Deck 26: Rational Expectations Redux: Monetary Policy Implications
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Rational Expectations Redux: Monetary Policy Implications
1
During the Revolutionary War in the United States, lack of commitment to lower budget deficits led to higher inflation.
True
2
In the new classical framework, anti-inflationary monetary policy could lead to an increase in output if the policy change was more aggressive than expected.
False
3
To fight inflation, central banks must hold the line on AS.
False
4
The inflationary effect of anticipated EMP is less in the new Keynesian model than in the traditional AS-AD model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under rational expectations, shifts in AS take less time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Central bank independence is the only factor affecting the credibility of anti-inflation policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Starting from the natural rate, if prices are sticky, anticipated EMP will raise equilibrium output and inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If prices (and wages) are flexible and all policy changes are anticipated, there is no distinction between the long run and the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the new classical framework, inflation can be lowered with a credible commitment by monetary policymakers without any decrease in output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Compared to the standard IS-LM model, the new Keynesian model implies that policy changes move equilibrium value in the same direction but at different magnitudes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The short-run effect of unanticipated policy changes is the same for the traditional AS-AD, new Keynesian and new classical models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the new classical framework, fiscal policy is ineffective as long as policy is anticipated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
New Keynesians believe that anticipated policies have some short-term effects due to wage and price stickiness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Longer term contracts between firms and suppliers would tend to make EMP less effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Unlike new Keynesian models, new classical models assume rational expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the new Keynesian model, a credible commitment to lower inflation will cause output to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Credibility of the monetary policymaker is important according to the new Keynesian model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If expectations are rational, the credibility of an anti-inflation announcement reduces the resulting fall in employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
New Keynesian economists believe that EMP cannot increase output above the natural rate in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
New classical economists tend to favor non-activist policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The new Keynesian model assumes price and wages are flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sargent is one of a number of economists who introduced rational expectations into macroeconomic models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an increase in the money supply is less than what was expected, output will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Reputation plays a role in the credibility of a central banker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Lucas stressed the importance of fiscal policy for stabilizing the real economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Wages and prices adjustments are slow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In Bolivia, the creation of an independent central bank was the key factor in reducing inflation in the late 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Unanticipated EMP has ____ effect on output in the new Keynesian model compared to the standard version.
A) a greater
B) less of an
C) the same
D) cannot be determined
A) a greater
B) less of an
C) the same
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If an increase in the federal funds rate is less than what was expected, prices could rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A large change in expectations can cause EMP to lead to a reduction in output if the shift in _____ is not sufficiently large.
A) IS
B) LM
C) AD
D) none of the above
A) IS
B) LM
C) AD
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Activist policy is NOT effective according to which model?
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) It is effective for all of them.
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) It is effective for all of them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A primary cause of inflation during the Revolutionary War was
A) a lack of commitment to reduce budget deficits.
B) a commitment to the gold standard.
C) the government's reputation for allowing high inflation.
D) all of the above.
A) a lack of commitment to reduce budget deficits.
B) a commitment to the gold standard.
C) the government's reputation for allowing high inflation.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An open market sale of bonds could lead to an increase in equilibrium output if the change in the federal funds rate is less than expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the new Keynesian model, expansionary monetary policy can be effective if it is
A) anticipated.
B) unanticipated.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.
A) anticipated.
B) unanticipated.
C) both of the above.
D) neither of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Anticipated EMP has ____ effect on output in the new Keynesian model compared to the standard version.
A) a greater
B) less of an
C) the same
D) cannot be determined
A) a greater
B) less of an
C) the same
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the new Keynesian framework, disinflation policies are costly in terms of lowered output, since expectations are not rational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a central bank announces that it will lower inflation, it is attempting to influence
A) IS.
B) AD.
C) AS.
D) money demand.
A) IS.
B) AD.
C) AS.
D) money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Unanticipated monetary policy designed to reduce inflation would lead to a reduction in employment under which model?
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One danger of using monetary policy to end a recession is that
A) sticky wages will have the purchasing power eroded.
B) prices will rise and workers will demand higher wages.
C) it might not be possible for AD to shift enough.
D) none of the above.
A) sticky wages will have the purchasing power eroded.
B) prices will rise and workers will demand higher wages.
C) it might not be possible for AD to shift enough.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
U.S. economy in the early 1980s gave support for the key assumptions of the new Keynesian model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If autonomous consumption rises more than expected, then output rises under the
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Credibility of an inflation reduction policy does NOT matter in which of the following models?
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the federal funds rates falls less than expected, then output falls under the
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Assuming flexible prices, if the currency depreciates more than anticipated, then equilibrium output should _____ and the equilibrium price level should _____ in the short run.
A) rise, rise
B) rise, fall
C) fall, rise
D) fall, fall
A) rise, rise
B) rise, fall
C) fall, rise
D) fall, fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the new Keynesian model, the cost of disinflation due to lower employment depends on
A) the rationality of expectations.
B) the flexibility of prices.
C) laws regarding unionization.
D) all of the above.
A) the rationality of expectations.
B) the flexibility of prices.
C) laws regarding unionization.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If government spending rises more than anticipated, then equilibrium output should _____ and the equilibrium price level should _____ in the short run.
A) rise, rise
B) rise, fall
C) fall, rise
D) fall, fall
A) rise, rise
B) rise, fall
C) fall, rise
D) fall, fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the new classical model, if the money supply falls less than expected, then the shift to the _____ by AD will be _____ than the shift to the _____ by AS in the short run.
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the major element introduced to macroeconomics models by new classical economists?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The credibility of an anti-inflation announcement depends on
A) the independence of the central bank.
B) past behavior of the central bank.
C) government budget deficits.
D) all of the above.
A) the independence of the central bank.
B) past behavior of the central bank.
C) government budget deficits.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If government spending rises less than expected, then the equilibrium price level rises under the
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.
A) new classical model.
B) new Keynesian model.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Inflation can be reduced by
A) announcing the policy.
B) taking steps to ensure its credibility.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.
A) announcing the policy.
B) taking steps to ensure its credibility.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The disinflation policies of the early 1980s were not costly due to
A) central bank independence.
B) sticky prices.
C) high government budget deficits.
D) all of the above.
A) central bank independence.
B) sticky prices.
C) high government budget deficits.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Unanticipated policy changes do NOT affect equilibrium output in which of the following models?
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) Output is unaffected in all of the above.
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) Output is unaffected in all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Anticipated policy changes have no effect on unemployment in which of the following models?
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above
A) standard Keynesian
B) new classical
C) new Keynesian
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Central bankers can increase their credibility by
A) making the banks more independent.
B) promising to lower taxes.
C) promising to fight inflation.
D) all of the above.
A) making the banks more independent.
B) promising to lower taxes.
C) promising to fight inflation.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Assuming flexible prices, if the federal funds rate rises more than expected, then the shift to the _____ by AD will be _____ than the shift to the _____ by AS in the short run.
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are the implications about the long run under new classical assumptions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assuming flexible prices, if the federal funds rate falls less than expected, then the shift to the _____ by AD will be _____ than the shift to the _____ by AS in the short run.
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If output was above the natural rate and the central bank raised interest rates to shift AD left so output fell back to the natural rate, the AS curve would respond by
A) shifting to the right.
B) shifting to the left.
C) not shifting at all.
D) rotating right
A) shifting to the right.
B) shifting to the left.
C) not shifting at all.
D) rotating right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If taxes rise more than expected, then the shift to the _____ by AD will be _____ than the shift to the _____ by AS in the short run.
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left
A) left, greater, right
B) left, less, right
C) right, greater, left
D) right, less, left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why do new classical economists say that activist policy might be not just ineffective but mistaken?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Show a graph of AS-AD where expansionary monetary policy that does not meet expectations leads to a reduction in output.
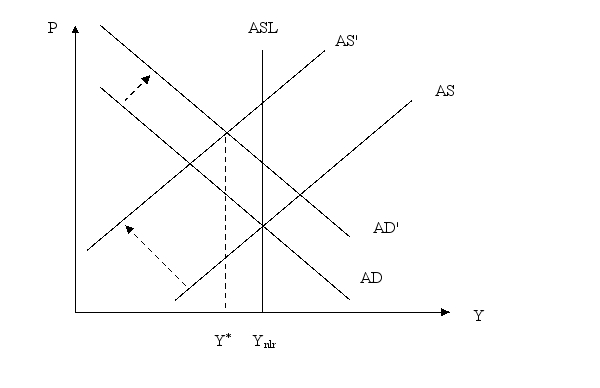


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
At the beginning of the Reagan administration, AS shifted in spite of the Fed's commitment to lower inflation. What does this imply about the labor market and the validity of the new classical assumptions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Some countries use price indexation, meaning many contracts are adjusted for inflation automatically. How would full indexation of all contracts and agreements affect the effectiveness of EMP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use an AS-AD graph to show difference in the short-run effect of EMP in a standard Keynesian and a new Keynesian model.
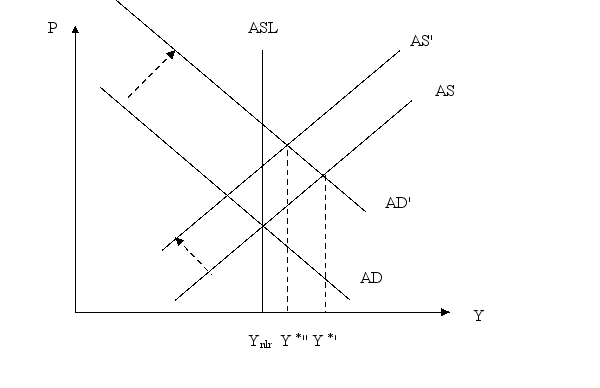


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Starting from the natural rate of output on an AS-AD diagram, show and explain how a new classical economist would recommend using monetary policy to lower the equilibrium price.
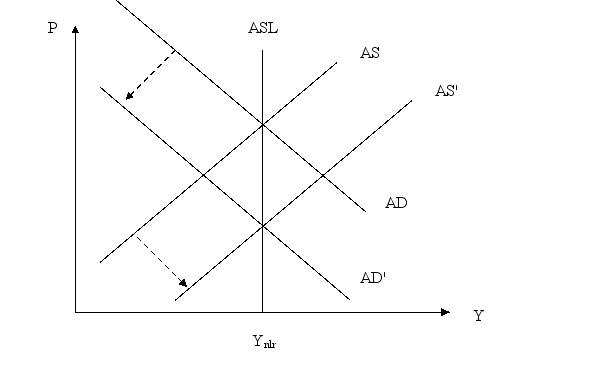


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If output starts below the natural rate, and the central bank reduces the interest rate to shift AD and raise output back to the natural rate, what is the difference in the response of AS under the new Keynesian and new Classical models?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain why the new Keynesian model is less optimistic about curbing inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is a major difference in the conduct of the Fed and the ECB that might affect their credibility as inflation fighters?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



