Deck 36: Transport in Vascular Plants
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Transport in Vascular Plants
1
A student examined a leaf and observed that it was dark green, thin, had stoma on the lower surface only, and had a total surface area of more than two square meters. In which environment was the leaf most likely growing?
A) a large, still pond
B) a tropical rain forest
C) an oasis within a grassland
D) the floor of a deciduous forest
A) a large, still pond
B) a tropical rain forest
C) an oasis within a grassland
D) the floor of a deciduous forest
B
2
A plant developed a mineral deficiency after being treated with a fungicide. What is the most probable cause of the deficiency?
A) Mineral receptor proteins in the plant membrane were not functioning.
B) Mycorrhizal fungi were killed.
C) Active transport of minerals was inhibited.
D) The genes for the synthesis of transport proteins were destroyed.
A) Mineral receptor proteins in the plant membrane were not functioning.
B) Mycorrhizal fungi were killed.
C) Active transport of minerals was inhibited.
D) The genes for the synthesis of transport proteins were destroyed.
B
3
Which of the following is another term for solute potential in a cell?
A) water potential
B) osmotic potential
C) potential gradient
D) pressure potential
A) water potential
B) osmotic potential
C) potential gradient
D) pressure potential
B
4
Which of the following describes the transmembrane route for transport within plant tissue?
A) water and solutes move out of one cell, across the cell wall, and into the neighboring cell
B) water and solutes move out of one cell, through the plasmodesmata, and into the neighboring cell
C) water moves out of one cell, across the cell wall, and into the neighboring cell
D) solutes move out of one cell, across the plasmodesmata, and into the neighboring cell
A) water and solutes move out of one cell, across the cell wall, and into the neighboring cell
B) water and solutes move out of one cell, through the plasmodesmata, and into the neighboring cell
C) water moves out of one cell, across the cell wall, and into the neighboring cell
D) solutes move out of one cell, across the plasmodesmata, and into the neighboring cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following structures or molecules are required for active transport of amino acids in plants?
A) channel proteins
B) vascular tissue
C) sodium/potassium pumps
D) ATP, transport proteins, and a proton gradient
A) channel proteins
B) vascular tissue
C) sodium/potassium pumps
D) ATP, transport proteins, and a proton gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of following ions play the primary role in basic transport processes in plant cells?
A) H+
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Ca2+
A) H+
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the function of proton pumps localized in the plant plasma membrane?
A) to transfer phosphorus groups from ATP to proteins
B) to transfer metal ions across the plasma membrane
C) to transfer anions across the plasma membrane
D) to create a membrane potential
A) to transfer phosphorus groups from ATP to proteins
B) to transfer metal ions across the plasma membrane
C) to transfer anions across the plasma membrane
D) to create a membrane potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which structure or compartment is separate from the apoplastic transport route?
A) the lumen of a xylem vessel
B) the lumen of a sieve tube
C) the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D) the cell wall of a root hair
A) the lumen of a xylem vessel
B) the lumen of a sieve tube
C) the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D) the cell wall of a root hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following best predicts the movement of water across biological membranes?
A) prevailing weather conditions
B) aquaporins
C) level of active transport
D) water potentials
A) prevailing weather conditions
B) aquaporins
C) level of active transport
D) water potentials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following does not correctly match the form with its function?
A) stem-water and minerals are transported upward
B) xylem sap-transport water and nutrients from roots to shoots upward
C) stomata-loss of water by transpiration
D) root hairs-decrease surface area in contact with the soil
A) stem-water and minerals are transported upward
B) xylem sap-transport water and nutrients from roots to shoots upward
C) stomata-loss of water by transpiration
D) root hairs-decrease surface area in contact with the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in plants?
A) a difference in solute concentrations
B) receptor proteins in the membrane
C) aquaporins
D) a difference in water potential
A) a difference in solute concentrations
B) receptor proteins in the membrane
C) aquaporins
D) a difference in water potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The leaf area index is described by which of the following ratios?
A) upper leaf surface of a single plant divided by the surface area of the land on which the plant grows
B) lower leaf surface of a single plant divided by the total surface area of leaves on the plant
C) upper leaf surface of a single plant multiplied by the surface area of the land on which the plant grows
D) lower leaf surface of a single plant multiplied by the total surface area of leaves on the plant
A) upper leaf surface of a single plant divided by the surface area of the land on which the plant grows
B) lower leaf surface of a single plant divided by the total surface area of leaves on the plant
C) upper leaf surface of a single plant multiplied by the surface area of the land on which the plant grows
D) lower leaf surface of a single plant multiplied by the total surface area of leaves on the plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The apoplast in plant tissues may include which of the following?
A) cell walls, extracellular spaces, and plasmodesmata
B) cell walls, extracellular spaces, and vessel elements
C) vessel elements, plasmodesmata, and extracellular spaces
D) cell walls, plasma membrane, and cytosol
A) cell walls, extracellular spaces, and plasmodesmata
B) cell walls, extracellular spaces, and vessel elements
C) vessel elements, plasmodesmata, and extracellular spaces
D) cell walls, plasma membrane, and cytosol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following terms describes the physical property that predicts the direction of water flow in plants?
A) potassium pump
B) water potential
C) osmotic potential
D) sodium pump
A) potassium pump
B) water potential
C) osmotic potential
D) sodium pump

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following played a critical role in water absorption necessary for the successful colonization of land by plants?
A) ground tissue
B) bacterial association
C) mycorrhizae
D) cuticle on leaf surface
A) ground tissue
B) bacterial association
C) mycorrhizae
D) cuticle on leaf surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following accurately describes the direction phloem sap can flow?
A) from leaves to stems only
B) from stems to leaves only
C) from leaves to roots only
D) from leaves to roots or roots to leaves
A) from leaves to stems only
B) from stems to leaves only
C) from leaves to roots only
D) from leaves to roots or roots to leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If isolated plant cells with a water potential averaging -0.5 MPa are placed into a solution with a water potential of -0.3 MPa which of the following would be the most likely outcome?
A) The pressure potential of the cells would increase.
B) Water would move out of the cells.
C) The cell walls would rupture, killing the cells.
D) Solutes would move out of the cells.
A) The pressure potential of the cells would increase.
B) Water would move out of the cells.
C) The cell walls would rupture, killing the cells.
D) Solutes would move out of the cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The value for Ψ in root tissue was found to be -0.15 MPa If the root tissue were placed in a 0.1 M solution of sucrose (Ψ = -0.23 MPa) the net water flow will be in which of the following directions?
A) from the tissue into the sucrose solution
B) from the sucrose solution into the tissue
C) in both directions, and the concentration of water would remain equal
D) impossible to determine from the values given here
A) from the tissue into the sucrose solution
B) from the sucrose solution into the tissue
C) in both directions, and the concentration of water would remain equal
D) impossible to determine from the values given here

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given that early land plants most likely share a common ancestor with green algae, the earliest land plants most likely belonged to which of the following categories?
A) nonvascular plants that grew leafless, photosynthetic shoots
B) nonvascular plants with well-developed diploid bodies
C) vascular plants with well-defined root systems
D) nonvascular plants with well-developed leaves
A) nonvascular plants that grew leafless, photosynthetic shoots
B) nonvascular plants with well-developed diploid bodies
C) vascular plants with well-defined root systems
D) nonvascular plants with well-developed leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The phyllotaxy of mature shoots can be described by a phyllotactic fraction where the numerator indicates the number of times you must go around the stem to get to another leaf directly above (or below) the starting leaf and the denominator indicates the number of leaves passed through to get back in-line with the starting leaf. These two numbers can also be used to calculate the angle between successive leaves. The most common patterns are summarized in the table below.

What is an advantage to plants as the numbers of leaves passed through increase?
A) The shoot apex will get larger as it produces larger numbers of leaves.
B) The number of leaves passed through will always increase at a faster rate than the number of times around the stem so there will be more photosynthesis.
C) The phyllotactic fraction is random, so a "counting mechanism" is not necessary.
D) The angle between leaves approaches 137.5o which minimizes shading of lower leaves by upper leaves.

What is an advantage to plants as the numbers of leaves passed through increase?
A) The shoot apex will get larger as it produces larger numbers of leaves.
B) The number of leaves passed through will always increase at a faster rate than the number of times around the stem so there will be more photosynthesis.
C) The phyllotactic fraction is random, so a "counting mechanism" is not necessary.
D) The angle between leaves approaches 137.5o which minimizes shading of lower leaves by upper leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When an animal cell is placed in a hypotonic solution and water enters the cell via osmosis, the volume of the cell increases until it bursts. Which of the following explains why this does not happen to plant cells?
A) they have large central vacuoles, which provide abundant space for storage of incoming water
B) they have cell walls, which prevent the entry of water by osmosis
C) they have cell walls, which provide pressure to counteract the pressure of the incoming water
D) certain gated channel proteins embedded in their plasma membranes open as osmotic pressure decreases, allowing excess water to leave the cell
A) they have large central vacuoles, which provide abundant space for storage of incoming water
B) they have cell walls, which prevent the entry of water by osmosis
C) they have cell walls, which provide pressure to counteract the pressure of the incoming water
D) certain gated channel proteins embedded in their plasma membranes open as osmotic pressure decreases, allowing excess water to leave the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following contribute to the surface area available for water absorption from the soil by a plant root system?
I) root hairs
II) endodermis
III) mycorrhizae
IV) branching
A) II and III
B) I, III, and IV
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, II, III, and IV
I) root hairs
II) endodermis
III) mycorrhizae
IV) branching
A) II and III
B) I, III, and IV
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following observations provides the strongest evidence against root pressure being the principal mechanism of water transport in the xylem?
A) Not all soils have high concentrations of ions.
B) Root pressure requires movement of water into the xylem from surrounding cells in the roots.
C) Over long distances, the force of root pressure is not enough to overcome the force of gravity.
D) There is no water potential gradient between roots and shoots.
A) Not all soils have high concentrations of ions.
B) Root pressure requires movement of water into the xylem from surrounding cells in the roots.
C) Over long distances, the force of root pressure is not enough to overcome the force of gravity.
D) There is no water potential gradient between roots and shoots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The value for Ψ in root tissue was found to be -0.15 MPA. Which of the following best describes water flow if the root tissue was placed it in a 0.1 M solution of sucrose (Ψ = -0.23 MPa)?
A) Water would flow from the tissue into the sucrose solution.
B) Water would flow from the sucrose solution into the tissue.
C) Water would flow in both directions and the concentrations would remain equal.
D) Water would flow only if ATP was hydrolyzed in the tissue.
A) Water would flow from the tissue into the sucrose solution.
B) Water would flow from the sucrose solution into the tissue.
C) Water would flow in both directions and the concentrations would remain equal.
D) Water would flow only if ATP was hydrolyzed in the tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following are important components of long-distance transport process in xylem?
I) the cohesion of water molecules
II) a negative water potential
III) the active transport of solutes
IV) bulk flow from source to sink
A) I and II only
B) 1 and III only
C) I, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV
I) the cohesion of water molecules
II) a negative water potential
III) the active transport of solutes
IV) bulk flow from source to sink
A) I and II only
B) 1 and III only
C) I, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Long-distance transport in phloem requires which of the following processes?
I) a positive water potential
II) active transport through parenchyma cells
III) cohesion between water molecules
IV) evaporation of water molecules
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, II, III, and IV
I) a positive water potential
II) active transport through parenchyma cells
III) cohesion between water molecules
IV) evaporation of water molecules
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The graph below shows daily water potential in the xylem of a woody plant. Which of the following statements is best supported using the data? 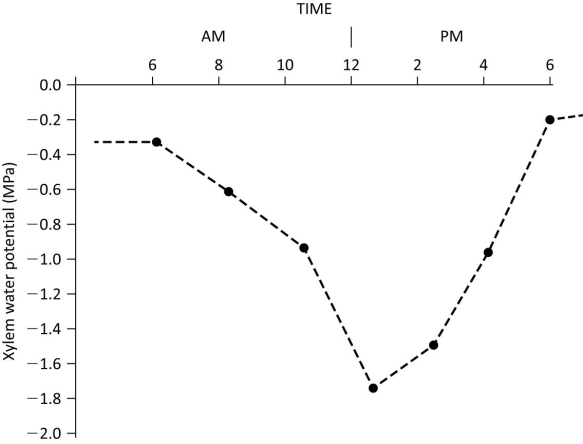
A) Water potential decreases, beginning around 6 am, because of increased mineral uptake.
B) High water potential results in greater transpiration.
C) Water potential at noon is a reflection of high rates of transpiration.
D) Increasing pressure potential after noon results in decreasing water potential.

A) Water potential decreases, beginning around 6 am, because of increased mineral uptake.
B) High water potential results in greater transpiration.
C) Water potential at noon is a reflection of high rates of transpiration.
D) Increasing pressure potential after noon results in decreasing water potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How does the same cell differ if it is a flaccid cell compared to a turgid cell?
A) The flaccid cell has higher pressure potential.
B) The flaccid cell has lower pressure potential.
C) The flaccid cell has higher solute potential.
D) The flaccid cell has lower solute potential.
A) The flaccid cell has higher pressure potential.
B) The flaccid cell has lower pressure potential.
C) The flaccid cell has higher solute potential.
D) The flaccid cell has lower solute potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If Ψ P = 0.3 MPa and ΨS = -0.45 MPa what will be the resulting Ψ?
A) +0.75 MPa
B) -0.75 MPa
C) -0.15 MPa
D) +0.15 MPa
A) +0.75 MPa
B) -0.75 MPa
C) -0.15 MPa
D) +0.15 MPa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A water molecule could move all the way through a plant from soil to root to leaf to air and pass through a living cell only once. This living cell would be a part of which structure?
A) a guard cell
B) the root epidermis
C) the endodermis
D) the root cortex
A) a guard cell
B) the root epidermis
C) the endodermis
D) the root cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best describes the protoplast?
A) all cell components other than the nucleus
B) all cell components other than the cell membrane
C) only the cytoplasm and nucleus
D) the living part of the cell, including the cell membrane
A) all cell components other than the nucleus
B) all cell components other than the cell membrane
C) only the cytoplasm and nucleus
D) the living part of the cell, including the cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following describes the Casparian strip in plant roots?
A) it contains dense clusters of plasmodesmata
B) it forms within primary cell walls
C) it contains waxy deposits of cutin
D) it forms an impermeable barrier through the cytoplasm of endodermal cells
A) it contains dense clusters of plasmodesmata
B) it forms within primary cell walls
C) it contains waxy deposits of cutin
D) it forms an impermeable barrier through the cytoplasm of endodermal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Water potential is generally most negative in which of the following parts of a plant?
A) mesophyll cells of the leaf
B) xylem vessels in leaves
C) xylem vessels in roots
D) cells of the root cortex
A) mesophyll cells of the leaf
B) xylem vessels in leaves
C) xylem vessels in roots
D) cells of the root cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Compared to a cell with few aquaporins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporins will have which of the following?
A) a faster rate of osmosis
B) a lower water potential
C) a higher water potential
D) a faster rate of active transport
A) a faster rate of osmosis
B) a lower water potential
C) a higher water potential
D) a faster rate of active transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following defines the loss of water from the aerial parts of plants?
A) homeostasis
B) respiration
C) gas exchange
D) transpiration
A) homeostasis
B) respiration
C) gas exchange
D) transpiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Under which of the following conditions would guttation be most likely to occur?
A) transpiration rates are high
B) root pressure exceeds transpiration pull
C) the preceding evening was hot, windy, and dry
D) roots are not absorbing minerals from the soil
A) transpiration rates are high
B) root pressure exceeds transpiration pull
C) the preceding evening was hot, windy, and dry
D) roots are not absorbing minerals from the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the overall charge on the cytoplasmic side of a plant cell plasma membrane?
A) positive
B) negative
C) neutral
D) variable, depending on co-transport
A) positive
B) negative
C) neutral
D) variable, depending on co-transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Most of the water absorbed by a plant is used for what purpose?
A) as a solvent for reactions
B) as a hydrogen source in photosynthesis
C) to replace water lost during transpiration
D) to keep cells turgid
A) as a solvent for reactions
B) as a hydrogen source in photosynthesis
C) to replace water lost during transpiration
D) to keep cells turgid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which process provides the main force driving water within xylem vessels?
A) active transport of ions into the stele
B) evaporation of water through stoma
C) the force of root pressure
D) osmosis in the root
A) active transport of ions into the stele
B) evaporation of water through stoma
C) the force of root pressure
D) osmosis in the root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If you place a flaccid plant cell in pure water, which of the following will occur?
A) Water will not enter the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and low water potential.
B) Water enters the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and low water potential.
C) Water enters the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and high water potential.
D) Water will not enter the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and high water potential.
A) Water will not enter the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and low water potential.
B) Water enters the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and low water potential.
C) Water enters the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and high water potential.
D) Water will not enter the cell because the flaccid cell has solutes and high water potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following supports the finding that sugar translocation in phloem is an active (energy-requiring) process?
A) Sucrose occurs in higher concentrations in companion cells than in the mesophyll cells where it is produced.
B) Movement of water occurs from xylem to phloem and back again.
C) Strong pH differences exist between the cytoplasm of the companion cell and the mesophyll cell.
D) ATPases are abundant in the plasma membranes of the mesophyll cells.
A) Sucrose occurs in higher concentrations in companion cells than in the mesophyll cells where it is produced.
B) Movement of water occurs from xylem to phloem and back again.
C) Strong pH differences exist between the cytoplasm of the companion cell and the mesophyll cell.
D) ATPases are abundant in the plasma membranes of the mesophyll cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Plants adapted to arid environments are described as which of the following?
A) mesophytes
B) xerophytes
C) hydrophytes
D) halophytes
A) mesophytes
B) xerophytes
C) hydrophytes
D) halophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The water lost during transpiration is a negative side effect of the plant's requirement for gas exchange. Which of the following is a positive effect of this water loss?
A) increased turgor and increased growth
B) increased mineral transport and increased growth
C) evaporative cooling and increased turgor
D) evaporative cooling and increased mineral transport
A) increased turgor and increased growth
B) increased mineral transport and increased growth
C) evaporative cooling and increased turgor
D) evaporative cooling and increased mineral transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following best explains decreased photosynthesis in wilted leaves?
A) the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded
B) flaccid mesophyll cells are incapable of photosynthesis
C) stomata close, preventing carbon dioxide from entering the leaf
D) accumulation of carbon dioxide in the leaf inhibits enzymes
A) the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded
B) flaccid mesophyll cells are incapable of photosynthesis
C) stomata close, preventing carbon dioxide from entering the leaf
D) accumulation of carbon dioxide in the leaf inhibits enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following best describes why water flows into the source end of a sieve tube?
A) sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic
B) water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water
C) the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water
D) sucrose has been transported out of the sieve tube by active transport, making it hypotonic
A) sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic
B) water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water
C) the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water
D) sucrose has been transported out of the sieve tube by active transport, making it hypotonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following experimental procedures would most likely reduce transpiration while allowing the normal growth of a plant?
A) subjecting the leaves of the plant to a partial vacuum
B) increasing the level of carbon dioxide around the plant
C) putting the plant in drier soil
D) decreasing the relative humidity around the plant
A) subjecting the leaves of the plant to a partial vacuum
B) increasing the level of carbon dioxide around the plant
C) putting the plant in drier soil
D) decreasing the relative humidity around the plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The flux of which one of the following ions plays a dominant role in adjusting the turgor of guard cells during the opening and closing of stomata?
A) H+
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Ca2+
A) H+
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Several tomato plants are growing in a small garden plot. If soil water potential were to drop significantly on a hot, summer afternoon, which of the following would most likely occur?
A) Size of stomatal openings would decrease.
B) Transpiration would increase.
C) The leaves would become more turgid.
D) The uptake of carbon dioxide would be enhanced.
A) Size of stomatal openings would decrease.
B) Transpiration would increase.
C) The leaves would become more turgid.
D) The uptake of carbon dioxide would be enhanced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following primarily enters a plant somewhere other than through the roots?
A) carbon dioxide
B) nitrogen
C) potassium
D) water
A) carbon dioxide
B) nitrogen
C) potassium
D) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the advantage of having small, needlelike leaves?
A) increased transpiration rate
B) decreased transpiration rate
C) increased efficiency of light capture
D) decreased efficiency of light capture
A) increased transpiration rate
B) decreased transpiration rate
C) increased efficiency of light capture
D) decreased efficiency of light capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following statements about the transport of nutrients in phloem is correct?
A) Solute particles are actively transported from phloem at the source.
B) Companion cells control the rate and direction of movement of phloem sap.
C) Differences in osmotic concentration at the source and sink cause a hydrostatic pressure gradient to be formed.
D) A sink is the part of a plant where a particular solute is produced.
A) Solute particles are actively transported from phloem at the source.
B) Companion cells control the rate and direction of movement of phloem sap.
C) Differences in osmotic concentration at the source and sink cause a hydrostatic pressure gradient to be formed.
D) A sink is the part of a plant where a particular solute is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is a net sugar source for a deciduous angiosperm tree?
A) new leaves in early spring
B) fruits in summer
C) roots in early spring
D) roots in early autumn
A) new leaves in early spring
B) fruits in summer
C) roots in early spring
D) roots in early autumn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is a result of the high surface-to-volume ratio of leaves?
A) thick leaves
B) decreased light absorption
C) increased CO2 absorption
D) decreased transpiration
A) thick leaves
B) decreased light absorption
C) increased CO2 absorption
D) decreased transpiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Pressure data, measured from one of the vascular tissue types connecting leaf to root in a 11 m tall tree, is presented in the graph below. 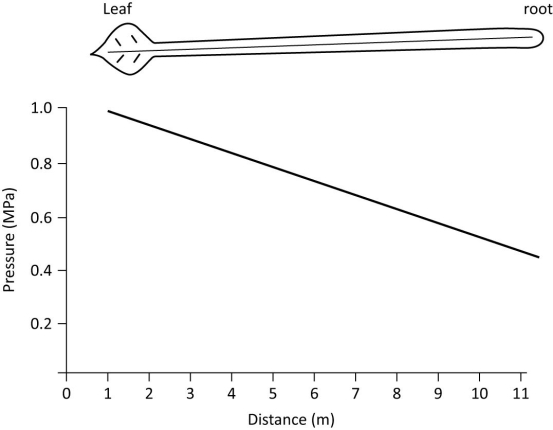 Which of the following is the most appropriate title for this graph?
Which of the following is the most appropriate title for this graph?
A) xylem flow from root to leaf
B) xylem flow from leaf to root
C) phloem flow from root to leaf
D) phloem flow from leaf to root
 Which of the following is the most appropriate title for this graph?
Which of the following is the most appropriate title for this graph?A) xylem flow from root to leaf
B) xylem flow from leaf to root
C) phloem flow from root to leaf
D) phloem flow from leaf to root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following does not contribute to forming the curved upper surface of water inside a narrow tube such as a tracheid or vessel?
A) the downward pull of gravity on the water column in the tube
B) downward pressure from the atmosphere on the topmost layer of water molecules
C) the water molecules adjacent to the tube wall being pulled upward by adhesion to the wall
D) the topmost layer of water molecules being pulled downward by cohesion to the water molecules below
A) the downward pull of gravity on the water column in the tube
B) downward pressure from the atmosphere on the topmost layer of water molecules
C) the water molecules adjacent to the tube wall being pulled upward by adhesion to the wall
D) the topmost layer of water molecules being pulled downward by cohesion to the water molecules below

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The opening of stomata involves which of the following processes?
A) an increase in the solute concentration of the guard cells
B) active transport of water out of the guard cells
C) decreased turgor pressure in guard cells
D) movement of K+ from the guard cells
A) an increase in the solute concentration of the guard cells
B) active transport of water out of the guard cells
C) decreased turgor pressure in guard cells
D) movement of K+ from the guard cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Xerophytes employ a number of different strategies to survive in very dry environments. The following table summarizes average stomatal densities from desert plants with four different ecological strategies.
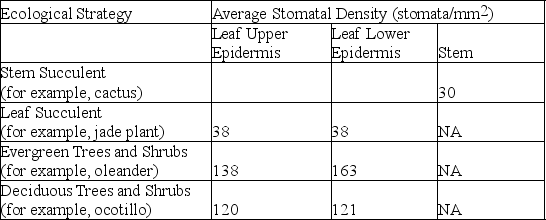
Based on the data, plants adopting which ecological strategy are most likely to have stomata sunken below the epidermis or in crypts?
A) stem succulents
B) leaf succulents
C) evergreen trees and shrubs
D) deciduous trees and shrubs

Based on the data, plants adopting which ecological strategy are most likely to have stomata sunken below the epidermis or in crypts?
A) stem succulents
B) leaf succulents
C) evergreen trees and shrubs
D) deciduous trees and shrubs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Arrange the following five events in an order that explains the mass flow of materials in the phloem.
1) Water diffuses into the sieve tubes.
2) Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis.
3) Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes.
4) Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf.
5) Sugar moves down the stem.
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 4, 3, 1, 5
C) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5
D) 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
1) Water diffuses into the sieve tubes.
2) Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis.
3) Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes.
4) Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf.
5) Sugar moves down the stem.
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 4, 3, 1, 5
C) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5
D) 2, 4, 1, 3, 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Based on the figure, at what time of day is the concentration of the hormone ABA most likely to be highest? 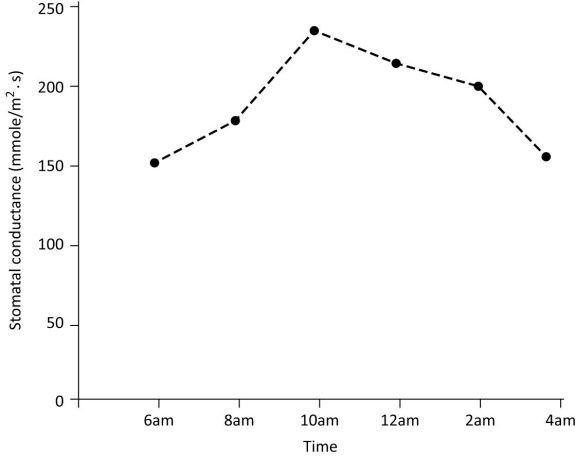
A) 8 am
B) 10 am
C) 12 pm
D) 4 pm

A) 8 am
B) 10 am
C) 12 pm
D) 4 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Ignoring all other factors, what weather conditions would result in the fastest delivery of water and minerals to the leaves of an oak tree?
A) a cool, dry day
B) a warm, dry day
C) a warm, humid day
D) a cool, humid day
A) a cool, dry day
B) a warm, dry day
C) a warm, humid day
D) a cool, humid day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Movement of phloem sap from a source to a sink ________.
A) occurs through the apoplast of sieve-tube elements
B) depends ultimately on the activity of proton pumps
C) depends on tension, or negative pressure potential
D) results mainly from diffusion
A) occurs through the apoplast of sieve-tube elements
B) depends ultimately on the activity of proton pumps
C) depends on tension, or negative pressure potential
D) results mainly from diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compared with a cell with few aquaporin proteins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporin proteins will ________.
A) have a faster rate of osmosis
B) have a lower water potential
C) have a higher water potential
D) accumulate water by active transport
A) have a faster rate of osmosis
B) have a lower water potential
C) have a higher water potential
D) accumulate water by active transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which structure or compartment is part of the symplast?
A) the interior of a vessel element
B) the interior of a sieve tube
C) the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D) an extracellular air space
A) the interior of a vessel element
B) the interior of a sieve tube
C) the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D) an extracellular air space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the pressure-flow mechanism, loading of sucrose from companion cells to sieve-tube elements requires which of the following?
A) plasmodesmata
B) facilitated diffusion
C) sucrose-K+ symporters
D) sucrose-H+ antiporters
A) plasmodesmata
B) facilitated diffusion
C) sucrose-K+ symporters
D) sucrose-H+ antiporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is an adaptation that enhances the uptake of water and minerals by roots?
A) mycorrhizae
B) pumping through plasmodesmata
C) active uptake by vessel elements
D) rhythmic contractions by cells in the root cortex
A) mycorrhizae
B) pumping through plasmodesmata
C) active uptake by vessel elements
D) rhythmic contractions by cells in the root cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The symplastic route can transport which of the following?
A) sugars, mRNA, and mitochondria
B) mRNA, mitochondria, and proteins
C) mitochondria, mRNA, and viruses
D) viruses, sugars, and mRNA
A) sugars, mRNA, and mitochondria
B) mRNA, mitochondria, and proteins
C) mitochondria, mRNA, and viruses
D) viruses, sugars, and mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What would enhance water uptake by a plant cell?
A) decreasing the C of the surrounding solution
B) positive pressure on the surrounding solution
C) the loss of solutes from the cell
D) increasing the C of the cytoplasm
A) decreasing the C of the surrounding solution
B) positive pressure on the surrounding solution
C) the loss of solutes from the cell
D) increasing the C of the cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a water molecule in a plant did "circulate" (that is, go from one point in a plant to another and back in the same day), it would require the activity of which of the following?
A) only the xylem
B) only the phloem
C) only the endodermis
D) both the xylem and the phloem
A) only the xylem
B) only the phloem
C) only the endodermis
D) both the xylem and the phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following would tend to increase transpiration?
A) spiny leaves
B) sunken stomata
C) a thicker cuticle
D) higher stomatal density
A) spiny leaves
B) sunken stomata
C) a thicker cuticle
D) higher stomatal density

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Plasmodesmata can change in number and, when dilated, can provide a passageway for which of the following?
A) macromolecules
B) ribosomes
C) chloroplasts
D) mitochondria
A) macromolecules
B) ribosomes
C) chloroplasts
D) mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a correct statement about sugar movement in phloem?
A) Diffusion can account for the observed rates of transport.
B) Movement can occur both upward and downward in the plant.
C) Sugar is translocated from sinks to sources.
D) Only phloem cells with nuclei can perform sugar movement.
A) Diffusion can account for the observed rates of transport.
B) Movement can occur both upward and downward in the plant.
C) Sugar is translocated from sinks to sources.
D) Only phloem cells with nuclei can perform sugar movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because ________.
A) the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded
B) accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes
C) stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf
D) photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency
A) the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded
B) accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes
C) stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf
D) photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A plant cell with a Cs of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a Cs of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a ________.
A) Cp of +0.65 MPa
B) C of -0.65 MPa
C) Cp of +0.35 MPa
D) Cp of 0 MPa
A) Cp of +0.65 MPa
B) C of -0.65 MPa
C) Cp of +0.35 MPa
D) Cp of 0 MPa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



