Deck 6: Energy for Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Energy for Life
1
As climate change leads to drier and drier summers in the southeastern United States, more and more homeowners find that they have crabgrass growing in their yards. The reason for this is that
A) crabgrass is a type of cactus, so it grows better in dry climates.
B) as the climate changes, homeowners are not caring for their yards as well.
C) crabgrass is a tropical plant that likes hot, dry climates.
D) crabgrass is a type of C 3 plant that does well in dry climates.
E) crabgrass is a type of C 4 plant that does well in dry climates.
A) crabgrass is a type of cactus, so it grows better in dry climates.
B) as the climate changes, homeowners are not caring for their yards as well.
C) crabgrass is a tropical plant that likes hot, dry climates.
D) crabgrass is a type of C 3 plant that does well in dry climates.
E) crabgrass is a type of C 4 plant that does well in dry climates.
E
2
Which of the following events takes place in the Calvin cycle?
A) transfer of electrons to the reaction center of photosystem I
B) generation of ATP from ADP + P i
C) splitting of water, releasing an electron
D) generation of NADPH from NADP +
E) CO 2is converted intoG3P
A) transfer of electrons to the reaction center of photosystem I
B) generation of ATP from ADP + P i
C) splitting of water, releasing an electron
D) generation of NADPH from NADP +
E) CO 2is converted intoG3P
E
3
Which compounds link the light reactions with the Calvin cycle reactions?
A) ATP and NADPH
B) H + and ATP
C) G3P and ATP
D) H + and G3P
E) G3P and NADPH
A) ATP and NADPH
B) H + and ATP
C) G3P and ATP
D) H + and G3P
E) G3P and NADPH
A
4
Which of the following organisms can perform photosynthesis?
A) algae
B) fungi
C) animals
D) invertebrates
E) vertebrates
A) algae
B) fungi
C) animals
D) invertebrates
E) vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why do plants contain other pigments besides chlorophyll?
A) The additional pigments are able to absorb other light wavelengths that chlorophyll cannot.
B) The additional pigments can only absorb violet or ultraviolet light.
C) Chlorophyll is unable to absorb visible light.
D) When chlorophyll breaks down, the additional pigments can absorb the same wavelengths of light.
E) When the additional pigments break down, the chlorophyll can absorb other wavelengths of light.
A) The additional pigments are able to absorb other light wavelengths that chlorophyll cannot.
B) The additional pigments can only absorb violet or ultraviolet light.
C) Chlorophyll is unable to absorb visible light.
D) When chlorophyll breaks down, the additional pigments can absorb the same wavelengths of light.
E) When the additional pigments break down, the chlorophyll can absorb other wavelengths of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Inside the chloroplasts, chlorophyll is found in the
A) mesophyll.
B) thylakoid space.
C) thylakoid membrane.
D) stroma.
E) cytoplasm.
A) mesophyll.
B) thylakoid space.
C) thylakoid membrane.
D) stroma.
E) cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The innermost compartment of a chloroplast formed by the interconnected thylakoids is the
A) stroma.
B) thylakoid membrane.
C) chlorophyll.
D) thylakoid space.
E) leaf space.
A) stroma.
B) thylakoid membrane.
C) chlorophyll.
D) thylakoid space.
E) leaf space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How does ATP synthase obtain the energy to produce ATP?
A) Hydrogen ions flow down a concentration gradient from the thylakoid space to the stroma through ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
B) Water splits, releasing electrons that flow from the stroma to the thylakoid space and attach to the active site of ATP synthase.
C) Electrons from the reaction site center of photosystem II are funneled to ATP synthase, which uses the energy to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
D) Hydrogen ions in the thylakoid space combine with electrons from the stroma at ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
E) A hydrogen ion from NADPH is used by ATP synthase to power the production of ATP from ADP + P i, and an electron is released, splitting water.
A) Hydrogen ions flow down a concentration gradient from the thylakoid space to the stroma through ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
B) Water splits, releasing electrons that flow from the stroma to the thylakoid space and attach to the active site of ATP synthase.
C) Electrons from the reaction site center of photosystem II are funneled to ATP synthase, which uses the energy to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
D) Hydrogen ions in the thylakoid space combine with electrons from the stroma at ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + P i.
E) A hydrogen ion from NADPH is used by ATP synthase to power the production of ATP from ADP + P i, and an electron is released, splitting water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The production of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) in the Calvin cycle requires six molecules each of ATP and NADPH. Another three molecules of ATP are then used in the cycle. What is the purpose of these three additional ATP molecules?
A) to regenerate the starter molecule RuBP
B) to attract the next CO 2 molecule to enter the Calvin cycle
C) to reduce the molecules of G3P to form glucose
D) to join acetyl CoA into pyruvate, preparing it to enter the citric acid cycle
E) to fix carbon dioxide to RuBP
A) to regenerate the starter molecule RuBP
B) to attract the next CO 2 molecule to enter the Calvin cycle
C) to reduce the molecules of G3P to form glucose
D) to join acetyl CoA into pyruvate, preparing it to enter the citric acid cycle
E) to fix carbon dioxide to RuBP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Chlorophyll is to the light reactions as ________ is to the Calvin cycle.
A) NADP +
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) ATP synthase
E) RuBP
A) NADP +
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) ATP synthase
E) RuBP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The light reactions act much as a battery to power the reactions of the Calvin cycle. This energy is stored as
A) ATP and NADP +.
B) ADP + P i.
C) ADP + P i and NADP +.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) NADPH and NADP +.
A) ATP and NADP +.
B) ADP + P i.
C) ADP + P i and NADP +.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) NADPH and NADP +.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center of a photosystem participate directly in the capture of solar energy. What is the purpose of the accessory pigments? 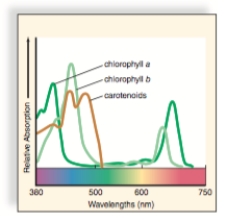
A) They participate in the Calvin cycle.
B) They absorb additional wavelengths of light and pass on the energy tothe chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
C) They split the water molecule to supply electrons to the chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
D) They change the color of the leaves to discourage predators.
E) They have no purpose.

A) They participate in the Calvin cycle.
B) They absorb additional wavelengths of light and pass on the energy tothe chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
C) They split the water molecule to supply electrons to the chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
D) They change the color of the leaves to discourage predators.
E) They have no purpose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a function specific to photosystemI?
A) split water to release electrons
B) rebuild water molecules
C) produceNADPH
D) give off oxygen when stimulated by light
E) combine hydrogen ions with an electron to form water
A) split water to release electrons
B) rebuild water molecules
C) produceNADPH
D) give off oxygen when stimulated by light
E) combine hydrogen ions with an electron to form water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
During photosynthesis, ________ is oxidized, while ________ is reduced.
A) water; carbon dioxide
B) carbon dioxide; water
C) carbohydrate; carbon dioxide
D) carbon dioxide; carbohydrate
E) carbon dioxide; oxygen
A) water; carbon dioxide
B) carbon dioxide; water
C) carbohydrate; carbon dioxide
D) carbon dioxide; carbohydrate
E) carbon dioxide; oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In photosynthesis, the light reactions ________ while the Calvin cycle ________.
A) capture solar energy; converts the captured energy to chemical potential energy
B) can occur only in the light; can occur only in the dark
C) require the presence of ATP; makes ATP
D) can only function if the stomata are open; can only occur if the stomata are closed
E) use products manufactured in the dark reactions; creates products used in the dark reactions
A) capture solar energy; converts the captured energy to chemical potential energy
B) can occur only in the light; can occur only in the dark
C) require the presence of ATP; makes ATP
D) can only function if the stomata are open; can only occur if the stomata are closed
E) use products manufactured in the dark reactions; creates products used in the dark reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The light reactions of photosynthesis are said to be similar to a battery because they form a current. In which direction do the electrons of this circuit flow?
A) H 2O → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
B) H 2O → PSII → chlorophyll b → PSI → chlorophyll a → NADPH
C) NADPH → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADP +
D) NADP + → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
E) PSI → electron transport chain → PSII → electron transport chain → NADPH
A) H 2O → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
B) H 2O → PSII → chlorophyll b → PSI → chlorophyll a → NADPH
C) NADPH → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADP +
D) NADP + → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
E) PSI → electron transport chain → PSII → electron transport chain → NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The products of photosynthesis are water and carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a redox reaction, reduction means ________, and oxidation means ________.
A) loss of electrons; gain of electrons
B) gain of water; loss of water
C) gain of electrons; loss of electrons
D) loss of water; gain of water
E) gain of protons; loss of protons
A) loss of electrons; gain of electrons
B) gain of water; loss of water
C) gain of electrons; loss of electrons
D) loss of water; gain of water
E) gain of protons; loss of protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Thefluid-filled areawithin the chloroplast is called the
A) granum.
B) chlorophyll.
C) cytoplasm.
D) stroma.
E) christae
A) granum.
B) chlorophyll.
C) cytoplasm.
D) stroma.
E) christae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The light reactions produce ________, which are used in the Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle releases ________, which return to the light reactions.
A) ATP and NADPH; ADP and NADP
B) CO 2 and H 2O; glucose and O 2
C) ATP and CO 2; glucose and O 2
D) glucose and O 2; CO 2 and H 2O
E) ADP and NADH; ATP and NADPH
A) ATP and NADPH; ADP and NADP
B) CO 2 and H 2O; glucose and O 2
C) ATP and CO 2; glucose and O 2
D) glucose and O 2; CO 2 and H 2O
E) ADP and NADH; ATP and NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Replacement electrons for the reaction center of photosystem II are derived from
A) H 2O.
B) NADP +.
C) G3P.
D) NADPH.
E) CO 2.
A) H 2O.
B) NADP +.
C) G3P.
D) NADPH.
E) CO 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The three stages of the Calvin cycle reactions are
A) NADPH reduction, CO 2 fixation, and NADP + regeneration.
B) NADPH reduction, CO 2 fixation, and RuBP regeneration.
C) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration.
D) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and NADP + regeneration.
E) CO 2 reduction, NADPH reduction, and CO 2 regeneration.
A) NADPH reduction, CO 2 fixation, and NADP + regeneration.
B) NADPH reduction, CO 2 fixation, and RuBP regeneration.
C) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration.
D) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and NADP + regeneration.
E) CO 2 reduction, NADPH reduction, and CO 2 regeneration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The difference between bundle sheath cells in C 3 and C 4 plants is that
A) the bundle sheath cells in C 3 plants have chloroplasts, while those in C 4 plants do not.
B) the bundle sheath cells in C 4 plants have chloroplasts, while those in C 3 plants do not.
C) the bundle sheath cells in C 3 plants are arranged in columns just beneath the upper epidermis, while those in C 4 plants are arranged in a ring around veins.
D) the bundle sheath cells in C 4 plants are arranged in columns just beneath the upper epidermis, while those in C 3 plants are arranged in a ring around veins.
E) There is no difference in bundle sheath cells in C 3 and C 4 plants.
A) the bundle sheath cells in C 3 plants have chloroplasts, while those in C 4 plants do not.
B) the bundle sheath cells in C 4 plants have chloroplasts, while those in C 3 plants do not.
C) the bundle sheath cells in C 3 plants are arranged in columns just beneath the upper epidermis, while those in C 4 plants are arranged in a ring around veins.
D) the bundle sheath cells in C 4 plants are arranged in columns just beneath the upper epidermis, while those in C 3 plants are arranged in a ring around veins.
E) There is no difference in bundle sheath cells in C 3 and C 4 plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Calvin cycle produces
A) glucose.
B) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).
C) sucrose.
D) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).
E) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
A) glucose.
B) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).
C) sucrose.
D) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).
E) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a high latitude rainforest, the dominant type of photosynthesis is most likely to be
A) both C 3 and CAM.
B) C 4.
C) CAM.
D) both C 4 and CAM.
E) C 3.
A) both C 3 and CAM.
B) C 4.
C) CAM.
D) both C 4 and CAM.
E) C 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Energy to drive the formation of ATP in photosynthesis is derived from
A) the H + gradient.
B) NADP +.
C) G3P.
D) NADPH.
E) CO 2.
A) the H + gradient.
B) NADP +.
C) G3P.
D) NADPH.
E) CO 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The O 2 given off during photosynthesis is derived from
A) both CO 2 and H 2O.
B) RuBP.
C) CO 2.
D) NADP +.
E) H 2O.
A) both CO 2 and H 2O.
B) RuBP.
C) CO 2.
D) NADP +.
E) H 2O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In C 4 plants, the light reactions will stop during the daytime when the supply of what compound is limited?
A) chlorophyll a
B) NADP +
C) H 2O
D) CO 2
E) O 2
A) chlorophyll a
B) NADP +
C) H 2O
D) CO 2
E) O 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A poison that disrupts the H + gradient in the thylakoid space would most likely cause which of the following to accumulate during the Calvin cycle reactions?
A) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
B) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
D) NADPH
E) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
A) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
B) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
D) NADPH
E) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
ATP and NADPH are both used during the Calvin cycle. What is the function of each?
A) ATP supplies energy and NADPH supplies electrons for reducing power.
B) ATP supplies energy and NADPH fixes CO 2 so it can enter the cycle.
C) Both ATP and NADPH supply energy to the Calvin cycle.
D) NADPH supplies energy and ATP supplies electrons for reducing power.
E) ATP and NADPH are joined into the starter molecule, RuBP, to form glucose.
A) ATP supplies energy and NADPH supplies electrons for reducing power.
B) ATP supplies energy and NADPH fixes CO 2 so it can enter the cycle.
C) Both ATP and NADPH supply energy to the Calvin cycle.
D) NADPH supplies energy and ATP supplies electrons for reducing power.
E) ATP and NADPH are joined into the starter molecule, RuBP, to form glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Before being converted into sucrose, starch, or cellulose, G3P must first be converted into which compound?
A) glucose
B) galactose
C) glucose phosphate
D) fructose
E) 3PG
A) glucose
B) galactose
C) glucose phosphate
D) fructose
E) 3PG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The reaction center of photosystem I consists of what type of molecule?
A) chlorophyll a
B) chlorophyll b
C) carotenoids
D) NADP +
E) electron transport proteins
A) chlorophyll a
B) chlorophyll b
C) carotenoids
D) NADP +
E) electron transport proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In C 4 plants, chloroplasts are located in
A) mesophyll cells.
B) the stomata.
C) both mesophyll and bundle sheath cells.
D) bundle sheath cells.
E) epidermal cells of the leaf.
A) mesophyll cells.
B) the stomata.
C) both mesophyll and bundle sheath cells.
D) bundle sheath cells.
E) epidermal cells of the leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A new species of plant is discovered and you are asked to help classify it. Upon examination under a microscope, you find that there is a layer of bundle sheath cells containing chloroplasts around the vein of the leaf of the plant. What can you tell about the plant from this information?
A) This plant is unlike any other plant that has ever been discovered and is a completely new category of plant.
B) This plant very likely carries out C 4 photosynthesis.
C) This plant falls into the category of CAM-type plants.
D) This plant uses chemosynthesis rather than photosynthesis.
E) This is a C 3 type of plant.
A) This plant is unlike any other plant that has ever been discovered and is a completely new category of plant.
B) This plant very likely carries out C 4 photosynthesis.
C) This plant falls into the category of CAM-type plants.
D) This plant uses chemosynthesis rather than photosynthesis.
E) This is a C 3 type of plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A small, low-growing plant found on the surface of a sun-exposed rock in a desert would most likely use which type of photosynthesis?
A) CAM
B) C 3
C) C 4
D) both C 4 and CAM
E) both C 3 and CAM
A) CAM
B) C 3
C) C 4
D) both C 4 and CAM
E) both C 3 and CAM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
CAM photosynthesis limits CO 2 fixation to nighttime hours in order to
A) allow water to enter leaf spaces during the daylight hours.
B) open stomata only at night, limiting water loss because of heat and low humidity.
C) allow NADPH and ATP to enter leaf spaces.
D) limit the Calvin cycle reactions to nighttime only.
E) limit water uptake from the soil during daytime hours.
A) allow water to enter leaf spaces during the daylight hours.
B) open stomata only at night, limiting water loss because of heat and low humidity.
C) allow NADPH and ATP to enter leaf spaces.
D) limit the Calvin cycle reactions to nighttime only.
E) limit water uptake from the soil during daytime hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which steps of photosynthesis does C 4 photosynthesis partition in space?
A) carbon fixation and Calvin cycle reactions
B) carbon fixation and light reactions
C) light reactions and Calvin cycle reactions
D) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) formation and glucose phosphate formation
E) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) formation and glucose phosphate formation
A) carbon fixation and Calvin cycle reactions
B) carbon fixation and light reactions
C) light reactions and Calvin cycle reactions
D) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) formation and glucose phosphate formation
E) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) formation and glucose phosphate formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Calvin cycle reactions occur in bundle sheath cells in a C 4 plant
A) to shield the Calvin cycle reactions from O 2 in the leaf spaces.
B) to allow O 2 to enter bundle sheath cells.
C) because rubisco is only found in mesophyll cells.
D) so that they are adjacent to stomata.
E) so that H 2O is not available to mesophyll cells.
A) to shield the Calvin cycle reactions from O 2 in the leaf spaces.
B) to allow O 2 to enter bundle sheath cells.
C) because rubisco is only found in mesophyll cells.
D) so that they are adjacent to stomata.
E) so that H 2O is not available to mesophyll cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Sucrose, cellulose, amino acids, and starch are all made from what starter molecule in plants?
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
D) ATP
E) RuBP carboxylase
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
D) ATP
E) RuBP carboxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A plant that uses CAM photosynthesis is most likely to be successful in what type of environment?
A) cool, moist
B) hot, moist
C) cool, dry
D) hot, dry
E) semi-tropical
A) cool, moist
B) hot, moist
C) cool, dry
D) hot, dry
E) semi-tropical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The light-harvesting complexes of a chloroplast are located in the ________; the enzymes of the Calvin cycle reactions are located in the ________.
A) thylakoid membrane; stroma
B) stroma; thylakoid space
C) thylakoid space; thylakoid membrane
D) stroma; thylakoid membrane
E) thylakoid space; stroma
A) thylakoid membrane; stroma
B) stroma; thylakoid space
C) thylakoid space; thylakoid membrane
D) stroma; thylakoid membrane
E) thylakoid space; stroma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What two things are added to NADP + to convert it into NADPH?
A) H + and electrons
B) electrons and ATP
C) H + and ATP
D) H + and CO 2
E) electrons and CO 2
A) H + and electrons
B) electrons and ATP
C) H + and ATP
D) H + and CO 2
E) electrons and CO 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Not all molecules contain the same amount of chemical energy. What is the energy relationship between G3P and CO 2?
A) G3P and CO 2 have the same amount of energy.
B) G3P has less energy than CO 2.
C) Neither G3P nor CO 2 contain any chemical energy.
D) G3P has more energy than CO 2.
E) There is not enough information provided to answer the question.
A) G3P and CO 2 have the same amount of energy.
B) G3P has less energy than CO 2.
C) Neither G3P nor CO 2 contain any chemical energy.
D) G3P has more energy than CO 2.
E) There is not enough information provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which stages of the Calvin cycle reactions require the use of energy from ATP?
A) CO 2 fixation and CO 2 reduction
B) CO 2 reduction and RuBP regeneration
C) CO 2 fixation and RuBP regeneration
D) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration
E) CO 2 reduction and RuBP oxidation
A) CO 2 fixation and CO 2 reduction
B) CO 2 reduction and RuBP regeneration
C) CO 2 fixation and RuBP regeneration
D) CO 2 fixation, CO 2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration
E) CO 2 reduction and RuBP oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is a coenzyme?
A) starch
B) cellulose
C) glucose phosphate
D) NADP +
E) sucrose
A) starch
B) cellulose
C) glucose phosphate
D) NADP +
E) sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The localization of the electron transport chains to the thylakoid membrane ensures that
A) the energy released can be used to establish an H + ion gradient.
B) the energy released is stored in the stroma.
C) NADP + does not enter the thylakoid space.
D) CO 2 remains in the stroma for the Calvin cycle reactions and does not enter the thylakoid space.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) is produced in the thylakoid space.
A) the energy released can be used to establish an H + ion gradient.
B) the energy released is stored in the stroma.
C) NADP + does not enter the thylakoid space.
D) CO 2 remains in the stroma for the Calvin cycle reactions and does not enter the thylakoid space.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) is produced in the thylakoid space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In which of the labeled cells of a C 4 leaf are the Calvin cycle reactions performed? 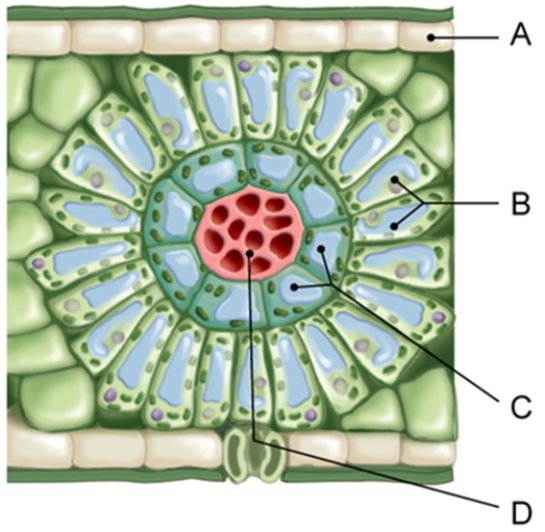
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) A and D
D) B only
E) C only

A) A and B
B) B and C
C) A and D
D) B only
E) C only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
ATP synthasederives energy for the generation of ATP from
A) the movement of hydrogen ions against their concentration gradient into the thylakoid space.
B) the splitting of H 2O, which releases electrons.
C) solar energy captured by the light reactions changing the shape of the enzyme.
D) electrons transferred from NADPH causing the enzyme to change shape.
E) the movement of hydrogen ions down their concentration gradient from the thylakoid space to the stroma.
A) the movement of hydrogen ions against their concentration gradient into the thylakoid space.
B) the splitting of H 2O, which releases electrons.
C) solar energy captured by the light reactions changing the shape of the enzyme.
D) electrons transferred from NADPH causing the enzyme to change shape.
E) the movement of hydrogen ions down their concentration gradient from the thylakoid space to the stroma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The _______ from the light reactions is used to reduce CO 2 to a carbohydrate using energy derived from ______.
A) NADPH; ATP
B) NADP +; ATP
C) RuBP; ATP
D) NADPH; RuBP
E) rubisco; RuBP
A) NADPH; ATP
B) NADP +; ATP
C) RuBP; ATP
D) NADPH; RuBP
E) rubisco; RuBP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the labeled cells of a C 3 leaf is known as a bundle sheath cell? 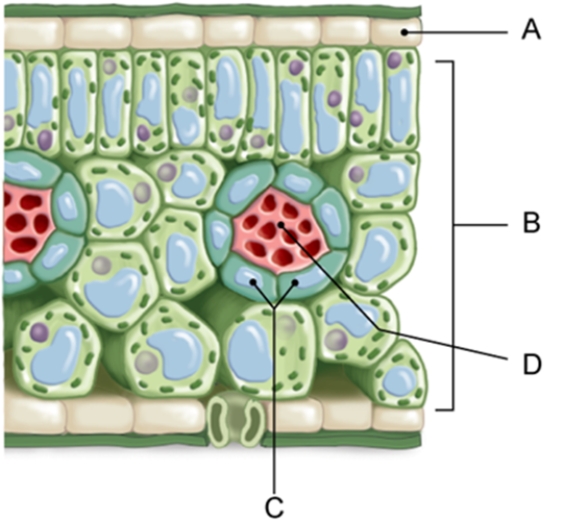
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) C3 plants do not have bundle sheath cells.

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) C3 plants do not have bundle sheath cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is a coenzyme?
A) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
B) chlorophyll a
C) electron transport protein
D) rubisco
E) NADP +
A) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
B) chlorophyll a
C) electron transport protein
D) rubisco
E) NADP +

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
RuBP carboxylase (rubisco) is able to bind with both
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) carbon dioxide and oxygen.
C) carbon dioxide and NADPH.
D) oxygen and water.
E) NADPH and ATP.
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) carbon dioxide and oxygen.
C) carbon dioxide and NADPH.
D) oxygen and water.
E) NADPH and ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A coenzyme is defined as
A) a nonprotein helper that works with an enzyme.
B) another enzyme that assists an enzyme with a chemical reaction.
C) another enzyme in the same biochemical pathway.
D) a carbohydrate that assists an enzyme.
E) a protein that is not an enzyme.
A) a nonprotein helper that works with an enzyme.
B) another enzyme that assists an enzyme with a chemical reaction.
C) another enzyme in the same biochemical pathway.
D) a carbohydrate that assists an enzyme.
E) a protein that is not an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The addition of electrons and hydrogen ions to a substrate is called what?
A) reduction
B) oxidation
C) phosphorylation
D) metabolism
E) an enzyme-substrate complex
A) reduction
B) oxidation
C) phosphorylation
D) metabolism
E) an enzyme-substrate complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Grana are
A) interconnecting stomata.
B) stacks of thylakoids.
C) pores that open to allow gas exchange.
D) the sites of the Calvin cycle and production of sugars.
E) enzymes that bind CO 2.
A) interconnecting stomata.
B) stacks of thylakoids.
C) pores that open to allow gas exchange.
D) the sites of the Calvin cycle and production of sugars.
E) enzymes that bind CO 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How many times must the Calvin cycle turn to yield a single molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Carotenoids are found in high concentrations in yellow and orange leaves or vegetables. Why do these leaves and vegetables appear yellow or orange?
A) The carotenoids reflect and transmit yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
B) The carotenoids absorb yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
C) The carotenoids absorb or transmit yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
D) The carotenoids absorb or reflect yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
E) The carotenoids absorb all wavelengths of light and then transmit yellow and orange wavelengths.
A) The carotenoids reflect and transmit yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
B) The carotenoids absorb yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
C) The carotenoids absorb or transmit yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
D) The carotenoids absorb or reflect yellow and orange wavelengths of light.
E) The carotenoids absorb all wavelengths of light and then transmit yellow and orange wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How many turns of the Calvin cycle would be required for a plant to make one molecule of glucose?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 12
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is a disadvantage of C 4 photosynthesis relative to C 3 photosynthesis?
A) inability of rubisco to obtain O 2
B) C4 plants need energy to move fixed carbon compounds into bundle sheath cells
C) need for stomata to close to conserve H 2O
D) need for energy to move H 2O into bundle sheath cells
E) inability of ATP synthase to utilize H + gradient for energy
A) inability of rubisco to obtain O 2
B) C4 plants need energy to move fixed carbon compounds into bundle sheath cells
C) need for stomata to close to conserve H 2O
D) need for energy to move H 2O into bundle sheath cells
E) inability of ATP synthase to utilize H + gradient for energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which complex or enzyme of photosynthesis splits H 2O?
A) photosystem I
B) photosystem II
C) rubisco
D) electron transport chain
E) ATP synthase
A) photosystem I
B) photosystem II
C) rubisco
D) electron transport chain
E) ATP synthase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement is accurate about how C 4 plants are able to survive hot, dry spells during the growing season?
A) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase(rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells, is not exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This prevents RuBP carboxylase from binding to oxygen instead of carbon dioxide.
B) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the mesophyll cells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.
C) When the stomata are open during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells, is equally exposed to both the carbon dioxide and the oxygen in the leaf spaces.
D) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheathcells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.
E) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.
A) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase(rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells, is not exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This prevents RuBP carboxylase from binding to oxygen instead of carbon dioxide.
B) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the mesophyll cells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.
C) When the stomata are open during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells, is equally exposed to both the carbon dioxide and the oxygen in the leaf spaces.
D) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheathcells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.
E) When the stomata close during the heat of the day, RuBP carboxylase (rubisco), which is located in the bundle sheath cells,is exposed to the increasing oxygen concentration in the leaf spaces. This help facilitate the binding of RuBP carboxylase to oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The removal of electrons and hydrogen ions from a substrate is called what?
A) oxidation
B) reduction
C) phosphorylation
D) metabolism
E) an enzyme-substrate complex
A) oxidation
B) reduction
C) phosphorylation
D) metabolism
E) an enzyme-substrate complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



