
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) Wien's law
C) Coulomb force
D) Balmer series

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What causes an atom to become excited?
A) emitting a photon
B) colliding with another atom or electron
C) reflecting a photon
D) gaining an extra electron
A) emitting a photon
B) colliding with another atom or electron
C) reflecting a photon
D) gaining an extra electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the explanation for the pattern of granulation seen on the visible surface of the Sun?
A) The granules form the base of a circulation pattern that extends from the photosphere to the outer corona.
B) The granules are regions of nuclear energy generation in the Sun's photosphere.
C) Each granule contains a strong magnetic field, which compresses and heats the gas underneath it.
D) The granules are the tops of hot gases that have risen from the Sun's convective zone.
A) The granules form the base of a circulation pattern that extends from the photosphere to the outer corona.
B) The granules are regions of nuclear energy generation in the Sun's photosphere.
C) Each granule contains a strong magnetic field, which compresses and heats the gas underneath it.
D) The granules are the tops of hot gases that have risen from the Sun's convective zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What can we use to show that sunspots are cooler than the rest of the Sun's photosphere?
A) thermometers dropped into sunspots
B) Wien's law and the Stefan-Boltzmann law
C) the Doppler effect
D) the Zeeman effect
A) thermometers dropped into sunspots
B) Wien's law and the Stefan-Boltzmann law
C) the Doppler effect
D) the Zeeman effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the process of removing an electron from a stable nucleus called?
A) ionization
B) Doppler broadening
C) collisional broadening
D) a red shift
A) ionization
B) Doppler broadening
C) collisional broadening
D) a red shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Is it possible for a red star to emit more energy than a blue star?
A) No, because the red star has a lower temperature.
B) Yes, if the red star has a larger area.
C) Yes, if the red star has a larger wavelength of maximum intensity.
D) No, because red stars are less massive than blue stars.
A) No, because the red star has a lower temperature.
B) Yes, if the red star has a larger area.
C) Yes, if the red star has a larger wavelength of maximum intensity.
D) No, because red stars are less massive than blue stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
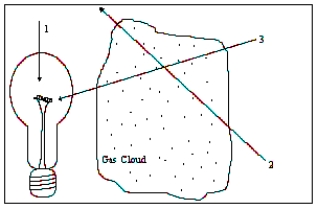
The diagram illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight (the observer is located at the numbered positions). Along which line of sight would an observer see an emission spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The energy of the first level in an atom is 2.2×10-18 J, and the energy of the second energy level is 1.6×10-18 J. What is the energy of the photon that is emitted if an electron moves from the second level to the first?
A) 3.5×10-36 J
B) 6.0 ×10-18 J
C) 3.5×10-18 J
D) 6.0×10-19 J
A) 3.5×10-36 J
B) 6.0 ×10-18 J
C) 3.5×10-18 J
D) 6.0×10-19 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Doppler effect means that the motion of an object affects the light emitted from it. What result does the Doppler effect cause?
A) It shifts the wavelength of spectral lines.
B) It changes the speed of light emitted from the object.
C) It makes the object appear hotter.
D) It makes the object appear cooler.
A) It shifts the wavelength of spectral lines.
B) It changes the speed of light emitted from the object.
C) It makes the object appear hotter.
D) It makes the object appear cooler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why is Cecilia Payne's Ph.D. thesis sometimes called "the most important in astronomy"?
A) She was the first person to show that the Sun is mostly hydrogen.
B) She was the first person to analyze spectra of stars.
C) Her analysis of stellar spectra showed that stars generate their own light.
D) Her analysis of the Sun's spectrum resulted in the discovery of helium.
A) She was the first person to show that the Sun is mostly hydrogen.
B) She was the first person to analyze spectra of stars.
C) Her analysis of stellar spectra showed that stars generate their own light.
D) Her analysis of the Sun's spectrum resulted in the discovery of helium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A certain spectral line of hydrogen has a wavelength of 410.2 nm when observed in the laboratory. If the same line appears in a star's spectrum at 410.0 nm, what can you conclude about the motion of the star?
A) The star is moving away from the observer.
B) The star is moving toward the observer.
C) The star is moving but the direction is not known.
D) The star is not moving toward or away from the observer.
A) The star is moving away from the observer.
B) The star is moving toward the observer.
C) The star is moving but the direction is not known.
D) The star is not moving toward or away from the observer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the term for the absorption lines in the visible portion of the spectrum of a star that are produced by hydrogen?
A) Lyman series
B) Balmer series
C) Paschen series
D) Brackett series
A) Lyman series
B) Balmer series
C) Paschen series
D) Brackett series

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

The diagram illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight (the observer is located at the numbered positions). Along which line of sight would an observer see a continuous spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

The diagram illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight (the observer is located at the numbered positions). Along which line of sight would an observer see an absorption spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You are standing near a railway track and a train is moving toward you at 100 kph and blowing its whistle. What will you notice as the train moves past you?
A) As the train approaches, the horn will sound lower in pitch than when the train is moving away.
B) As the train approaches, the horn will sound higher in pitch than when the train is moving away.
C) As the train approaches, the headlight will appear bluer than when the train is moving away.
D) As the train approaches, the headlight will appear redder than when the train is moving away.
A) As the train approaches, the horn will sound lower in pitch than when the train is moving away.
B) As the train approaches, the horn will sound higher in pitch than when the train is moving away.
C) As the train approaches, the headlight will appear bluer than when the train is moving away.
D) As the train approaches, the headlight will appear redder than when the train is moving away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Would you expect to see hydrogen Balmer lines in the spectra of stars with temperatures of 3200 K?
A) Yes; these stars are so hot that most of the hydrogen is ionized and the atoms cannot absorb energy.
B) No; these stars are so cool that nearly all of the electrons in the hydrogen atom are in the ground state.
C) No; stars of this temperature are too cool to produce an absorption spectrum.
D) Yes; stars of this temperature are too hot to produce an absorption spectrum.
A) Yes; these stars are so hot that most of the hydrogen is ionized and the atoms cannot absorb energy.
B) No; these stars are so cool that nearly all of the electrons in the hydrogen atom are in the ground state.
C) No; stars of this temperature are too cool to produce an absorption spectrum.
D) Yes; stars of this temperature are too hot to produce an absorption spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is a plausible example of a Doppler blueshift?
A) A star appears to have a much higher temperature when moving toward the Earth than when moving away.
B) An ambulance's siren changes to a higher pitch as it speeds toward you.
C) A star's colour becomes redder as it moves away from the Earth.
D) A moving train's whistle shifts to a frequency so high that humans can't hear it.
A) A star appears to have a much higher temperature when moving toward the Earth than when moving away.
B) An ambulance's siren changes to a higher pitch as it speeds toward you.
C) A star's colour becomes redder as it moves away from the Earth.
D) A moving train's whistle shifts to a frequency so high that humans can't hear it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The Hγ line has a wavelength of 434.0 nm when observed in the laboratory. If the Hγ line appears in the spectrum of a star moving away from you, at what wavelength will you observe the line?
A) less than 434 nm
B) 434.0 nm
C) greater than 434 nm
D) the wavelength depends on the composition of the star
A) less than 434 nm
B) 434.0 nm
C) greater than 434 nm
D) the wavelength depends on the composition of the star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following can be measured by using the Doppler Effect?
A) the apparent speed of an airplane moving across the sky
B) the apparent velocity of a star across the sky
C) the apparent velocity of a planet across the sky
D) the radial velocity of a star
A) the apparent speed of an airplane moving across the sky
B) the apparent velocity of a star across the sky
C) the apparent velocity of a planet across the sky
D) the radial velocity of a star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What everyday object is an example of a place where electrons jump through energy levels and emit energy?
A) the full Moon
B) a gas stove
C) a neon sign
D) an incandescent light bulb
A) the full Moon
B) a gas stove
C) a neon sign
D) an incandescent light bulb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Would you expect to see hydrogen Balmer lines in the spectra of stars with temperatures of 45,000 K?
A) No; these stars are so hot that most of the hydrogen is ionized and the atoms cannot absorb energy.
B) Yes; these stars are so cool that nearly all of the electrons in the hydrogen atom are in the ground state.
C) Stars of this temperature are too cool to produce an absorption spectrum.
D) Stars of this temperature are too hot to produce an absorption spectrum.
A) No; these stars are so hot that most of the hydrogen is ionized and the atoms cannot absorb energy.
B) Yes; these stars are so cool that nearly all of the electrons in the hydrogen atom are in the ground state.
C) Stars of this temperature are too cool to produce an absorption spectrum.
D) Stars of this temperature are too hot to produce an absorption spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the lowest energy level in an atom called?
A) the absolute zero temperature
B) the ground state
C) the ionization level
D) the excited state
A) the absolute zero temperature
B) the ground state
C) the ionization level
D) the excited state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are the three layers of the Sun's atmosphere, in order of increasing distance from the surface?
A) corona, chromosphere, photosphere
B) photosphere, corona, chromosphere
C) photosphere, chromosphere, corona
D) chromosphere, photosphere, corona
A) corona, chromosphere, photosphere
B) photosphere, corona, chromosphere
C) photosphere, chromosphere, corona
D) chromosphere, photosphere, corona

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Why does each element have its own set of characteristic absorption lines?
A) The temperature of each element varies.
B) Elements can exist in different forms of matter.
C) Electron energy levels differ for each element.
D) Each element has a different mass.
A) The temperature of each element varies.
B) Elements can exist in different forms of matter.
C) Electron energy levels differ for each element.
D) Each element has a different mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following can be determined from the spectrum of a star, without additional information?
A) radial velocity
B) core temperature
C) distance
D) velocity across the sky
A) radial velocity
B) core temperature
C) distance
D) velocity across the sky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Sun emits light in a continuous spectrum but a neon lamp does not, because the Sun's light originates mainly from which of the following?
A) the collisions of electrons
B) nuclear fusion
C) electrons changing energy levels
D) chemical reactions
A) the collisions of electrons
B) nuclear fusion
C) electrons changing energy levels
D) chemical reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What does helioseismology measure?
A) the height of the Sun's corona
B) the strength of the solar wind
C) magnetic fields of sunspots
D) vibrations on the Sun's surface
A) the height of the Sun's corona
B) the strength of the solar wind
C) magnetic fields of sunspots
D) vibrations on the Sun's surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How can the corona of the Sun be observed?
A) during a lunar eclipse
B) with a coronagraph
C) using filtergrams
D) using the Zeeman effect
A) during a lunar eclipse
B) with a coronagraph
C) using filtergrams
D) using the Zeeman effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a space probe with extremely effective heat shielding were sent directly into the Sun, what would it experience as it falls through the Sun's chromosphere?
A) The temperature and density both decrease.
B) The temperature decreases and density increases.
C) The temperature increases and density decreases.
D) The temperature and density both increase.
A) The temperature and density both decrease.
B) The temperature decreases and density increases.
C) The temperature increases and density decreases.
D) The temperature and density both increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Where are sunspots found during a sunspot maximum?
A) 15 to 30 degrees north and south of the Sun's equator
B) evenly distributed over the Sun's surface
C) near the Sun's equator
D) near the poles of the Sun (latitudes 90° north and south)
A) 15 to 30 degrees north and south of the Sun's equator
B) evenly distributed over the Sun's surface
C) near the Sun's equator
D) near the poles of the Sun (latitudes 90° north and south)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why is the temperature at the region of a sunspot cooler than the photosphere?
A) Sunspots are holes in the photosphere that reveal the lower-temperature gases in the deeper layers.
B) Sunspots represent points where streams of cool gas from the corona lower the temperature in those regions of the photosphere.
C) Powerful magnetic fields in the sunspots act upon the atoms of the photosphere to prevent them from emitting light.
D) Powerful magnetic fields in the sunspots inhibit the convective flow of the gases of the photosphere downward, allowing the area to cool for longer than would normally be possible.
A) Sunspots are holes in the photosphere that reveal the lower-temperature gases in the deeper layers.
B) Sunspots represent points where streams of cool gas from the corona lower the temperature in those regions of the photosphere.
C) Powerful magnetic fields in the sunspots act upon the atoms of the photosphere to prevent them from emitting light.
D) Powerful magnetic fields in the sunspots inhibit the convective flow of the gases of the photosphere downward, allowing the area to cool for longer than would normally be possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is the term for the hot gases that are the moving extension of the Sun's corona?
A) solar wind
B) prominences
C) supergranules
D) spicules
A) solar wind
B) prominences
C) supergranules
D) spicules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
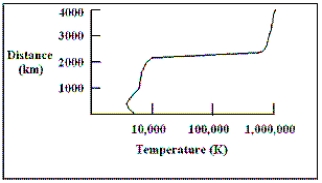
The diagram shows a plot of the temperature of the Sun as a function of distance above the bottom of the photosphere. At what distance above the bottom of the photosphere does the temperature of the Sun change the most rapidly with distance?
A) 400 km
B) 1,000 km
C) 2,300 km
D) 2,500 km to 4,000 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You measure the spectrum of a star and are unable to see absorption lines associated with iron. What can you conclude?
A) There is no iron in the star's atmosphere.
B) There is no iron in the star's core.
C) There may be iron in the star's atmosphere, depending on the temperature.
D) There may be iron in the star's atmosphere, depending on the age of the star.
A) There is no iron in the star's atmosphere.
B) There is no iron in the star's core.
C) There may be iron in the star's atmosphere, depending on the temperature.
D) There may be iron in the star's atmosphere, depending on the age of the star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What are the two most abundant elements in the Sun?
A) nitrogen and oxygen
B) hydrogen and helium
C) carbon and hydrogen
D) carbon and nitrogen
A) nitrogen and oxygen
B) hydrogen and helium
C) carbon and hydrogen
D) carbon and nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

The diagram shows a plot of the temperature of the Sun as a function of distance above the bottom of the photosphere. At what height above the bottom of the photosphere is the temperature of the Sun the coolest?
A) 500 km
B) 1,000 km
C) 2,300 km
D) 2,500 km to 4000 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
As the Moon covers the solar disk during a solar eclipse, a flash spectrum of the Sun's chromosphere can be recorded. This flash spectrum reveals an emission spectrum and provides information on the properties of the chromosphere. As the Moon moves from the inner chromosphere to the outer chromosphere, the spectral lines present in the flash spectrum change. What is going on in the chromosphere as the distance from the photosphere increases that produces the changes in the flash spectrum?
A) temperature and density both decrease
B) temperature decreases and density increases
C) temperature increases and density decreases
D) temperature and density both increase
A) temperature and density both decrease
B) temperature decreases and density increases
C) temperature increases and density decreases
D) temperature and density both increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What pattern of movement is found in the rotation of the Sun's photosphere?
A) fastest at the equator, slower at mid-latitudes, and slowest near the poles
B) slowest at the equator, faster at mid-latitudes, and fastest near the poles
C) fastest at the equator, and slowest at mid-latitudes and the poles, which travel at the same speed
D) the same speed regardless of latitude
A) fastest at the equator, slower at mid-latitudes, and slowest near the poles
B) slowest at the equator, faster at mid-latitudes, and fastest near the poles
C) fastest at the equator, and slowest at mid-latitudes and the poles, which travel at the same speed
D) the same speed regardless of latitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following describes the kind of light used to produce a filtergram, a photograph of the Sun's surface?
A) a wide band of wavelengths in the infrared
B) a wide band of wavelengths in the ultraviolet
C) a narrow band of Zeeman effect wavelengths
D) a narrow band of wavelengths in a specific spectral line
A) a wide band of wavelengths in the infrared
B) a wide band of wavelengths in the ultraviolet
C) a narrow band of Zeeman effect wavelengths
D) a narrow band of wavelengths in a specific spectral line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is a property of the Sun's chromosphere?
A) hotter than the photosphere
B) is above the corona
C) is below the visible surface of the Sun
D) produces a coronal filtergram
A) hotter than the photosphere
B) is above the corona
C) is below the visible surface of the Sun
D) produces a coronal filtergram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is differential rotation of the Sun?
A) Heating in the chromosphere and corona makes them hotter than the photosphere.
B) A magnetic dynamo operates inside the Sun.
C) The equatorial regions of the Sun rotate more rapidly than the polar regions.
D) The rotation of the Sun's southern and northern hemispheres goes in opposite directions.
A) Heating in the chromosphere and corona makes them hotter than the photosphere.
B) A magnetic dynamo operates inside the Sun.
C) The equatorial regions of the Sun rotate more rapidly than the polar regions.
D) The rotation of the Sun's southern and northern hemispheres goes in opposite directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

The diagram shows a plot of the temperature of the Sun as a function of distance above the bottom of the photosphere. What is the temperature of the Sun at a height of 2,000 km?
A) 500 K
B) 900 K
C) 5,000 K
D) 9,000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Where are spicules most easily visible?
A) at the solar equator, in the lowest levels of the photosphere
B) at the centres of sunspots
C) in the corona near the north and south poles of the Sun during a total solar eclipse
D) in filtergrams of the solar chromosphere
A) at the solar equator, in the lowest levels of the photosphere
B) at the centres of sunspots
C) in the corona near the north and south poles of the Sun during a total solar eclipse
D) in filtergrams of the solar chromosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What has a negative charge and much less mass than a proton?
A) a neutron
B) an electron
C) a molecule
D) a nucleus
A) a neutron
B) an electron
C) a molecule
D) a nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What do astronomers believe heats up the corona and chromosphere of the Sun?
A) shock waves rising from below the photosphere
B) the solar wind
C) sunspots
D) turbulent motions of the Sun's magnetic field
A) shock waves rising from below the photosphere
B) the solar wind
C) sunspots
D) turbulent motions of the Sun's magnetic field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What occurs when a rapidly rotating conductor is stirred by convection to produce a magnetic field?
A) dynamo effect
B) Zeeman effect
C) Babcock effect
D) aurora
A) dynamo effect
B) Zeeman effect
C) Babcock effect
D) aurora

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



