Deck 48: Osmoregulation and Disposal of Metabolic Wastes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 48: Osmoregulation and Disposal of Metabolic Wastes
1
In contrast to the excretory system of annelids, the excretory system of insects:
A) has many openings on the body wall.
B) contains flame cells.
C) is not connected to the gut.
D) excretes uric acid from the rectum.
E) relies on diffusion across the body wall.
A) has many openings on the body wall.
B) contains flame cells.
C) is not connected to the gut.
D) excretes uric acid from the rectum.
E) relies on diffusion across the body wall.
D
2
One disadvantage in excreting urea rather than uric acid is that:
A) urea is more toxic than uric acid.
B) urea is less toxic than uric acid.
C) urea is excreted by respiratory structures.
D) urea requires more water for excretion.
E) urea is produced from ammonia, not nucleic acids.
A) urea is more toxic than uric acid.
B) urea is less toxic than uric acid.
C) urea is excreted by respiratory structures.
D) urea requires more water for excretion.
E) urea is produced from ammonia, not nucleic acids.
D
3
Figure 48-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).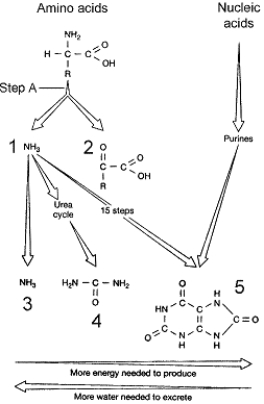
Which of the structures in Figure 48-1 represents the nitrogenous waste urea?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Which of the structures in Figure 48-1 represents the nitrogenous waste urea?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
D
4
Excretory systems maintain homeostasis through all of the following except:
A) adjusting the concentrations of various substances in body fluids.
B) removing excess water from the body.
C) adjusting body temperature.
D) ridding the body of harmful substances.
E) removing metabolic wastes from the body.
A) adjusting the concentrations of various substances in body fluids.
B) removing excess water from the body.
C) adjusting body temperature.
D) ridding the body of harmful substances.
E) removing metabolic wastes from the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The major function of the protonephridia in the flatworm is to:
A) conserve water.
B) conserve salts.
C) eliminate waste materials such as ammonia and urea.
D) eliminate excess water.
E) regulate the pH of the gastrovascular cavity.
A) conserve water.
B) conserve salts.
C) eliminate waste materials such as ammonia and urea.
D) eliminate excess water.
E) regulate the pH of the gastrovascular cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The main osmoregulatory and excretory organ in most vertebrates is the:
A) skin.
B) gill.
C) metanephridium.
D) lung.
E) kidney.
A) skin.
B) gill.
C) metanephridium.
D) lung.
E) kidney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 48-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The process represented at step A of Figure 48-1 is referred to as:
A) filtration.
B) secretion.
C) excretion.
D) deamination.
E) elimination.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The process represented at step A of Figure 48-1 is referred to as:
A) filtration.
B) secretion.
C) excretion.
D) deamination.
E) elimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 48-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Osmoconformers would most likely be found in:
A) estuaries.
B) coastal zones that receive freshwater.
C) freshwater.
D) terrestrial habitats.
E) open ocean waters.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Osmoconformers would most likely be found in:
A) estuaries.
B) coastal zones that receive freshwater.
C) freshwater.
D) terrestrial habitats.
E) open ocean waters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Deamination is a process that removes:
A) the amino group from amino acids.
B) the amino group from nucleic acids.
C) amines from the bloodstream.
D) amines from nucleic acids.
E) ammonia from blood.
A) the amino group from amino acids.
B) the amino group from nucleic acids.
C) amines from the bloodstream.
D) amines from nucleic acids.
E) ammonia from blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An animal adapted to life in a coastal environment where fresh water enters the ocean:
A) would have excretory structures to remove excess salt.
B) would have excretory structures to remove excess water.
C) would drink large amounts of water.
D) would likely be an osmoregulator.
E) More than one of these.
A) would have excretory structures to remove excess salt.
B) would have excretory structures to remove excess water.
C) would drink large amounts of water.
D) would likely be an osmoregulator.
E) More than one of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about the Malpighian tubules is false?
A) Water and some solutes are transported into the Malpighian tubules via active transport.
B) The Malpighian tubules empty into the gut of the insect.
C) Water, some salts, and other solutes are reabsorbed into the hemolymph in the rectum.
D) The excretory system of an insect may contain up to several hundred Malpighian tubules.
E) The blind ends of the Malpighian tubules are bathed in hemolymph.
A) Water and some solutes are transported into the Malpighian tubules via active transport.
B) The Malpighian tubules empty into the gut of the insect.
C) Water, some salts, and other solutes are reabsorbed into the hemolymph in the rectum.
D) The excretory system of an insect may contain up to several hundred Malpighian tubules.
E) The blind ends of the Malpighian tubules are bathed in hemolymph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The main point of entry of water into the blood of freshwater fishes is through:
A) the skin.
B) the gills.
C) the mouth.
D) the anus.
E) the eyes.
A) the skin.
B) the gills.
C) the mouth.
D) the anus.
E) the eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Metanephridial organs are common in:
A) mollusks.
B) flatworms.
C) cnidarians.
D) sponges.
E) insects.
A) mollusks.
B) flatworms.
C) cnidarians.
D) sponges.
E) insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a nitrogenous waste of animals?
A) amino acids
B) carbon dioxide
C) ammonia
D) water
E) sugars
A) amino acids
B) carbon dioxide
C) ammonia
D) water
E) sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following relationships is correct?
A) insects: Malpighian tubules: urea as major nitrogenous waste
B) annelids: protonephridia: ammonia as major nitrogenous waste
C) freshwater fish: kidney: large volume of hypertonic urine
D) sharks: kidney: large volume of hypotonic urine
E) earthworm: kidney: ammonia as major nitrogenous waste
A) insects: Malpighian tubules: urea as major nitrogenous waste
B) annelids: protonephridia: ammonia as major nitrogenous waste
C) freshwater fish: kidney: large volume of hypertonic urine
D) sharks: kidney: large volume of hypotonic urine
E) earthworm: kidney: ammonia as major nitrogenous waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 48-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Refer to Figure 48-1.Which compound is the primary nitrogenous waste product of amphibians?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Refer to Figure 48-1.Which compound is the primary nitrogenous waste product of amphibians?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How do terrestrial animals prevent toxic accumulation of ammonia in their tissues?
A) They use ammonia in other metabolic processes.
B) They convert ammonia to less toxic forms.
C) They vent ammonia across the body wall.
D) They eliminate ammonia rather than excreting it.
E) Animals do not produce ammonia.
A) They use ammonia in other metabolic processes.
B) They convert ammonia to less toxic forms.
C) They vent ammonia across the body wall.
D) They eliminate ammonia rather than excreting it.
E) Animals do not produce ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The main difference between protonephridia and metanephridia is that:
A) protonephridia are involved in osmoregulation, while metanephridia are involved in excretion.
B) protonephridia consist of blind flame cells, while metanephridia consist of tubules open at both ends.
C) protonephridia are involved in excretion, while metanephridia are involved in osmoregulation.
D) protonephridia consist of tubules open at both ends, while metanephridia consist of blind flame cells.
E) protonephridia are found in annelids and metanephridia are found in flatworms.
A) protonephridia are involved in osmoregulation, while metanephridia are involved in excretion.
B) protonephridia consist of blind flame cells, while metanephridia consist of tubules open at both ends.
C) protonephridia are involved in excretion, while metanephridia are involved in osmoregulation.
D) protonephridia consist of tubules open at both ends, while metanephridia consist of blind flame cells.
E) protonephridia are found in annelids and metanephridia are found in flatworms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 48-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Which nitrogenous waste product would be least toxic to an embryo developing in the aqueous environment found inside a shelled egg?
A) ammonia
B) urea
C) uric acid
D) amino acids
E) purines
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Which nitrogenous waste product would be least toxic to an embryo developing in the aqueous environment found inside a shelled egg?
A) ammonia
B) urea
C) uric acid
D) amino acids
E) purines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not an advantage of uric acid excretion in terrestrial animals?
A) Uric acid can be excreted as a paste, thereby conserving water.
B) Uric acid is not toxic and can be safely stored.
C) Uric acid can be stored in the eggs of animals without harm to the embryos.
D) Uric acid is soluble in water and can be easily excreted.
E) Uric acid can be excreted along with feces in some animals.
A) Uric acid can be excreted as a paste, thereby conserving water.
B) Uric acid is not toxic and can be safely stored.
C) Uric acid can be stored in the eggs of animals without harm to the embryos.
D) Uric acid is soluble in water and can be easily excreted.
E) Uric acid can be excreted along with feces in some animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is the correct sequence of structures through which the filtrate would pass? 1)
Bowman's capsule
2)
Collecting duct
3)
Distal convoluted tubule
4)
Proximal convoluted tubule
5)
Ascending loop of Henle
6)
Descending loop of Henle
A) 1 3 4 5 6 2
B) 1 4 5 6 3 2
C) 1 6 5 4 3 2
D) 1 3 F 4 2 6 5
E) 1 4 6 5 3 2
Bowman's capsule
2)
Collecting duct
3)
Distal convoluted tubule
4)
Proximal convoluted tubule
5)
Ascending loop of Henle
6)
Descending loop of Henle
A) 1 3 4 5 6 2
B) 1 4 5 6 3 2
C) 1 6 5 4 3 2
D) 1 3 F 4 2 6 5
E) 1 4 6 5 3 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
__________ directly deliver blood to the glomeruli.
A) Afferent arterioles
B) Efferent arterioles
C) Peritubular capillaries
D) Renal arteries
E) Renal venules
A) Afferent arterioles
B) Efferent arterioles
C) Peritubular capillaries
D) Renal arteries
E) Renal venules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).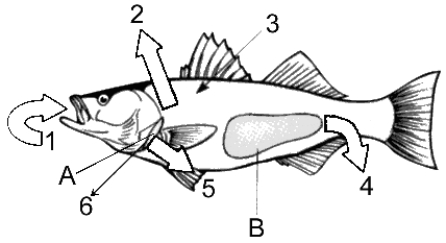
Marine cartilaginous fishes overcome water loss to their environments by:
A) having specialized chloride cells in their gills that prevent water loss.
B) having specialized chloride cells in their gills that continuously excrete salts.
C) storing urea in their body fluids, which causes them to be hypertonic to seawater.
D) producing very small quantities of urine.
E) drinking large quantities of freshwater.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Marine cartilaginous fishes overcome water loss to their environments by:
A) having specialized chloride cells in their gills that prevent water loss.
B) having specialized chloride cells in their gills that continuously excrete salts.
C) storing urea in their body fluids, which causes them to be hypertonic to seawater.
D) producing very small quantities of urine.
E) drinking large quantities of freshwater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The ureters connect:
A) the bladder to the body exterior.
B) the kidney to the bladder.
C) the bladder to the urethra.
D) the kidney to the body exterior.
E) the kidney to the urethra.
A) the bladder to the body exterior.
B) the kidney to the bladder.
C) the bladder to the urethra.
D) the kidney to the body exterior.
E) the kidney to the urethra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The efferent arterioles transport blood directly into the:
A) afferent arterioles.
B) Bowman's capsule.
C) glomerulus.
D) peritubular capillaries.
E) renal artery.
A) afferent arterioles.
B) Bowman's capsule.
C) glomerulus.
D) peritubular capillaries.
E) renal artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Trace the flow of urine through the following structures. 1)
Bladder
2)
Renal papilla
3)
Ureter
4)
Renal pelvis
5)
Urethra
A) 4 2 5 1 3
B) 1 2 4 3 5
C) 2 4 3 1 5
D) 2 1 4 3 5
E) 4 1 2 3 5
Bladder
2)
Renal papilla
3)
Ureter
4)
Renal pelvis
5)
Urethra
A) 4 2 5 1 3
B) 1 2 4 3 5
C) 2 4 3 1 5
D) 2 1 4 3 5
E) 4 1 2 3 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the significance of having specialized epithelium and smooth muscle in the urinary bladder?
A) It helps reabsorb water.
B) It helps reabsorb salts.
C) It permits the diffusion of gases.
D) It is capable of shrinkage and stretching.
E) It protects the bladder from nitrogenous wastes.
A) It helps reabsorb water.
B) It helps reabsorb salts.
C) It permits the diffusion of gases.
D) It is capable of shrinkage and stretching.
E) It protects the bladder from nitrogenous wastes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following does not contribute to the maintenance of homeostasis in mammals?
A) sweat glands
B) the digestive system
C) lungs
D) specialized gill cells
E) the kidneys
A) sweat glands
B) the digestive system
C) lungs
D) specialized gill cells
E) the kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The renal medulla contains the:
A) renal pyramids.
B) Bowman's capsules.
C) distal convoluted tubules.
D) glomeruli.
E) proximal convoluted tubules.
A) renal pyramids.
B) Bowman's capsules.
C) distal convoluted tubules.
D) glomeruli.
E) proximal convoluted tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The main nitrogenous waste of adult amphibians is:
A) ammonia.
B) urea.
C) uric acid.
D) peptides.
E) purines.
A) ammonia.
B) urea.
C) uric acid.
D) peptides.
E) purines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
For a freshwater fish, the output from the kidney in Figure 48-2 would be:
A) a small volume of hypotonic urine.
B) a large volume of hypotonic urine.
C) a small volume of hypertonic urine.
D) a large volume of hypertonic urine.
E) a small volume of isotonic urine.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

For a freshwater fish, the output from the kidney in Figure 48-2 would be:
A) a small volume of hypotonic urine.
B) a large volume of hypotonic urine.
C) a small volume of hypertonic urine.
D) a large volume of hypertonic urine.
E) a small volume of isotonic urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The outermost region of the kidney is called the:
A) adventitia.
B) mucosa.
C) pelvis.
D) cortex.
E) medulla.
A) adventitia.
B) mucosa.
C) pelvis.
D) cortex.
E) medulla.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
For a marine fish, the output from the kidney in Figure 48-2 would be:
A) a small volume of hypotonic urine.
B) a large volume of hypotonic urine.
C) a small volume of hypertonic urine.
D) a large volume of hypertonic urine.
E) a small volume of isotonic urine.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

For a marine fish, the output from the kidney in Figure 48-2 would be:
A) a small volume of hypotonic urine.
B) a large volume of hypotonic urine.
C) a small volume of hypertonic urine.
D) a large volume of hypertonic urine.
E) a small volume of isotonic urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The high-pressure flow of blood through the glomerular capillaries:
A) allows little plasma to be filtered in the kidney.
B) is a result of the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capillaries.
C) is due to the large diameter of the efferent arterioles of the glomerular capillaries.
D) is due to the small surface area for filtration provided by the glomerular capillaries.
E) is due to the low permeability of the glomerular capillaries.
A) allows little plasma to be filtered in the kidney.
B) is a result of the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capillaries.
C) is due to the large diameter of the efferent arterioles of the glomerular capillaries.
D) is due to the small surface area for filtration provided by the glomerular capillaries.
E) is due to the low permeability of the glomerular capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which portion of the renal tubule empties directly into the collecting duct?
A) Bowman's capsule
B) distal convoluted tubule
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) descending loop of Henle
E) ascending loop of Henle
A) Bowman's capsule
B) distal convoluted tubule
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) descending loop of Henle
E) ascending loop of Henle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The main nitrogenous waste of freshwater fishes is:
A) ammonia.
B) urea.
C) uric acid.
D) amino acids.
E) purines.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The main nitrogenous waste of freshwater fishes is:
A) ammonia.
B) urea.
C) uric acid.
D) amino acids.
E) purines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The __________ is shorter in females than it is in males, which explains the greater likelihood of developing bladder infections in __________.
A) ureter; females
B) ureter; males
C) renal papilla; females
D) urethra; males
E) urethra; females
A) ureter; females
B) ureter; males
C) renal papilla; females
D) urethra; males
E) urethra; females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the difference between cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons?
A) Juxtamedullary nephrons are more numerous than cortical ones.
B) Cortical nephrons do not have loops of Henle, while juxtamedullary ones do.
C) Juxtamedullary nephrons have larger glomeruli than do cortical ones.
D) Juxtamedullary nephrons do not have loops of Henle, while cortical ones do.
E) Juxtamedullary nephrons have more glomeruli than do cortical ones.
A) Juxtamedullary nephrons are more numerous than cortical ones.
B) Cortical nephrons do not have loops of Henle, while juxtamedullary ones do.
C) Juxtamedullary nephrons have larger glomeruli than do cortical ones.
D) Juxtamedullary nephrons do not have loops of Henle, while cortical ones do.
E) Juxtamedullary nephrons have more glomeruli than do cortical ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
In a freshwater environment, what is the function of the structure on Figure 48-2 labeled A?
A) salt uptake
B) water gain by osmosis
C) drinking
D) removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
E) release of nitrogenous wastes
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

In a freshwater environment, what is the function of the structure on Figure 48-2 labeled A?
A) salt uptake
B) water gain by osmosis
C) drinking
D) removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
E) release of nitrogenous wastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 48-2
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
In a marine environment, what is the function of the structure on Figure 48-2 labeled A?
A) salt excretion
B) water gain by osmosis
C) drinking
D) removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
E) release of nitrogenous wastes
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

In a marine environment, what is the function of the structure on Figure 48-2 labeled A?
A) salt excretion
B) water gain by osmosis
C) drinking
D) removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
E) release of nitrogenous wastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages associated with the production of ammonia, urea, and uric acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Simple epithelial cells of the renal tubule have abundant __________ to increase the surface area for reabsorption and numerous __________ to provide energy for actively transporting materials.
A) microvilli; mitochondria
B) cilia; mitochondria
C) microvilli; Golgi complexes
D) cilia; Golgi complexes
E) cilia; capillaries
A) microvilli; mitochondria
B) cilia; mitochondria
C) microvilli; Golgi complexes
D) cilia; Golgi complexes
E) cilia; capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the function of antidiuretic hormone?
A) It increases the permeability of the collecting ducts to sodium so more is reabsorbed.
B) It causes a high volume of less concentrated urine to be produced.
C) It increases aldosterone secretion.
D) It decreases renin secretion.
E) It increases the permeability of the collecting ducts to water so more is reabsorbed.
A) It increases the permeability of the collecting ducts to sodium so more is reabsorbed.
B) It causes a high volume of less concentrated urine to be produced.
C) It increases aldosterone secretion.
D) It decreases renin secretion.
E) It increases the permeability of the collecting ducts to water so more is reabsorbed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Atrial natriuretic peptide has been found to:
A) decrease sodium secretion and increase blood pressure.
B) constrict afferent arterioles, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate.
C) be produced by the adrenal cortex.
D) inhibit sodium reabsorption by the collecting ducts by inhibiting secretion of aldosterone.
E) increase the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
A) decrease sodium secretion and increase blood pressure.
B) constrict afferent arterioles, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate.
C) be produced by the adrenal cortex.
D) inhibit sodium reabsorption by the collecting ducts by inhibiting secretion of aldosterone.
E) increase the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following would increase the production of highly diluted urine?
A) decreased secretion of aldosterone
B) increased salt in the diet
C) decreased blood pressure
D) increased secretion of antidiuretic hormone
E) increased sweat production
A) decreased secretion of aldosterone
B) increased salt in the diet
C) decreased blood pressure
D) increased secretion of antidiuretic hormone
E) increased sweat production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The secretion of __________ is an important homeostatic mechanism involved in maintaining normal heart rhythm.
A) hydrogen ions
B) potassium
C) water
D) glucose
E) urea
A) hydrogen ions
B) potassium
C) water
D) glucose
E) urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Podocytes are located in the wall of:
A) Bowman's capsule.
B) the glomerulus.
C) the peritubular capillaries.
D) the renal artery.
E) the proximal convoluted tubule.
A) Bowman's capsule.
B) the glomerulus.
C) the peritubular capillaries.
D) the renal artery.
E) the proximal convoluted tubule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Glomerular capillary walls and podocytes form a __________ that allows fluid and small solutes in plasma to pass through and become part of the filtrate.
A) glomerular filtrate
B) tubular transport
C) renal threshold
D) filtration membrane
E) filtration slits
A) glomerular filtrate
B) tubular transport
C) renal threshold
D) filtration membrane
E) filtration slits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In which of the following is there a counterflow of filtrate?
A) distal convoluted tubule
B) loop of Henle
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) collecting duct
E) glomerulus
A) distal convoluted tubule
B) loop of Henle
C) proximal convoluted tubule
D) collecting duct
E) glomerulus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is true of filtration by the kidneys?
A) About 25% of the plasma passing through the glomerulus becomes part of the glomerular filtrate.
B) Solutes dissolved in the plasma, such as glucose, amino acids, and various salts, become part of the filtrate.
C) The normal glomerular filtration rate adds up to about 80 L every 24 hours.
D) Approximately 75% of the filtrate is reabsorbed into the blood through the renal tubules.
E) The filtration membrane prevents the passage of cells, but allows large molecules to pass through.
A) About 25% of the plasma passing through the glomerulus becomes part of the glomerular filtrate.
B) Solutes dissolved in the plasma, such as glucose, amino acids, and various salts, become part of the filtrate.
C) The normal glomerular filtration rate adds up to about 80 L every 24 hours.
D) Approximately 75% of the filtrate is reabsorbed into the blood through the renal tubules.
E) The filtration membrane prevents the passage of cells, but allows large molecules to pass through.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is only partially reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule?
A) glucose
B) amino acids
C) sodium ions
D) vitamins
E) nutrients
A) glucose
B) amino acids
C) sodium ions
D) vitamins
E) nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following would not be secreted across the tubule?
A) ammonium ions
B) hydrogen ions
C) creatinine
D) carbon dioxide
E) penicillin
A) ammonium ions
B) hydrogen ions
C) creatinine
D) carbon dioxide
E) penicillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Most of the filtrate is reabsorbed through the walls of the:
A) distal convoluted tubule.
B) loop of Henle.
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) collecting duct.
E) glomerulus.
A) distal convoluted tubule.
B) loop of Henle.
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) collecting duct.
E) glomerulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following would not be a component of normal urine?
A) water
B) urea
C) bile pigments
D) salts
E) glucose
A) water
B) urea
C) bile pigments
D) salts
E) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements about the loop of Henle is true?
A) The walls of the descending loop are relatively impermeable to water.
B) The walls of the descending loop are relatively permeable to sodium.
C) The walls of the ascending loop are relatively permeable to water.
D) The walls of the ascending loop are relatively permeable to sodium.
E) The loop of Henle is specialized to produce a low concentration of sodium chloride in the medulla.
A) The walls of the descending loop are relatively impermeable to water.
B) The walls of the descending loop are relatively permeable to sodium.
C) The walls of the ascending loop are relatively permeable to water.
D) The walls of the ascending loop are relatively permeable to sodium.
E) The loop of Henle is specialized to produce a low concentration of sodium chloride in the medulla.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Secretion occurs mainly in the:
A) distal convoluted tubule.
B) loop of Henle.
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) collecting duct.
E) glomerulus.
A) distal convoluted tubule.
B) loop of Henle.
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) collecting duct.
E) glomerulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Low blood pressure would result in all of the following except:
A) a reduction in glomerular hydrostatic pressure.
B) a reduction in filtrate formation.
C) a reduction in urine formation.
D) a reduction in the number of filtration slits.
E) a stimulation of the rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway.
A) a reduction in glomerular hydrostatic pressure.
B) a reduction in filtrate formation.
C) a reduction in urine formation.
D) a reduction in the number of filtration slits.
E) a stimulation of the rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the vasa recta?
A) looped extensions of the afferent arterioles
B) looped extensions of the efferent arterioles
C) regions of the renal tubule
D) vessels that supply blood to the glomerulus
E) vessels that supply blood to the proximal convoluted tubule
A) looped extensions of the afferent arterioles
B) looped extensions of the efferent arterioles
C) regions of the renal tubule
D) vessels that supply blood to the glomerulus
E) vessels that supply blood to the proximal convoluted tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Diabetes insipidus results from an insufficient production of:
A) ADH.
B) aldosterone.
C) angiotensin II.
D) ANP.
E) renin.
A) ADH.
B) aldosterone.
C) angiotensin II.
D) ANP.
E) renin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When you drink a large volume of water, the release of __________ by the pituitary gland __________.
A) aldosterone; increases
B) aldosterone; decreases
C) ADH; increases
D) ADH; decreases
E) ANP; increases
A) aldosterone; increases
B) aldosterone; decreases
C) ADH; increases
D) ADH; decreases
E) ANP; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The nephridial organs of flatworms are called metanephridia.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Filtrate flows from the proximal convoluted tubule directly into the distal convoluted tubule.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Birds store most of their waste nitrogen as uric acid.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
MATCHING
Match the part of the human urinary system with its description.
a.Bowman's capsule
e.loop of Henle
b.collecting duct
f.proximal convoluted tubule
c.distal convoluted tubule
g.ureter
d.glomerulus
h.urethra
urine flows out of the body via this structure
Match the part of the human urinary system with its description.
a.Bowman's capsule
e.loop of Henle
b.collecting duct
f.proximal convoluted tubule
c.distal convoluted tubule
g.ureter
d.glomerulus
h.urethra
urine flows out of the body via this structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
One of the direct products of deamination is urea.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
ADH makes the walls of the collecting duct more permeable to water.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Urine flows from the ureters directly into the urethra.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The renal medulla is the inner portion of the kidney.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare and contrast the osmoregulatory challenges and solutions used by sharks and freshwater fishes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In humans, urea and uric acid are produced by the kidneys.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Freshwater fishes excrete most of their nitrogenous wastes through the kidneys.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The walls of the descending limb of the loop of Henle are relatively permeable to sodium.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Blood flows from the efferent arterioles directly into the peritubular capillaries.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Most reabsorption occurs in the distal convoluted tubule.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Filtration slits are located between adjacent podocytes.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Aldosterone is responsible for increasing the reabsorption of sodium.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Compare and contrast osmoregulation of freshwater fish vs.marine fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Insects have an excretory system consisting of Malphighian tubules.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Sharks excrete a small volume of dilute urine.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Briefly explain the role of Malpighian tubules in arthropods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



