Deck 8: Gases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Gases
1
A methane gas bubble forms on the floor of the ocean at a depth of 1000 m. Assume there is no exchange of heat or mass with the bubble's surroundings. By what fraction would the volume of the bubble increase by the time it breaks through the surface of the water at sea level?
A)9.8 × 103
B)1 × 106
C)9.8 × 106
D)1 × 107
A)9.8 × 103
B)1 × 106
C)9.8 × 106
D)1 × 107
9.8 × 106
2
Air enters the lungs at 15°C, and reaches the lungs at body temperature (37°C). Given that the tidal volume of the lungs is 0.5 L, what is the change in the energy of the air for each inhalation?
A)11.6 J
B)5.8 J
C)-5.8 J
D)-11.6 J
A)11.6 J
B)5.8 J
C)-5.8 J
D)-11.6 J
5.8 J
3
Air in a room of dimensions 3 m × 4 m × 2 m is being heated by the Sun shining perpendicularly through a window of area 2 m2, from a temperature of 10°C to 20°C in a time of 2 hours. Given that sunlight emits radiation with a total intensity of 1.361 kW/m2, and assuming a pressure of 1 atm and that the mass of air in the room is constant, what fraction of this energy is absorbed by the air, thus warming up the room?
A)2.2 × 10-3
B)3.3 × 10-3
C)6.7 × 10-3
D)1.1 × 10-2
A)2.2 × 10-3
B)3.3 × 10-3
C)6.7 × 10-3
D)1.1 × 10-2
3.3 × 10-3
4
If molecules hitting the walls of a vessel did so inelastically instead of elastically, what pressure would one expect compared to the pressure caused by elastic collisions?
A)It would be the same.
B)It would decrease.
C)It would increase.
D)It is not possible to determine from the information given.
A)It would be the same.
B)It would decrease.
C)It would increase.
D)It is not possible to determine from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Gas in a container with a volume of 1.50 L at a temperature of 0°C exerts a pressure of 2.00 atm. How many moles of gas are in the container?
A)0.13 moles
B)0.26 moles
C)1.30 moles
D)130 moles
A)0.13 moles
B)0.26 moles
C)1.30 moles
D)130 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these statements does NOT apply to isobaric change?
A)Density is proportional to temperature.
B)Volume is proportional to temperature.
C)Pressure is constant.
D)Density is inversely proportional to temperature.
A)Density is proportional to temperature.
B)Volume is proportional to temperature.
C)Pressure is constant.
D)Density is inversely proportional to temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In Boyle's experiment, what determines the pressure in the volume of air in the sealed space?
A)the excess height of Hg between the two columns
B)the height of Hg in the open column
C)the excess height of Hg between the two columns, and the atmospheric pressure
D)the height of the air space in the sealed column
A)the excess height of Hg between the two columns
B)the height of Hg in the open column
C)the excess height of Hg between the two columns, and the atmospheric pressure
D)the height of the air space in the sealed column

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The weight of a 1000 kg car is supported equally by four tires, which are inflated to the same gauge pressure. What gauge pressure is required so the area of contact of each tire with the road is 90 cm2?
A)27 kPa
B)28 kPa
C)272 kPa
D)280 kPa
A)27 kPa
B)28 kPa
C)272 kPa
D)280 kPa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the ratio of the root-mean-square velocities of molecules of O2 to water vapour molecules (of molar masses 32 and 18 respectively) in a gas in thermal equilibrium?
A)0.75
B)1.33
C)1.78
D)Cannot be determined with information given.
A)0.75
B)1.33
C)1.78
D)Cannot be determined with information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following properties does NOT describe an ideal gas?
A)A gas gives zero volume at a temperature of -273.15 K.
B)Mean energy per particle is proportional to absolute temperature.
C)Interactive forces between molecules are included.
D)The size of the molecules is neglected in comparison with their mean distance apart.
A)A gas gives zero volume at a temperature of -273.15 K.
B)Mean energy per particle is proportional to absolute temperature.
C)Interactive forces between molecules are included.
D)The size of the molecules is neglected in comparison with their mean distance apart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Pressure in a gas is reduced by half, and the temperature is reduced to 80% of its initial value. What is the ratio of the final to the initial volume of the gas?
A)0.62
B)0.75
C)1.25
D)1.60
A)0.62
B)0.75
C)1.25
D)1.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 8.1 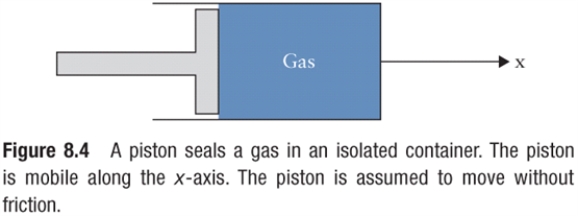 Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
In Fig. 8.1, a piston of cross-sectional area 1 m2 seals a cylinder of gas, of length 0.5 m, at atmospheric pressure (so that there is no net force on the piston). The gas is at the ambient temperature of 20°C, then the gas is heated to 100°C. What extra force must the piston exert to contain the gas in the cylindrical space of reduced length 0.4 m?
A)3.0 × 104 N
B)6.0 × 104 N
C)1.2 × 105 N
D)5.3 × 105 N
 Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.In Fig. 8.1, a piston of cross-sectional area 1 m2 seals a cylinder of gas, of length 0.5 m, at atmospheric pressure (so that there is no net force on the piston). The gas is at the ambient temperature of 20°C, then the gas is heated to 100°C. What extra force must the piston exert to contain the gas in the cylindrical space of reduced length 0.4 m?
A)3.0 × 104 N
B)6.0 × 104 N
C)1.2 × 105 N
D)5.3 × 105 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The gas in a constant-volume gas thermometer registers a pressure of 95.0 kPa at 100°C. Assume ideal behaviour. What is the temperature of this gas when the pressure is 250 kPa?
A)142°C
B)263°C
C)709°C
D)982°C
A)142°C
B)263°C
C)709°C
D)982°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two gases, O2 and CO2, with molar masses of 32 g/mol and 44 g/mol respectively, are in a closed vessel separated by an impermeable membrane into two equal sub-volumes. If both the temperatures and the densities of each gas are the same, what is the ratio of the O2 to CO2 pressures exerted on the membrane?
A)0.7
B)1.0
C)1.4
D)2.8
A)0.7
B)1.0
C)1.4
D)2.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A cylindrical glass, closed at one end, of length 15 cm and cross-section 35 cm2, is filled to a depth of 10 cm. A card is placed over the top and held there while the glass is inverted. What volume of water must leave the glass in order that the rest of the water should remain in the glass? Neglect the weight of the card.
A)0.85 × 10-4 m3
B)1.74 × 10-4 m3
C)2.19 × 10-4 m3
D)3.48 × 10-4 m3
A)0.85 × 10-4 m3
B)1.74 × 10-4 m3
C)2.19 × 10-4 m3
D)3.48 × 10-4 m3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 8.1  Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
A certain gas in a closed container at 0.001 atm of pressure is irradiated with ionizing radiation, causing, on average, one electron to be stripped off each atom. The ionizing radiation also heats the gas from 20°C to 3000°C. The resulting ionized gas ("plasma") behaves like an ideal gas. What is the pressure in the plasma?
A)3.04 × 105 Pa
B)4.92 × 103 Pa
C)2.46 × 103 Pa
D)1.23 × 103 Pa
 Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.A certain gas in a closed container at 0.001 atm of pressure is irradiated with ionizing radiation, causing, on average, one electron to be stripped off each atom. The ionizing radiation also heats the gas from 20°C to 3000°C. The resulting ionized gas ("plasma") behaves like an ideal gas. What is the pressure in the plasma?
A)3.04 × 105 Pa
B)4.92 × 103 Pa
C)2.46 × 103 Pa
D)1.23 × 103 Pa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In kinetic gas theory, which one of the following is an assumption and NOT a prediction of the theory?
A)Internal energy is proportional to absolute temperature.
B)The average speed of molecules depends only on absolute temperature.
C)The mean velocity of molecules is zero.
D)The product of pressure and volume of a gas is proportional to the number of molecules times their individual mean energy.
A)Internal energy is proportional to absolute temperature.
B)The average speed of molecules depends only on absolute temperature.
C)The mean velocity of molecules is zero.
D)The product of pressure and volume of a gas is proportional to the number of molecules times their individual mean energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Molybdenum melts at a temperature of 2623°C. What is the corresponding temperature on the Kelvin scale?
A)2350 K
B)2591 K
C)2723 K
D)2896 K
A)2350 K
B)2591 K
C)2723 K
D)2896 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 15 m diameter spherical balloon is filled with air at a temperature of 60°C through a hole at the bottom of the balloon. Assume an outside atmospheric pressure of 1 atm and the average molecular mass of air is 29 g/mol. What is the mass of air contained within the balloon?
A)937 kg
B)1250 kg
C)1874 kg
D)3896 kg
A)937 kg
B)1250 kg
C)1874 kg
D)3896 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 8.1  Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
A 0.5 L bottle containing air at 30°C is sealed at sea level, where the atmospheric pressure is 1 atm. The bottle is re-opened at the top of a 2000-m-high mountain, where the pressure is 0.8 atm and the temperature is 0°C. What mass of air escapes the bottle, assuming that the air has a molar mass of 29 g/mol?
A)7.4 × 10-5 kg
B)3.7 × 10-4 kg
C)-7.4 × 10-3 kg (that is, air enters the bottle)
D)7.4 × 10-2 kg
 Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.
Piston seals off a cylindrical container of oxygen.A 0.5 L bottle containing air at 30°C is sealed at sea level, where the atmospheric pressure is 1 atm. The bottle is re-opened at the top of a 2000-m-high mountain, where the pressure is 0.8 atm and the temperature is 0°C. What mass of air escapes the bottle, assuming that the air has a molar mass of 29 g/mol?
A)7.4 × 10-5 kg
B)3.7 × 10-4 kg
C)-7.4 × 10-3 kg (that is, air enters the bottle)
D)7.4 × 10-2 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Mercury barometers measure atmospheric pressure by the height of a column of mercury in a sealed tube containing a vacuum. What effect does cross-sectional area have on the accuracy of measurements of pressure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In kinetic gas theory, we can predict the speed of an escaping particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Describe why the compression ratio in a diesel engine must be higher than that in a gas engine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The mean speed of molecules escaping from the atmosphere of a planet into outer space is greater than the mean speed of molecules that remain in the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In Dalton's law, the partial pressure of each component of a gas mixture is independent of temperature and total volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All gases in Earth's atmosphere escape from it at equal rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Dalton's law of partial pressures assumes that each component of a gas behaves as an ideal gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A car weighing 1.2 × 104 N rests on four tires. If the gauge pressure in each tire is 200 kPa, what is the area of each tire in contact with the road?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A high voltage is applied across a sealed vessel containing gas at a very low pressure. If the voltage is high enough, electrons are stripped off the neutral atoms of gas (ionization), forming a current through the vessel. Some electrons recombine with positively charged ions, thereby giving off electromagnetic radiation, while other electrons cause further ionization of neutral atoms. Describe what happens to the pressure inside the vessel when the ionizing voltage is applied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During the day, the atmosphere is at a higher temperature than at night. What effects do you expect this will have on atmospheric density?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The transmural pressure is the difference in pressure between two sides of a wall, or a separator. In the human respiratory system, the transmural pressure (trans means "across" and murus means "wall" in Latin) is a pressure difference between the lungs and the pleura. The pleura is a double-layered membrane surrounding the lungs and, with a small amount of fluid, allows frictionless movements of the lungs against the rib cage, preventing the hard ribs from puncturing the soft lung tissue. Gauge pressure is the pressure value relative to atmospheric pressure. Palveoli represents the gauge pressure inside the lungs, and Ppleura represents the gauge pressure in the pleura. What happens with transmural pressure in the lungs an the environment where atmospheric pressure is much lower, such as on the 4205-m-high Mauna Kea volcano summit on the Big Island, Hawaii? Are there other considerations that need to be taken into account when thinking about respiration at high altitudes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
On a sunny day, air rises over black surfaces, such as roads, which are warmed more effectively than areas of vegetation (cooled by transpiration). Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If two bodies at the same temperature are brought into contact, no heat flows between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Weather balloons are only partially filled when released from the ground because pressure inside the balloon increases as the balloon rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Gauge pressure is pressure value relative to 0 Pa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Deviations from ideal gas behaviour occur at high densities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Boyle's and Charles's experiments could be carried out for any gas, or mixture of gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Helium gas liquefies at a very low temperature (4 K), whereas water vapour liquefies at a much higher temperature. Describe briefly what causes this difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The ideal gas law assumes no interactions between molecules of the gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In 1742, Anders Celsius was the first to propose a quantitative method for measuring temperatures. He defined the temperature scale, which we call in his honour the Celsius scale: 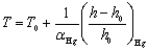 in which T0 is an arbitrary reference temperature, for example, the temperature at which the thermometer is filled with mercury. The term in the bracket is the fraction of the height change of the mercury column during a temperature change, and áHg is the coefficient of linear expansion of mercury. What is the unit of áHg?
in which T0 is an arbitrary reference temperature, for example, the temperature at which the thermometer is filled with mercury. The term in the bracket is the fraction of the height change of the mercury column during a temperature change, and áHg is the coefficient of linear expansion of mercury. What is the unit of áHg?
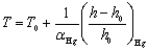 in which T0 is an arbitrary reference temperature, for example, the temperature at which the thermometer is filled with mercury. The term in the bracket is the fraction of the height change of the mercury column during a temperature change, and áHg is the coefficient of linear expansion of mercury. What is the unit of áHg?
in which T0 is an arbitrary reference temperature, for example, the temperature at which the thermometer is filled with mercury. The term in the bracket is the fraction of the height change of the mercury column during a temperature change, and áHg is the coefficient of linear expansion of mercury. What is the unit of áHg?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Two gases of different composition, but at the same temperature and pressure, are mixed together. What happens to the temperature of the mixture?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A barometer may be constructed by immersing the open end of a glass tube that is partially filled with water and sealed at the other end, into a jar of water, leaving an air space above the water in the tube. It is proposed to measure changes in atmospheric pressure by changes in the height of the water in the column. Describe what effects might intrude to give erroneous readings of the actual pressure changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Water boils when the partial pressure of water vapour equals the ambient atmospheric pressure. Explain why it is not possible to cook some foods above a certain altitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Dalton's law assumes ideal gas behaviour. Discuss under what conditions deviations from ideal gas behaviour might occur, and justify your claims.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



