Deck 8: Competitive Firms and Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Competitive Firms and Markets
1
If a firm happened to be the only seller of a particular product, it might behave as a price taker as long as
A)buyers have full information about the firm's price.
B)the transaction costs of doing business with this firm are low.
C)there are many buyers.
D)there is free entry and exit.
A)buyers have full information about the firm's price.
B)the transaction costs of doing business with this firm are low.
C)there are many buyers.
D)there is free entry and exit.
there is free entry and exit.
2
If all conditions for a perfectly competitive market are met,
A)firms face sunk cost when entering the market.
B)firms' demand curves are horizontal.
C)the market demand curve is horizontal.
D)the firms' demand curves are downward-sloping.
A)firms face sunk cost when entering the market.
B)firms' demand curves are horizontal.
C)the market demand curve is horizontal.
D)the firms' demand curves are downward-sloping.
firms' demand curves are horizontal.
3
The "Got Milk?" advertising campaign is a good example of
A)advertising in a competitive market.
B)how advertising in a competitive market does not pay off for a single firm.
C)interest groups financed by the industry advertise for the whole industry.
D)All of the above.
A)advertising in a competitive market.
B)how advertising in a competitive market does not pay off for a single firm.
C)interest groups financed by the industry advertise for the whole industry.
D)All of the above.
All of the above.
4
Economists define a market to be competitive when the firms
A)spend large amounts of money on advertising to lure customers away from the competition.
B)watch each other's behavior closely.
C)are price takers.
D)All of the above.
A)spend large amounts of money on advertising to lure customers away from the competition.
B)watch each other's behavior closely.
C)are price takers.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Many used car owners and used car dealers describe their different cars for sale in the local newspapers and list their asking price. Many people shopping for a used car consider the different choices listed in the paper. The market for used cars could be described as
A)relatively competitive.
B)perfectly competitive.
C)non-competitive.
D)having high transaction costs.
A)relatively competitive.
B)perfectly competitive.
C)non-competitive.
D)having high transaction costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Firms that exhibit price-taking behavior
A)wait for other firms to set price, take it as given, and charge a higher price.
B)have outputs that are too small to influence market price and thus take it as given.
C)take pricing behavior in their own hands.
D)are independently capable of setting price.
A)wait for other firms to set price, take it as given, and charge a higher price.
B)have outputs that are too small to influence market price and thus take it as given.
C)take pricing behavior in their own hands.
D)are independently capable of setting price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A special license is required to operate a taxi in many cities. The number of licenses is restricted. More drivers want licenses than are issued. This describes a non-perfectly competitive market because
A)taxi services are very different.
B)firms cannot freely enter and exit the market.
C)transaction costs are high.
D)the government generates revenue from the licenses.
A)taxi services are very different.
B)firms cannot freely enter and exit the market.
C)transaction costs are high.
D)the government generates revenue from the licenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The perfectly competitive model makes a lot of fairly unrealistic assumptions. Why do economics textbooks still talk a lot about this model?
A)Many markets are close to being perfectly competitive.
B)It is an important model to use as a benchmark to compare other markets structures to.
C)Perfectly competitive markets maximize societal welfare.
D)All of the above.
A)Many markets are close to being perfectly competitive.
B)It is an important model to use as a benchmark to compare other markets structures to.
C)Perfectly competitive markets maximize societal welfare.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a firm operates in a perfectly competitive market, then
A)all firms will advertise.
B)no firms will advertise.
C)the market leader will advertise.
D)new firms will advertise.
A)all firms will advertise.
B)no firms will advertise.
C)the market leader will advertise.
D)new firms will advertise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a competitive market, if buyers did not know all the prices charged by the many firms,
A)all firms still face horizontal demand curves.
B)firms sell a differentiated product.
C)demand curves can be downward sloping for some or all firms.
D)the number of firms will most likely decrease.
A)all firms still face horizontal demand curves.
B)firms sell a differentiated product.
C)demand curves can be downward sloping for some or all firms.
D)the number of firms will most likely decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A market's structure is described by
A)the number of firms in the market.
B)the ease with which firms can enter and exit the market.
C)the ability of firms to differentiate their product.
D)All of the above.
A)the number of firms in the market.
B)the ease with which firms can enter and exit the market.
C)the ability of firms to differentiate their product.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Many car owners and car dealers describe their different cars for sale in the local newspapers and list their asking price. Many people shopping for a used car consider the different choices listed in the paper. The absence of which condition prohibits this market from being described as perfectly competitive?
A)Buyers and sellers know the prices.
B)Firms freely enter and exit.
C)Transaction costs are low.
D)Consumers believe all firms sell identical products.
A)Buyers and sellers know the prices.
B)Firms freely enter and exit.
C)Transaction costs are low.
D)Consumers believe all firms sell identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the absence of any government regulation on price, if a firm has no power to set price on its own, one can safely conclude
A)the demand curve for the firm's product is horizontal.
B)there aren't many firms in the industry.
C)the market is in long-run equilibrium.
D)the firms in this industry are not profitable.
A)the demand curve for the firm's product is horizontal.
B)there aren't many firms in the industry.
C)the market is in long-run equilibrium.
D)the firms in this industry are not profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following are NOT characteristics of a competitive market?
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are zero transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers and sellers have complete information.
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are zero transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers and sellers have complete information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If consumers view the output of any firm in a market to be identical to the output of any other firm in the market, the demand curve for the output of any given firm
A)will be identical to the market demand curve.
B)will be horizontal.
C)will be vertical.
D)cannot be determined from the information given.
A)will be identical to the market demand curve.
B)will be horizontal.
C)will be vertical.
D)cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand curve that an individual competitive firm faces is known as its
A)excess demand curve.
B)market demand curve.
C)residual demand curve.
D)leftover demand curve.
A)excess demand curve.
B)market demand curve.
C)residual demand curve.
D)leftover demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A horizontal demand curve for a firm implies that
A)the firm is a monopoly.
B)the market the firm is operating in is not competitive.
C)the firm is selling in a competitive market.
D)the products of that firm are very different from other firms' products.
A)the firm is a monopoly.
B)the market the firm is operating in is not competitive.
C)the firm is selling in a competitive market.
D)the products of that firm are very different from other firms' products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Even if two products have different characteristics, such as color, the products are only considered heterogeneous if consumers
A)consider the two products as perfect complements.
B)consider the two products as perfect substitutes.
C)consider the two products as imperfect substitutes.
D)consider the two products as imperfect complements.
A)consider the two products as perfect complements.
B)consider the two products as perfect substitutes.
C)consider the two products as imperfect substitutes.
D)consider the two products as imperfect complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a perfectly competitive market,
A)firms can freely enter and exit.
B)firms sell a differentiated product.
C)transaction costs are high.
D)All of the above.
A)firms can freely enter and exit.
B)firms sell a differentiated product.
C)transaction costs are high.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a firm operates in a perfectly competitive market, then it will most likely
A)advertise its product on television.
B)take the price of its product as determined by the market.
C)have a difficult time obtaining information about the market price.
D)have an easy time keeping other firms out of the market.
A)advertise its product on television.
B)take the price of its product as determined by the market.
C)have a difficult time obtaining information about the market price.
D)have an easy time keeping other firms out of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a competitive market where the elasticity of the market demand curve is -2, the elasticity of the supply curve is 1, and an individual firm faces a residual demand curve with an elasticity of -98. What happens to the individual firm's residual demand curve when the number of firms serving this market declines?
A)It becomes less elastic.
B)It becomes more elastic.
C)It does not change.
D)It cannot be determined.
A)It becomes less elastic.
B)It becomes more elastic.
C)It does not change.
D)It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A small business owner earns $50,000 in revenue annually. The explicit annual costs equal $30,000. The owner could work for someone else and earn $25,000 annually. The owner's business profit is ________ and the economic profit is ________.
A)$20,000; $5,000
B)$20,000; -$5,000
C)$25,000; -$5,000
D)$45,000; -$5,000
A)$20,000; $5,000
B)$20,000; -$5,000
C)$25,000; -$5,000
D)$45,000; -$5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Many auction sites, such as eBay, provide a reputation score by which previous customers can rate a seller. Which of the following characteristics of a competitive market is this policy trying to emulate?
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are very low transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers have more complete information.
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are very low transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers have more complete information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If transaction costs are high, then it is more likely a firm's demand curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How can the market demand for a product be inelastic but the demand for a particular firm is elastic?
A)There is no advertising.
B)There is a sufficiently large number of sellers.
C)There is only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers do not have complete information.
A)There is no advertising.
B)There is a sufficiently large number of sellers.
C)There is only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers do not have complete information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a competitive market where the elasticity of the market demand curve is -0.5, there are 100 identical firms, and the elasticity of the supply curve to the other 99 firms is 4. What is the elasticity of the demand curve of the 100th firm?
A)-446
B)-489
C)-50
D)-0.5
A)-446
B)-489
C)-50
D)-0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a competitive market where the elasticity of the market demand curve is -2, the elasticity of the supply curve is 1, and an individual firm faces a residual demand curve with an elasticity of -98. What is the number of firms in this market?
A)10
B)20
C)33
D)Cannot be determined.
A)10
B)20
C)33
D)Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
All else equal, a smaller elasticity of the supply curve to the other firms leads to a ________ individual firm's residual elasticity of demand.
A)less elastic
B)unit elastic
C)more elastic
D)zero
A)less elastic
B)unit elastic
C)more elastic
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following characteristics of a competitive market make auction sites such as eBay so popular?
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are very low transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers and sellers have complete information.
A)There is freedom of entry and exit.
B)There are very low transaction costs.
C)There are only one or two sellers.
D)Buyers and sellers have complete information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If marginal revenue equals marginal cost, the firm is maximizing profits as long as
A)the resulting profits are positive.
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue for greater levels of output.
C)the average cost curve lies above the demand curve.
D)All of the above are required.
A)the resulting profits are positive.
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue for greater levels of output.
C)the average cost curve lies above the demand curve.
D)All of the above are required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The model of perfect competition is valuable for
A)prediction.
B)comparison to other markets.
C)Either A or B
D)None of the above.
A)prediction.
B)comparison to other markets.
C)Either A or B
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a competitive market where the elasticity of the market demand curve is -1.5, the number of firms is 20, and an individual firm faces a residual demand curve with an elasticity of -68. What is the elasticity of the supply curve?
A)0.5
B)1.2
C)2
D)Cannot be determined.
A)0.5
B)1.2
C)2
D)Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a competitive market, one would expect to see
A)no advertising.
B)false advertising.
C)advertising only in the Sunday papers.
D)minimal advertising.
A)no advertising.
B)false advertising.
C)advertising only in the Sunday papers.
D)minimal advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a firm makes zero economic profit, then the firm
A)has total revenues greater than its economic costs.
B)must shut down.
C)can be earning positive business profit.
D)must have no fixed costs.
A)has total revenues greater than its economic costs.
B)must shut down.
C)can be earning positive business profit.
D)must have no fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Explain why individual firms in competitive markets face more elastic demand curves than the market as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A small business owner earns $60,000 in revenue annually. The explicit annual costs equal $10,000. The owner could work for someone else and earn $25,000 annually. The owner's accounting profit is ________ and owner's economic profit is ________.
A)$20,000; $5,000
B)$50,000; $25,000
C)$25,000; -$5,000
D)$45,000; -$5,000
A)$20,000; $5,000
B)$50,000; $25,000
C)$25,000; -$5,000
D)$45,000; -$5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a firm makes zero economic profit, then the firm
A)has no incentive to stay in the industry.
B)is better off exiting the industry.
C)is indifferent between staying and exiting the industry.
D)will shut down.
A)has no incentive to stay in the industry.
B)is better off exiting the industry.
C)is indifferent between staying and exiting the industry.
D)will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a competitive firm's marginal profit is positive at an output of 1000 units,
A)at 1000 units, MR = MC.
B)it should produce more than 1000 units.
C)it should produce less than 1000 units.
D)at 1000 units, MR < MC.
A)at 1000 units, MR = MC.
B)it should produce more than 1000 units.
C)it should produce less than 1000 units.
D)at 1000 units, MR < MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A market is perfectly competitive even if firms have the ability to set their own price as long as the price difference reflects differences in the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a firm is operating at an output level where losses are minimized, the firm
A)has no incentive to stay in the industry.
B)is better off exiting the industry.
C)is maximizing profits.
D)will shut down.
A)has no incentive to stay in the industry.
B)is better off exiting the industry.
C)is maximizing profits.
D)will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a profit-maximizing firm finds that, at its current level of production, MR > MC, it will
A)earn greater profits than if MR = MC.
B)increase output.
C)decrease output.
D)shut down.
A)earn greater profits than if MR = MC.
B)increase output.
C)decrease output.
D)shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a profit-maximizing firm finds that, at its current level of production, MR < MC, it will
A)decrease output.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)operate at a loss.
A)decrease output.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)operate at a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a firm doesn't make an economic profit, it will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose a competitive firm's total revenue is $1,000,000 where MR = MC, its explicit variable costs are $900,000, its fixed costs are $90,000 of which $60,000 are sunk in the short run. If its implicit opportunity costs are $50,000, the firm should
A)produce because its economic profit is positive.
B)produce because its economic profit is zero.
C)produce even though its economic profit is negative.
D)shut down.
A)produce because its economic profit is positive.
B)produce because its economic profit is zero.
C)produce even though its economic profit is negative.
D)shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose a firm has the following total cost function: TC = 50 + 2q2. What is the minimum price necessary for the firm to earn profit?
A)p = $20
B)p = $30
C)p = $35
D)p = $40
A)p = $20
B)p = $30
C)p = $35
D)p = $40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
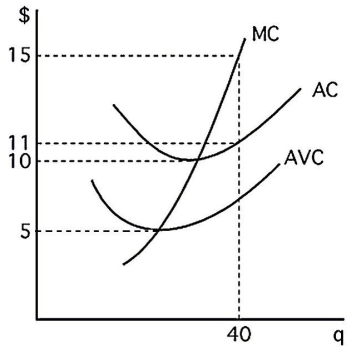
The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. The firm will incur economic losses if the price is less than
A)$0.
B)$5.
C)$10.
D)$11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose there are 20 competitive firms in a market. The supply curve of each firm is q = 2p. The market demand is Q = 200 - 2p. What is the residual demand curve facing a typical firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the market price is $15 per unit, the firm will earn profits of
A)$0.
B)$4.
C)$40.
D)$160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a firm goes out of business because of negative economic profits, its books
A)might indicate a positive accounting profit.
B)might indicate that opportunity costs were zero.
C)might indicate that taxes are too high.
D)might suggest a mistaken value of explicit costs.
A)might indicate a positive accounting profit.
B)might indicate that opportunity costs were zero.
C)might indicate that taxes are too high.
D)might suggest a mistaken value of explicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the firm is to earn economic profit, price must exceed
A)$0.
B)$5.
C)$10.
D)$11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a firm traded on the New York Stock Exchange posts an accounting profit of $10 million, then the firm is making a positive economic profit
A)only if the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)approves the accounting report.
B)only if the firm's opportunity cost is less than $10 million.
C)only if the firm's opportunity benefit is more than $10 million.
D)only if the firm's management receives stock compensation.
A)only if the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)approves the accounting report.
B)only if the firm's opportunity cost is less than $10 million.
C)only if the firm's opportunity benefit is more than $10 million.
D)only if the firm's management receives stock compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a competitive firm finds that it maximizes short-run profits by shutting down, which of the following must be TRUE?
A)p < AVC for all levels of output.
B)p < AVC only for the level of output at which p = MC.
C)p < AVC only if the firm has no fixed costs.
D)The firm will earn zero profit.
A)p < AVC for all levels of output.
B)p < AVC only for the level of output at which p = MC.
C)p < AVC only if the firm has no fixed costs.
D)The firm will earn zero profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain why shutting down and going out-of-business are different concepts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Even though fixed costs do not affect the output decision, an increase in fixed costs results in a wider range of prices for which the firm operates at a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose a firm has the following total cost function: TC = 100 + 4q2. What is the minimum price necessary for the firm to earn profit? Below what price will the firm shut down in the short run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a firm sets marginal revenue equal to marginal cost, it will make an economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a competitive firm maximizes short-run profits by producing some quantity of output, which of the following must be TRUE at that level of output?
A)p = MC
B)MR = MC
C)p ≥ AVC
D)All of the above.
A)p = MC
B)MR = MC
C)p ≥ AVC
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a competitive firm maximizes short-run profits by producing some quantity of output, which of the following must be TRUE at that level of output?
A)p > MC
B)MR > MC
C)p ≥ AVC
D)All of the above.
A)p > MC
B)MR > MC
C)p ≥ AVC
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A firm should always shut down if its revenue is
A)declining.
B)less than its average fixed costs.
C)less than its total costs.
D)less than its avoidable costs.
A)declining.
B)less than its average fixed costs.
C)less than its total costs.
D)less than its avoidable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
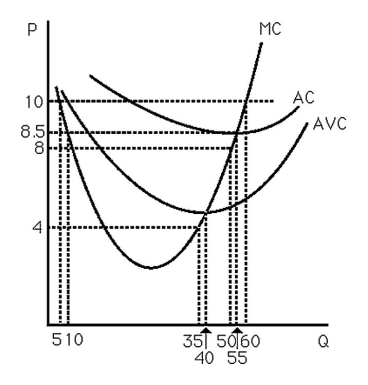
The above figure shows the cost curves for a typical firm in a competitive market. Note that if p = 10, then MC = p at both q = 5 and q = 60. Can they both yield maximum profit? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An increase in the cost of an input will result in
A)a leftward shift in the firm's supply curve.
B)an upward shift of the firm's marginal cost curve.
C)a leftward shift of the market supply curve.
D)All of the above.
A)a leftward shift in the firm's supply curve.
B)an upward shift of the firm's marginal cost curve.
C)a leftward shift of the market supply curve.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A firm will shut down in the short run if
A)total fixed costs are too high.
B)total revenue from operating would not cover all costs.
C)total revenue from operating would not cover variable costs.
D)total revenue from operating would not cover fixed costs.
A)total fixed costs are too high.
B)total revenue from operating would not cover all costs.
C)total revenue from operating would not cover variable costs.
D)total revenue from operating would not cover fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a firm is a price taker, then its marginal revenue will always equal
A)price.
B)total cost.
C)zero.
D)one.
A)price.
B)total cost.
C)zero.
D)one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
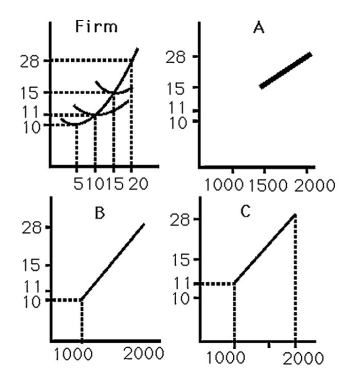
The above figure shows the cost curves for a typical firm in a market and three possible market supply curves. If there are 100 identical firms, the market supply curve is best represented by
A)curve A.
B)curve B.
C)curve C.
D)either curve A or B, but definitely not C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose TC = 10 + (0.1 ∗ q2). If p = 10, the firm's profit-maximizing level of output is
A)40.
B)50.
C)60.
D)0, since the firm will shut down.
A)40.
B)50.
C)60.
D)0, since the firm will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the production of a good involves several inputs, an increase in the cost of one input will usually cause total costs to
A)rise more than in proportion.
B)rise less than in proportion.
C)remain unchanged.
D)rise by the exact amount of the input price increase.
A)rise more than in proportion.
B)rise less than in proportion.
C)remain unchanged.
D)rise by the exact amount of the input price increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
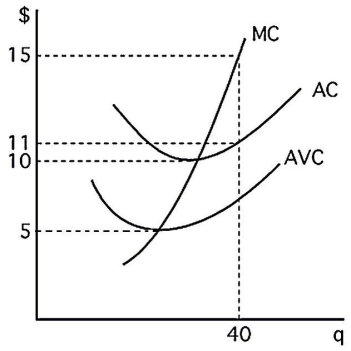
The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the firm is to operate in the short run, price must exceed
A)$0.
B)$5.
C)$10.
D)$11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

The above figure shows the cost curves for a competitive firm. If the profit-maximizing level of output is 40, price is equal to
A)$0.
B)$15.
C)$10.
D)$11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose TC = 10 + (0.1 ∗ q2). If there are 100 identical firms in the market, the market supply curve is
A)Q = 1000 ∗ p.
B)Q = 500 ∗ p.
C)Q = 100 ∗ p.
D)Q = 10.
A)Q = 1000 ∗ p.
B)Q = 500 ∗ p.
C)Q = 100 ∗ p.
D)Q = 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose a firm's costs are F + v ∗ q2 where F and v are positive real numbers and the firm sells its product at the market determined price p. Profits are calculated using
A)p ∗ q - F - v ∗ q2.
B)[p -(F/q + v ∗ q)] ∗ q.
C)[(p ∗ q)/q -(F + v ∗ q)/q] ∗ q.
D)Both A and B.
A)p ∗ q - F - v ∗ q2.
B)[p -(F/q + v ∗ q)] ∗ q.
C)[(p ∗ q)/q -(F + v ∗ q)/q] ∗ q.
D)Both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose that once a well is dug, water flows out of it continuously without any additional effort. Customers collect their water and pay a per gallon fee when they leave the site of the well. In the short run, the competitive firm in this market
A)has no variable costs.
B)has no fixed costs.
C)will shut down.
D)can produce water at no cost.
A)has no variable costs.
B)has no fixed costs.
C)will shut down.
D)can produce water at no cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose TC = 10 + (0.1 ∗ q2). If p = 10, the firm's profits will be
A)240.
B)250.
C)260.
D)-10 because the firm will shut down.
A)240.
B)250.
C)260.
D)-10 because the firm will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose that once a well is dug, water flows out of it continuously without any additional effort. Customers collect their water and pay a per gallon fee when they leave the site of the well. In the short run, the competitive firm in this market
A)will not shut down because variable costs are zero.
B)has no fixed costs.
C)faces diminishing marginal returns.
D)can act as a price setter.
A)will not shut down because variable costs are zero.
B)has no fixed costs.
C)faces diminishing marginal returns.
D)can act as a price setter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If a firm is currently in short-run equilibrium earning a profit, what impact will a lump-sum tax have on its production decision?
A)The firm will decrease output to earn a higher profit.
B)The firm will increase output but earn a lower profit.
C)The firm will not change output but earn a lower profit.
D)The firm will not change output and earn a higher profit.
A)The firm will decrease output to earn a higher profit.
B)The firm will increase output but earn a lower profit.
C)The firm will not change output but earn a lower profit.
D)The firm will not change output and earn a higher profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium, then
A)economic profits equal zero.
B)economic profits will be positive.
C)economic profits will be negative.
D)All of the above are possible in the short run.
A)economic profits equal zero.
B)economic profits will be positive.
C)economic profits will be negative.
D)All of the above are possible in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When the production of a good involves several inputs and inputs are used in fixed proportions, an increase in the cost of one input will usually cause total costs to
A)rise more than in proportion.
B)rise less than in proportion.
C)remain unchanged.
D)rise by the exact amount of the input price increase.
A)rise more than in proportion.
B)rise less than in proportion.
C)remain unchanged.
D)rise by the exact amount of the input price increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The competitive firm's supply curve is equal to
A)its marginal cost curve.
B)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AC.
C)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AVC.
D)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AFC.
A)its marginal cost curve.
B)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AC.
C)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AVC.
D)the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above AFC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The reasons why a competitive firm's short-run supply curve is upward sloping are
A)the law of diminishing marginal returns and profit maximization.
B)constant returns to scale and profit maximization.
C)decreasing returns to scale and profit maximization.
D)Both B and C.
A)the law of diminishing marginal returns and profit maximization.
B)constant returns to scale and profit maximization.
C)decreasing returns to scale and profit maximization.
D)Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium, then
A)profits equal zero.
B)it will not operate at a loss.
C)an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on profit.
D)an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on output.
A)profits equal zero.
B)it will not operate at a loss.
C)an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on profit.
D)an increase in its fixed cost will have no effect on output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a graph of a firm's short-run total costs and total revenue, the total cost and the total revenue curves, respectively, will intersect the vertical axis
A)above the origin, above the origin.
B)above the origin, at the origin.
C)at the origin, at the origin.
D)below the origin, below the origin.
A)above the origin, above the origin.
B)above the origin, at the origin.
C)at the origin, at the origin.
D)below the origin, below the origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



