Deck 11: Static Fluids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Static Fluids
1
A wooden log floats in a river (density 1000 kg/m3), with one-quarter above the water, carried toward the sea (density 1025 kg/m3) by the river current. What will be the change in the percentage of the volume of log above water when it comes to the sea?
A)The log will go up 2%.
B)The log will go down 2%.
C)The log will go up 27%.
D)The log will go down 27%.
A)The log will go up 2%.
B)The log will go down 2%.
C)The log will go up 27%.
D)The log will go down 27%.
The log will go up 2%.
2
What is the transmural ratio between a soap bubble of diameter D and another one with double the diameter, 2D?
A)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2 times larger than in the 2D bubble.
B)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2 times smaller than in the 2D bubble.
C)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2ð times larger than in the 2D bubble.
D)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2ð times smaller than in the 2D bubble.
A)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2 times larger than in the 2D bubble.
B)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2 times smaller than in the 2D bubble.
C)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2ð times larger than in the 2D bubble.
D)The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2ð times smaller than in the 2D bubble.
The pressure in a bubble with diameter D is 2 times larger than in the 2D bubble.
3
If, in an unknown liquid, we measure pressure of 1.2 atm at 0.15 m depth, at what depth will the pressure measure 2.4 atm?
A)0.08 m
B)0.30 m
C)1.05 m
D)2.10 m
A)0.08 m
B)0.30 m
C)1.05 m
D)2.10 m
1.05 m
4
A rock is sinking in the water. Which one of these statements correctly describes the buoyant force?
A)It is zero.
B)It is equal to the weight of the wood.
C)It is equal to all the other forces acting on the wood, but opposite in direction.
D)It is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction of the weight of the wood.
A)It is zero.
B)It is equal to the weight of the wood.
C)It is equal to all the other forces acting on the wood, but opposite in direction.
D)It is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction of the weight of the wood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If P is a pressure, ñ density, g gravitational acceleration, and h height (or depth) of a fluid, where is the relationship P = ñgh applicable?
A)only in liquids
B)only in gases
C)only in gases of uniform density (ideal gases)
D)in any type of fluid with uniform density (ideal fluid)
A)only in liquids
B)only in gases
C)only in gases of uniform density (ideal gases)
D)in any type of fluid with uniform density (ideal fluid)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An iceberg has a density 917 kg/m3, and seawater has a density 1025 kg/m3. What fraction of the iceberg is under the surface of the water?
A)9.3%
B)10.5%
C)89.5%
D)90.7%
A)9.3%
B)10.5%
C)89.5%
D)90.7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An air bubble is 50 cm below the surface of a lake. In that case, we assume that the bubble has only one surface to generate surface tension. The gauge pressure inside the bubble is 6.0 × 103 Pa. What is radius of the bubble? (The density of the water is ñH2O = 1000 kg/m3, and the surface tension is ó = 0.073 N/m.)
A)2.6 × 10-4 m
B)1.3 × 10-4 m
C)6.0 × 10-7 m
D)3.0 × 10-7 m
A)2.6 × 10-4 m
B)1.3 × 10-4 m
C)6.0 × 10-7 m
D)3.0 × 10-7 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How far below the surface of water do you need to dive to double the atmospheric pressure? (Note: Atmospheric pressure is Patm = 1.01 × 105 Pa, and density of water is ñ = 1000 kg/m3.)
A)1 m
B)2 m
C)10 m
D)20 m
A)1 m
B)2 m
C)10 m
D)20 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A metal cube fully submerged in water shows an apparent weight of 1.9 N. When completely submerged in acetone, its apparent weight is 2.2 N. What is the length of the side of the cube? (Note: The density of water is ñwater = 1000 kg/m3 and of acetone ñacetone = 784 kg/m3.)
A)5.0 × 10-2 m
B)2.5 × 10-3 m
C)1.4 × 10-4 m
D)We need to know the mass of the cube to calculate the length.
A)5.0 × 10-2 m
B)2.5 × 10-3 m
C)1.4 × 10-4 m
D)We need to know the mass of the cube to calculate the length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What unit is used to measure surface tension?
A)N m
B)Pa
C)kg/s2
D)kg m/s2
A)N m
B)Pa
C)kg/s2
D)kg m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A bucket of water has some ice floating in it. When water freezes into ice, the ice becomes less dense than water, and about 9% of ice volume is above the water. When the ice melts, what happens to the level of water in the bucket?
A)The level will go up 9%.
B)The level will go down 9%.
C)The level will go down more than 9%.
D)The level will remain the same.
A)The level will go up 9%.
B)The level will go down 9%.
C)The level will go down more than 9%.
D)The level will remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 11.1 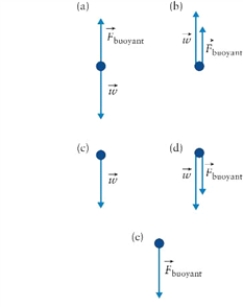
Dolphins are sleeping at the bottom of a cove, floating low above the ocean floor. Which diagram in Fig. 11.1 shows the correct forces acting on the dolphins?
A)diagram (a)
B)diagram (b)
C)diagram (c)
D)diagram (d)

Dolphins are sleeping at the bottom of a cove, floating low above the ocean floor. Which diagram in Fig. 11.1 shows the correct forces acting on the dolphins?
A)diagram (a)
B)diagram (b)
C)diagram (c)
D)diagram (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 0.25 kg balloon is filled with helium. If the balloon is a sphere with a radius of 4 m, what is the maximum number of standard men it can lift? (Note: The density of air is ñair = 1.20 kg/m3 and of helium ñhelium = 0.179 kg/m3; standard man has a mass of 70 kg.)
A)3 standard men
B)4 standard men
C)6 standard men
D)38 standard men
A)3 standard men
B)4 standard men
C)6 standard men
D)38 standard men

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a glass of water, an olive sits atop a cube of ice. When the olive falls and sinks in the water, what happens to the level of water in the glass?
A)The level will go up.
B)The level will go down.
C)The level will remain the same.
D)We need to know the mass of the olive to answer.
A)The level will go up.
B)The level will go down.
C)The level will remain the same.
D)We need to know the mass of the olive to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What would the perimeter of each foot have to be to enable a standard man (70 kg) to stand on the water on both feet, held up by surface tension? (Note: Surface tension for water ó = 0.073 N/m.)
A)9.3 × 103 m
B)4.7 × 103 m
C)9.6 × 102 m
D)4.8 × 102 m
A)9.3 × 103 m
B)4.7 × 103 m
C)9.6 × 102 m
D)4.8 × 102 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A piece of wood is floating on the water. Which one of these statements correctly describes buoyant force?
A)It is zero.
B)It is equal to the weight of the wood.
C)It is equal to all the other forces acting on the wood, but is opposite in direction.
D)It is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the weight of the wood.
A)It is zero.
B)It is equal to the weight of the wood.
C)It is equal to all the other forces acting on the wood, but is opposite in direction.
D)It is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the weight of the wood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these statements best describes the reason that fish can float in water?
A)The density of fish is higher than the density of water.
B)The weight of fish is higher than the weight of the same volume of water.
C)The density of fish is equal to the density of water.
D)The density of fish is lower than the density of water.
A)The density of fish is higher than the density of water.
B)The weight of fish is higher than the weight of the same volume of water.
C)The density of fish is equal to the density of water.
D)The density of fish is lower than the density of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A body is immersed in a fluid. Which of these statements correctly describes buoyant force?
A)It is equal to the weight of the object.
B)It is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
C)It is equal to the pressure of water below the object.
D)It is equal to the mass of the fluid displaced by the object.
A)It is equal to the weight of the object.
B)It is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
C)It is equal to the pressure of water below the object.
D)It is equal to the mass of the fluid displaced by the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the diameter of a capillary tube holding methanol, if the methanol rises to the same height as water in a 1 mm diameter tube? (Take 0° for contact angles, surface tension for water óH2O= 0.073 N/m, and of methanol ómethanol = 0.023 N/m. Density of water is ñH2O = 1000 kg/m3, and of methanol ñmethanol = 792 kg/m3.)
A)0.2 mm
B)0.4 mm
C)2.0 mm
D)4.0 mm
A)0.2 mm
B)0.4 mm
C)2.0 mm
D)4.0 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
You have a fluid in a beaker, but you need to increase the density of the contents of the beaker. How can you obtain higher density?
A)increase the fluid volume per unit mass
B)double the mass and volume of a fluid
C)halve the volume and mass of a fluid
D)increase the mass per unit volume
A)increase the fluid volume per unit mass
B)double the mass and volume of a fluid
C)halve the volume and mass of a fluid
D)increase the mass per unit volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Nautilus, a mollusk inside a spiral shell, sometimes dives as deep as 400 m below the ocean surface during the day in order to avoid heating by the sun. By what factor is the pressure exerted on the shell at that depth larger than the pressure at 60 m depth, where nautilus usually feeds on plankton? (Note: The density of sea water is ñ = 1030 kg/m3.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If no changes occur in a fluid, we say that it is in equilibrium. This statement includes all parameters of both macroscopic and microscopic motion of fluid molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Describe the position of a human body in which all the gauge pressures in the cardiovascular system are positive, and another position where you can expect negative gauge pressure to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At the surface of a fluid, the upward force from the fluid equals atmospheric pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Gauge pressure is the ratio of pressure to ambient (air) pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the apparent weight of an object immersed in a vessel filled with water, in a weightless environment, such as the International Space station?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Surface tension is a force per unit area of the surface of a liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a weightless environment such as on the International Space Station, water assumes the shape of a sphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We can breathe in and out as long as the pressure between the outside and the inside of the lungs is lower than 0.05 times normal atmospheric pressure. How deep can we snorkel in sea water with density ñ = 1.025 × 103 kg/m3, and in fresh water with density ñ = 1.0 × 103 kg/m3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ideal stationary fluid is incompressible. This means you cannot deform it. If you act on such a fluid to deform it, it responds with a change in density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 11.2: A hydraulic lift 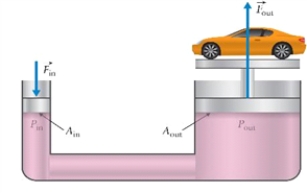
Hydraulic lift is shown in Fig. 11.2. The diameter of a large piston is 0.4 m. What is the diameter of a small piston if we can use a force of 147 N to lift a car of a mass 1500 kg?

Hydraulic lift is shown in Fig. 11.2. The diameter of a large piston is 0.4 m. What is the diameter of a small piston if we can use a force of 147 N to lift a car of a mass 1500 kg?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the radius of a capillary tube decreases by 3 times, the water will rise to triple its original height.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What percent of the weight of a ship's load has to be removed from a fully laden ship when it enters from the ocean into the St. Lawrence River? (Note: The density of sea water is ñ = 1.025 × 103 kg/m3, and the density of fresh water is ñ = 103 kg/m3.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the height of a column of mercury supported by a blood pressure of 0.16 Pa is 120 mm, what height would a column of water be if you used a water manometer to measure the same pressure? (Note: The density of mercury is ñ = 1.36 × 104 kg/m3, and the density of water is ñ = 103 kg/m3.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Major cargo ships sail up the Saint Lawrence Seaway from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes. If their ballast tanks are not adjusted, the ships will sink lower when they move from the ocean to the fresh-water seaway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Buoyant force is sometimes directed upward and sometimes downward, depending on whether the object is sinking or floating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use Pascal's law to determine the height of Earth's atmosphere. Compare the result to the height of Mount Everest, h = 8848 m. The real height of the atmosphere is about 500 km. What assumption in Pascal's law is the reason for this difference in results? (Note: Atmospheric pressure is Patm = 1.01 × 105 Pa, and density of air ñ = 1.2 kg/m3.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A shark has to swim constantly all its life to prevent its body from sinking because it is heavier than other types of fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The density of ice is 917 kg/m3, and the density of sea water is 1025 kg/m3. A walrus climbs onto a piece of floating ice that has a volume of 15.7 m3. How much does the walrus weigh if the ice is just submerged under the surface of water?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A body sinking in a fluid with terminal velocity has a weight equal to the buoyant force and the force of friction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Calculate the pressure in a water bubble of diameter 0.04 cm, and compare that with the pressure in the same diameter bubble of water-and-surfactant, which reduces surface tension by half. The surface tension of water is ó = 0.073 N/m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The fisher spider (Dolomedes triton), with mass of 0.7 g, walks on the water with eight legs. What length of each leg is in contact with the water so that the spider stays on the surface? Ignore the width of the leg; take into account only that each leg has two sides in contact with water. The surface tension of water is ó = 0.073 N/m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



