Deck 52: Behavioral Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 52: Behavioral Ecology
1
A stickleback fish will attack a fish model as long as the model has red coloring. Which of the following is illustrated by this observation?
A) sign stimulus
B) cognition
C) imprinting
D) classical conditioning
A) sign stimulus
B) cognition
C) imprinting
D) classical conditioning
A
2
Which of the following describes a way that some birds can navigate on an overcast night with solid cloud cover?
A) by detecting ultraviolet light from stars that penetrates the cloud cover
B) by detecting the Earth's rotation
C) by detecting the magnetic field of the Earth
D) by following rivers and major highways
A) by detecting ultraviolet light from stars that penetrates the cloud cover
B) by detecting the Earth's rotation
C) by detecting the magnetic field of the Earth
D) by following rivers and major highways
C
3
A cage containing male mosquitoes has a small earphone placed on top, through which the sound of a female mosquito is played. All the males immediately fly near the earphone and display behaviors associated with copulation. What is the best explanation for this behavior?
A) Copulation is a fixed action pattern, and the female flight sound is a sign stimulus that initiates it.
B) The sound from the earphone irritates the male mosquitoes, causing them to attempt to sting it.
C) The reproductive drive is so strong that when males are deprived of females, they will attempt to mate with anything that has even the slightest female characteristic.
D) Through classical conditioning, the male mosquitoes have associated the inappropriate stimulus from the earphone with the normal response of copulation.
A) Copulation is a fixed action pattern, and the female flight sound is a sign stimulus that initiates it.
B) The sound from the earphone irritates the male mosquitoes, causing them to attempt to sting it.
C) The reproductive drive is so strong that when males are deprived of females, they will attempt to mate with anything that has even the slightest female characteristic.
D) Through classical conditioning, the male mosquitoes have associated the inappropriate stimulus from the earphone with the normal response of copulation.
A
4
During a field trip, an instructor touched a moth resting on a tree trunk. The moth raised its forewings to reveal large eyespots on its hind wings. The instructor asked the students why the moth lifted its wings. One student answered that sensory receptors had fired and triggered a neuronal reflex culminating in the contraction of certain muscles. A second student responded that the behavior might frighten predators. Which of the following best characterizes these hypotheses?
A) The first explanation is correct, but the second is incorrect.
B) The first explanation refers to proximate causation, whereas the second refers to ultimate causation.
C) The first explanation is testable as a scientific hypothesis, whereas the second is not.
D) Both explanations are reasonable and simply represent a difference of opinion.
A) The first explanation is correct, but the second is incorrect.
B) The first explanation refers to proximate causation, whereas the second refers to ultimate causation.
C) The first explanation is testable as a scientific hypothesis, whereas the second is not.
D) Both explanations are reasonable and simply represent a difference of opinion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What type of communication is used by nocturnal and diurnal birds and mammals?
A) auditory
B) visual
C) olfactory
D) electromagnetic
A) auditory
B) visual
C) olfactory
D) electromagnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following usually influences circannual rhythms in birds?
A) periods of food availability
B) periods of daylight and darkness
C) magnetic fields
D) lunar cycles
A) periods of food availability
B) periods of daylight and darkness
C) magnetic fields
D) lunar cycles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following figures to answer the question. 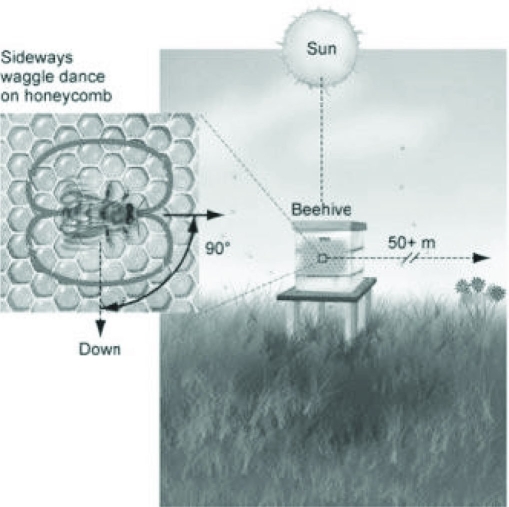 From the figures, what can we determine about the location of the food sources?
From the figures, what can we determine about the location of the food sources?
A) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is directly under the hive.
B) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is about the height of the hive.
C) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is close to the hive.
D) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is 90° to the right of the sun.
 From the figures, what can we determine about the location of the food sources?
From the figures, what can we determine about the location of the food sources?A) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is directly under the hive.
B) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is about the height of the hive.
C) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is close to the hive.
D) The waggle dance in the figure indicates that the food is 90° to the right of the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following types of sensory signals is long-lasting and works during both day and night?
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) tactile
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) tactile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What does the bobbing of a lizard's dewlap (a colorful flap of skin hanging from the lizard's throat) most likely represent?
A) a stimulus
B) a reflex
C) a signal
D) an innate releasing mechanism
A) a stimulus
B) a reflex
C) a signal
D) an innate releasing mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Many behaviors result from interactions with the environment. Which of the following ultimately modifies all behaviors?
A) hormones
B) evolution
C) pheromones
D) the nervous system
A) hormones
B) evolution
C) pheromones
D) the nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following figures to answer the question. 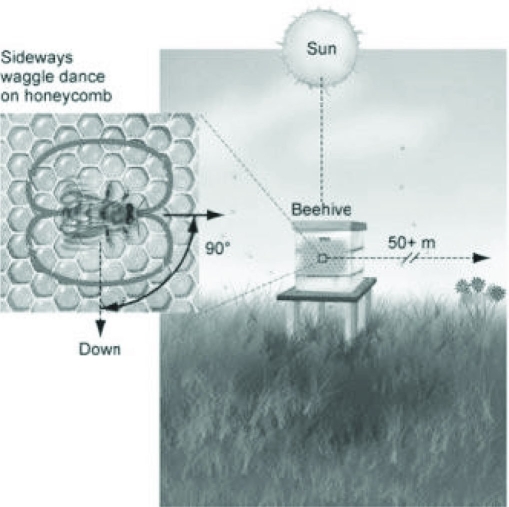 What could you conclude if the honeybee in the figure switched from the "waggle dance" to the "round dance"?
What could you conclude if the honeybee in the figure switched from the "waggle dance" to the "round dance"?
A) The food source is no longer available; all the nectar has been harvested.
B) The preferred food source was farther away than originally communicated.
C) The bee is trying to conserve energy by switching to the round dance.
D) The food source is closer to the hive than originally communicated.
 What could you conclude if the honeybee in the figure switched from the "waggle dance" to the "round dance"?
What could you conclude if the honeybee in the figure switched from the "waggle dance" to the "round dance"?A) The food source is no longer available; all the nectar has been harvested.
B) The preferred food source was farther away than originally communicated.
C) The bee is trying to conserve energy by switching to the round dance.
D) The food source is closer to the hive than originally communicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following types of displays are most effective for communication among nocturnal mammals?
A) visual and auditory
B) tactile and visual
C) olfactory and auditory
D) visual and olfactory
A) visual and auditory
B) tactile and visual
C) olfactory and auditory
D) visual and olfactory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following types of sensory signals is brief and can work at night amongst physical obstructions?
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) magnetic
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) magnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following types of sensory signals is fast and can be detected only in daylight in environments with no physical obstructions?
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) tactile
A) olfactory
B) visual
C) auditory
D) tactile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following examples describes a behavioral pattern that results from a proximate cause?
A) A young cat kills a mouse to obtain nutrients necessary for growth.
B) A male sheep fights with another male to improve his chances of attracting a mate.
C) A female bird lays its eggs when the length of daylight is greater than 12 hours.
D) A sparrow gathers leaves and small twigs to build a nest that will protect her eggs.
A) A young cat kills a mouse to obtain nutrients necessary for growth.
B) A male sheep fights with another male to improve his chances of attracting a mate.
C) A female bird lays its eggs when the length of daylight is greater than 12 hours.
D) A sparrow gathers leaves and small twigs to build a nest that will protect her eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Upon returning to its hive, how does a European honeybee communicate to other worker bees the presence of nearby food sources?
A) they vibrate their wings at varying frequencies
B) they perform a special dance
C) they produce high-frequency tones
D) they flash their wings sending visual cues
A) they vibrate their wings at varying frequencies
B) they perform a special dance
C) they produce high-frequency tones
D) they flash their wings sending visual cues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Squirrels will make alarm sounds when a model of an owl is placed in their territory. When a red block the same size of the owl is placed in the territory, the squirrels show no alarm. Which of the following best explains these observations?
A) The squirrels cannot see red objects, and so do not make alarm sounds.
B) The owl model, but not the red block, triggers the fixed action pattern of alarm vocalizations.
C) The owl model is the ultimate cause of alarm vocalization behavior.
D) The squirrel is trying to attract the owl into its territory.
A) The squirrels cannot see red objects, and so do not make alarm sounds.
B) The owl model, but not the red block, triggers the fixed action pattern of alarm vocalizations.
C) The owl model is the ultimate cause of alarm vocalization behavior.
D) The squirrel is trying to attract the owl into its territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the following figures to answer the question. 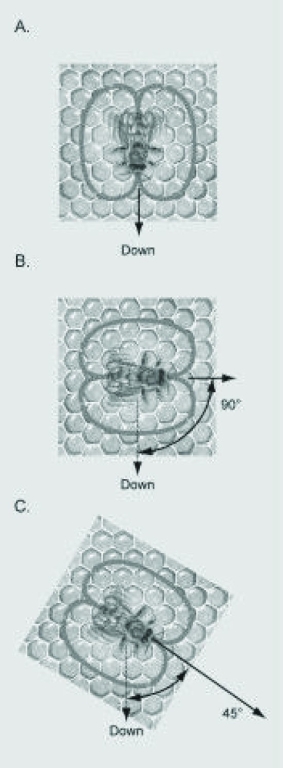 If the figure shows the dances of bees in a hive at noon on June 21 in the northern hemisphere (the sun is directly north of the hive), which dance is communicating that the food is to the south of the hive?
If the figure shows the dances of bees in a hive at noon on June 21 in the northern hemisphere (the sun is directly north of the hive), which dance is communicating that the food is to the south of the hive?
A) dance A
B) dance B
C) dance C
D) It is not possible to tell if any of the dances indicate that the food is to the south of the hive.
 If the figure shows the dances of bees in a hive at noon on June 21 in the northern hemisphere (the sun is directly north of the hive), which dance is communicating that the food is to the south of the hive?
If the figure shows the dances of bees in a hive at noon on June 21 in the northern hemisphere (the sun is directly north of the hive), which dance is communicating that the food is to the south of the hive?A) dance A
B) dance B
C) dance C
D) It is not possible to tell if any of the dances indicate that the food is to the south of the hive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In testing a hypothesis that "territorial defense in European robins is a fixed action pattern that is released by the sight of orange feathers," researchers found that robins defended their territory by attacking a ball that was about the size of a European robin that had an orange patch. Which of the following would be the best test of the hypothesis that the color was the cue that triggered the defense response?
A) Repeat the experiment using a blue patch instead of an orange patch.
B) Cover the eyes of the robin before placing the ball with the orange patch near the bird.
C) Repeat the experiment by using a ball that was twice the diameter and had the original orange patch.
D) Repeat the experiment by using a ball that had an orange patch that was twice the size of the original orange patch.
A) Repeat the experiment using a blue patch instead of an orange patch.
B) Cover the eyes of the robin before placing the ball with the orange patch near the bird.
C) Repeat the experiment by using a ball that was twice the diameter and had the original orange patch.
D) Repeat the experiment by using a ball that had an orange patch that was twice the size of the original orange patch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following would best test the hypothesis that moths stop flying in response to high-intensity bat sounds?
A) Isolate and characterize the neurons that control moth flight muscles.
B) Play recorded high-intensity bat sounds to wild flying moths and record what happens.
C) Observe responses of bats to moths in natural settings.
D) In an enclosure, compare the responses of moths to different models shaped like bats.
A) Isolate and characterize the neurons that control moth flight muscles.
B) Play recorded high-intensity bat sounds to wild flying moths and record what happens.
C) Observe responses of bats to moths in natural settings.
D) In an enclosure, compare the responses of moths to different models shaped like bats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Fred and Joe, two unrelated, mature male gorillas, encounter one another. Fred is courting a female. Fred grunts as Joe comes near. As Joe continues to advance, Fred begins drumming (pounding his chest) and bares his teeth. Joe then rolls on the ground on his back, gets up, and quickly leaves. This behavioral pattern is repeated several times during the mating season. Which of the following is best illustrated by this example?
A) agonistic behavior
B) territorial behavior
C) learned behavior
D) fixed action pattern
A) agonistic behavior
B) territorial behavior
C) learned behavior
D) fixed action pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following types of learning contributes most to the development of culture?
A) social learning
B) associative learning
C) imprinting
D) spatial learning
A) social learning
B) associative learning
C) imprinting
D) spatial learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Scientists have tried raising endangered whooping cranes in captivity by using sandhill cranes as foster parents. Which fact prompted this strategy to be abandoned?
A) the fostered whooping cranes' critical period was variable such that different chicks imprinted on different "mothers"
B) sandhill crane parents rejected their fostered whooping crane chicks soon after incubation
C) none of the fostered whooping cranes formed a pair-bond with a whooping crane mate
D) sandhill crane parents did not properly incubate whooping crane eggs
A) the fostered whooping cranes' critical period was variable such that different chicks imprinted on different "mothers"
B) sandhill crane parents rejected their fostered whooping crane chicks soon after incubation
C) none of the fostered whooping cranes formed a pair-bond with a whooping crane mate
D) sandhill crane parents did not properly incubate whooping crane eggs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A cat runs to its food dish when it hears the sound of a can opener. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A cat runs to its food dish when it hears the sound of a can opener. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Studies, in which researchers compare the behavior of identical twins raised apart with the behavior of twins raised in the same household, are often used to study human behaviors. What types of behavior questions are best addressed by such research using human twins?
A) questions about the influence of genetics and environment on behavior
B) questions about the evolution of culture
C) questions about the influence of geographic location on behavior
D) questions about the role of diet on behavior
A) questions about the influence of genetics and environment on behavior
B) questions about the evolution of culture
C) questions about the influence of geographic location on behavior
D) questions about the role of diet on behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You have captured a number of rats from a wild population and quickly surmise with tests that they are very good at avoiding food with poisons. Which of the following best explains this observation?
A) Rats are probably just intelligent enough to avoid poison.
B) Rats may experience a large variety of toxins in their environment and learn to avoid them.
C) Rats are taught by their parents to test small bits of food first and then return later if the food seems safe.
D) Rats may be able to tolerate large amounts of poison.
A) Rats are probably just intelligent enough to avoid poison.
B) Rats may experience a large variety of toxins in their environment and learn to avoid them.
C) Rats are taught by their parents to test small bits of food first and then return later if the food seems safe.
D) Rats may be able to tolerate large amounts of poison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You discover a rare new bird species, but you are unable to observe its mating behavior. You see that the male is large and ornamental compared with the female. Which of the following is most likely true about this species?
A) It is polygamous.
B) It is monogamous.
C) It is polyandrous.
D) It is agonistic.
A) It is polygamous.
B) It is monogamous.
C) It is polyandrous.
D) It is agonistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the word or phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Every morning at the same time, John went into the den to feed his new tropical fish. After a few weeks, he noticed that the fish swam to the top of the tank when he entered the room. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Every morning at the same time, John went into the den to feed his new tropical fish. After a few weeks, he noticed that the fish swam to the top of the tank when he entered the room. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following examples best reflects the optimal foraging model?
A) During foraging, a mule deer will consume food as soon as it finds it, regardless of the location.
B) A cheetah will continue a chase for prey, regardless of how long the chase lasts or how much energy is consumed.
C) A moose spends more time looking for food when the food is high quality than when the food is low quality.
D) If an animal is hungry it will consume food as soon as it is found, regardless of the food quality or the risk.
A) During foraging, a mule deer will consume food as soon as it finds it, regardless of the location.
B) A cheetah will continue a chase for prey, regardless of how long the chase lasts or how much energy is consumed.
C) A moose spends more time looking for food when the food is high quality than when the food is low quality.
D) If an animal is hungry it will consume food as soon as it is found, regardless of the food quality or the risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When does learning have the most influence on behavior?
A) when making mistakes does not result in death
B) when animals reproduce asexually
C) when animals have enormous cognitive ability
D) when making mistakes results in death
A) when making mistakes does not result in death
B) when animals reproduce asexually
C) when animals have enormous cognitive ability
D) when making mistakes results in death

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the word or phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A human baby performs a sucking behavior very well when it is in the presence of the nipple of its mother's breast. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A human baby performs a sucking behavior very well when it is in the presence of the nipple of its mother's breast. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following describes the process by which white-crowned sparrows learn the "crystallized" song for their species?
A) by listening to adult sparrow songs during a sensitive period as a fledgling, followed by a practice period until the juvenile matches its melody to its memorized fledgling song
B) by listening to the song of its own species during a critical period so that it will imprint to its own species song and not the songs of other songbird species
C) by performing the crystallized song as adults when they become sexually mature, as the song is programmed into the innate behavior for the species
D) by observing and practicing after receiving social confirmation from other adults at a critical period during their first episode of courtship behavior
A) by listening to adult sparrow songs during a sensitive period as a fledgling, followed by a practice period until the juvenile matches its melody to its memorized fledgling song
B) by listening to the song of its own species during a critical period so that it will imprint to its own species song and not the songs of other songbird species
C) by performing the crystallized song as adults when they become sexually mature, as the song is programmed into the innate behavior for the species
D) by observing and practicing after receiving social confirmation from other adults at a critical period during their first episode of courtship behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the word or phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Through trial and error, a rat learns to run a maze without mistakes to receive a food reward. Which of the following mechanisms results in the rat's behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Through trial and error, a rat learns to run a maze without mistakes to receive a food reward. Which of the following mechanisms results in the rat's behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You wake up in the middle of the night to use the restroom. You cannot see a thing in the dark and do not want to turn on lights, disturbing others sleeping near you. You have navigated your way to the restroom from your bed many times, and try to do so again. Which of the following most likely helped you remember your way?
A) social learning
B) associative learning
C) imprinting
D) spatial learning
A) social learning
B) associative learning
C) imprinting
D) spatial learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the word or phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Some dogs love attention, and Frodo the beagle learns that if he barks, he gets attention. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Some dogs love attention, and Frodo the beagle learns that if he barks, he gets attention. Which of the following mechanisms results in this behavior?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An owner of a new restaurant wants to locate near a college campus. Her new Veggie Burger restaurant can locate within 1 mile of campus or more cheaply 2 miles from the campus. But at 2 miles from campus, the restaurant may draw fewer customers. Which of the following behaviors relates best to aspects of the restaurant owner's decision, weighing the cost of the location, the distance from customers, and the profitability of the business?
A) game theory
B) agonistic behavior
C) optimal foraging model
D) factors affecting mate selection
A) game theory
B) agonistic behavior
C) optimal foraging model
D) factors affecting mate selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is a behavior that minimizes the cost of looking for food and maximizes the benefits of finding food?
A) directed foraging
B) cost-benefit consumption
C) offset scavenging
D) optimal foraging
A) directed foraging
B) cost-benefit consumption
C) offset scavenging
D) optimal foraging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One way to understand how early environment influences behaviors in similar species is through the "cross-fostering" experimental technique. Suppose that the curly-whiskered mud rat differs from the bald mud rat in several ways, including being much more aggressive. Which of the following would be the best cross-fostering experiment to determine, if environment plays a role in the curly-whiskered mud rat's aggression?
A) Cross curly-whiskered mud rats and bald mud rats and hand-rear the offspring to see if any grew up to be aggressive.
B) Place newborn curly-whiskered mud rats with bald mud rat parents and place newborn bald mud rats with curly-whiskered mud rat parents. Finally, let some mud rats of both species be raised by their own species. Then you would compare the outcomes.
C) Remove the offspring of curly-whiskered mud rats and bald mud rats from their parents, raise them in the same environment but without parents, and then compare the outcomes.
D) Replace normal newborn mud rats with deformed newborn mud rats to see if it triggered an altruistic response.
A) Cross curly-whiskered mud rats and bald mud rats and hand-rear the offspring to see if any grew up to be aggressive.
B) Place newborn curly-whiskered mud rats with bald mud rat parents and place newborn bald mud rats with curly-whiskered mud rat parents. Finally, let some mud rats of both species be raised by their own species. Then you would compare the outcomes.
C) Remove the offspring of curly-whiskered mud rats and bald mud rats from their parents, raise them in the same environment but without parents, and then compare the outcomes.
D) Replace normal newborn mud rats with deformed newborn mud rats to see if it triggered an altruistic response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Listed below are four types of animal behavior. Choose the letter of the word or phrase (A-D) that is most associated with the following example.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Which of the following mechanisms helps a mother goat recognize its own kid by smell?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting
Which of the following mechanisms helps a mother goat recognize its own kid by smell?
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) innate behavior
D) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You observe scrub jays hiding food and notice that one particular individual only pretends to hide food. Your experiments associate the presence of other scrub jays with the frequency of pretending to cache food. A colleague shows you groups of scrub jays that do not engage in pretend caching. Considering this new information, which of the following is the best hypothesis?
A) Pretending to hide food is learned.
B) The other scrub jays lost this behavior.
C) This was innate behavior in this one scrub jay.
D) This scrub jay learned this behavior from its parents.
A) Pretending to hide food is learned.
B) The other scrub jays lost this behavior.
C) This was innate behavior in this one scrub jay.
D) This scrub jay learned this behavior from its parents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
With which of the following groups would a person collectively share the most alleles?
A) one niece, two first cousins, and a brother
B) two sisters and two nieces
C) one son, one niece, and one first cousin
D) four nieces and one first cousin
A) one niece, two first cousins, and a brother
B) two sisters and two nieces
C) one son, one niece, and one first cousin
D) four nieces and one first cousin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is generally correct about animals that help other animals of the same species?
A) they have excess energy reserves
B) they are bigger and stronger than the other animals
C) they are usually closely related to the other animals
D) they are almost always female
A) they have excess energy reserves
B) they are bigger and stronger than the other animals
C) they are usually closely related to the other animals
D) they are almost always female

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following best describes an important function of the vasopressin receptor gene?
A) It is a master regulatory gene that directs the development of the urogenital system.
B) It controls the courtship ritual of female fruit flies.
C) It programs western garter snake males for appropriate courtship.
D) It affects the post-mating behavior in prairie voles.
A) It is a master regulatory gene that directs the development of the urogenital system.
B) It controls the courtship ritual of female fruit flies.
C) It programs western garter snake males for appropriate courtship.
D) It affects the post-mating behavior in prairie voles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following behaviors is represented by the tit-for-tat strategy of a vampire bat sharing blood with another bat that is not its kin?
A) optimal foraging behavior
B) reciprocal altruism
C) learned behavior
D) agonistic behavior
A) optimal foraging behavior
B) reciprocal altruism
C) learned behavior
D) agonistic behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Natural selection favors altruism when the benefit to the recipient multiplied by the coefficient of relatedness exceeds the cost to the altruist. Which of the following best describes the coefficient of relatedness?
A) It is a measure of the fraction of genes that, on average, are shared between an altruist and the organism that it benefits.
B) It is the number of generations that separate an altruist and the organism that it benefits.
C) It is a measure of the difference in frequencies of altruistic alleles in neighboring populations.
D) It is a measure of the rate of mutations in altruistic alleles.
A) It is a measure of the fraction of genes that, on average, are shared between an altruist and the organism that it benefits.
B) It is the number of generations that separate an altruist and the organism that it benefits.
C) It is a measure of the difference in frequencies of altruistic alleles in neighboring populations.
D) It is a measure of the rate of mutations in altruistic alleles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What correlates with the color of the throats of males in a population of side-blotched lizards?
A) ambient temperature: blue = cold; orange = normal; yellow = hot
B) stage of development/maturity
C) receptiveness to mate
D) the success of the mating behavior of each of the throat-color phenotypes
A) ambient temperature: blue = cold; orange = normal; yellow = hot
B) stage of development/maturity
C) receptiveness to mate
D) the success of the mating behavior of each of the throat-color phenotypes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following best describes "game theory" as it applies to animal behavior?
A) The fitness of a particular behavior is influenced by other behavioral phenotypes in the population.
B) The total of all of the behavioral displays, both male and female, is related to courtship.
C) The play behavior performed by juveniles allows them to practice adult behaviors that are needed for survival, such as hunting, defense, and courtship.
D) The evolutionary "game" is played between predator and prey. A behavior evolves in the prey in response to the nature of the predatory behavior.
A) The fitness of a particular behavior is influenced by other behavioral phenotypes in the population.
B) The total of all of the behavioral displays, both male and female, is related to courtship.
C) The play behavior performed by juveniles allows them to practice adult behaviors that are needed for survival, such as hunting, defense, and courtship.
D) The evolutionary "game" is played between predator and prey. A behavior evolves in the prey in response to the nature of the predatory behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to Hamilton's rule, ________.
A) Natural selection does not favor altruistic behavior that causes the death of the altruist
B) Natural selection favors altruistic acts when the resulting benefit to the recipient, corrected for relatedness, exceeds the cost to the altruist
C) Natural selection is more likely to favor altruistic behavior that benefits an offspring than altruistic behavior that benefits a sibling
D) The effects of kin selection are larger than the effects of direct natural selection on individuals
A) Natural selection does not favor altruistic behavior that causes the death of the altruist
B) Natural selection favors altruistic acts when the resulting benefit to the recipient, corrected for relatedness, exceeds the cost to the altruist
C) Natural selection is more likely to favor altruistic behavior that benefits an offspring than altruistic behavior that benefits a sibling
D) The effects of kin selection are larger than the effects of direct natural selection on individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How do altruistic behaviors arise through natural selection?
A) Altruistic behavior increases the likelihood that the altruist's genes will be represented in the next generation.
B) The altruist is appreciated by other members of the population because its survivability has been enhanced by virtue of its risky behavior.
C) Animals that perform altruistic acts are allowed by their population to breed more, thereby passing on their behavior genes to future generations.
D) Altruistic behaviors lower stress in populations, which increases the survivability of all the members of the population.
A) Altruistic behavior increases the likelihood that the altruist's genes will be represented in the next generation.
B) The altruist is appreciated by other members of the population because its survivability has been enhanced by virtue of its risky behavior.
C) Animals that perform altruistic acts are allowed by their population to breed more, thereby passing on their behavior genes to future generations.
D) Altruistic behaviors lower stress in populations, which increases the survivability of all the members of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following has a coefficient of relatedness of 0.25?
A) a mother to her son
B) an uncle to his nephew
C) a brother to his brother
D) a sister to her brother
A) a mother to her son
B) an uncle to his nephew
C) a brother to his brother
D) a sister to her brother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is a type of natural selection that favors altruism by enhancing the reproductive success of relatives?
A) kin selection
B) artificial selection
C) sexual selection
D) intrasexual selection
A) kin selection
B) artificial selection
C) sexual selection
D) intrasexual selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following treatments is most likely to prevent pair-bonding in a population of prairie voles?
A) disrupting the normal mating system by introducing meadow voles to a prairie vole population
B) administering a drug that inhibits the vasopressin receptor gene
C) dying the coat color from brown to blond in either male or female prairie voles
D) allowing the population size to reach critically low levels
A) disrupting the normal mating system by introducing meadow voles to a prairie vole population
B) administering a drug that inhibits the vasopressin receptor gene
C) dying the coat color from brown to blond in either male or female prairie voles
D) allowing the population size to reach critically low levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The head-butting behavior of male bighorn sheep helps to establish a mating hierarchy. Which of the following is illustrated by this behavior?
A) mate-choice copying
B) sexual dimorphism
C) agonistic behavior
D) polygamy
A) mate-choice copying
B) sexual dimorphism
C) agonistic behavior
D) polygamy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is true of innate behaviors?
A) Their expression is only weakly influenced by genes.
B) They occur with or without environmental stimuli.
C) They are expressed in most individuals in a population.
D) They occur in invertebrates and some vertebrates but not mammals.
A) Their expression is only weakly influenced by genes.
B) They occur with or without environmental stimuli.
C) They are expressed in most individuals in a population.
D) They occur in invertebrates and some vertebrates but not mammals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following figure to answer the question. 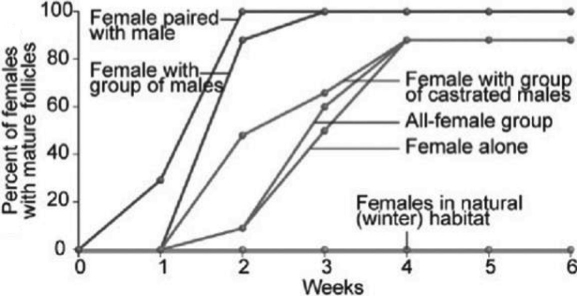 Based only on the information in the figure, which of the following claims is most consistent with the data?
Based only on the information in the figure, which of the following claims is most consistent with the data?
A) Females produce mature follicles more quickly when paired with one or more males.
B) Females produce mature follicles more quickly when exposed to many males than females paired with a male.
C) Isolated females and females with at least one male produce about the same number of mature follicles at about the same time.
D) After four weeks together, females with males produce mature follicles to the same extent as females without males.
 Based only on the information in the figure, which of the following claims is most consistent with the data?
Based only on the information in the figure, which of the following claims is most consistent with the data?A) Females produce mature follicles more quickly when paired with one or more males.
B) Females produce mature follicles more quickly when exposed to many males than females paired with a male.
C) Isolated females and females with at least one male produce about the same number of mature follicles at about the same time.
D) After four weeks together, females with males produce mature follicles to the same extent as females without males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A male stickleback fish will attack other male sticklebacks that invade its nesting territory. It will only attack male fish, which display the red belly characteristic of the species. Which of the following is an ultimate causation of this behavior?
A) The eyes and brain of male sticklebacks are extra sensitive to the color red, leading to the automatic attack of red invaders.
B) The CNS reaction to the color red is a fixed sequence of unlearned acts directly linked to the red invaders.
C) Having a territory increases the chances of attracting a mate and passing along more genes to the next generation.
D) The sight of red stimulates the autonomic nervous system of male sticklebacks, generating an aggressive physiological response to fight.
A) The eyes and brain of male sticklebacks are extra sensitive to the color red, leading to the automatic attack of red invaders.
B) The CNS reaction to the color red is a fixed sequence of unlearned acts directly linked to the red invaders.
C) Having a territory increases the chances of attracting a mate and passing along more genes to the next generation.
D) The sight of red stimulates the autonomic nervous system of male sticklebacks, generating an aggressive physiological response to fight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Upon observing a golden eagle flying overhead, a sentry prairie dog gives a warning call to other foraging members of the prairie dog community. Which of the following behaviors are represented by this example?
A) classical conditioning
B) innate behavior
C) imprinting
D) altruistic behavior
A) classical conditioning
B) innate behavior
C) imprinting
D) altruistic behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following led to the evolution of sexual dimorphism?
A) a monogamous mating system
B) mate-choice copying
C) game selection theory
D) sexual selection
A) a monogamous mating system
B) mate-choice copying
C) game selection theory
D) sexual selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following best explains why coastal and inland garter snakes react differently to banana slug prey?
A) Ancestors of coastal snakes that could detect and eat the abundant banana slugs had increased fitness. No such selection occurred inland, where banana slugs were absent.
B) Banana slugs are camouflaged, and inland snakes, which have poorer vision than coastal snakes, are less able to see them.
C) Garter snakes learn about acceptable prey from other garter snakes. Inland garter snakes are less social and so learn about fewer types of prey.
D) Coastal banana slugs are palatable to garter snakes. Inland banana slugs are distasteful, so inland snakes learn to avoid them.
A) Ancestors of coastal snakes that could detect and eat the abundant banana slugs had increased fitness. No such selection occurred inland, where banana slugs were absent.
B) Banana slugs are camouflaged, and inland snakes, which have poorer vision than coastal snakes, are less able to see them.
C) Garter snakes learn about acceptable prey from other garter snakes. Inland garter snakes are less social and so learn about fewer types of prey.
D) Coastal banana slugs are palatable to garter snakes. Inland banana slugs are distasteful, so inland snakes learn to avoid them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which one of the following statements about mating systems and parental care is true?
A) Monogamy is more common in species of birds that produce young that can care for themselves almost immediately after hatching.
B) Polygyny is more common in animal species that require two parents to feed and protect offspring.
C) High certainty of paternity is correlated with low male parental care in most species of birds and mammals.
D) Fish and amphibians are more likely to provide parental care with external fertilization than internal fertilization.
A) Monogamy is more common in species of birds that produce young that can care for themselves almost immediately after hatching.
B) Polygyny is more common in animal species that require two parents to feed and protect offspring.
C) High certainty of paternity is correlated with low male parental care in most species of birds and mammals.
D) Fish and amphibians are more likely to provide parental care with external fertilization than internal fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A region of the canary forebrain shrinks during the nonbreeding season and enlarges when breeding season begins. This change is probably associated with the annual ________.
A) addition of new syllables to a canary's song repertoire
B) crystallization of subsong into adult songs
C) sensitive period in which canary parents imprint on new offspring
D) elimination of the memorized template for songs sung the previous year
A) addition of new syllables to a canary's song repertoire
B) crystallization of subsong into adult songs
C) sensitive period in which canary parents imprint on new offspring
D) elimination of the memorized template for songs sung the previous year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Although many chimpanzees live in environments with oil palm nuts, members of only a few populations use stones to crack open the nuts. The likely explanation is that ________.
A) the behavioral difference is caused by genetic differences between populations
B) members of different populations have different nutritional requirements
C) the cultural tradition of using stones to crack nuts has arisen in only some populations
D) members of different populations differ in learning ability
A) the behavioral difference is caused by genetic differences between populations
B) members of different populations have different nutritional requirements
C) the cultural tradition of using stones to crack nuts has arisen in only some populations
D) members of different populations differ in learning ability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Female spotted sandpipers aggressively court males and, after mating, leave the clutch of eggs for the male to incubate. This sequence may be repeated several times with different males until no available males remain, forcing the female to incubate her last clutch. Which of the following terms best describes this behavior?
A) polygyny
B) polyandry
C) promiscuity
D) certainty of paternity
A) polygyny
B) polyandry
C) promiscuity
D) certainty of paternity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is not required for a behavioral trait to evolve by natural selection?
A) In each individual, the form of the behavior is determined entirely by genes.
B) The behavior varies among individuals.
C) An individual's reproductive success depends in part on how the behavior is performed.
D) Some component of the behavior is genetically inherited.
A) In each individual, the form of the behavior is determined entirely by genes.
B) The behavior varies among individuals.
C) An individual's reproductive success depends in part on how the behavior is performed.
D) Some component of the behavior is genetically inherited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



