Deck 22: The Atomic Nucleus
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: The Atomic Nucleus
1
What are isobaric nuclides?
A)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
B)nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
C)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of protons
D)nuclei of different elements with the same number of protons
A)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
B)nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
C)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of protons
D)nuclei of different elements with the same number of protons
nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
2
What are isotopic nuclides?
A)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
B)nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
C)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of protons
D)nuclei of different elements with the same number of protons
A)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
B)nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
C)nuclei of the same element with different numbers of protons
D)nuclei of different elements with the same number of protons
nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
3
Which of these particles is an alpha particle?
A)high energy photon
B)electron
C)positron
D)helium nucleus
A)high energy photon
B)electron
C)positron
D)helium nucleus
helium nucleus
4
How does the mass of an atomic nucleus compare with the sum of masses of its constituent nucleons separated?
A)The mass of a nucleus is larger than the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
B)The mass of a nucleus is smaller than the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
C)The mass of a nucleus is the same as the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
D)The answer depends on the mass number of the element.
A)The mass of a nucleus is larger than the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
B)The mass of a nucleus is smaller than the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
C)The mass of a nucleus is the same as the sum of the masses of individual nucleons.
D)The answer depends on the mass number of the element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the constituents of the atomic nucleus?
A)protons and neutrons
B)protons and electrons
C)photons and neutrons
D)positrons and neutrinos
A)protons and neutrons
B)protons and electrons
C)photons and neutrons
D)positrons and neutrinos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these changes occurs in the nucleus during beta decay?
A)The mass number decreases by 4, and the atomic number decreases by 2.
B)The mass number does not change, but the atomic number changes.
C)The mass number changes, but the atomic number does not change.
D)Neither the mass number nor the atomic number changes.
A)The mass number decreases by 4, and the atomic number decreases by 2.
B)The mass number does not change, but the atomic number changes.
C)The mass number changes, but the atomic number does not change.
D)Neither the mass number nor the atomic number changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the mass number of an atomic nucleus equal to?
A)the number of protons
B)the number of neutrons
C)the number of protons and neutrons
D)the number of electrons
A)the number of protons
B)the number of neutrons
C)the number of protons and neutrons
D)the number of electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many neutrons are in the nucleus of carbon 14C?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)14
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When an isomer decays, which of the following particles does it emit?
A)alpha particles
B)electrons
C)positrons
D)ã-photons
A)alpha particles
B)electrons
C)positrons
D)ã-photons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many protons are in the nucleus of oxygen 16O?
A)4
B)6
C)8
D)16
A)4
B)6
C)8
D)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Initially there are 6000 nuclei of an isotope with a half-life of 3 hours. How many nuclei of that isotope will be left after 12 hours?
A)375
B)750
C)1500
D)3000
A)375
B)750
C)1500
D)3000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these processes does NOT lead to the loss of a nucleon from a nucleus?
A)á-decay
B)â+-decay
C)â--decay
D)electron capture
A)á-decay
B)â+-decay
C)â--decay
D)electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the fraction of nuclei from the initial radioactive sample that have decayed after 3 half-lives?
A)7/8
B)3/4
C)1/2
D)1/8
A)7/8
B)3/4
C)1/2
D)1/8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these particles is a beta particle?
A)high energy photon
B)positron
C)helium atom
D)helium nucleus
A)high energy photon
B)positron
C)helium atom
D)helium nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of these changes occurs in the nucleus during an alpha decay?
A)The mass number decreases by 4, and the atomic number decreases by 2.
B)The mass number does not change, but the atomic number changes.
C)The mass number changes, but the atomic number does not change.
D)Neither the mass number nor the atomic number changes.
A)The mass number decreases by 4, and the atomic number decreases by 2.
B)The mass number does not change, but the atomic number changes.
C)The mass number changes, but the atomic number does not change.
D)Neither the mass number nor the atomic number changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these particles is emitted in gamma decay?
A)high energy photon
B)positron
C)helium atom
D)helium nucleus
A)high energy photon
B)positron
C)helium atom
D)helium nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the atomic number of an atomic nucleus equal to?
A)the number of protons
B)the number of neutrons
C)the number of protons and neutrons
D)the number of electrons
A)the number of protons
B)the number of neutrons
C)the number of protons and neutrons
D)the number of electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these processes does NOT lead to a loss of charge in a nucleus?
A)alpha decay
B)beta decay
C)gamma decay
D)electron capture
A)alpha decay
B)beta decay
C)gamma decay
D)electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How many neutrons are in the nucleus of potassium 40K?
A)20
B)21
C)22
D)40
A)20
B)21
C)22
D)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement accurately describes the binding energy of a nucleus?
A)It is the difference between the masses of separated nucleons and the mass of a nucleus, converted into energy.
B)It is the energy required for a nucleus to bond nucleons.
C)It is equal to the mass of nucleons when converted into energy.
D)It is the difference between the mass of the atom and the mass of the electrons, converted into energy.
A)It is the difference between the masses of separated nucleons and the mass of a nucleus, converted into energy.
B)It is the energy required for a nucleus to bond nucleons.
C)It is equal to the mass of nucleons when converted into energy.
D)It is the difference between the mass of the atom and the mass of the electrons, converted into energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Isotopic nuclides are nuclides with the same atomic number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The transition energy between two states of a spin- 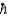 /2 nucleus in an external magnetic field is comparable to the Balmer series of electron transitions between energy states in the atom.
/2 nucleus in an external magnetic field is comparable to the Balmer series of electron transitions between energy states in the atom.
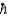 /2 nucleus in an external magnetic field is comparable to the Balmer series of electron transitions between energy states in the atom.
/2 nucleus in an external magnetic field is comparable to the Balmer series of electron transitions between energy states in the atom.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A radioactive sample is left to decay for 4 half-lives. The fraction of the sample that decayed is 1/16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Using Table 22.1, calculate the energy released in the process of uranium decay: 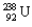 into
into 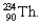
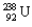 into
into 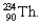

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Calculate the energy released in the process of decay of ![Calculate the energy released in the process of decay of into [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c<sup>2</sup>.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_abe4_bc0b_bbf42b9d4bda_TB8418_11.jpg) into
into ![Calculate the energy released in the process of decay of into [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c<sup>2</sup>.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_abe5_bc0b_81e026acf88e_TB8418_11.jpg) [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2.]
[Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2.]
![Calculate the energy released in the process of decay of into [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c<sup>2</sup>.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_abe4_bc0b_bbf42b9d4bda_TB8418_11.jpg) into
into ![Calculate the energy released in the process of decay of into [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c<sup>2</sup>.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_abe5_bc0b_81e026acf88e_TB8418_11.jpg) [Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2.]
[Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2.]
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Larmor frequency is the angular precession frequency of a nuclear spin in an external magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is the Larmor frequency independent of?
A)the angle between the magnetic dipole moment of the nucleus and the external magnetic field
B)the magnitude of the external magnetic field for a specific nucleus
C)the gyromagnetic ratio
D)the magnetic dipole moment of the nucleus
A)the angle between the magnetic dipole moment of the nucleus and the external magnetic field
B)the magnitude of the external magnetic field for a specific nucleus
C)the gyromagnetic ratio
D)the magnetic dipole moment of the nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nuclear force, like the electric force, acts only on charged particles. Neutrons are not affected by nuclear force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using Table 22.1, compare the mass of 12C with the sum of masses of its constituent nucleons, in unit u.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Isotopic nuclides are nuclides with the same mass number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Describe briefly an isomer. What is the difference between 12Cg and 12Cm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An isomer decays by emitting a gamma photon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Current loops act as magnetic dipoles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium?
[Note:![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_d2f8_bc0b_0d804afc83fd_TB8418_11.jpg)
![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_fa09_bc0b_81b599b86a2c_TB8418_11.jpg)
![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_fa0a_bc0b_7b810cef4d2b_TB8418_11.jpg) + e- + v.]
+ e- + v.]
[Note:
![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_d2f8_bc0b_0d804afc83fd_TB8418_11.jpg)
![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_fa09_bc0b_81b599b86a2c_TB8418_11.jpg)
![What is the maximal kinetic energy of an electron (â-particle) in the decay of sodium into magnesium? [Note: + e<sup>-</sup> + v.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8418/11eb7f12_ec74_fa0a_bc0b_7b810cef4d2b_TB8418_11.jpg) + e- + v.]
+ e- + v.]
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using Table 22.1, calculate the binding energy per nucleon of the 14C isotope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The activity of a radioactive sample is a positive or negative value of the decay rate, depending on the radioactive sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The radioactive gas radon has a half-life of 3.8 days. How long will it take for the radon in a basement to decay to 50% of its present level?
A)1.9 days
B)3.8 days
C)7.6 days
D)16.4 days
A)1.9 days
B)3.8 days
C)7.6 days
D)16.4 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Electron capture is the equivalent of a beta radioactive decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
11C, 12C, 13C, and 14C are examples of isobaric nuclides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The half-life is half the time needed for a radioactive sample to completely decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Discuss briefly how transition energy, ÄE, between two states of a spin- 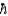 /2 nucleus in an external magnetic field of 1 T (f = 50 MHz) compares to the Balmer series in a H atom, for example, the electron transition between n2 and n3 levels that involves a photon of wavelength ë = 655 nm.
/2 nucleus in an external magnetic field of 1 T (f = 50 MHz) compares to the Balmer series in a H atom, for example, the electron transition between n2 and n3 levels that involves a photon of wavelength ë = 655 nm.
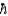 /2 nucleus in an external magnetic field of 1 T (f = 50 MHz) compares to the Balmer series in a H atom, for example, the electron transition between n2 and n3 levels that involves a photon of wavelength ë = 655 nm.
/2 nucleus in an external magnetic field of 1 T (f = 50 MHz) compares to the Balmer series in a H atom, for example, the electron transition between n2 and n3 levels that involves a photon of wavelength ë = 655 nm.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe briefly electron capture and its difference from and similarity to beta decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A decay of 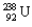 into
into 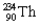 is an example of what type of a decay? What particle is released in the process?
is an example of what type of a decay? What particle is released in the process?
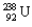 into
into 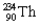 is an example of what type of a decay? What particle is released in the process?
is an example of what type of a decay? What particle is released in the process?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calculate the strength of an NMR magnet if the Larmor frequency of protons in that field is 100 MHz. The gyromagnetic ratio for protons is ã/2ð = 42.58 MHz/T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What kind of decay is the decay of 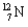 into
into 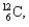 and which particles are being emitted?
and which particles are being emitted?
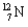 into
into 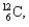 and which particles are being emitted?
and which particles are being emitted?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A child mummy is found high in the Andes, and the archaeologists say that the child lived more than 2000 years ago. What is the fraction of 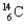 found in the specimen compared to that found in a living body? The half-life of
found in the specimen compared to that found in a living body? The half-life of 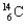 is 5700 years.
is 5700 years.
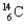 found in the specimen compared to that found in a living body? The half-life of
found in the specimen compared to that found in a living body? The half-life of 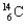 is 5700 years.
is 5700 years.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What kind of decay is the decay of 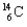 into
into 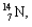 and which particles are being emitted?
and which particles are being emitted?
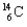 into
into 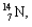 and which particles are being emitted?
and which particles are being emitted?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



