Deck 44: Animal Excretory Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 44: Animal Excretory Systems
1
Excessive formation of uric acid crystals in humans leads to which of the following medical conditions?
A) diabetes, where excessive urine formation occurs
B) insatiable thirst and excessive urine formation
C) gout, a painful inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints
D) osteoarthritis, an inevitable consequence of aging
A) diabetes, where excessive urine formation occurs
B) insatiable thirst and excessive urine formation
C) gout, a painful inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints
D) osteoarthritis, an inevitable consequence of aging
C
2
Unlike most bony fishes, sharks maintain body fluids that are isoosmotic to seawater, so they are considered by many to be osmoconformers. Nonetheless, sharks osmoregulate at least partially by ________.
A) using their gills and kidneys to rid themselves of sea salts
B) monitoring dehydration at the cellular level with special gated aquaporins
C) tolerating high urea concentrations that are balanced with internal salt concentrations to seawater osmolarity
D) synthesizing uric acid, a chemical that binds and precipitates salts inside cells
A) using their gills and kidneys to rid themselves of sea salts
B) monitoring dehydration at the cellular level with special gated aquaporins
C) tolerating high urea concentrations that are balanced with internal salt concentrations to seawater osmolarity
D) synthesizing uric acid, a chemical that binds and precipitates salts inside cells
C
3
Compared to the seawater around them, most marine invertebrates are ________.
A) hyperosmotic
B) hypoosmotic
C) isoosmotic
D) both hyperosmotic and isoosmotic
A) hyperosmotic
B) hypoosmotic
C) isoosmotic
D) both hyperosmotic and isoosmotic
C
4
Which of the following processes must freshwater fish undertake to maintain homeostasis?
A) excrete large quantities of electrolytes
B) consume large quantities of water
C) excrete large quantities of water
D) take in electrolytes through simple diffusion
A) excrete large quantities of electrolytes
B) consume large quantities of water
C) excrete large quantities of water
D) take in electrolytes through simple diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes the role of transport epithelia in osmoregulation of marine fish with bony skeletons?
A) They actively transport salt into the animal through the gills.
B) They mediate the movement of water from seawater through the gills.
C) They are involved in excretion of excess salt.
D) They allow the fish to produce dilute urine.
A) They actively transport salt into the animal through the gills.
B) They mediate the movement of water from seawater through the gills.
C) They are involved in excretion of excess salt.
D) They allow the fish to produce dilute urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement describes an advantage to birds that secrete uric acid as their nitrogenous waste?
A) Uric acid is readily soluble in water.
B) Uric acid is metabolically less expensive to synthesize than other excretory products.
C) Uric acid requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal.
D) Uric acid can be reused by birds as a protein source.
A) Uric acid is readily soluble in water.
B) Uric acid is metabolically less expensive to synthesize than other excretory products.
C) Uric acid requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal.
D) Uric acid can be reused by birds as a protein source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Single-celled Paramecium live in pond water (a hyposmotic environment relative to the cytosol). They have a structural feature, a contractile vacuole, that enables them to osmoregulate. If sucrose or sodium chloride was added to the pond water, at which final concentration is the contractile vacuole likely to be most active?
A) 0.0 mM sucrose
B) 0.05 mM saline
C) 0.08 mM sucrose
D) 1.0 mM saline
A) 0.0 mM sucrose
B) 0.05 mM saline
C) 0.08 mM sucrose
D) 1.0 mM saline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Nitrogenous waste from an unknown animal is collected and analyzed. The waste is sticky like glue or paste, and upon chemical analysis contains a molecule composed of two fused rings. The waste is most likely from which of the following animals?
A) a salmon
B) a tiger shark
C) a mouse
D) a garden snail
A) a salmon
B) a tiger shark
C) a mouse
D) a garden snail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In animals, the catabolism of which molecules contributes most to the production of nitrogenous wastes?
A) starch and cellulose
B) triglycerides and steroids
C) proteins and nucleic acids
D) phospholipids and glycolipids
A) starch and cellulose
B) triglycerides and steroids
C) proteins and nucleic acids
D) phospholipids and glycolipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The force driving simple diffusion is ________, while an energy source that drives active transport is ________.
A) the concentration gradient; ADP
B) the concentration gradient; ATP
C) transmembrane pumps; electron transport
D) phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP
A) the concentration gradient; ADP
B) the concentration gradient; ATP
C) transmembrane pumps; electron transport
D) phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Studies of cricket Malpighian tubules revealed that potassium ions accumulated inside the tubule, moving against the potassium concentration gradient. Based on the information, which of the following is the best inference about the mechanism of potassium transport?
A) Potassium transport is a passive process.
B) Movement of potassium into the lumen of the Malpighian tubules is likely an energy-requiring process.
C) Potassium moves out of the tubules at a faster rate than it moves into the lumen of the tubules.
D) Sodium ions will follow potassium ions.
A) Potassium transport is a passive process.
B) Movement of potassium into the lumen of the Malpighian tubules is likely an energy-requiring process.
C) Potassium moves out of the tubules at a faster rate than it moves into the lumen of the tubules.
D) Sodium ions will follow potassium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ammonia is likely to be the primary nitrogenous waste from organisms that evolved in which of the following habitats?
A) a freshwater environment that supports fish
B) a marine environment that supports sea birds
C) a terrestrial environment that supports crickets
D) a moist system of burrows that supports naked mole rats
A) a freshwater environment that supports fish
B) a marine environment that supports sea birds
C) a terrestrial environment that supports crickets
D) a moist system of burrows that supports naked mole rats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following best explains the death of a freshwater fish that had been placed accidentally in saltwater?
A) loss of water by osmosis from cells in vital organs resulted in cell death and organ failure
B) high amounts of salt had diffused into the fish's cells, causing them to swell and lyse
C) the kidneys were not able to keep up with the water removal necessary in this hyperosmotic environment, creating an irrevocable loss of homeostasis
D) the gills became encrusted with salt, resulting in inadequate gas exchange and a resulting asphyxiation
A) loss of water by osmosis from cells in vital organs resulted in cell death and organ failure
B) high amounts of salt had diffused into the fish's cells, causing them to swell and lyse
C) the kidneys were not able to keep up with the water removal necessary in this hyperosmotic environment, creating an irrevocable loss of homeostasis
D) the gills became encrusted with salt, resulting in inadequate gas exchange and a resulting asphyxiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which answer best describes the formation of urea in mammals?
A) It forms in the liver from NH3 and carbon dioxide.
B) It forms in the liver from glycogen.
C) It forms in the kidneys from glycerol and fatty acids.
D) It forms in the bladder from uric acid and water.
A) It forms in the liver from NH3 and carbon dioxide.
B) It forms in the liver from glycogen.
C) It forms in the kidneys from glycerol and fatty acids.
D) It forms in the bladder from uric acid and water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an advantage of excreting nitrogenous wastes as urea rather than as ammonia?
A) urea can be removed as a semi-solid paste
B) urea is less toxic than ammonia
C) urea does not affect the osmotic gradient
D) less nitrogen is removed from the body
A) urea can be removed as a semi-solid paste
B) urea is less toxic than ammonia
C) urea does not affect the osmotic gradient
D) less nitrogen is removed from the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Salmon eggs hatch in fresh water. The fish then migrate to the ocean (a hyperosmotic solution) and, after several years of feeding and growing, return to fresh water to breed. Which statement best explains how these organisms make the transition from fresh water to ocean water and back to fresh water?
A) The rectal gland functions in the ocean water, and chloride cells function in fresh water.
B) The salt transport mechanisms of the gill epithelia change during migration.
C) Salmon in fresh water excrete concentrated urine, and salmon in salt water secrete dilute urine.
D) Their metabolism changes in salt water to degrade electrolytes.
A) The rectal gland functions in the ocean water, and chloride cells function in fresh water.
B) The salt transport mechanisms of the gill epithelia change during migration.
C) Salmon in fresh water excrete concentrated urine, and salmon in salt water secrete dilute urine.
D) Their metabolism changes in salt water to degrade electrolytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Studies of cricket Malpighian tubules revealed that potassium ions move against the concentration gradient and accumulate inside the tubule. Which statement best predicts the effect of the potassium concentration gradient on the movement of water in the Malpighian tubules?
A) Water will be forced out of the lumen of the Malpighian tubules through an osmotic gradient.
B) The potassium gradient will have no effect on water movement.
C) There will be a net movement of water into the lumen of the tubules.
D) Water will be conserved, forming a hypertonic solution in the Malpighian tubules.
A) Water will be forced out of the lumen of the Malpighian tubules through an osmotic gradient.
B) The potassium gradient will have no effect on water movement.
C) There will be a net movement of water into the lumen of the tubules.
D) Water will be conserved, forming a hypertonic solution in the Malpighian tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be ________ with its ________ environment.
A) hyperosmotic; freshwater
B) hyperosmotic; seawater
C) isoosmotic; seawater
D) hypoosmotic; seawater
A) hyperosmotic; freshwater
B) hyperosmotic; seawater
C) isoosmotic; seawater
D) hypoosmotic; seawater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Materials are returned to the blood from the filtrate by which of the following processes?
A) filtration
B) reabsorption
C) secretion
D) excretion
A) filtration
B) reabsorption
C) secretion
D) excretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following best explains the death of a marine sea star that had been mistakenly placed in fresh water?
A) it was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to the new conditions
B) it was so hyperosmotic to the fresh water that it could not osmoregulate and thus its tissues swelled
C) its kidney had ruptured
D) its cells dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize
A) it was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to the new conditions
B) it was so hyperosmotic to the fresh water that it could not osmoregulate and thus its tissues swelled
C) its kidney had ruptured
D) its cells dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement best describes the process of secretion?
A) reabsorption of nutrients from a filtrate
B) selective elimination of excess ions and toxins from body fluids
C) formation of an osmotic gradient along an excretory structure
D) expulsion of urine from the body
A) reabsorption of nutrients from a filtrate
B) selective elimination of excess ions and toxins from body fluids
C) formation of an osmotic gradient along an excretory structure
D) expulsion of urine from the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which statement best explains the relatively high metabolic rate of kidneys compared to the other body organs?
A) they have membranes of varying permeability to water
B) they operate an extensive set of ion pumps
C) they are the body's only means of shedding excess nutrients
D) they have an abundance of myogenic smooth muscle
A) they have membranes of varying permeability to water
B) they operate an extensive set of ion pumps
C) they are the body's only means of shedding excess nutrients
D) they have an abundance of myogenic smooth muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is characteristic of juxtamedullary nephrons?
A) large Bowman's capsule
B) absence of proximal tubule
C) limited branching of vasa recta
D) long loop of Henle
A) large Bowman's capsule
B) absence of proximal tubule
C) limited branching of vasa recta
D) long loop of Henle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Researchers at a pharmaceutical company are working to develop a new drug that would cause a patient to produce urine that is less concentrated. Which of the following drugs would likely work best to produce this outcome?
A) a drug that opens sodium channels in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle
B) a drug that opens aquaporin channels in the descending limb of the loop of Henle
C) a drug that opens urea channels in the collecting duct
D) a drug that opens aquaporin channels in the collecting duct
A) a drug that opens sodium channels in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle
B) a drug that opens aquaporin channels in the descending limb of the loop of Henle
C) a drug that opens urea channels in the collecting duct
D) a drug that opens aquaporin channels in the collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which process does not display solute specificity?
A) H+ pumping to control pH
B) reabsorption along the proximal tubule
C) filtration from the glomerular capillaries
D) secretion along the distal tubule
A) H+ pumping to control pH
B) reabsorption along the proximal tubule
C) filtration from the glomerular capillaries
D) secretion along the distal tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Urolithiasis is a medical condition in which minerals stick together in concentrated urine, forming kidney stones. Suppose that a patient is diagnosed with urolithiasis and through ultrasound it is found that a kidney stone is blocking urine flow in the ureter. The flow of urine to which structure will be most directly affected by the blockage?
A) kidney
B) bladder
C) urethra
D) nephron
A) kidney
B) bladder
C) urethra
D) nephron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following occurs in processing of filtrate in the proximal and distal tubules?
A) conversion of toxic ammonia to less toxic urea
B) maintenance of homeostasis of pH in body fluids
C) regulation of the speed of blood flow through the nephrons
D) reabsorption of urea to maintain osmotic balance
A) conversion of toxic ammonia to less toxic urea
B) maintenance of homeostasis of pH in body fluids
C) regulation of the speed of blood flow through the nephrons
D) reabsorption of urea to maintain osmotic balance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Excretory organs known as Malpighian tubules are present in which of the following organisms?
A) flatworms
B) insects
C) jellyfish
D) sea stars
A) flatworms
B) insects
C) jellyfish
D) sea stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following stimuli is most likely to increase secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
A) drinking a large volume of pure water
B) sweating-induced dehydration
C) eating a small sugary snack
D) abnormally high blood pressure
A) drinking a large volume of pure water
B) sweating-induced dehydration
C) eating a small sugary snack
D) abnormally high blood pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following figure to answer the question. 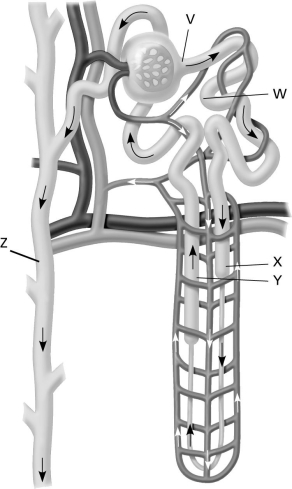 Which labeled structure identifies where filtration take place in the kidney?
Which labeled structure identifies where filtration take place in the kidney?
A) structure V
B) structure W
C) structure X
D) structure Z
 Which labeled structure identifies where filtration take place in the kidney?
Which labeled structure identifies where filtration take place in the kidney?A) structure V
B) structure W
C) structure X
D) structure Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The loop of Henle dips into the renal cortex. Which statement best explains the advantage of this feature for osmoregulation in terrestrial vertebrates?
A) absorptive processes taking place in the loop of Henle are hormonally regulated
B) differential permeabilities of ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle are important in establishing an osmotic gradient
C) the loop of Henle plays an important role in detoxification
D) additional filtration takes place along the loop of Henle
A) absorptive processes taking place in the loop of Henle are hormonally regulated
B) differential permeabilities of ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle are important in establishing an osmotic gradient
C) the loop of Henle plays an important role in detoxification
D) additional filtration takes place along the loop of Henle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you are hiking through the desert for several days, drinking which of the following would best ensure proper hydration?
A) a drink with a combination of water and electrolytes
B) a caffeinated beverage
C) bottled water kept at room temperature
D) bottled water that had been frozen to ensure that it would be as cold as possible
A) a drink with a combination of water and electrolytes
B) a caffeinated beverage
C) bottled water kept at room temperature
D) bottled water that had been frozen to ensure that it would be as cold as possible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An excretory system that is partly based on the filtration of fluid under high hydrostatic pressure is the ________.
A) flame-bulb system of flatworms
B) protonephridia of rotifers
C) Malpighian tubules of insects
D) kidneys of vertebrates
A) flame-bulb system of flatworms
B) protonephridia of rotifers
C) Malpighian tubules of insects
D) kidneys of vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following figure to answer the question. 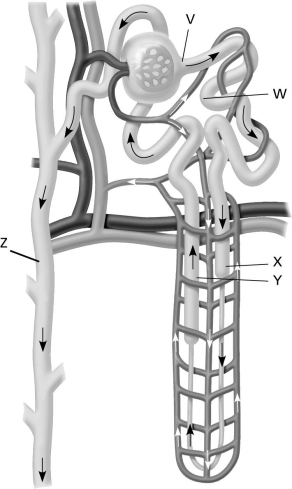 Which labeled structure identifies where passive water reabsorption takes place in the kidney?
Which labeled structure identifies where passive water reabsorption takes place in the kidney?
A) only in structure W
B) only in structures W and Y
C) in structures W, X, and Y
D) in structures V and Z
 Which labeled structure identifies where passive water reabsorption takes place in the kidney?
Which labeled structure identifies where passive water reabsorption takes place in the kidney?A) only in structure W
B) only in structures W and Y
C) in structures W, X, and Y
D) in structures V and Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which option correctly associates the mechanism for osmoregulation or nitrogen removal with the appropriate animal?
A) protonephridium-earthworm
B) Malpighian tubule-frog
C) flame bulb-flat worm
D) exchange across the body surface-snake
A) protonephridium-earthworm
B) Malpighian tubule-frog
C) flame bulb-flat worm
D) exchange across the body surface-snake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consuming alcohol results in increased urine excretion due to which of the following?
A) increased aldosterone production
B) increased blood pressure
C) inhibited secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) increased reabsorption of water in the proximal tubule
A) increased aldosterone production
B) increased blood pressure
C) inhibited secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) increased reabsorption of water in the proximal tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following figure to answer the question. 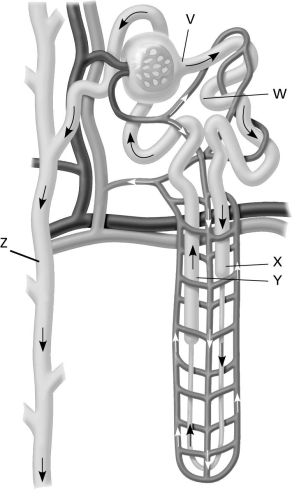 Which labeled structure is influenced by hormones to change the concentration of the urine?
Which labeled structure is influenced by hormones to change the concentration of the urine?
A) structure W
B) structure X
C) structure Y
D) structure Z
 Which labeled structure is influenced by hormones to change the concentration of the urine?
Which labeled structure is influenced by hormones to change the concentration of the urine?A) structure W
B) structure X
C) structure Y
D) structure Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the following figure to answer the question. 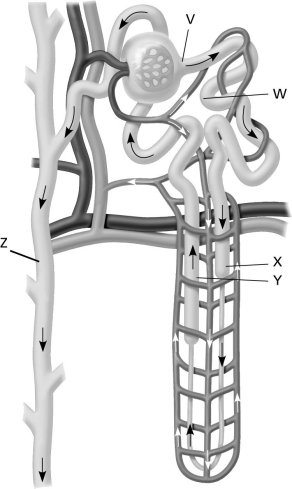 Which labeled structure identifies where selective secretion of toxins and drugs take place?
Which labeled structure identifies where selective secretion of toxins and drugs take place?
A) structure V
B) structure W
C) structure X
D) structure Y
 Which labeled structure identifies where selective secretion of toxins and drugs take place?
Which labeled structure identifies where selective secretion of toxins and drugs take place?A) structure V
B) structure W
C) structure X
D) structure Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement best describes the transfer of fluid from the glomerulus to Bowman's capsule?
A) transfer results from active transport
B) the fluid is mostly made up of red blood cells
C) the transfer is very selective as to which sub-protein-sized molecules are transferred
D) blood pressure in the capillaries of the glomerulus causes transfer to occur
A) transfer results from active transport
B) the fluid is mostly made up of red blood cells
C) the transfer is very selective as to which sub-protein-sized molecules are transferred
D) blood pressure in the capillaries of the glomerulus causes transfer to occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following can trigger osmoregulatory adjustment via the atrial natriuretic peptide system?
A) sleeping for one hour
B) severe sweating on a hot day
C) eating a pizza with olives and pepperoni
D) drinking several glasses of water
A) sleeping for one hour
B) severe sweating on a hot day
C) eating a pizza with olives and pepperoni
D) drinking several glasses of water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Unlike an earthworm's metanephridia, a mammalian nephron ________.
A) is intimately associated with a capillary network
B) functions in both osmoregulation and excretion
C) receives filtrate from blood instead of coelomic fluid
D) has a transport epithelium
A) is intimately associated with a capillary network
B) functions in both osmoregulation and excretion
C) receives filtrate from blood instead of coelomic fluid
D) has a transport epithelium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following will likely occur in a human who has no access to fresh water but is forced to drink seawater instead?
A) production of excessive antidiuretic hormone to remove more water but hold back salts
B) passive excretion of excess water in feces in order to remove the high concentration of ingested salt
C) release of atrial natriuretic peptide to decrease blood pressure
D) development of a risk of becoming overhydrated within twelve hours
A) production of excessive antidiuretic hormone to remove more water but hold back salts
B) passive excretion of excess water in feces in order to remove the high concentration of ingested salt
C) release of atrial natriuretic peptide to decrease blood pressure
D) development of a risk of becoming overhydrated within twelve hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The high osmolarity of the renal medulla is maintained by which of the following?
A) active transport of salt from the upper region of the descending limb.
B) the loose packing of juxtamedullary nephrons.
C) diffusion of urea into the collecting duct.
D) diffusion of salt from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.
A) active transport of salt from the upper region of the descending limb.
B) the loose packing of juxtamedullary nephrons.
C) diffusion of urea into the collecting duct.
D) diffusion of salt from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following animals generally has the lowest volume of urine production?
A) vampire bat
B) salmon in fresh water
C) marine bony fish
D) freshwater flatworm
A) vampire bat
B) salmon in fresh water
C) marine bony fish
D) freshwater flatworm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In which of the following species should natural selection favor the highest proportion of juxtamedullary nephrons?
A) a river otter
B) a mouse species living in a temperate broadleaf forest
C) a mouse species living in a desert
D) a beaver
A) a river otter
B) a mouse species living in a temperate broadleaf forest
C) a mouse species living in a desert
D) a beaver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following describes how antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) work together to maintaining osmoregulatory homeostasis?
A) ADH regulates the osmolarity of the blood by altering renal reabsorption of water, and the RAAS maintains the osmolarity of the blood by stimulating both Na+ and water reabsorption.
B) ADH and the RAAS work antagonistically; ADH stimulates water reabsorption during dehydration, and the RAAS causes increased excretion of water when it is in excess in body fluids.
C) Both stimulate the adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone, which increases both blood volume and pressure via its receptors in the urinary bladder.
D) ADH and the RAAS combine at the receptor sites of proximal tubule cells, where reabsorption of essential nutrients takes place.
A) ADH regulates the osmolarity of the blood by altering renal reabsorption of water, and the RAAS maintains the osmolarity of the blood by stimulating both Na+ and water reabsorption.
B) ADH and the RAAS work antagonistically; ADH stimulates water reabsorption during dehydration, and the RAAS causes increased excretion of water when it is in excess in body fluids.
C) Both stimulate the adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone, which increases both blood volume and pressure via its receptors in the urinary bladder.
D) ADH and the RAAS combine at the receptor sites of proximal tubule cells, where reabsorption of essential nutrients takes place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An increase in protein kinase A activity in all cells of the collecting duct cells will most likely have which effect on kidney function?
A) ADH production will increase
B) more-concentrated urine will be produced
C) fewer aquaporin channels will be inserted into the cell membrane
D) blood osmolarity will decrease
A) ADH production will increase
B) more-concentrated urine will be produced
C) fewer aquaporin channels will be inserted into the cell membrane
D) blood osmolarity will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
African lungfish, which are often found in small, stagnant pools of fresh water, produce urea as a nitrogenous waste. What is an advantage of this adaptation?
A) Urea takes less energy to synthesize than ammonia.
B) Small, stagnant pools do not provide enough water to dilute ammonia, which is toxic.
C) Urea forms an insoluble precipitate.
D) Urea makes lungfish tissue hypoosmotic to the pool.
A) Urea takes less energy to synthesize than ammonia.
B) Small, stagnant pools do not provide enough water to dilute ammonia, which is toxic.
C) Urea forms an insoluble precipitate.
D) Urea makes lungfish tissue hypoosmotic to the pool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which process in the nephron is least selective?
A) filtration
B) reabsorption
C) active transport
D) secretion
A) filtration
B) reabsorption
C) active transport
D) secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



