Deck 54: Community Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 54: Community Ecology
1
Select the answer choice that best describes facilitation.
A) a species interaction that modifies and enhances the local environment for other species
B) a species interaction that modifies and detracts from the local environment, inhibiting other species
C) an interaction between members of a population that enhances the local environment for other members of the same population
D) an interaction between members of a population that detracts from the local environment, inhibiting other members of the same population
E) a species interaction that enhances the local environment for a previously extant species
A) a species interaction that modifies and enhances the local environment for other species
B) a species interaction that modifies and detracts from the local environment, inhibiting other species
C) an interaction between members of a population that enhances the local environment for other members of the same population
D) an interaction between members of a population that detracts from the local environment, inhibiting other members of the same population
E) a species interaction that enhances the local environment for a previously extant species
A
2
An organism's ecological role within the structure and function of a particular community is its:
A) habitat.
B) trophic level.
C) population.
D) ecological niche.
E) competition.
A) habitat.
B) trophic level.
C) population.
D) ecological niche.
E) competition.
D
3
Large-scale experiments conducted in oak forests of the northeastern United States linked bumper acorn crops to booming mouse populations.The conclusion from these experiments is that:
A) increased levels of first trophic level productivity cause an increase in disease vector activities.
B) competition can result in a more limited realized niche.
C) high biological diversity results in a decrease in Lyme disease transmission to human beings.
D) extermination of mouse populations is the most effective way of reducing Lyme disease transmission.
E) potential threat of Lyme disease in human beings is eliminated following a bumper crop of acorns.
A) increased levels of first trophic level productivity cause an increase in disease vector activities.
B) competition can result in a more limited realized niche.
C) high biological diversity results in a decrease in Lyme disease transmission to human beings.
D) extermination of mouse populations is the most effective way of reducing Lyme disease transmission.
E) potential threat of Lyme disease in human beings is eliminated following a bumper crop of acorns.
C
4
Figure 54-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).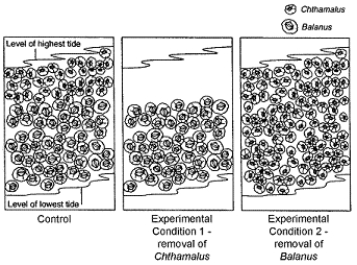
In Experimental Condition 2 of Figure 54-1, the distribution of Chthamalus suggests:
A) that interspecific competition kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
B) that intraspecific competition kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
C) that a limiting factor kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
D) that a barnacle parasite kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
E) that predation kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

In Experimental Condition 2 of Figure 54-1, the distribution of Chthamalus suggests:
A) that interspecific competition kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
B) that intraspecific competition kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
C) that a limiting factor kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
D) that a barnacle parasite kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.
E) that predation kept Chthamalus from extending lower into the intertidal area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Most likely, which of the following would not be an example of a limiting resource?
A) temperature in a terrestrial habitat
B) mineral content of the soil
C) amount of precipitation
D) salinity in an aquatic habitat
E) growth rate
A) temperature in a terrestrial habitat
B) mineral content of the soil
C) amount of precipitation
D) salinity in an aquatic habitat
E) growth rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A community consists of __________ species in a given area.
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) all
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Resource partitioning may include all of the following except:
A) relocating nesting sites.
B) changing the time of day when feeding occurs.
C) specialization on different types of prey.
D) changing the season when reproduction occurs.
E) intraspecific competition.
A) relocating nesting sites.
B) changing the time of day when feeding occurs.
C) specialization on different types of prey.
D) changing the season when reproduction occurs.
E) intraspecific competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not one of the main types of interactions that occur among species in a community?
A) intraspecific competition
B) predation
C) reproduction
D) symbiosis
E) interspecific competition
A) intraspecific competition
B) predation
C) reproduction
D) symbiosis
E) interspecific competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which is not a property that is characteristic of a community?
A) energy and nutrient flow throughout the community
B) the types of species present
C) the relative abundance of each species
D) the interactions among different species
E) All of these are properties that are characteristic of a community.
A) energy and nutrient flow throughout the community
B) the types of species present
C) the relative abundance of each species
D) the interactions among different species
E) All of these are properties that are characteristic of a community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which are the three main roles played by organisms in community life?
A) producer, detritivore, decomposer
B) consumer, detritivore.decomposer
C) producer, consumer, decomposer
D) facilitator, decomposer, consumer
E) realized niche, fundamental niche, habitat
A) producer, detritivore, decomposer
B) consumer, detritivore.decomposer
C) producer, consumer, decomposer
D) facilitator, decomposer, consumer
E) realized niche, fundamental niche, habitat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Niches apply to:
A) individual organisms.
B) individual species.
C) groups of species.
D) communities.
E) ecosystems.
A) individual organisms.
B) individual species.
C) groups of species.
D) communities.
E) ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 54-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
In Experimental Condition 1 of Figure 54-1, the distribution of Balanus suggests:
A) that interspecific competition kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
B) that intraspecific competition kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
C) that an unfavorable environmental factor kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
D) that Balanus is less motile than Chthamalus.
E) that Balanus is more motile than Chthamalus.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

In Experimental Condition 1 of Figure 54-1, the distribution of Balanus suggests:
A) that interspecific competition kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
B) that intraspecific competition kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
C) that an unfavorable environmental factor kept Balanus from extending higher into the intertidal area.
D) that Balanus is less motile than Chthamalus.
E) that Balanus is more motile than Chthamalus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The associated figure provides support for which of the following processes? 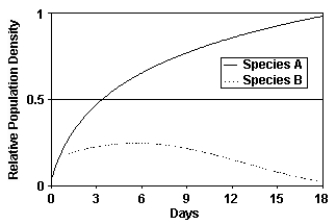
A) secondary succession
B) competitive exclusion
C) coevolution
D) mutualism
E) resource partitioning

A) secondary succession
B) competitive exclusion
C) coevolution
D) mutualism
E) resource partitioning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Since the realized niche and the fundamental niche are not typically the same, this illustrates that:
A) two different species cannot share the same niche.
B) resource partitioning is necessary for two species whose fundamental niches overlap to survive.
C) interspecific competition is necessary for two species whose fundamental niches overlap to survive.
D) communities with greater species diversity have more unrealized fundamental niches.
E) complex interactions among numerous species produce each species' realized niche.
A) two different species cannot share the same niche.
B) resource partitioning is necessary for two species whose fundamental niches overlap to survive.
C) interspecific competition is necessary for two species whose fundamental niches overlap to survive.
D) communities with greater species diversity have more unrealized fundamental niches.
E) complex interactions among numerous species produce each species' realized niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Habitat is best described as:
A) the local environment in which a species lives.
B) what a species eats.
C) what competes with a species.
D) the abiotic components of a species' environment.
E) the totality of adaptations by a species to its environment.
A) the local environment in which a species lives.
B) what a species eats.
C) what competes with a species.
D) the abiotic components of a species' environment.
E) the totality of adaptations by a species to its environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The realized niche for the green anole was determined by:
A) a limiting resource.
B) competition.
C) symbiosis.
D) coevolution.
E) disease.
A) a limiting resource.
B) competition.
C) symbiosis.
D) coevolution.
E) disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A(n) __________ has both biotic and abiotic components.
A) population
B) community
C) ecosystem
D) species
E) genus
A) population
B) community
C) ecosystem
D) species
E) genus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The __________ niche is the broadest role that an organism can potentially have in a community.
A) realized
B) fundamental
C) displaced
D) excluded
E) limited
A) realized
B) fundamental
C) displaced
D) excluded
E) limited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The community found on a rotting log would not include:
A) mosses.
B) rainwater.
C) bacteria.
D) termites.
E) lichens.
A) mosses.
B) rainwater.
C) bacteria.
D) termites.
E) lichens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a community?
A) the microorganisms living within the soil of your yard
B) the life within a pond
C) the organisms living within a dead tree in a forest
D) the population of western gulls on a beach
E) nurse logs which shelter plants and other organisms
A) the microorganisms living within the soil of your yard
B) the life within a pond
C) the organisms living within a dead tree in a forest
D) the population of western gulls on a beach
E) nurse logs which shelter plants and other organisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A frog that lacks chemical defenses, yet resembles a poison arrow frog, would exhibit:
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) mutualism.
C) camouflage.
D) Müllerian mimicry.
E) epistasis.
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) mutualism.
C) camouflage.
D) Müllerian mimicry.
E) epistasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which habitat would most likely have the greatest species richness?
A) prairie
B) savanna
C) tundra
D) temperate desert
E) tropical rain forest
A) prairie
B) savanna
C) tundra
D) temperate desert
E) tropical rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a lake, a certain native species of zooplankton is found evenly distributed in the water column.After introduction of a different species of zooplankton, the native species is only found in the shallow water zone.This is most likely an illustration of:
A) character displacement.
B) species richness.
C) primary succession.
D) secondary succession.
E) competitive exclusion.
A) character displacement.
B) species richness.
C) primary succession.
D) secondary succession.
E) competitive exclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Competitive exclusion is a result of:
A) interspecific competition.
B) intraspecific competition.
C) character displacement.
D) succession.
E) community complexity.
A) interspecific competition.
B) intraspecific competition.
C) character displacement.
D) succession.
E) community complexity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During __________ between predator and prey species, the predatory species becomes more efficient at catching prey, while the prey species becomes better at escaping predators.
A) character displacement
B) coevolution
C) Batesian mimicry
D) competitive exclusion
E) succession
A) character displacement
B) coevolution
C) Batesian mimicry
D) competitive exclusion
E) succession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Animals with chemical defenses are also typically:
A) fast runners.
B) aposematic.
C) small in size.
D) large in size.
E) camouflaged.
A) fast runners.
B) aposematic.
C) small in size.
D) large in size.
E) camouflaged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of mutualism is:
A) mycorrhizae and epiphytes.
B) epiphytes and tapeworms.
C) monarch and viceroy butterflies.
D) silverfish and army ants.
E) Rhizobium and legumes.
A) mycorrhizae and epiphytes.
B) epiphytes and tapeworms.
C) monarch and viceroy butterflies.
D) silverfish and army ants.
E) Rhizobium and legumes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which habitat would be expected to have the greatest species richness?
A) an island
B) a polar habitat
C) an ecotone
D) an agricultural habitat
E) a mountain top
A) an island
B) a polar habitat
C) an ecotone
D) an agricultural habitat
E) a mountain top

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a parasitic relationship where the host contracts a disease and sometimes dies, the parasite is called:
A) a predator.
B) a keystone species.
C) a mutualistic symbiont.
D) an interspecific competitor.
E) a pathogen.
A) a predator.
B) a keystone species.
C) a mutualistic symbiont.
D) an interspecific competitor.
E) a pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Many poisonous snakes share warning colors of red, yellow, and black.This is an example of:
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) mutualism.
C) camouflage.
D) Müllerian mimicry.
E) character displacement.
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) mutualism.
C) camouflage.
D) Müllerian mimicry.
E) character displacement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An example of both chemical protection and coevolution is seen in:
A) yellow goldenrod spiders and goldenrod.
B) milkweeds and monarch caterpillars.
C) the poison arrow frog and flying insects.
D) coral animals and dinoflagellates.
E) mycorrhizae.
A) yellow goldenrod spiders and goldenrod.
B) milkweeds and monarch caterpillars.
C) the poison arrow frog and flying insects.
D) coral animals and dinoflagellates.
E) mycorrhizae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you were to study all of the insect-eating birds in a forest, you would see that many birds eat insects, yet you may not see any evidence of competition.What is the most probable explanation?
A) The birds have coevolved.
B) The birds are exhibiting resource partitioning.
C) The birds are exhibiting intraspecific competition only.
D) There is no keystone species in this community.
E) There is not enough species richness to see evidence of competition.
A) The birds have coevolved.
B) The birds are exhibiting resource partitioning.
C) The birds are exhibiting intraspecific competition only.
D) There is no keystone species in this community.
E) There is not enough species richness to see evidence of competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In which of the following habitat types would species diversity be expected to be relatively low?
A) high environmental stress
B) low environmental stress
C) continental ecosystems
D) ecotones
E) mature successional communities
A) high environmental stress
B) low environmental stress
C) continental ecosystems
D) ecotones
E) mature successional communities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Species diversity is often very high in the region between two distinct communities, known as:
A) an ecotone.
B) a secondary successional area.
C) a primary successional area.
D) a fundamental niche.
E) a realized niche.
A) an ecotone.
B) a secondary successional area.
C) a primary successional area.
D) a fundamental niche.
E) a realized niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The relationship between reef-building coral animals and zooxanthellae is classified as:
A) mutualism.
B) commensalism.
C) Batesian mimicry.
D) parasitism.
E) character displacement.
A) mutualism.
B) commensalism.
C) Batesian mimicry.
D) parasitism.
E) character displacement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Keystone species:
A) are always symbionts.
B) are typically not the most abundant species in the community.
C) illustrate secondary succession.
D) always form the base of a food chain.
E) are only found in tropical communities.
A) are always symbionts.
B) are typically not the most abundant species in the community.
C) illustrate secondary succession.
D) always form the base of a food chain.
E) are only found in tropical communities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Pollution affects species diversity, thus the species richness of a highly polluted stream is __________ compared with that of a nearby pristine stream.
A) low
B) high
C) no different
D) more dense
E) complex
A) low
B) high
C) no different
D) more dense
E) complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Mycorrhizae are associations between:
A) coral animals and dinoflagellates.
B) two types of insects.
C) fungi and plant roots.
D) wasps and orchids.
E) epiphytes and rainforest trees.
A) coral animals and dinoflagellates.
B) two types of insects.
C) fungi and plant roots.
D) wasps and orchids.
E) epiphytes and rainforest trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which country would be expected to have the greatest species richness per unit area?
A) Japan
B) United States
C) Brazil
D) Canada
E) New Zealand
A) Japan
B) United States
C) Brazil
D) Canada
E) New Zealand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following organisms is a keystone species in a tropical rain forest?
A) gray wolf
B) fruit-eating bats
C) poison arrow frogs
D) fig trees
E) fruit-eating monkeys
A) gray wolf
B) fruit-eating bats
C) poison arrow frogs
D) fig trees
E) fruit-eating monkeys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Primary succession may be seen:
A) on new lava or on sand dunes.
B) after a fire.
C) when farmland is abandoned.
D) only in tropical rain forests.
E) in any community that has periodic disturbances.
A) on new lava or on sand dunes.
B) after a fire.
C) when farmland is abandoned.
D) only in tropical rain forests.
E) in any community that has periodic disturbances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The idea that older, more stable habitats have greater species richness than habitats subjected to frequent, widespread disturbances is known as:
A) natural selection.
B) the time hypothesis.
C) island biogeography.
D) the theory of community stability.
E) the disturbance hypothesis.
A) natural selection.
B) the time hypothesis.
C) island biogeography.
D) the theory of community stability.
E) the disturbance hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Competition between species 1 and species 2 is beneficial for species 1 and harmful for species 2.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
__________ begins in an area where there was a preexisting community and well-formed soil.
A) Character displacement
B) Species richness
C) Primary succession
D) Secondary succession
E) Competitive exclusion
A) Character displacement
B) Species richness
C) Primary succession
D) Secondary succession
E) Competitive exclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Traditionally, most ecologists have assumed that community stability is a consequence of:
A) competition.
B) predation.
C) community complexity.
D) the relative size of realized niches among species.
E) disease.
A) competition.
B) predation.
C) community complexity.
D) the relative size of realized niches among species.
E) disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The potential ecological niche of a species is its realized niche.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ecologist James H.Brown of the University of New Mexico has addressed species composition and richness in experiments conducted since 1977 in the Chihuahuan desert of southeastern Arizona.In one experiment, the removal of three dominant species, all kangaroo rats, from several plots resulted in an increased diversity of other rodent species.This increase was ascribed both to lowered competition for food and also to an altered habitat, because the abundance of grass species __________ after the removal of the kangaroo rats.
A) increased
B) decreased
C) did not change
D) was threatened
E) shrunk
A) increased
B) decreased
C) did not change
D) was threatened
E) shrunk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Discuss coevolution as it relates to predator-prey interactions.Include a brief discussion of two specific examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Species richness is __________ when any one species enjoys a position of dominance.
A) no different
B) more dense
C) reduced
D) increased
E) complex
A) no different
B) more dense
C) reduced
D) increased
E) complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the studies by David Tilman of the University of Minnesota and John Downing of the University of Iowa, reported in the journal Nature in 1994, they established and monitored 207 plots of Minnesota grasslands for seven years.During the study period, Minnesota's worst drought in 50 years occurred (1987-1988).The ecologists found that those plots with the greatest number of plant species lost __________ ground cover, as measured by dry weight, and recovered faster than species-poor plots.
A) less
B) more
C) no detectable
D) only deciduous
E) detectable
A) less
B) more
C) no detectable
D) only deciduous
E) detectable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Nicotine synthesis is an adaptation of plant chemical defense against insects.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Explain the ecological significance of limiting resources, using three specific examples in your discussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Adaptations that exert a strong competitive force on a predator are the result of coevolution.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Destructive outbreaks of pests are __________ in cultivated fields, which are low-diversity communities, than in natural communities with greater species richness.
A) less common
B) more common
C) equally common
D) most easily prevented
E) rarely occur
A) less common
B) more common
C) equally common
D) most easily prevented
E) rarely occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Within a community; a dominant species may appropriate a disproportionate share of available resources, thus __________ other species.
A) increasing competition with
B) increasing disease transmission with
C) undergrazing
D) outcompeting
E) decreasing disease transmission
A) increasing competition with
B) increasing disease transmission with
C) undergrazing
D) outcompeting
E) decreasing disease transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The almost complete loss of the American chestnut tree to the chestnut blight fungus had __________ ecological impact on the moderately diverse Appalachian woodlands of which it was formerly a part.
A) little
B) great
C) moderate
D) undetectable
E) detectable.
A) little
B) great
C) moderate
D) undetectable
E) detectable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain Gleason's individualistic model describing community structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The current concept of a climax community states that forest communities:
A) never reach a state of permanent equilibrium.
B) never are disturbed.
C) are determined solely by climate.
D) are not permanently affected by fires or floods.
E) are the inevitable end-point of succession.
A) never reach a state of permanent equilibrium.
B) never are disturbed.
C) are determined solely by climate.
D) are not permanently affected by fires or floods.
E) are the inevitable end-point of succession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The orderly replacement of one community by another is known as:
A) character displacement.
B) succession.
C) coevolution.
D) the edge effect.
E) competitive exclusion.
A) character displacement.
B) succession.
C) coevolution.
D) the edge effect.
E) competitive exclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The species richness of high-latitude communities is __________ compared with that of low-latitude communities.
A) low
B) high
C) no different
D) more dense
E) complex
A) low
B) high
C) no different
D) more dense
E) complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Species richness is a measure of both the number of species and the relative importance of each species based on its abundance, productivity, or size.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Humans have small mites that live in hair follicles and oil glands around the nose and eyelashes.What would you need to know to classify them as exhibiting mutualism, commensalisms, or parasitism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In Mullerian mimicry a defenseless species is protected by its resemblance to a dangerous species.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
MATCHING
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
community ecology
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
community ecology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe the ongoing research concerning the relationship between species richness and community stability.What research supports or fails to support this relationship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The association of nitrogen fixing bacteria of the genus Rhizobium with legumes such as peas is an example of mutualism.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe the factors that affect species richness.Describe the parameters that would probably result in an environment with the greatest possible species richness.Knowing what you do about the tropical rain forests, do they meet these expected parameters?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
MATCHING
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
habitat
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
habitat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
MATCHING
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
limiting resource
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
limiting resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In ecosystems bottom up processes, predators affect the abundances of other populations in the ecological community.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Cryptic coloration advertises a species unpalatability to potential predators.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
MATCHING
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
ecosystem
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
MATCHING
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
ecological niche
a.restricts ecological niche species
d.finding common patterns and processes within the community
b.local environment in which a species lives
e.biological community and its abiotic environment
c.species' ecological role within the structure and function of a community
ecological niche

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The impact of a keystone species is proportionate to their abundance in an ecosystem.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



