Deck 51: Animal Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 51: Animal Development
1
The release of calcium ions into the egg cytoplasm during fertilization causes all of the following actions except:
A) an increase in aerobic respiration.
B) onset of the cortical reaction.
C) inhibition of acrosomal enzymes.
D) activation of protein synthesis.
E) onset of a slow block to polyspermy.
A) an increase in aerobic respiration.
B) onset of the cortical reaction.
C) inhibition of acrosomal enzymes.
D) activation of protein synthesis.
E) onset of a slow block to polyspermy.
C
2
Which of the following is not considered part of the process of morphogenesis per se?
A) Cells become specialized.
B) Cells migrate into specific areas.
C) Certain cells undergo changes in shape.
D) Cells become organized into intricate patterns of tissues and organs.
E) Some cells undergo apoptosis.
A) Cells become specialized.
B) Cells migrate into specific areas.
C) Certain cells undergo changes in shape.
D) Cells become organized into intricate patterns of tissues and organs.
E) Some cells undergo apoptosis.
A
3
Which of the following statements concerning fertilization is false?
A) Fertilization restores the diploid chromosome number.
B) Fertilization stimulates the initiation of development.
C) Fertilization can determine the sex of the offspring.
D) Fertilization permits the formation of gametes with new genetic combinations.
E) In fertilization, a sperm fuses with an ovum to produce a zygote.
A) Fertilization restores the diploid chromosome number.
B) Fertilization stimulates the initiation of development.
C) Fertilization can determine the sex of the offspring.
D) Fertilization permits the formation of gametes with new genetic combinations.
E) In fertilization, a sperm fuses with an ovum to produce a zygote.
D
4
The fast block to polyspermy involves the:
A) release of inhibitors of acrosomal enzymes.
B) synthesis of a new sperm-resistant membrane.
C) accumulation of calcium ions in the acrosome.
D) opening of ion channels that change the polarity of the egg membrane.
E) destruction of excess bindin receptors on the sperm.
A) release of inhibitors of acrosomal enzymes.
B) synthesis of a new sperm-resistant membrane.
C) accumulation of calcium ions in the acrosome.
D) opening of ion channels that change the polarity of the egg membrane.
E) destruction of excess bindin receptors on the sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In most animals, the sperm and egg contribute an equal __________ to the zygote.
A) amount of cytoplasm
B) number of chromosomes
C) number of enzymes
D) number of mitochondria
E) number of ribosomes
A) amount of cytoplasm
B) number of chromosomes
C) number of enzymes
D) number of mitochondria
E) number of ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements would apply to both the fast block to polyspermy and nerve conductance?
A) The plasma membrane is depolarized.
B) Calcium ions accumulate in the cytoplasm.
C) The sodium-potassium pump maintains the transmembrane potential.
D) A signal transduction pathway opens ion channels.
E) The cytoplasm is positively charged relative to the extracellular space.
A) The plasma membrane is depolarized.
B) Calcium ions accumulate in the cytoplasm.
C) The sodium-potassium pump maintains the transmembrane potential.
D) A signal transduction pathway opens ion channels.
E) The cytoplasm is positively charged relative to the extracellular space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In sea urchins, the fertilization envelope forms from the:
A) vitelline envelope.
B) jelly coat.
C) zona pellucida.
D) plasma membrane.
E) granulosa cells.
A) vitelline envelope.
B) jelly coat.
C) zona pellucida.
D) plasma membrane.
E) granulosa cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Following cleavage of the zygote, which of the following is the first to occur?
A) blastula
B) gastrula
C) neural crest
D) morula
E) primitive streak
A) blastula
B) gastrula
C) neural crest
D) morula
E) primitive streak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about sperm entry is true?
A) The fertilization cone formed by microvilli of the egg membrane contracts and draws the sperm inward.
B) The egg phagocytizes the acrosome of the sperm so it can enter the cell.
C) The cilia on the egg membrane beat and sweep the sperm inside.
D) The sperm releases calcium ions, which make the egg membrane permeable to its entry.
E) The egg secretes bindin protein, which allows sperm penetration.
A) The fertilization cone formed by microvilli of the egg membrane contracts and draws the sperm inward.
B) The egg phagocytizes the acrosome of the sperm so it can enter the cell.
C) The cilia on the egg membrane beat and sweep the sperm inside.
D) The sperm releases calcium ions, which make the egg membrane permeable to its entry.
E) The egg secretes bindin protein, which allows sperm penetration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following consists of a hollow ball of cells?
A) gastrula
B) morula
C) blastula
D) blastocoel
E) zygote
A) gastrula
B) morula
C) blastula
D) blastocoel
E) zygote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Animal growth primarily occurs by an increase in the:
A) number of tissues and organs.
B) number of cells.
C) types of cells produced.
D) number of cell functions.
E) number of cell shapes.
A) number of tissues and organs.
B) number of cells.
C) types of cells produced.
D) number of cell functions.
E) number of cell shapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Before a sperm can compete in fertilization, it must undergo a maturation process in the female reproductive tract known as:
A) the acrosome reaction.
B) the cortical reaction.
C) spermatogenesis.
D) determination.
E) capacitation.
A) the acrosome reaction.
B) the cortical reaction.
C) spermatogenesis.
D) determination.
E) capacitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following indicates the correct sequence of mammalian egg coverings, beginning at the outside and moving inward?
A) plasma membrane, jelly coat, zona pellucida
B) zona pellucida, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
C) vitelline envelope, plasma membrane, jelly coat
D) granulosa cells, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
E) zona pellucida, granulosa cells, plasma membrane
A) plasma membrane, jelly coat, zona pellucida
B) zona pellucida, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
C) vitelline envelope, plasma membrane, jelly coat
D) granulosa cells, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
E) zona pellucida, granulosa cells, plasma membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following indicates the correct sequence of sea urchin egg coverings, beginning at the outside and moving inward?
A) granulosa cells, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
B) zona pellucida, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
C) jelly coat, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
D) plasma membrane, jelly coat, zona pellucida
E) vitelline envelope, jelly coat, plasma membrane
A) granulosa cells, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
B) zona pellucida, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
C) jelly coat, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane
D) plasma membrane, jelly coat, zona pellucida
E) vitelline envelope, jelly coat, plasma membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The principle of nuclear equivalence states that:
A) developing cells become specialized to carry out specific functions.
B) developing cells follow particular differentiation pathways.
C) there is no loss of genetic information through determination or differentiation.
D) differential gene expression is responsible for variation among cells.
E) nuclear changes can take place during the entire life of an individual.
A) developing cells become specialized to carry out specific functions.
B) developing cells follow particular differentiation pathways.
C) there is no loss of genetic information through determination or differentiation.
D) differential gene expression is responsible for variation among cells.
E) nuclear changes can take place during the entire life of an individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
During an acrosome reaction, the acrosome:
A) detaches, allowing the sperm to penetrate the egg.
B) releases enzymes that digest the outer layer of the egg.
C) secretes calcium ions, which cause the sperm to fuse with the egg.
D) releases bindin, which causes the sperm to bind to the egg.
E) secretes a chemical that attracts the egg to the sperm.
A) detaches, allowing the sperm to penetrate the egg.
B) releases enzymes that digest the outer layer of the egg.
C) secretes calcium ions, which cause the sperm to fuse with the egg.
D) releases bindin, which causes the sperm to bind to the egg.
E) secretes a chemical that attracts the egg to the sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the correct sequence through which early development proceeds?
A) morula zygote gastrula blastula
B) zygote blastula morula gastrula
C) zygote blastula gastrula morula
D) zygote gastrula blastula morula
E) zygote morula blastula gastrula
A) morula zygote gastrula blastula
B) zygote blastula morula gastrula
C) zygote blastula gastrula morula
D) zygote gastrula blastula morula
E) zygote morula blastula gastrula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Most invertebrates have:
A) isolecithal eggs and meroblastic cleavage.
B) telolecithal eggs and meroblastic cleavage.
C) isolecithal eggs and holoblastic cleavage.
D) telolecithal eggs and holoblastic cleavage.
E) isolecithal eggs and radial cleavage.
A) isolecithal eggs and meroblastic cleavage.
B) telolecithal eggs and meroblastic cleavage.
C) isolecithal eggs and holoblastic cleavage.
D) telolecithal eggs and holoblastic cleavage.
E) isolecithal eggs and radial cleavage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not part of the activation program of the egg?
A) increase in aerobic respiration
B) capacitation
C) activation of enzymes
D) increase in protein synthesis
E) completion of meiosis
A) increase in aerobic respiration
B) capacitation
C) activation of enzymes
D) increase in protein synthesis
E) completion of meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which the following does not occur in the egg following fertilization?
A) Meiosis II is completed.
B) Microtubules are formed.
C) Calcium concentrations increase.
D) The acrosomal reaction occurs.
E) The cortical reaction occurs.
A) Meiosis II is completed.
B) Microtubules are formed.
C) Calcium concentrations increase.
D) The acrosomal reaction occurs.
E) The cortical reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 51-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).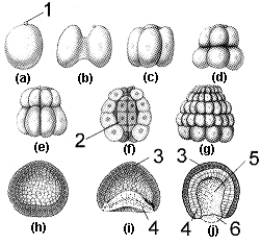
The type of cleavage pattern represented in Figure 51-1 is:
A) holoblastic and radial.
B) holoblastic and spiral.
C) meroblastic and radial.
D) meroblastic and spiral.
E) holoblastic and mosaic.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The type of cleavage pattern represented in Figure 51-1 is:
A) holoblastic and radial.
B) holoblastic and spiral.
C) meroblastic and radial.
D) meroblastic and spiral.
E) holoblastic and mosaic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The gray crescent region of the amphibian zygote is thought to contain:
A) growth factors and developmental determinants.
B) hormones and ribosomes.
C) yolk and dark pigment granules.
D) mitochondria and ribosomes.
E) neurotransmitters and hormones.
A) growth factors and developmental determinants.
B) hormones and ribosomes.
C) yolk and dark pigment granules.
D) mitochondria and ribosomes.
E) neurotransmitters and hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The term "archenteron" refers to the developing:
A) gut.
B) lung.
C) notochord.
D) nerve tube.
E) skin.
A) gut.
B) lung.
C) notochord.
D) nerve tube.
E) skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 51-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).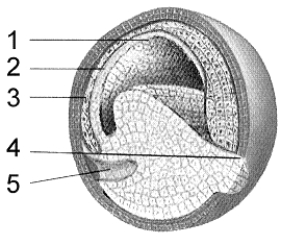
The developing embryo in Figure 51-2 is representative of development in:
A) a bird.
B) an annelid.
C) a sea star.
D) a frog.
E) a mammal.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The developing embryo in Figure 51-2 is representative of development in:
A) a bird.
B) an annelid.
C) a sea star.
D) a frog.
E) a mammal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 51-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The structure labeled 3 in Figure 51-2 is the:
A) archenteron.
B) endoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) blastocoel.
E) ectoderm..
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The structure labeled 3 in Figure 51-2 is the:
A) archenteron.
B) endoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) blastocoel.
E) ectoderm..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The first system to develop in the vertebrate embryo is the:
A) circulatory system.
B) digestive system.
C) excretory system.
D) reproductive system.
E) nervous system.
A) circulatory system.
B) digestive system.
C) excretory system.
D) reproductive system.
E) nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 51-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Which of the stages or structures in Figure 51-1 was formed by the process of gastrulation?
A) 1
B) f
C) g
D) 3
E) 5
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Which of the stages or structures in Figure 51-1 was formed by the process of gastrulation?
A) 1
B) f
C) g
D) 3
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following organisms exhibits meroblastic cleavage?
A) echinoderms
B) amphibians
C) mollusks
D) annelids
E) birds
A) echinoderms
B) amphibians
C) mollusks
D) annelids
E) birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 51-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The developmental stage represented in Figure 51-2 is:
A) a morula.
B) an early blastula.
C) a late blastula.
D) an early gastrula.
E) a middle gastrula.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The developmental stage represented in Figure 51-2 is:
A) a morula.
B) an early blastula.
C) a late blastula.
D) an early gastrula.
E) a middle gastrula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 51-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Refer to Figure 51-2.Which structure will form the blastocoel?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Refer to Figure 51-2.Which structure will form the blastocoel?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following occurs during gastrulation?
A) formation of the gray crescent region
B) formation of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
C) closure of the archenteron
D) formation of the blastocoel
E) radial cleavage takes place
A) formation of the gray crescent region
B) formation of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
C) closure of the archenteron
D) formation of the blastocoel
E) radial cleavage takes place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements concerning a blastodisc is false?
A) It can be further divided into an upper epiblast and below that, the hypoblast.
B) It results from meroblastic cleavage.
C) It is found in isolecithal eggs.
D) It is a small disc of cytoplasm at the animal pole.
E) It is characteristic of cell division in bird eggs.
A) It can be further divided into an upper epiblast and below that, the hypoblast.
B) It results from meroblastic cleavage.
C) It is found in isolecithal eggs.
D) It is a small disc of cytoplasm at the animal pole.
E) It is characteristic of cell division in bird eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Embryonic endoderm gives rise to:
A) muscle.
B) the lining of the digestive tract.
C) the nervous system.
D) skin.
E) skeletal tissue.
A) muscle.
B) the lining of the digestive tract.
C) the nervous system.
D) skin.
E) skeletal tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In organogenesis, the ectoderm gives rise to:
A) muscle.
B) the digestive tract.
C) sense organs.
D) the circulatory system.
E) skeletal tissue.
A) muscle.
B) the digestive tract.
C) sense organs.
D) the circulatory system.
E) skeletal tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Amphibian eggs have large amounts of yolk at the __________ pole, and most metabolism takes place at the __________ pole.
A) animal; vegetal
B) animal; animal
C) vegetal; vegetal
D) vegetal; animal
E) totipotent; telolecithal
A) animal; vegetal
B) animal; animal
C) vegetal; vegetal
D) vegetal; animal
E) totipotent; telolecithal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Embryonic mesoderm forms the:
A) epidermis.
B) lining of the digestive tract.
C) pituitary gland.
D) excretory system.
E) nervous system.
A) epidermis.
B) lining of the digestive tract.
C) pituitary gland.
D) excretory system.
E) nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 51-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The structure labeled 2 in Figure 51-1 is the:
A) endoderm layer.
B) mesoderm layer.
C) blastopore.
D) blastocoel.
E) archenteron.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The structure labeled 2 in Figure 51-1 is the:
A) endoderm layer.
B) mesoderm layer.
C) blastopore.
D) blastocoel.
E) archenteron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A primitive groove is the equivalent of a:
A) neural crest.
B) branchial groove.
C) blastodisc.
D) blastopore.
E) neural groove.
A) neural crest.
B) branchial groove.
C) blastodisc.
D) blastopore.
E) neural groove.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 51-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Refer to Figure 51-2.The nervous system will develop from which structure?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) a structure not numbered in this figure
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Refer to Figure 51-2.The nervous system will develop from which structure?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) a structure not numbered in this figure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Hensen's node is located:
A) in the walls of the archenteron.
B) at the end of the primitive streak.
C) on the outer side of the chorion.
D) inside a blastomere.
E) inside the neural groove.
A) in the walls of the archenteron.
B) at the end of the primitive streak.
C) on the outer side of the chorion.
D) inside a blastomere.
E) inside the neural groove.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In mammals, the __________ is a temporary center for the formation of blood cells.
A) amnion
B) allantois
C) yolk sac
D) chorion
E) archenterons
A) amnion
B) allantois
C) yolk sac
D) chorion
E) archenterons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following structures is the last to develop?
A) neural tube
B) neural groove
C) neural crest
D) neural folds
E) neural plate
A) neural tube
B) neural groove
C) neural crest
D) neural folds
E) neural plate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A teratogen is a drug that:
A) increases fertility.
B) prevents fertilization.
C) prevents implantation of the embryo in the endometrium.
D) induces labor.
E) interferes with morphogenesis.
A) increases fertility.
B) prevents fertilization.
C) prevents implantation of the embryo in the endometrium.
D) induces labor.
E) interferes with morphogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Place the following in developmental order beginning with the earliest event. 1)
Limb buds appear
2)
Face begins to look human
3)
Muscles differentiate
4)
Downy hair covers the fetus
5)
Sex can be determined by external inspection
A) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5
B) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
C) 1, 3, 2, 5, 4
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
E) 1, 3, 5, 2, 4
Limb buds appear
2)
Face begins to look human
3)
Muscles differentiate
4)
Downy hair covers the fetus
5)
Sex can be determined by external inspection
A) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5
B) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
C) 1, 3, 2, 5, 4
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
E) 1, 3, 5, 2, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Monozygotic twins:
A) occur when two eggs are ovulated.
B) may be of different sexes.
C) have different sets of genes.
D) are called identical twins.
E) result from the fertilization of two sperm cells.
A) occur when two eggs are ovulated.
B) may be of different sexes.
C) have different sets of genes.
D) are called identical twins.
E) result from the fertilization of two sperm cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is not an extraembryonic membrane?
A) yolk sac
B) somite
C) chorion
D) amnion
E) allantois
A) yolk sac
B) somite
C) chorion
D) amnion
E) allantois

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The first breath of the neonate is initiated by the:
A) passage through the birth canal.
B) removal of amniotic fluid from its mouth.
C) accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood.
D) detection of light by its visual receptors.
E) increase in oxygen concentration in the lungs.
A) passage through the birth canal.
B) removal of amniotic fluid from its mouth.
C) accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood.
D) detection of light by its visual receptors.
E) increase in oxygen concentration in the lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements about the notochord is false?
A) It is lost when it is replaced by the vertebral column.
B) It develops in chordate embryos.
C) It develops from mesodermal tissue.
D) It induces formation of the neural plate.
E) It grows along the longitudinal axis of the organism.
A) It is lost when it is replaced by the vertebral column.
B) It develops in chordate embryos.
C) It develops from mesodermal tissue.
D) It induces formation of the neural plate.
E) It grows along the longitudinal axis of the organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The extraembryonic membrane closest to the embryo is the:
A) amnion.
B) archenteron.
C) chorion.
D) blastocyst.
E) neural plate.
A) amnion.
B) archenteron.
C) chorion.
D) blastocyst.
E) neural plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is not a function of the placenta?
A) exchanges blood between mother and fetus
B) secretes hormones to maintain pregnancy
C) provides oxygen for the fetus
D) eliminates wastes from the fetus
E) provides nutrients for the fetus
A) exchanges blood between mother and fetus
B) secretes hormones to maintain pregnancy
C) provides oxygen for the fetus
D) eliminates wastes from the fetus
E) provides nutrients for the fetus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The trophoblast secretes ______ that signals the corpus luteum that pregnancy has begun.
A) estrogen.
B) a gray crescent.
C) progesterone.
D) hCG.
E) an enzyme.
A) estrogen.
B) a gray crescent.
C) progesterone.
D) hCG.
E) an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In humans, the allantois:
A) stores embryonic nitrogenous wastes.
B) eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the embryo.
C) contributes to the formation of the blood vessels in the umbilical cord.
D) secretes amniotic fluid.
E) serves as a temporary center for formation of blood cells.
A) stores embryonic nitrogenous wastes.
B) eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the embryo.
C) contributes to the formation of the blood vessels in the umbilical cord.
D) secretes amniotic fluid.
E) serves as a temporary center for formation of blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following are incorrectly paired?
A) heroin-premature births and low birth weight
B) thalidomide-babies born without toes
C) accutane-associated with malformations of the brain
D) cocaine-constricts fetal arteries, which leads to retarded development
E) cigarette smoking-an addiction to nicotine
A) heroin-premature births and low birth weight
B) thalidomide-babies born without toes
C) accutane-associated with malformations of the brain
D) cocaine-constricts fetal arteries, which leads to retarded development
E) cigarette smoking-an addiction to nicotine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
All of the following are functions of the extraembryonic membranes except:
A) protecting the embryo.
B) making food available to the embryo.
C) eliminating wastes from the embryo.
D) keeping the embryo dry and warm.
E) obtaining oxygen for the embryo.
A) protecting the embryo.
B) making food available to the embryo.
C) eliminating wastes from the embryo.
D) keeping the embryo dry and warm.
E) obtaining oxygen for the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The percentage of twins being born has increased in the past 20 years because of:
A) the increased use of fertility inducing drugs.
B) increases in hospital care.
C) the desire of more couples to have twins.
D) the increased use of thalidomide.
E) the increased incidence of German measles.
A) the increased use of fertility inducing drugs.
B) increases in hospital care.
C) the desire of more couples to have twins.
D) the increased use of thalidomide.
E) the increased incidence of German measles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements about early embryonic development in humans is false?
A) The embryo is moved along the oviduct by ciliary action and muscular contraction.
B) The embryo develops through the blastula stage while floating free in the uterus.
C) The embryo enters the uterus about 24 hours after fertilization.
D) Early division of the embryo occurs in the oviduct.
E) Implantation of the embryo occurs about seven days after fertilization.
A) The embryo is moved along the oviduct by ciliary action and muscular contraction.
B) The embryo develops through the blastula stage while floating free in the uterus.
C) The embryo enters the uterus about 24 hours after fertilization.
D) Early division of the embryo occurs in the oviduct.
E) Implantation of the embryo occurs about seven days after fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following teratogens is specifically linked to high rates of fetal mortality?
A) heroin
B) thalidomide
C) HIV
D) cocaine
E) ionizing radiation
A) heroin
B) thalidomide
C) HIV
D) cocaine
E) ionizing radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following structures will be the most immediate precursor of the brain?
A) neural tube
B) neural groove
C) neural crest
D) neural folds
E) neural plate
A) neural tube
B) neural groove
C) neural crest
D) neural folds
E) neural plate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A human embryo is capable of movement and has gonads that are distinguishable as either testes or ovaries by the end of the:
A) second week.
B) fourth week.
C) sixth week.
D) eighth week.
E) first trimester.
A) second week.
B) fourth week.
C) sixth week.
D) eighth week.
E) first trimester.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the function of the chorion?
A) to absorb shock
B) to form blood cells
C) to provide nourishment
D) to permit freedom of movement
E) to permit gas exchange
A) to absorb shock
B) to form blood cells
C) to provide nourishment
D) to permit freedom of movement
E) to permit gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Inside the zona pellucida is a layer of granulosa cells.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Programmed cell death is called apoptosis.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Gastrulation is the process by which an embryo becomes three-layered.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the amphibian embryo, the first cleavage bisects the gray crescent.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The chorion is the extraembryonic membrane closest to the embryo proper.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the roles of cell division and morphogenesis in the development of an animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Identify two changes that occur at or shortly after birth that allow the neonate to live independently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In birds and reptiles, the allanotois stores nitrogenous wastes.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During capacitation, sperm become mature.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The eggs of birds and reptiles are telolecithal.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In echinoderms, gastrulation takes place through a primitive groove.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Human chorionic gonadotropin signals the placenta to produce large amounts of estrogen and progesterone.
___________________
___________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
As part of the fertilization process, the egg completes meiosis I.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The notochord induces the neural plate.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Isolecithal eggs exhibit holoblastic cleavage.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The fertilization envelope forms during the acrosomal reaction.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The blastopore is the opening to the blastocoel.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When a human embryo is implanted in the uterus, the embryo is in the morula stage.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The morula can be described as an embryo consisting of a hollow sphere of cells.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An embryo having a blastodisc exhibits holoblastic cleavage.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



