Deck 23: Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/191
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Perfect Competition
1
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly horizontal.
D) perfectly vertical.
E) downward or upward sloping depending upon the type of product offered for sale.
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly horizontal.
D) perfectly vertical.
E) downward or upward sloping depending upon the type of product offered for sale.
A
2
The theory of perfect competition generally assumes that
A) sellers act independently of other sellers, but buyers do not act independently of other buyers.
B) buyers act independently of other buyers, but sellers do not act independently of other sellers.
C) buyers and sellers act independently of other buyers and sellers.
D) neither buyers nor sellers act independently of other buyers and sellers.
A) sellers act independently of other sellers, but buyers do not act independently of other buyers.
B) buyers act independently of other buyers, but sellers do not act independently of other sellers.
C) buyers and sellers act independently of other buyers and sellers.
D) neither buyers nor sellers act independently of other buyers and sellers.
C
3
Exhibit 23-1
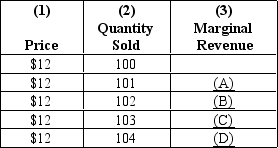
Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The dollar amounts that go in blanks (A)and (B)are,respectively,
A) $1 and $12.
B) $12 and $12.
C) $8.42 and $8.50.
D) $12 and $6.

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The dollar amounts that go in blanks (A)and (B)are,respectively,
A) $1 and $12.
B) $12 and $12.
C) $8.42 and $8.50.
D) $12 and $6.
B
4
The demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm
A) is downward sloping.
B) is upward sloping.
C) is perfectly horizontal.
D) is perfectly vertical.
E) may be downward or upward sloping, depending upon the type of product offered for sale.
A) is downward sloping.
B) is upward sloping.
C) is perfectly horizontal.
D) is perfectly vertical.
E) may be downward or upward sloping, depending upon the type of product offered for sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Does a real-world market have to meet all the assumptions of the theory of perfect competition before it is considered a perfectly competitive market?
A) No, probably no real-world market meets all the assumptions of the theory of perfect competition. All that is necessary is that a real-world market behave as if it satisfies all the assumptions.
B) Yes, if a real-world market does not meet the assumptions, then it cannot be considered a perfectly competitive market.
C) Yes, unless it is a new market such as the computer market. New markets are not held to the same assumptions as old, more established markets.
D) No, but it does have to meet the assumption of producing and selling a homogeneous product. It does not have to fully meet the other assumptions.
A) No, probably no real-world market meets all the assumptions of the theory of perfect competition. All that is necessary is that a real-world market behave as if it satisfies all the assumptions.
B) Yes, if a real-world market does not meet the assumptions, then it cannot be considered a perfectly competitive market.
C) Yes, unless it is a new market such as the computer market. New markets are not held to the same assumptions as old, more established markets.
D) No, but it does have to meet the assumption of producing and selling a homogeneous product. It does not have to fully meet the other assumptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of perfect competition?
A) There are many sellers and many buyers, none of which is large in relation to total sales or purchases.
B) Each firm produces and sells a differentiated product.
C) Buyers and sellers have all relevant information with respect to prices, product quality, and sources of supply.
D) There is easy entry and exit.
A) There are many sellers and many buyers, none of which is large in relation to total sales or purchases.
B) Each firm produces and sells a differentiated product.
C) Buyers and sellers have all relevant information with respect to prices, product quality, and sources of supply.
D) There is easy entry and exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Marginal revenue is
A) total revenue divided by the quantity of output.
B) total profit minus total costs.
C) the change in total output brought about by using an additional unit of a variable input.
D) the change in total revenue brought about by selling an additional unit of the good.
E) the change in total revenue minus the change in total costs.
A) total revenue divided by the quantity of output.
B) total profit minus total costs.
C) the change in total output brought about by using an additional unit of a variable input.
D) the change in total revenue brought about by selling an additional unit of the good.
E) the change in total revenue minus the change in total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The price at which a perfectly competitive firm sells its product is determined by
A) the individual seller based on his costs of production and his profit margin.
B) all sellers and buyers of the product.
C) the buyers of the product, because there are so many sellers that they cannot agree on a price.
D) the government, because there are so many buyers and sellers of the product that together they cannot agree on the price.
A) the individual seller based on his costs of production and his profit margin.
B) all sellers and buyers of the product.
C) the buyers of the product, because there are so many sellers that they cannot agree on a price.
D) the government, because there are so many buyers and sellers of the product that together they cannot agree on the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For a perfectly competitive firm,
A) the marginal revenue curve and the demand curve are the same.
B) the marginal revenue curve and the marginal cost curve are the same.
C) the supply curve and the marginal revenue curve are the same.
D) the demand curve and the marginal cost curve are the same.
E) none of the above
A) the marginal revenue curve and the demand curve are the same.
B) the marginal revenue curve and the marginal cost curve are the same.
C) the supply curve and the marginal revenue curve are the same.
D) the demand curve and the marginal cost curve are the same.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Real-world markets that approximate the four assumptions of the theory of perfect competition include
A) some agricultural markets.
B) the soft drink market.
C) the stock market.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c
A) some agricultural markets.
B) the soft drink market.
C) the stock market.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A "price taker" is a firm that
A) does not have the ability to control the price of the product it sells.
B) does have the ability, although limited, to control the price of the product it sells.
C) can raise the price of the product (above the market price) and still sell some units of its product.
D) sells a differentiated product.
E) none of the above
A) does not have the ability to control the price of the product it sells.
B) does have the ability, although limited, to control the price of the product it sells.
C) can raise the price of the product (above the market price) and still sell some units of its product.
D) sells a differentiated product.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Exhibit 23-1

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The dollar amounts that go in blanks (C)and (D)are,respectively,
A) $1 and $12.
B) $12 and $12.
C) $8.58 and $8.67.
D) $4 and $3.

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The dollar amounts that go in blanks (C)and (D)are,respectively,
A) $1 and $12.
B) $12 and $12.
C) $8.58 and $8.67.
D) $4 and $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the theory of perfect competition,
A) the market demand curve is horizontal.
B) the single firm's demand curve is horizontal.
C) the single firm's demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the market demand curve is downward sloping.
E) b and d
A) the market demand curve is horizontal.
B) the single firm's demand curve is horizontal.
C) the single firm's demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the market demand curve is downward sloping.
E) b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The perfectly competitive firm will seek to produce the output level for which
A) average variable cost is at a minimum.
B) average total cost is at a minimum.
C) average fixed cost is at a minimum.
D) marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
A) average variable cost is at a minimum.
B) average total cost is at a minimum.
C) average fixed cost is at a minimum.
D) marginal cost equals marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the theory of perfect competition,
A) sellers of the product are not influenced by other sellers and therefore have virtually complete control over the production and pricing of their product.
B) buyers of the product may have a preference as to whom they purchase from based on brand loyalty.
C) buyers and sellers of the product know everything that there is to know about the product.
D) it can be quite expensive for a firm to enter this type of market, but once the firm is established, it will be a profitable venture.
A) sellers of the product are not influenced by other sellers and therefore have virtually complete control over the production and pricing of their product.
B) buyers of the product may have a preference as to whom they purchase from based on brand loyalty.
C) buyers and sellers of the product know everything that there is to know about the product.
D) it can be quite expensive for a firm to enter this type of market, but once the firm is established, it will be a profitable venture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Exhibit 23-1

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The firm's demand curve represented by the information in this table is
A) downward-sloping.
B) upward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The firm's demand curve represented by the information in this table is
A) downward-sloping.
B) upward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is horizontal at the market price.
B) The theory of perfect competition is completely and accurately descriptive of most real-world firms.
C) If Firm X does not strictly meet all the assumptions of the theory of perfect competition, but behaves as if it does, then the theory of perfect competition is relevant to it.
D) In perfect competition, the market price is established at the intersection of the market demand and market supply curves.
A) The perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is horizontal at the market price.
B) The theory of perfect competition is completely and accurately descriptive of most real-world firms.
C) If Firm X does not strictly meet all the assumptions of the theory of perfect competition, but behaves as if it does, then the theory of perfect competition is relevant to it.
D) In perfect competition, the market price is established at the intersection of the market demand and market supply curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Perfectly competitive industries are
A) difficult to enter because there are already so many producers in the industry.
B) not particularly appealing or attractive to enter because there tend to be so many buyers that it is difficult to deal with them.
C) relatively easy to enter but not so easy to exit from.
D) a and b
E) none of the above
A) difficult to enter because there are already so many producers in the industry.
B) not particularly appealing or attractive to enter because there tend to be so many buyers that it is difficult to deal with them.
C) relatively easy to enter but not so easy to exit from.
D) a and b
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 23-1

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The data in this table are relevant to a perfectly competitive firm because
A) its total revenue is different at different levels of quantities sold.
B) its total revenue is the same at all levels of quantities sold.
C) it doesn't have to lower price to sell additional units of the product.
D) marginal revenue is greater than price.

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The data in this table are relevant to a perfectly competitive firm because
A) its total revenue is different at different levels of quantities sold.
B) its total revenue is the same at all levels of quantities sold.
C) it doesn't have to lower price to sell additional units of the product.
D) marginal revenue is greater than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Perfectly competitive firms are price takers for all of the following reasons except that
A) each firm is quite small relative to the total market supply.
B) buyers and sellers have all the necessary information about prices, etc.
C) the product is homogeneous.
D) barriers to exit force firms to sell at the market price.
A) each firm is quite small relative to the total market supply.
B) buyers and sellers have all the necessary information about prices, etc.
C) the product is homogeneous.
D) barriers to exit force firms to sell at the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the following data: equilibrium price = $8.50,quantity of output produced = 100 units,average total cost = $10,and average variable cost = $9.What will the firm do and why?
A) Shut down in the short run, because price is below average variable cost.
B) Shut down in the short run, because it will be taking a loss of $100.
C) Continue to produce in the short run, because price is greater than average variable cost.
D) Continue to produce in the short run, because firms are always stuck with having to produce in the short run.
E) none of the above
A) Shut down in the short run, because price is below average variable cost.
B) Shut down in the short run, because it will be taking a loss of $100.
C) Continue to produce in the short run, because price is greater than average variable cost.
D) Continue to produce in the short run, because firms are always stuck with having to produce in the short run.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the
A) upward-sloping portion of its average total cost curve.
B) horizontal portion of its marginal revenue curve.
C) portion of its average variable cost curve that lies above the average fixed cost curve.
D) upward-sloping portion of its marginal cost curve.
E) portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve.
A) upward-sloping portion of its average total cost curve.
B) horizontal portion of its marginal revenue curve.
C) portion of its average variable cost curve that lies above the average fixed cost curve.
D) upward-sloping portion of its marginal cost curve.
E) portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 23-2
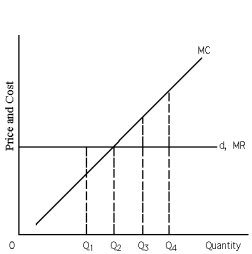
Refer to Exhibit 23-2.What quantity does the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing firm produce?
A) Q1, where "what is coming in" on the last unit is greater than "what is going out."
B) Q2, where the difference between "what is coming in" on the last unit and "what is going out" is zero.
C) Q3, where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Q4, which maximizes the excess of marginal cost over marginal revenue.

Refer to Exhibit 23-2.What quantity does the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing firm produce?
A) Q1, where "what is coming in" on the last unit is greater than "what is going out."
B) Q2, where the difference between "what is coming in" on the last unit and "what is going out" is zero.
C) Q3, where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Q4, which maximizes the excess of marginal cost over marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The perfectly competitive firm will produce in the
A) short run if price is below average variable cost.
B) long run if price is below average variable cost.
C) short run if price is below average total cost but above average variable cost.
D) long run if price is below average total cost but above average variable cost.
A) short run if price is below average variable cost.
B) long run if price is below average variable cost.
C) short run if price is below average total cost but above average variable cost.
D) long run if price is below average total cost but above average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 23-4
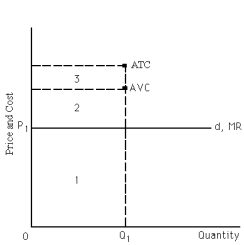
Refer to Exhibit 23-4.Equilibrium price is P?,and the firm produces Q?.At this level of output,average variable cost and average total cost are indicated by the dots.Given this situation,the firm is
A) receiving a profit equal to area 3.
B) taking a loss equal to areas 2 + 3.
C) earning total revenue equal to areas 1 + 2.
D) receiving a profit equal to area 2.
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.Equilibrium price is P?,and the firm produces Q?.At this level of output,average variable cost and average total cost are indicated by the dots.Given this situation,the firm is
A) receiving a profit equal to area 3.
B) taking a loss equal to areas 2 + 3.
C) earning total revenue equal to areas 1 + 2.
D) receiving a profit equal to area 2.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 23-3
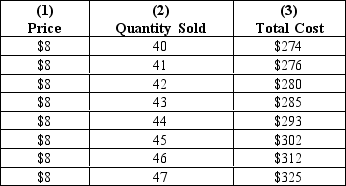
Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the increase in profit that would result from producing 43 units of the product rather than producing 40 units?
A) $60
B) $48
C) $28
D) $16
E) $13

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the increase in profit that would result from producing 43 units of the product rather than producing 40 units?
A) $60
B) $48
C) $28
D) $16
E) $13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 23-3

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What quantity of output should the profit-maximizing firm produce?
A) 41 units
B) 42 units
C) 44 units
D) 45 units
E) 46 units

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What quantity of output should the profit-maximizing firm produce?
A) 41 units
B) 42 units
C) 44 units
D) 45 units
E) 46 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 23-2

Refer to Exhibit 23-2.If the firm produces the quantity of output at which marginal revenue (MR)equals marginal cost (MC),is it guaranteed maximum profit or minimized loss?
A) Yes, when MR = MC, it follows that MR - MC = 0, and thus the firm maximizes profit and minimizes losses.
B) No, at the quantity of output at which MR = MC, it could be the case that average variable cost is greater than price and the firm would do better to shut down.
C) Yes, when the firm produces the quantity at which MR = MC, it has maximized both revenue and profit.
D) Yes, because if the MC curve is rising, the average total cost curve always lies below it and thus profit is earned.

Refer to Exhibit 23-2.If the firm produces the quantity of output at which marginal revenue (MR)equals marginal cost (MC),is it guaranteed maximum profit or minimized loss?
A) Yes, when MR = MC, it follows that MR - MC = 0, and thus the firm maximizes profit and minimizes losses.
B) No, at the quantity of output at which MR = MC, it could be the case that average variable cost is greater than price and the firm would do better to shut down.
C) Yes, when the firm produces the quantity at which MR = MC, it has maximized both revenue and profit.
D) Yes, because if the MC curve is rising, the average total cost curve always lies below it and thus profit is earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 23-3

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.Is it possible for this firm to produce "too much" in the short-run?
A) Any quantity above 42 units is too much.
B) Any quantity above 44 units is too much.
C) Any quantity above 40 units is too much.
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.Is it possible for this firm to produce "too much" in the short-run?
A) Any quantity above 42 units is too much.
B) Any quantity above 44 units is too much.
C) Any quantity above 40 units is too much.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In order for a firm to continue producing,price must exceed __________ and total revenue must exceed __________.
A) marginal cost, total cost
B) ATC; total cost
C) AFC; total fixed cost
D) AVC; total variable costs
E) price; total cost
A) marginal cost, total cost
B) ATC; total cost
C) AFC; total fixed cost
D) AVC; total variable costs
E) price; total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the following data: equilibrium price = $9,quantity of output produced = 1,000 units,average total cost = $7,and average variable cost $5.Given this,total revenue is __________,total cost is __________,and total fixed cost is __________.
A) $6,000; $8,000; $1,000
B) $9,000; $7,000; $5,000
C) $10,000; $8,000; $3,000
D) $9,000; $7,000; $2,000
E) none of the above
A) $6,000; $8,000; $1,000
B) $9,000; $7,000; $5,000
C) $10,000; $8,000; $3,000
D) $9,000; $7,000; $2,000
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the following data: equilibrium price = $10,quantity of output produced = 100 units,average total cost = $13,and average variable cost = $7.What will the firm do and why?
A) Shut down in the short run, because it is taking a loss of $200.
B) Continue to produce in the short run, because price is greater than average variable cost.
C) Shut down in the short run, because average variable cost is less than average total cost.
D) Continue to produce in the short run, because firms are always stuck with having to produce in the short run.
A) Shut down in the short run, because it is taking a loss of $200.
B) Continue to produce in the short run, because price is greater than average variable cost.
C) Shut down in the short run, because average variable cost is less than average total cost.
D) Continue to produce in the short run, because firms are always stuck with having to produce in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If MR > MC,then
A) profits will be at their maximum.
B) the firm is producing too much of the good to be maximizing profits.
C) the firm can increase its profits or minimize its losses by increasing output.
D) the firm is necessarily incurring losses.
A) profits will be at their maximum.
B) the firm is producing too much of the good to be maximizing profits.
C) the firm can increase its profits or minimize its losses by increasing output.
D) the firm is necessarily incurring losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the short-run,if P < ATC,a perfectly competitive firm should
A) increase production to the output level at which P = ATC.
B) continue producing at a loss.
C) shut down.
D) continue producing at a profit.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) increase production to the output level at which P = ATC.
B) continue producing at a loss.
C) shut down.
D) continue producing at a profit.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Exhibit 23-1

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The marginal revenue curve represented by the information in this table is
A) downward-sloping.
B) upward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Refer to Exhibit 23-1.The marginal revenue curve represented by the information in this table is
A) downward-sloping.
B) upward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exhibit 23-3

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the maximum profit?
A) $65
B) $59
C) $20
D) $376

Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the maximum profit?
A) $65
B) $59
C) $20
D) $376

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a perfectly competitive firm,profit maximization or loss minimization occurs at the output at which
A) MR = MC.
B) MR = AVC.
C) P = ATC.
D) MR = ATC.
A) MR = MC.
B) MR = AVC.
C) P = ATC.
D) MR = ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If,for the last unit of a good produced by a perfectly competitive firm,MR > MC,then in producing that unit the firm
A) added more to total costs than it added to total revenue.
B) added more to total revenue than it added to total costs.
C) added an equal amount to both total revenue and total costs.
D) maximized profits or minimized losses.
A) added more to total costs than it added to total revenue.
B) added more to total revenue than it added to total costs.
C) added an equal amount to both total revenue and total costs.
D) maximized profits or minimized losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A perfectly competitive firm should increase its level of production as long as
A) total revenue is less than total cost.
B) the total revenue curve is rising.
C) marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
D) the marginal revenue curve is rising.
A) total revenue is less than total cost.
B) the total revenue curve is rising.
C) marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
D) the marginal revenue curve is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Exhibit 23-2

Refer to Exhibit 23-2.For the firm that faces the demand curve in the exhibit,
A) marginal revenue is constant.
B) price equals marginal revenue.
C) if the firm maximizes profits, it produces the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

Refer to Exhibit 23-2.For the firm that faces the demand curve in the exhibit,
A) marginal revenue is constant.
B) price equals marginal revenue.
C) if the firm maximizes profits, it produces the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Demand increases in an increasing-cost industry that is initially in long-run competitive equilibrium.After full adjustment,price will be
A) equal to its original level.
B) below its original level.
C) above its original level.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) equal to its original level.
B) below its original level.
C) above its original level.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If an industry is in long-run competitive equilibrium and experiences a decrease in demand,then as a result the equilibrium price will __________,which will cause the representative firm's __________ curve to shift downward and some firms will __________ the industry.
A) rise; marginal cost; enter
B) fall; marginal cost; enter
C) rise; marginal revenue; enter
D) fall; demand; exit
E) fall; marginal cost; exit
A) rise; marginal cost; enter
B) fall; marginal cost; enter
C) rise; marginal revenue; enter
D) fall; demand; exit
E) fall; marginal cost; exit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If firms are earning zero economic profits,they must be producing at an output level at which
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) price equals average total cost.
C) price equals average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) none of the above
A) price equals marginal cost.
B) price equals average total cost.
C) price equals average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the perfectly competitive firm is producing an output level at which price equals marginal cost,it is
A) earning profits.
B) taking losses.
C) earning normal profit.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) earning profits.
B) taking losses.
C) earning normal profit.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 23-4

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.The firm sells its product at P? and produces Q?.Given this situation,
A) total variable cost is equal to areas 1 + 2.
B) total revenue is equal to area 1.
C) total cost is equal to areas 2 + 3.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.The firm sells its product at P? and produces Q?.Given this situation,
A) total variable cost is equal to areas 1 + 2.
B) total revenue is equal to area 1.
C) total cost is equal to areas 2 + 3.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When the perfectly competitive firm produces the quantity of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost,it naturally
A) produces the quantity of output at which marginal cost equals price, since for the perfectly competitive firm price equals marginal revenue.
B) produces the quantity of output at which short-run average total cost equals price, since for the perfectly competitive firm short-run average total cost equals marginal revenue.
C) earns a profit, since equating marginal revenue and marginal cost guarantees profit.
D) takes a loss.
A) produces the quantity of output at which marginal cost equals price, since for the perfectly competitive firm price equals marginal revenue.
B) produces the quantity of output at which short-run average total cost equals price, since for the perfectly competitive firm short-run average total cost equals marginal revenue.
C) earns a profit, since equating marginal revenue and marginal cost guarantees profit.
D) takes a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why must profits be zero in long-run competitive equilibrium?
A) If profits are not zero, firms will enter or exit the industry.
B) If profits are not zero, firms will produce higher-quality goods.
C) If profits are not zero, marginal revenue will rise.
D) If profits are not zero, marginal cost will rise.
A) If profits are not zero, firms will enter or exit the industry.
B) If profits are not zero, firms will produce higher-quality goods.
C) If profits are not zero, marginal revenue will rise.
D) If profits are not zero, marginal cost will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Assume the following for a certain industry: (l)there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry; (2)for some firms in the industry,short-run average total cost is greater than long-run average total cost at the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; (3)all firms in the industry are currently producing the quantity of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.Is the industry in long-run competitive equilibrium?
A) Yes.
B) No, because of number 2.
C) No, because of numbers 2 and 3.
D) No, because of numbers 1 and 2.
E) No, because of numbers 1, 2, and 3.
A) Yes.
B) No, because of number 2.
C) No, because of numbers 2 and 3.
D) No, because of numbers 1 and 2.
E) No, because of numbers 1, 2, and 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Firm X is producing the quantity of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.It is
A) receiving a positive economic profit.
B) taking a loss.
C) earning a normal profit.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) receiving a positive economic profit.
B) taking a loss.
C) earning a normal profit.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following conditions does not characterize long-run competitive equilibrium?
A) Economic profit is zero.
B) Price is greater than marginal cost.
C) No firm has an incentive to change its plant size.
D) No firm has an incentive to produce more or less output.
A) Economic profit is zero.
B) Price is greater than marginal cost.
C) No firm has an incentive to change its plant size.
D) No firm has an incentive to produce more or less output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The short-run industry supply curve is the
A) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
B) vertical summation of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
C) average of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
D) same as that of the typical firm in the industry.
A) horizontal summation of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
B) vertical summation of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
C) average of the short-run supply curves for all firms in the industry.
D) same as that of the typical firm in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As firms exit an industry,the industry supply curve shifts __________ and the equilibrium price __________ until long-run competitive equilibrium is established and the surviving firms are earning __________ economic profits.
A) leftward; rises; zero
B) leftward; falls; positive
C) leftward; rises; positive
D) rightward; falls; negative
E) rightward; rises; positive
A) leftward; rises; zero
B) leftward; falls; positive
C) leftward; rises; positive
D) rightward; falls; negative
E) rightward; rises; positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 23-4

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.Where can you find the lowest price that will motivate the firm to produce Q? in the short run?
A) at the horizontal line running to "ATC"
B) at the horizontal line running to "AVC"
C) P1
D) $0

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.Where can you find the lowest price that will motivate the firm to produce Q? in the short run?
A) at the horizontal line running to "ATC"
B) at the horizontal line running to "AVC"
C) P1
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Resource allocative efficiency occurs when a firm
A) minimizes costs of production yet charges the highest possible price.
B) produces the quantity of output at which price exceeds average total cost by the greatest amount.
C) produces the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.
D) produces the quantity of output at which price equals average total cost.
E) produces the quantity of output at which price equals average variable cost.
A) minimizes costs of production yet charges the highest possible price.
B) produces the quantity of output at which price exceeds average total cost by the greatest amount.
C) produces the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.
D) produces the quantity of output at which price equals average total cost.
E) produces the quantity of output at which price equals average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 23-4

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.The firm sells its product at P? and produces Q?.Given this situation,
A) total variable cost is equal to areas 2 + 3.
B) total revenue is equal to areas 1 + 2.
C) total cost is equal to areas 1 + 2 + 3.
D) profit equals area 1.
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 23-4.The firm sells its product at P? and produces Q?.Given this situation,
A) total variable cost is equal to areas 2 + 3.
B) total revenue is equal to areas 1 + 2.
C) total cost is equal to areas 1 + 2 + 3.
D) profit equals area 1.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Is it possible for a perfectly competitive firm to be maximizing profits,but not achieving resource allocative efficiency?
A) Definitely yes, because it is impossible to achieve both at the same time.
B) Yes, it is possible, but it is not possible to minimize losses without also achieving resource allocative efficiency.
C) No, it is not possible, because the output at which MR = MC is also the output at which P = MC.
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.
A) Definitely yes, because it is impossible to achieve both at the same time.
B) Yes, it is possible, but it is not possible to minimize losses without also achieving resource allocative efficiency.
C) No, it is not possible, because the output at which MR = MC is also the output at which P = MC.
D) There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Assume a constant-cost industry that is initially in long-run competitive equilibrium.An increase in demand will cause a(n)__________ in prices and profits,and as a result,firms will __________ the industry,causing the market supply curve to shift __________,which,in turn,will eventually cause the equilibrium price to be __________ before.
A) decrease; exit; leftward; lower than
B) increase; enter; rightward; higher than
C) decrease; exit; rightward; higher than
D) increase; enter; rightward; the same as
E) increase; exit; leftward; lower than
A) decrease; exit; leftward; lower than
B) increase; enter; rightward; higher than
C) decrease; exit; rightward; higher than
D) increase; enter; rightward; the same as
E) increase; exit; leftward; lower than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Resources are allocated efficiently when
A) the exchange value of the resources to demanders equals the opportunity cost of the resources.
B) the marginal benefit to demanders of the resources in the goods they purchase is equal to the marginal cost to suppliers of the resources they use in producing the goods.
C) firms produce the quantity of output at which price is equal to marginal cost.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) the exchange value of the resources to demanders equals the opportunity cost of the resources.
B) the marginal benefit to demanders of the resources in the goods they purchase is equal to the marginal cost to suppliers of the resources they use in producing the goods.
C) firms produce the quantity of output at which price is equal to marginal cost.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A constant-cost industry has a long-run (industry)supply curve that is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) U-shaped.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) U-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Assume a decreasing-cost industry that is initially in long-run competitive equilibrium.A decrease in demand will cause a(n)__________ in prices and profits,and as a result,firms will __________ the industry,causing the market supply curve to shift __________,which,in turn,will eventually cause the equilibrium price to be __________ before.
A) a decrease; exit; rightward; lower than
B) an increase; enter; rightward; higher than
C) a decrease; exit; leftward; higher than
D) an increase; enter; rightward; the same as
E) an increase; exit; leftward; lower than
A) a decrease; exit; rightward; lower than
B) an increase; enter; rightward; higher than
C) a decrease; exit; leftward; higher than
D) an increase; enter; rightward; the same as
E) an increase; exit; leftward; lower than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the long run,a firm earns zero economic profit,given the condition that
A) P = MR.
B) P = AVC.
C) P = ATC.
D) (P - MC) = 0.
E) none of the above
A) P = MR.
B) P = AVC.
C) P = ATC.
D) (P - MC) = 0.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Marginal revenue is defined as
A) the difference between costs and revenues.
B) the change in total revenue caused by selling one additional unit of output.
C) price times quantity.
D) total revenue divided by the level of output.
E) total revenue minus the level of output.
A) the difference between costs and revenues.
B) the change in total revenue caused by selling one additional unit of output.
C) price times quantity.
D) total revenue divided by the level of output.
E) total revenue minus the level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is the best example of a homogeneous good?
A) new cars
B) ice cream
C) soft drinks
D) wheat
A) new cars
B) ice cream
C) soft drinks
D) wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In perfect competition,the firm's marginal revenue curve is
A) perfectly elastic.
B) the same as the firm's demand curve.
C) the same as the firm's total revenue curve.
D) a and b
E) a and c
A) perfectly elastic.
B) the same as the firm's demand curve.
C) the same as the firm's total revenue curve.
D) a and b
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The price charged by a perfectly competitive firm is determined by
A) the firm's demand curve alone.
B) the firm's cost curves alone.
C) market demand and market supply, together.
D) market demand alone.
E) market supply alone.
A) the firm's demand curve alone.
B) the firm's cost curves alone.
C) market demand and market supply, together.
D) market demand alone.
E) market supply alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
At the quantity where total revenue equals total cost,
A) profit is zero.
B) cost is minimized.
C) cost is maximized.
D) quantity is minimized.
E) profit is maximized.
A) profit is zero.
B) cost is minimized.
C) cost is maximized.
D) quantity is minimized.
E) profit is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the theory of perfect competition,the assumptions of many buyers and sellers,the production of a homogeneous product,and the possession of all relevant information by buyers and sellers imply that the perfectly competitive firm
A) sets the price it wishes.
B) has a demand curve that is downward sloping.
C) has a demand curve that is perfectly elastic.
D) a and b
E) a and c
A) sets the price it wishes.
B) has a demand curve that is downward sloping.
C) has a demand curve that is perfectly elastic.
D) a and b
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the theory of perfect competition,the assumption of easy entry into and exit from the market implies
A) positive economic profits in the long run.
B) losses in the long-run equilibrium.
C) zero economic profits in the long run.
D) zero economic profits in both the short run and the long run.
E) positive economic profits in both the short run and the long run.
A) positive economic profits in the long run.
B) losses in the long-run equilibrium.
C) zero economic profits in the long run.
D) zero economic profits in both the short run and the long run.
E) positive economic profits in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a firm is a price taker,its demand curve is
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In a perfectly competitive industry,there is a motive for __________ to advertise in order to induce a rightward shift of the demand curve.
A) the typical firm
B) the industry as a whole
C) both the typical firm and the industry as a whole
D) neither the typical firm nor the industry as a whole
A) the typical firm
B) the industry as a whole
C) both the typical firm and the industry as a whole
D) neither the typical firm nor the industry as a whole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The perfectly competitive firm will shut down in the short run if price is
A) less than average variable cost.
B) greater than average variable cost but less than average total cost.
C) greater than average total cost.
D) equal to average total cost.
E) a and b
A) less than average variable cost.
B) greater than average variable cost but less than average total cost.
C) greater than average total cost.
D) equal to average total cost.
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A perfectly competitive firm faces a __________ demand curve.
A) nonlinear
B) downward-sloping
C) perfectly elastic
D) perfectly inelastic
E) unit-elastic
A) nonlinear
B) downward-sloping
C) perfectly elastic
D) perfectly inelastic
E) unit-elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If an industry advertises,then it
A) is definitely not a perfectly competitive industry.
B) must be a perfectly competitive industry.
C) may or may not be a perfectly competitive industry.
D) is not using its resources wisely.
E) will surely be able to increase its sales.
A) is definitely not a perfectly competitive industry.
B) must be a perfectly competitive industry.
C) may or may not be a perfectly competitive industry.
D) is not using its resources wisely.
E) will surely be able to increase its sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose one firm in a perfectly competitive industry experiences an increase in its costs of production.Which of the following best describes the most likely long run adjustment to this situation?
A) Eventually, all firms in the industry will also experience this same increase in costs.
B) Eventually, the price of the product will increase, and consumers will pay for the increase in costs.
C) The firm in question may suffer losses and exit the industry.
D) none of the above
A) Eventually, all firms in the industry will also experience this same increase in costs.
B) Eventually, the price of the product will increase, and consumers will pay for the increase in costs.
C) The firm in question may suffer losses and exit the industry.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the theory of perfect competition,the market demand curve is __________ and the firm's demand curve is __________.
A) perfectly elastic; perfectly elastic
B) downward sloping; downward sloping
C) perfectly elastic; downward sloping
D) downward sloping; perfectly elastic
E) perfectly inelastic; downward sloping
A) perfectly elastic; perfectly elastic
B) downward sloping; downward sloping
C) perfectly elastic; downward sloping
D) downward sloping; perfectly elastic
E) perfectly inelastic; downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not a characteristic of perfect competition?
A) buyers and sellers having no influence on price
B) no barriers to entry and exit
C) a heterogeneous product
D) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
E) none of the above
A) buyers and sellers having no influence on price
B) no barriers to entry and exit
C) a heterogeneous product
D) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
A) many sellers and few buyers
B) many buyers and few sellers
C) a heterogeneous product
D) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
E) high barriers to entry and exit
A) many sellers and few buyers
B) many buyers and few sellers
C) a heterogeneous product
D) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
E) high barriers to entry and exit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In short-run equilibrium,the perfectly competitive firm may be making __________ economic profits.
A) positive
B) zero
C) negative
D) a or b
E) any of the above
A) positive
B) zero
C) negative
D) a or b
E) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In long-run equilibrium,the perfectly competitive firm earns __________ economic profits.
A) positive
B) zero
C) negative
D) any of the above
A) positive
B) zero
C) negative
D) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the assumptions in the theory of perfect competition assures us that economic profit will be zero in the long run?
A) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
B) firms producing homogeneous goods
C) too few buyers
D) easy entry and exit
E) smallness of firms with respect to the market
A) buyers and sellers having all relevant information
B) firms producing homogeneous goods
C) too few buyers
D) easy entry and exit
E) smallness of firms with respect to the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



